Featured
-
-
Perspective |
 Accelerating anticancer drug development — opportunities and trade-offs
Accelerating anticancer drug development — opportunities and trade-offs
With the expansion of the precision medicine paradigm, seamless trial approaches to drug development hold great promise for accelerating the accessibility of novel therapeutic agents but are also accompanied by important trade-offs. The authors describe several opportunities to improve the efficiency of drug development in oncology, as well as new mechanisms to obtain information about anticancer therapies throughout their life cycle.
- Sharyl J. Nass
- , Mace L. Rothenberg
- & Richard L. Schilsky
-
Review Article |
 Alternative splicing in prostate cancer
Alternative splicing in prostate cancer
Androgen receptor (AR) splice variants (AR-Vs) are truncated isoforms of the AR, of which a subset remain constitutively active in the absence of circulating androgens. AR-Vs have been proposed to contribute to therapeutic resistance. The authors of this Review outline the current understanding of the role of the spliceosome in prostate cancer progression and explore the therapeutic utility of manipulating alternative splicing.
- Alec Paschalis
- , Adam Sharp
- & Johann. S. de Bono
-
News & Views |
Reinforcing the social compromise of accelerated approval
Accelerated approval enables investigational drugs to reach the US market on the basis of their demonstrated effects in unvalidated surrogate measures, only reasonably likely to predict clinical response. To fulfil the social compromise, regulators should ensure that confirmatory trials testing clinically meaningful end points are already underway at the time of approval.
- Bishal Gyawali
- & Aaron S. Kesselheim
-
Review Article |
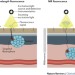 Beyond the margins: real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores
Beyond the margins: real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores
Intraoperative fluorescence enables highly specific real-time detection of tumours at the time of surgery. In particular, near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence is a promising tool currently being tested in clinical settings. Zhang et al. discuss the latest developments in NIR fluorophores, cancer-targeting strategies, and detection instrumentation for intraoperative cancer detection, as well as the challenges associated with their effective application in clinical settings.
- Ray R. Zhang
- , Alexandra B. Schroeder
- & Jamey P. Weichert
-
Consensus Statement
| Open Access Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies
Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies
Imaging biomarkers (IBs) are used extensively in drug development and cancer research, but important differences exist between IBs and biospecimen-derived biomarkers. A tailored 'roadmap' is required for the development of new IBs to be used either in clinical research or for decision-making in healthcare. In this Consensus statement, a group of experts assembled by CRUK and the EORTC present 14 key recommendations for accelerating the clinical translation of IBs.
- James P. B. O'Connor
- , Eric O. Aboagye
- & John C. Waterton
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials
Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials
Agents targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway have been shown to be safe and effective in treating a number of tumour types. This Review outlines the background to these inhibitors and discusses the second-generation inhibitors of this pathway. The authors propose that the way forward for the development of inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway might be a systems biology approach and biomarker-driven studies.
- Jordi Rodon
- , Rodrigo Dienstmann
- & Josep Tabernero
-

 Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology
Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology Dressed to ImPRESs
Dressed to ImPRESs