Featured
-
-
Article |
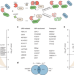 Proteome-scale discovery of protein degradation and stabilization effectors
Proteome-scale discovery of protein degradation and stabilization effectors
A synthetic proteome-scale strategy enables the identification of a diverse range of human proteins that can induce the degradation or stabilization of a target protein in a proximity-dependent way.
- Juline Poirson
- , Hanna Cho
- & Mikko Taipale
-
News & Views |
 Mammalian cells repress random DNA that yeast transcribes
Mammalian cells repress random DNA that yeast transcribes
In experiments dubbed the Random Genome Project, researchers have integrated DNA strands with random sequences into yeast and mouse cells to find the default transcriptional state of their genomes.
- Sean R. Eddy
-
Article
| Open Access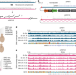 Synthetic reversed sequences reveal default genomic states
Synthetic reversed sequences reveal default genomic states
Introduction of a long synthetic DNA into yeast genomic loci results in high default transcriptional activity in yeast but low activity in mouse, suggesting distinct default levels of genomic activity in these organisms.
- Brendan R. Camellato
- , Ran Brosh
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
Article
| Open Access Adding α,α-disubstituted and β-linked monomers to the genetic code of an organism
Adding α,α-disubstituted and β-linked monomers to the genetic code of an organism
tRNA display enables the direct selection of orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that acylate orthogonal tRNAs with non-canonical monomers, enabling in vivo synthesis of proteins that include these monomers and expanding the repertoire of the genetic code.
- Daniel L. Dunkelmann
- , Carlos Piedrafita
- & Jason W. Chin
-
Perspective |
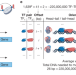 Hold out the genome: a roadmap to solving the cis-regulatory code
Hold out the genome: a roadmap to solving the cis-regulatory code
A roadmap towards solving the cis-regulatory code using a combination of machine learning and massively parallel assays of exogenous DNA is proposed.
- Carl G. de Boer
- & Jussi Taipale
-
Article
| Open Access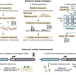 Cell-type-directed design of synthetic enhancers
Cell-type-directed design of synthetic enhancers
Deep learning models were used to design synthetic cell-type-specific enhancers that work in fruit fly brains and human cell lines, an approach that also provides insights into these gene regulatory elements.
- Ibrahim I. Taskiran
- , Katina I. Spanier
- & Stein Aerts
-
News |
 Engineered yeast breaks new record: a genome with over 50% synthetic DNA
Engineered yeast breaks new record: a genome with over 50% synthetic DNA
Highly edited strain survives and replicates despite containing 7.5 artificial chromosomes.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Article
| Open Access Mouse genome rewriting and tailoring of three important disease loci
Mouse genome rewriting and tailoring of three important disease loci
This study describes a method to insert large stretches of exogenous DNA into mammalian genomes, which is used to insert human ACE2 loci into mouse to produce a model of human SARS-CoV-2 infection.
- Weimin Zhang
- , Ilona Golynker
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
News & Views |
 Pig-to-primate organ transplants require genetic modifications of donor
Pig-to-primate organ transplants require genetic modifications of donor
A raft of alterations to the pig genome — removing three antigen-encoding genes, adding seven human genes and eliminating a retrovirus — allows kidneys to be transplanted into monkeys, with implications for clinical trials.
- Muhammad M. Mohiuddin
-
Article
| Open Access Design and testing of a humanized porcine donor for xenotransplantation
Design and testing of a humanized porcine donor for xenotransplantation
Using kidneys from a genetically engineered porcine donor transplanted into a cynomolgus monkey model, the design, creation and long-term function of kidney grafts supporting life are explored.
- Ranjith P. Anand
- , Jacob V. Layer
- & Wenning Qin
-
Article |
 Sub-1.4 cm3 capsule for detecting labile inflammatory biomarkers in situ
Sub-1.4 cm3 capsule for detecting labile inflammatory biomarkers in situ
A biosensor comprising bacteria engineered to respond to transient inflammatory signals has been packaged with electronic readout and transmission circuits in a small device that could be swallowed to monitor gastrointestinal health.
- M. E. Inda-Webb
- , M. Jimenez
- & T. K. Lu
-
Nature Podcast |
 Even a ‘minimal cell’ can grow stronger, thanks to evolution
Even a ‘minimal cell’ can grow stronger, thanks to evolution
Exploring evolution in a ‘minimal cell’, and Galaxy-wide gravitational waves.
- Benjamin Thompson
- & Shamini Bundell
-
Article |
 Continuous synthesis of E. coli genome sections and Mb-scale human DNA assembly
Continuous synthesis of E. coli genome sections and Mb-scale human DNA assembly
BAC stepwise insertion synthesis (BASIS) can be used to build synthetic genomes for diverse organisms, and continuous genome synthesis (CGS) enables the rapid synthesis of entire Escherichia coli genomes from functional designs.
- Jérôme F. Zürcher
- , Askar A. Kleefeldt
- & Jason W. Chin
-
Technology Feature |
 How scientists are hacking the genetic code to give proteins new powers
How scientists are hacking the genetic code to give proteins new powers
By modifying the blueprint of life, researchers are endowing proteins with chemistries they’ve never had before.
- Diana Kwon
-
Research Briefing |
 Machine-learning model makes predictions about network biology
Machine-learning model makes predictions about network biology
A deep-learning model called Geneformer has been developed and pretrained using about 30 million single-cell gene-expression profiles to enable it to make predictions about gene-network biology in instances in which gene-expression data are limited. Geneformer can be tuned for many downstream applications to accelerate discovery of key gene-network regulators and candidate therapeutic targets.
-
Research Briefing |
 New protein–protein interactions designed by a computer
New protein–protein interactions designed by a computer
Creating protein interactions through computational design is a key challenge in the fields of both basic and translational biology. An approach that uses the machine-learned fingerprints of protein-surface features was used to produce synthetic proteins that engage immunotherapeutic or viral targets with binding affinities comparable to those of naturally occurring proteins.
-
Article |
 Large-scale mapping and mutagenesis of human transcriptional effector domains
Large-scale mapping and mutagenesis of human transcriptional effector domains
A high throughput recruitment assay testing the transcriptional activity of more than 100,000 protein fragments tiling across most human chromatin regulators and transcription factors maps the locations and strengths of activation, repression and bifunctional domains, and identifies the sequences necessary for these functions.
- Nicole DelRosso
- , Josh Tycko
- & Lacramioara Bintu
-
News & Views |
 Synthetic bacterial genome upgraded for viral defence and biocontainment
Synthetic bacterial genome upgraded for viral defence and biocontainment
Bacteria with a synthetic genome were engineered to alter the way that the DNA code instructs cells to make proteins. This ‘language barrier’ serves to isolate the cells genetically, and makes them immune to viral infection.
- Benjamin A. Blount
-
Nature Podcast |
 How to build a virus-proof cell
How to build a virus-proof cell
A streamlined genome makes bacteria immune to viral infection, and designing mini-MRI scanners for low- and middle-income countries.
- Shamini Bundell
- & Nick Petrić Howe
-
Article |
 A swapped genetic code prevents viral infections and gene transfer
A swapped genetic code prevents viral infections and gene transfer
A study details the creation of an Escherichia coli genetically recoded organism that is resistant to viral infection, and describes a further modification that keeps the organism and its genetic information biocontained.
- Akos Nyerges
- , Svenja Vinke
- & George M. Church
-
Article |
 Co-opting signalling molecules enables logic-gated control of CAR T cells
Co-opting signalling molecules enables logic-gated control of CAR T cells
Logic gating is used to develop a CAR T cell platform that is highly specific and allows the activity of T cells to be restricted to the encounter of two antigens, thus reducing on-target, off-tumour toxicity.
- Aidan M. Tousley
- , Maria Caterina Rotiroti
- & Robbie G. Majzner
-
Article
| Open Access Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules
Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules
Synthetic cell adhesion molecules yield customized cell–cell interactions with adhesion properties that are similar to native interactions, and offer abilities for cell and tissue engineering and for systematically studying multicellular organization.
- Adam J. Stevens
- , Andrew R. Harris
- & Wendell A. Lim
-
Article |
 Real-time bioelectronic sensing of environmental contaminants
Real-time bioelectronic sensing of environmental contaminants
The combination of synthetic biology and materials engineering enabled the development of biosensors that produce electrical readouts and real-time detection capabilities.
- Joshua T. Atkinson
- , Lin Su
- & Caroline M. Ajo-Franklin
-
News & Views |
 Life brought to artificial cells
Life brought to artificial cells
Can artificial cells be built from basic components? Systems that have complex architectures and functions evocative of natural cells have been prepared by recycling the contents of bacterial cells in synthetic droplets.
- N. Amy Yewdall
-
Article |
 Living material assembly of bacteriogenic protocells
Living material assembly of bacteriogenic protocells
A bacteriogenic strategy for constructing membrane-bounded, molecularly crowded, and compositionally, structurally and morphologically complex synthetic cells provides opportunities for the fabrication of new synthetic cell modules and augmented living/synthetic cell constructs.
- Can Xu
- , Nicolas Martin
- & Stephen Mann
-
Nature Video |
 The geometry of life: when mathematics meets synthetic biology
The geometry of life: when mathematics meets synthetic biology
How researchers created complex tiling patterns with bioengineered bacteria
- Sara Reardon
-
News & Views |
 Sticky logic programs bacteria to form multicellular patterns
Sticky logic programs bacteria to form multicellular patterns
The engineering of cells to express synthetic adhesion molecules creates a simple logic for patterning cell populations with visible boundaries. The approach paves the way for smart living materials and programmable biosensors.
- Luis Ángel Fernández
-
Article
| Open Access 4-bit adhesion logic enables universal multicellular interface patterning
4-bit adhesion logic enables universal multicellular interface patterning
A synthetic cell-cell adhesion logic using swarming E. coli with 4 bits of information is introduced, enabling the programming of interfaces that combine to form universal tessellation patterns over a large scale.
- Honesty Kim
- , Dominic J. Skinner
- & Ingmar H. Riedel-Kruse
-
Article |
 Recording gene expression order in DNA by CRISPR addition of retron barcodes
Recording gene expression order in DNA by CRISPR addition of retron barcodes
Retro-Cascorder, a system for time-ordered recording of transcriptional output, uses retrons as a tag to mediate DNA barcode acquisition in a CRISPR array.
- Santi Bhattarai-Kline
- , Sierra K. Lear
- & Seth L. Shipman
-
Article
| Open Access A time-resolved, multi-symbol molecular recorder via sequential genome editing
A time-resolved, multi-symbol molecular recorder via sequential genome editing
A DNA memory device, DNA Typewriter, uses sequential prime editing to record the order of multiple cellular events.
- Junhong Choi
- , Wei Chen
- & Jay Shendure
-
Article
| Open Access Potentiating adoptive cell therapy using synthetic IL-9 receptors
Potentiating adoptive cell therapy using synthetic IL-9 receptors
Synthetic chimeric orthogonal IL-2 receptors that incorporate the intracellular domain of receptors for other γ-chain cytokines such as IL-9 can reroute orthogonal signalling and alter the phenotype of T cells to improve anti-tumour responses.
- Anusha Kalbasi
- , Mikko Siurala
- & K. Christopher Garcia
-
News & Views |
 Designer protein circuits enable safe cancer immunotherapy
Designer protein circuits enable safe cancer immunotherapy
Synthetic receptor proteins can enable customized and flexible control of immune cells called T lymphocytes. A defined framework for the proteins’ design now improves their potential for use in cancer immunotherapy.
- Mohamad Hamieh
- & Maria Themeli
-
Article |
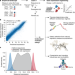 The evolution, evolvability and engineering of gene regulatory DNA
The evolution, evolvability and engineering of gene regulatory DNA
A framework for studying and engineering gene regulatory DNA sequences, based on deep neural sequence-to-expression models trained on large-scale libraries of random DNA, provides insight into the evolution, evolvability and fitness landscapes of regulatory DNA.
- Eeshit Dhaval Vaishnav
- , Carl G. de Boer
- & Aviv Regev
-
News |
 Last-resort cancer therapy holds back disease for more than a decade
Last-resort cancer therapy holds back disease for more than a decade
Two of the first people treated with CAR-T-cell cancer therapies are still in remission 12 years on.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News & Views |
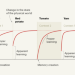 Context is key for learning motor skills
Context is key for learning motor skills
A sophisticated theory for learning motor skills places emphasis on the need for inferring context — drawing conclusions about the structure of the environment — for efficiently storing and expressing motor memories.
- Anne G. E. Collins
- & Samuel D. McDougle
-
Research Highlight |
 Mutant enzymes give ordinary bacteria unnatural powers
Mutant enzymes give ordinary bacteria unnatural powers
Common bacteria make a compound not found in nature after being kitted out with an artificial enzyme.
-
Book Review |
 Synthetic biology — a call to meddle better
Synthetic biology — a call to meddle better
An expansive survey of the hopes and fears, hypes and fails of genetic manipulation.
- Gaia Vince
-
Research Highlight |
 Complex, lab-made ‘cells’ react to change like the real thing
Complex, lab-made ‘cells’ react to change like the real thing
Synthetic structures that grow artificial ‘organelles’ could provide insights into the operation of living cells.
-
Technology Feature |
 Technology alliance boosts efforts to store data in DNA
Technology alliance boosts efforts to store data in DNA
Trade group aims to advance technologies for storing big data.
- Sarah Vitak
-
Article |
 De novo design of modular and tunable protein biosensors
De novo design of modular and tunable protein biosensors
A modular de novo designed biosensor platform consisting of a cage and key molecule is developed, and used to create sensors for seven distinct proteins including the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2 and anti-SARS antibodies.
- Alfredo Quijano-Rubio
- , Hsien-Wei Yeh
- & David Baker
-
Research Highlight |
 Thrifty bacteria thrive on something in the air
Thrifty bacteria thrive on something in the air
Borrowed genes help E. coli to subsist on the relatively modest levels of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere.
-
News & Views |
 Genetically engineered yeast makes medicinal plant products
Genetically engineered yeast makes medicinal plant products
Yeast has been engineered to convert simple sugars and amino acids into drugs that inhibit a neurotransmitter molecule. The work marks a step towards making the production of these drugs more reliable and sustainable.
- José Montaño López
- & José L. Avalos
-
News |
 Cyber-spinach turns sunlight into sugar
Cyber-spinach turns sunlight into sugar
Combination of biological membrane and artificial chemistry could power future synthetic organisms.
- Colin Barras
-
Career Feature |
 Behind the scenes in the biosafety office
Behind the scenes in the biosafety office
It’s never a dull day for those tasked with keeping biological research safe for all.
- Kendall Powell
-
Technology Feature |
 How to build a genome
How to build a genome
A powerful set of molecular tools helps synthetic biologists to assemble DNA of different sizes, from the gene to the chromosome scale.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Obituary |
 Jack Baldwin (1938–2020)
Jack Baldwin (1938–2020)
Organic chemist whose rules aided the synthesis of natural products.
- Georgina Ferry
-
Outlook |
 Therapeutic microbes to tackle disease
Therapeutic microbes to tackle disease
Modified bacteria and carefully formulated microbial communities could form the basis of new living treatments.
- Claire Ainsworth
-
Letter |
 Modular and tunable biological feedback control using a de novo protein switch
Modular and tunable biological feedback control using a de novo protein switch
DegronLOCKR designer-protein technology is used to implement synthetic positive- and negative-feedback systems in the yeast mating pathway as well as feedback control of a synthetic gene circuit.
- Andrew H. Ng
- , Taylor H. Nguyen
- & Hana El-Samad
-
Article |
 De novo design of bioactive protein switches
De novo design of bioactive protein switches
A technique for the de novo design of switchable protein systems controlled by induced conformational change is demonstrated for three functional motifs, in vitro and in yeast and mammalian cells.
- Robert A. Langan
- , Scott E. Boyken
- & David Baker

 The beauty of what science can do when urgently needed
The beauty of what science can do when urgently needed