Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic characteristics of graphene composites—evolution from thermal conductors to thermal insulators
Cryogenic characteristics of graphene composites—evolution from thermal conductors to thermal insulators
Graphene composites can serve both as efficient thermal insulators at low temperatures and thermal conductors at high temperatures. Here, the authors report the evolution of thermal conductivity of composites with graphene fillers from cryogenic to room temperature.
- Zahra Ebrahim Nataj
- , Youming Xu
- & Alexander A. Balandin
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous rotational symmetry breaking in KTaO3 heterointerface superconductors
Spontaneous rotational symmetry breaking in KTaO3 heterointerface superconductors
Superconducting interfaces involving KTaO3 have recently attracted attention due to their relatively high transition temperature. Here, the authors study amorphous-YAlO3/KTaO3 interfaces and find two-fold symmetry in the superconducting regime, possibly due to a mixed-parity superconducting state.
- Guanqun Zhang
- , Lijie Wang
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Bimodal ionic photomemristor based on a high-temperature oxide superconductor/semiconductor junction
Bimodal ionic photomemristor based on a high-temperature oxide superconductor/semiconductor junction
Designing efficient photonic neuromorphic systems remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a new class of memristor sensitive to the dual electro-optical history obtained by exploiting electrochemical, photovoltaic and photo-assisted oxygen ion motion effects at a high temperature superconductor / semiconductor interface.
- Ralph El Hage
- , Vincent Humbert
- & Javier E. Villegas
-
Article
| Open Access Lithium crystallization at solid interfaces
Lithium crystallization at solid interfaces
In solid-state lithium metal batteries, the crystallization of Li-ions deposited at interfaces remains unclear. Here, authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal lithium crystallization pathways and energy barriers, guiding improved interfacial engineering and accelerated crystal growth.
- Menghao Yang
- , Yunsheng Liu
- & Yifei Mo
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic signature of obstructed surface states in SrIn2P2
Spectroscopic signature of obstructed surface states in SrIn2P2
The authors observe spectroscopic signature of obstructed surface states on the (0001) plane of SrIn2P2. Due to structural reconstruction, the surface state undergoes an adiabatic evolution and split into two branches, the upper of which being spatially localized with unusual negative differential conductance.
- Xiang-Rui Liu
- , Hanbin Deng
- & Chang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial interaction and intense interfacial ultraviolet light emission at an incoherent interface
Interfacial interaction and intense interfacial ultraviolet light emission at an incoherent interface
Incoherent interfaces usually have weak interfacial interactions and lack of unique properties. Here, Yan et al. demonstrate unexpected strong interfacial interactions and intense ultraviolet light emission at an incoherent AlN/Al2O3 interface.
- Xuexi Yan
- , Yixiao Jiang
- & Xiu-Liang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous enhancement of charge density wave in kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 approaching the 2D limit
Anomalous enhancement of charge density wave in kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 approaching the 2D limit
The kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 exhibits a charge density wave (CDW) as well as superconductivity (SC). Here, the authors find that the CDW transition temperature decreases with decreasing sample thickness to 72 K at 27 atomic layers, but then unexpectedly increases to 120 K at 5 layers, an opposite trend to SC.
- Boqin Song
- , Tianping Ying
- & Shiyan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon transition across an isotopic interface
Phonon transition across an isotopic interface
Here, the authors probe the phonon changes across an atomically sharp h-10BN/h-11BN isotope interface with sub-unit-cell spatial resolution and momentum resolution. The observed phonon delocalization suggests strong electron-phonon coupling at isotopic interface.
- Ning Li
- , Ruochen Shi
- & Peng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Para-hydrodynamics from weak surface scattering in ultraclean thin flakes
Para-hydrodynamics from weak surface scattering in ultraclean thin flakes
Classical hydrodynamics applies to electron fluids as well, provided the system has a high electron–electron collision rate. Now, model calculations show that regimes in which other scattering processes are at play can explain hydrodynamic electron transport in thin flakes of the 2D material WTe2.
- Yotam Wolf
- , Amit Aharon-Steinberg
- & Tobias Holder
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrachromatic vision-inspired neuromorphic sensors with ultraweak ultraviolet detection
Tetrachromatic vision-inspired neuromorphic sensors with ultraweak ultraviolet detection
Sensing and processing UV light is essential for advanced artificial visual perception system. Here, the authors report a controllable UV-ultrasensitive neuromorphic vision sensor using organic phototransistors to integrate sensing, memory and processing functions, and perform the static image and dynamic movie recognition.
- Ting Jiang
- , Yiru Wang
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article
| Open Access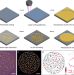 Random fractal-enabled physical unclonable functions with dynamic AI authentication
Random fractal-enabled physical unclonable functions with dynamic AI authentication
In order to be used on a large scale, unclonable tags for anti-counterfeiting should allow mass production at low cost, as well as fast and easy authentication. Here, the authors show how to use one-step annealing of gold films to quickly realize robust tags with high capacity, allowing fast deep-learning based authentication via smartphone readout.
- Ningfei Sun
- , Ziyu Chen
- & Qian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Superfluid response of an atomically thin gate-tuned van der Waals superconductor
Superfluid response of an atomically thin gate-tuned van der Waals superconductor
Superconductivity has been discovered in atomically thin two-dimensional van der Waals materials by resistance measurements, but magnetic measurements are lacking. Here, the authors use a micron-scale SQUID magnetometer to measure the superfluid response of exfoliated MoS2.
- Alexander Jarjour
- , G. M. Ferguson
- & Katja C. Nowack
-
Article
| Open Access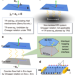 Time-reversal even charge hall effect from twisted interface coupling
Time-reversal even charge hall effect from twisted interface coupling
A linear Hall response in isolated systems with time reversal symmetry is forbidden by Onsager relations. Here the authors show that this restriction is lifted by interlayer hopping in twisted bilayers, leading to a linear charge Hall effect under time reversal symmetry.
- Dawei Zhai
- , Cong Chen
- & Wang Yao
-
Article
| Open Access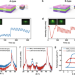 Interface-engineered ferroelectricity of epitaxial Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin films
Interface-engineered ferroelectricity of epitaxial Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin films
Ferroelectric hafnia-based thin films are promising for applications in memories and neuromorphic devices due to their robust ferroelectricity at reduced dimensions. Here, the authors demonstrate stabilization of the metastable orthorhombic phase in Hf0.5 Zr0.5O2 films by interface engineering with a hole doping mechanism.
- Shu Shi
- , Haolong Xi
- & Jingsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of a superconducting vortex diode
Direct observation of a superconducting vortex diode
A nonreciprocal critical current is known as the superconducting diode effect (SDE). Here, the authors use SQUID-on-tip to study SDE in a EuS/Nb bilayer and find that the stray field from magnetized EuS creates screening currents in the Nb, which lead to SDE by affecting vortex flow dynamics.
- Alon Gutfreund
- , Hisakazu Matsuki
- & Yonathan Anahory
-
Article
| Open Access Limits to the strain engineering of layered square-planar nickelate thin films
Limits to the strain engineering of layered square-planar nickelate thin films
The discovery of superconductivity in the infinite-layer nickelates reignites an interest in the nickelates as cuprate analogues. Here, the authors investigate the role of epitaxial strain in the synthesis of the n=3 layered nickelate, Nd4Ni3O8.
- Dan Ferenc Segedin
- , Berit H. Goodge
- & Julia A. Mundy
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous magnetoresistance by breaking ice rule in Bi2Ir2O7/Dy2Ti2O7 heterostructure
Anomalous magnetoresistance by breaking ice rule in Bi2Ir2O7/Dy2Ti2O7 heterostructure
Spin ice compounds are typically insulating and introducing carriers can destroy the spin ice state, making integration into electronic devices problematic. Here the authors report a transport response to an ice-rule-breaking transition in a heterostructure of a pyrochlore spin ice and a nonmagnetic metal.
- Han Zhang
- , Chengkun Xing
- & Jian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Signatures of the exciton gas phase and its condensation in monolayer 1T-ZrTe2
Signatures of the exciton gas phase and its condensation in monolayer 1T-ZrTe2
Signatures of an excitonic insulator have been reported in several two-dimensional materials. Here the authors report electronic properties of monolayer ZrTe2 from ARPES and STM measurements that are consistent with the preformed exciton gas phase, a precursor for the excitonic insulator.
- Yekai Song
- , Chunjing Jia
- & Shujie Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of high-temperature exciton condensation in a two-dimensional semimetal
Evidence of high-temperature exciton condensation in a two-dimensional semimetal
Two-dimensional materials are promising platforms for the realization of an excitonic insulator state. Here the authors report evidence for an excitonic insulator in a single-layer ZrTe2 based on ARPES measurements.
- Qiang Gao
- , Yang-hao Chan
- & Peng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable superconductivity and its origin at KTaO3 interfaces
Tunable superconductivity and its origin at KTaO3 interfaces
A distinct dependence of the superconducting transition temperature on carrier density for electron gases formed at KTaO3 interfaces is reported. In addition, these interfaces are shown to play a role in mediating superconductivity in this system. The crystallographic orientation and carrier density dependent superconductivity at KTaO3 interfaces can be explained by Cooper pairing via inter-orbital interactions and quantum confinement.
- Changjiang Liu
- , Xianjing Zhou
- & Anand Bhattacharya
-
Article
| Open Access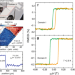 Creation of chiral interface channels for quantized transport in magnetic topological insulator multilayer heterostructures
Creation of chiral interface channels for quantized transport in magnetic topological insulator multilayer heterostructures
Quantum anomalous Hall junctions show great promise for advancing next-generation electronic circuits. Here, the authors demonstrate a scalable method for synthesizing heterostructures of magnetic topological insulators with regions of distinct Chern numbers and characterize the chiral interface modes that emerge at the interface.
- Yi-Fan Zhao
- , Ruoxi Zhang
- & Cui-Zu Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Strong charge carrier scattering at grain boundaries of PbTe caused by the collapse of metavalent bonding
Strong charge carrier scattering at grain boundaries of PbTe caused by the collapse of metavalent bonding
Studying the charge transport across individual grain boundaries is challenging yet important for materials design. Here, the authors find that metavalent bonding collapses at grain boundaries, increasing the barrier height for charge transport.
- Riga Wu
- , Yuan Yu
- & Matthias Wuttig
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent consolidation of trillions of nucleations for mono-atom step-level flat surfaces
Coherent consolidation of trillions of nucleations for mono-atom step-level flat surfaces
Constructing atomically flat surface in a single crystal ultrathin film is difficult owing to the coherent merging of trillions of clusters. Here the authors establish the initial growth mechanism of a single crystal Cu thin film with atomically flat surface using atomic sputtering epitaxy.
- Taewoo Ha
- , Yu-Seong Seo
- & Se-Young Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Antiferromagnetism-driven two-dimensional topological nodal-point superconductivity
Antiferromagnetism-driven two-dimensional topological nodal-point superconductivity
Magnet/superconductor hybrids have been explored for the realization of topological superconductivity but have mainly focused on ferromagnets with full gaps. Here, the authors find that the antiferromagnet/superconductor heterostructure of monolayer Mn on a Nb(110) surface is a topological nodal-point superconductor.
- Maciej Bazarnik
- , Roberto Lo Conte
- & Roland Wiesendanger
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of cation diffusion driven surface reconstruction at van der Waals gaps
Direct observation of cation diffusion driven surface reconstruction at van der Waals gaps
Weak interlayer van der Waals (vdW) bonding has significant impact on the structure and properties of vdW layered materials. Here authors use in-situ aberration-corrected ADF-STEM for an atomistic insight into the cation diffusion in the vdW gaps and the etching of vdW surfaces at high temperatures.
- Wenjun Cui
- , Weixiao Lin
- & Xiahan Sang
-
Article
| Open Access The importance of the interface for picosecond spin pumping in antiferromagnet-heavy metal heterostructures
The importance of the interface for picosecond spin pumping in antiferromagnet-heavy metal heterostructures
By placing an antiferromagnet next to a heavy metal such as platinum, magnetic excitations in the antiferromagnet drive a spin current in the heavy metal, leading to terahertz emission. Here, Kholid et al study the terahertz emission of two antiferromagnets, KCoF3 and KNiF3 with very different magnon frequencies, and find that the opening of a gap in the magnon density of states drastically alters the spin-transfer efficiency.
- Farhan Nur Kholid
- , Dominik Hamara
- & Chiara Ciccarelli
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving the intrinsic short-range ordering of K+ ions on cleaved muscovite mica
Resolving the intrinsic short-range ordering of K+ ions on cleaved muscovite mica
Mica is a naturally occurring 2D mineral that has been heavily studied in many diverse areas. Here authors present atomic force microscopy images to study the mica surface in ultra-high vacuum conditions; they unveil the distribution of its surface K+ ions and give insights into the distribution of subsurface Al3+ ions.
- Giada Franceschi
- , Pavel Kocán
- & Ulrike Diebold
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of enhanced nanoscale creep flow of crystalline metals enabled by controlling surface wettability
Observation of enhanced nanoscale creep flow of crystalline metals enabled by controlling surface wettability
Solid-solid interface friction usually becomes the bottleneck at micro/nanoscale. Here, Xiang and Liu show that the nanoscale creep flow rate of crystalline metals can increase by orders of magnitude when the contact metal is in diffusion deformation and the thermally activated boundary slip is active.
- Jun-Xiang Xiang
- & Ze Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of electric-field-tunable interfacial ferromagnetism in 2D antiferromagnet heterostructures
Emergence of electric-field-tunable interfacial ferromagnetism in 2D antiferromagnet heterostructures
One particularly useful feature of van der Waals materials is the ability to combine layers of different materials into a single heterostructure, which can have superior properties than any of the constituent materials alone. Here, Cheng et al. combine two interlayer-antiferromagnetic chromium trihalides, CrI3 and CrCl3 in close proximity, and demonstrate ferromagnetic coupling between them.
- Guanghui Cheng
- , Mohammad Mushfiqur Rahman
- & Yong P. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Ba+2 ion trapping using organic submonolayer for ultra-low background neutrinoless double beta detector
Ba+2 ion trapping using organic submonolayer for ultra-low background neutrinoless double beta detector
One of the possible events signaling a neutrinoless double beta decay is a Xe atom decaying into a Ba ion and two electrons. Aiming at the realisation of a detector for such a process, the authors show that Ba ions can be efficiently trapped (chelated) in vacuum by an organic molecule layer on a surface.
- P. Herrero-Gómez
- , J. P. Calupitan
- & J. T. White
-
Article
| Open Access 2D honeycomb transformation into dodecagonal quasicrystals driven by electrostatic forces
2D honeycomb transformation into dodecagonal quasicrystals driven by electrostatic forces
Quasicrystals are perfectly ordered crystals lacking translational symmetry. Here the authors unravel the formation mechanism of two-dimensional dodecagonal quasicrystals that arise from systematic modifications of a hexagonal honeycomb structure.
- Sebastian Schenk
- , Oliver Krahn
- & Wolf Widdra
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of gapped Dirac cones in a two-dimensional Su-Schrieffer-Heeger lattice
Observation of gapped Dirac cones in a two-dimensional Su-Schrieffer-Heeger lattice
The Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model is a prototypical model of topological states, initially proposed to describe spinless electrons on a one-dimensional (1D) dimerized lattice. Here, the authors realize a 2D SSH model in a rectangular lattice of silicon atoms on a silver substrate, observing gapped Dirac cones by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy.
- Daiyu Geng
- , Hui Zhou
- & Baojie Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal growth in confinement
Crystal growth in confinement
How confinement affects the growth of crystals is poorly understood. Experiments in which NaClO3 and CaCO3 crystals are grown close to a glass substrate now show that new molecular layers can form via the transport of mass through the liquid film at the crystal-substrate interface.
- Felix Kohler
- , Olivier Pierre-Louis
- & Dag Kristian Dysthe
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional skyrmionic cocoons in magnetic multilayers
Three-dimensional skyrmionic cocoons in magnetic multilayers
Three dimensional topological spin textures, such as hopfions and skyrmion tubes, have seen a surge of interest for their potential technological applications. They offer greater flexibility than their two dimensional counterparts, but have been hampered by the limited material platforms. Here, Grelier et al. look at aperiodic multilayers, and observe a three dimensional skyrmionic cocoon.
- Matthieu Grelier
- , Florian Godel
- & Nicolas Reyren
-
Article
| Open Access The composition and structure of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon contamination on van der Waals materials
The composition and structure of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon contamination on van der Waals materials
Here, the authors attribute the ambient surface contamination of van der Waals materials to a self-organized molecular layer of normal alkanes with lengths of 20-26 carbon atoms. The alkane adlayer displaces the manifold other airborne contaminant species, capping the surface of graphene, graphite, hBN and MoS2.
- András Pálinkás
- , György Kálvin
- & Péter Nemes-Incze
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous time-reversal symmetry breaking in twisted double bilayer graphene
Spontaneous time-reversal symmetry breaking in twisted double bilayer graphene
Twisted double bilayer graphene (tDBG) comprises two Bernal-stacked bilayer graphene sheets with a twist between them. Here, the authors report a strong anomalous Hall effect in the correlated-metal regime of tDBG, indicating time reversal symmetry breaking from orbital ferromagnetism, likely associated with valley polarization.
- Manabendra Kuiri
- , Christopher Coleman
- & Joshua Folk
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent helical edge states in a hybridized three-dimensional topological insulator
Emergent helical edge states in a hybridized three-dimensional topological insulator
As the thickness of a three-dimensional (3D) topological insulator (TI) becomes comparable to the penetration depth of surface states, hybridization turns their gapless Dirac electronic structure into a gapped spectrum. Here, authors show that 2D topological states can exist in the 3D TI BiSbTeSe2 when the Fermi level is inside the hybridization gap.
- Su Kong Chong
- , Lizhe Liu
- & Vikram V. Deshpande
-
Article
| Open Access Optoelectronic properties and ultrafast carrier dynamics of copper iodide thin films
Optoelectronic properties and ultrafast carrier dynamics of copper iodide thin films
Deep understanding of defect physics, excitonic properties and the ultrafast carrier dynamics in the high mobility p-type transparent CuI is vital for its optoelectronic applications. Here, Liu et al. employ a synergistic approach to unveil these fundamental properties.
- Zhan Hua Li
- , Jia Xing He
- & Chao Ping Liu
-
Article
| Open Access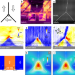 Electric-field control of the nucleation and motion of isolated three-fold polar vertices
Electric-field control of the nucleation and motion of isolated three-fold polar vertices
Despite various known topological polar structures, the dynamic property of isolated ones is still poorly understood. Here, the authors show the controlled nucleation and ability to move of isolated three-fold vertices under an applied electric field.
- Mingqiang Li
- , Tiannan Yang
- & Peng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning the many-body interactions in a helical Luttinger liquid
Tuning the many-body interactions in a helical Luttinger liquid
In one-dimensional systems, electronic interactions lead to a breakdown of Fermi liquid theory and the formation of a Tomonaga Luttinger Liquid (TLL), as recently reported in the helical edge states of quantum spin Hall insulators. Here, the authors show that the many-body interactions in the helical TLL of 1T’- WTe2 can be effectively controlled by the dielectric screening via the substrate.
- Junxiang Jia
- , Elizabeth Marcellina
- & Bent Weber
-
Article
| Open Access An unconstrained approach to systematic structural and energetic screening of materials interfaces
An unconstrained approach to systematic structural and energetic screening of materials interfaces
Predicting structures and stabilities of solid-solid interfaces presents an ongoing and increasingly important challenge for development of new technologies. Here authors report an unconstrained and generally applicable non-periodic screening method for systematic exploration of material´s interfaces.
- Giovanni Di Liberto
- , Ángel Morales-García
- & Stefan T. Bromley
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of exciton-libron coupling in chirally adsorbed single molecules
Evidence of exciton-libron coupling in chirally adsorbed single molecules
Vibronic coupling in molecules plays an essential role in photophysics. Here, the authors observe optical fingerprints of the coupling between librational states and charged excited states in a single phthalocyanine molecule chirally absorbed on a surface.
- Jiří Doležal
- , Sofia Canola
- & Martin Švec
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-scale collinear multi-Q states driven by higher-order interactions
Nano-scale collinear multi-Q states driven by higher-order interactions
Multi-Q states are 2D typically non-collinear spin textures that can be stabilized at the nanoscale and at zero magnetic field by interactions between multiple spins. Gutzeit et al. uncover a variety of multi-Q states in Fe/Rh atomic bilayers on the Ir(111) surface, including unexpected 2D collinear states.
- Mara Gutzeit
- , André Kubetzka
- & Kirsten von Bergmann
-
Article
| Open Access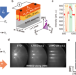 Giant spin-to-charge conversion at an all-epitaxial single-crystal-oxide Rashba interface with a strongly correlated metal interlayer
Giant spin-to-charge conversion at an all-epitaxial single-crystal-oxide Rashba interface with a strongly correlated metal interlayer
The interface between perovskite-oxide SrTiO3 and other oxides realizes efficient spin-to-charge current conversion; however, the typically insulating oxides hinder the propagation of spin-currents. Here the authors achieve a record efficiency by replacing an oxide insulator with a strongly-correlated polar metal.
- Shingo Kaneta-Takada
- , Miho Kitamura
- & Shinobu Ohya
-
Article
| Open Access Vacancy driven surface disorder catalyzes anisotropic evaporation of ZnO (0001) polar surface
Vacancy driven surface disorder catalyzes anisotropic evaporation of ZnO (0001) polar surface
Evaporation and crystal growth occur at different rates on different surfaces. Here authors show dissociative evaporation from ZnO (0001) polar surfaces is accelerated by the formation of a Zn-deficient quasi-liquid layer derived from the formation and inward diffusion of Zn vacancies that stabilize the polar surface.
- Zhen Wang
- , Jinho Byun
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Breakdown of bulk-projected isotropy in surface electronic states of topological Kondo insulator SmB6(001)
Breakdown of bulk-projected isotropy in surface electronic states of topological Kondo insulator SmB6(001)
Previous work exploring the robustness of topological surface states to perturbations has mostly focused on surfaces with the same atomic structure as the bulk. Here the authors demonstrate the effect of surface reconstruction on the topological surfaces on the (100) surface of SmB6.
- Yoshiyuki Ohtsubo
- , Toru Nakaya
- & Shin-Ichi Kimura
-
Article
| Open Access Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
The effect of aliovalent doping on grain boundary is not yet fully understood at the atomic level. Here, the authors report grain boundary structural transformation in α-Al2O3 is induced by co-segregation of multiple dopants using atomic-resolution electron microscopy and theoretical calculations.
- Toshihiro Futazuka
- , Ryo Ishikawa
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access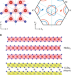 Spontaneous spin-valley polarization in NbSe2 at a van der Waals interface
Spontaneous spin-valley polarization in NbSe2 at a van der Waals interface
Van der Waals heterostructures made of 2D materials offer a rich platform for the study of novel proximity effects. Here, by means of Hall effect measurements, the authors show a proximity-induced ferromagnetic/ferrovalley ground state with spontaneous spin-valley polarization in a V5Se8/NbSe2 heterostructure.
- Hideki Matsuoka
- , Tetsuro Habe
- & Masaki Nakano
-
Article
| Open Access Localized interlayer excitons in MoSe2–WSe2 heterostructures without a moiré potential
Localized interlayer excitons in MoSe2–WSe2 heterostructures without a moiré potential
The spectrally narrow photoluminescence lines occurring in transition metal dichalcogenides (TMD) heterostructures at low temperature have been attributed to interlayer excitons (IXs) localized by the moiré potential between the TMD layers. Here, the authors show that these lines are present even when the moiré potential is suppressed by inserting an hBN spacer between the TMD layers.
- Fateme Mahdikhanysarvejahany
- , Daniel N. Shanks
- & John R. Schaibley

 Strain-tunable Berry curvature in quasi-two-dimensional chromium telluride
Strain-tunable Berry curvature in quasi-two-dimensional chromium telluride