Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access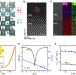 Light-induced giant enhancement of nonreciprocal transport at KTaO3-based interfaces
Light-induced giant enhancement of nonreciprocal transport at KTaO3-based interfaces
Optical control is an alternative pathway to boost nonlinear transport in noncentrosymmetric systems. Here, the authors observe a light-induced giant enhancement of nonreciprocal transport coefficient as high as 105 A−1 T−1 at KTaO3-based Rashba interfaces.
- Xu Zhang
- , Tongshuai Zhu
- & Xuefeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access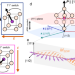 Switching the spin cycloid in BiFeO3 with an electric field
Switching the spin cycloid in BiFeO3 with an electric field
Previous understanding of the coupling between ferroelectric structure and magnetic texture in BiFeO3 has relied on mesoscale measurements. Here, the authors image coupling directly, showing a complex spin cycloid controlled with electric field.
- Peter Meisenheimer
- , Guy Moore
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Article
| Open Access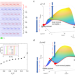 Intrinsic exchange biased anomalous Hall effect in an uncompensated antiferromagnet MnBi2Te4
Intrinsic exchange biased anomalous Hall effect in an uncompensated antiferromagnet MnBi2Te4
Exchange bias occurs in a variety of magnetic materials and heterostructures. The quintessential example occurs in antiferromagnetic/ferromagnetic heterostructures and has been employed extensively in magnetic memory devices. Here, via a specific field training protocol, the authors demonstrate an exchange bias of up to 400mT in odd layered MnBi2Te4.
- Su Kong Chong
- , Yang Cheng
- & Kang L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancement of electrocatalysis through magnetic field effects on mass transport
Enhancement of electrocatalysis through magnetic field effects on mass transport
Magnetic fields can enhance electrocatalysis, yet its effect on mass transport has been overlooked. Here, the authors track the motion induced on the electrolyte ions, demonstrating that mass transport effects can double the catalyst activity with low reactant availability, as in oxygen reduction.
- Priscila Vensaus
- , Yunchang Liang
- & Magalí Lingenfelder
-
Article
| Open Access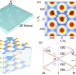 Topological minibands and interaction driven quantum anomalous Hall state in topological insulator based moiré heterostructures
Topological minibands and interaction driven quantum anomalous Hall state in topological insulator based moiré heterostructures
Moiré patterns have been experimentally observed in heterostructures comprised of topological insulator films. Here, the authors propose that topological insulator-based moiré heterostructures could be a host of isolated topologically non-trivial moiré minibands for the study of the interplay between topology and correlation.
- Kaijie Yang
- , Zian Xu
- & Chao-Xing Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-potential enabled multiscale simulation of gallium nitride devices on boron arsenide cooling substrates
Deep-potential enabled multiscale simulation of gallium nitride devices on boron arsenide cooling substrates
Efficient heat dissipation is critical to optimize high-power devices. Here, the authors report high interfacial thermal conductance in GaN-BAs heterostructures and investigate the competition between grain size and boundary resistance by multiscale simulations.
- Jing Wu
- , E Zhou
- & Guangzhao Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic driving forces in contact electrification between polymeric materials
Thermodynamic driving forces in contact electrification between polymeric materials
Contact electrification is a widely observed phenomenon in nature and in materials. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to show the importance of thermodynamic driving forces in contact electrification in insulating materials.
- Hang Zhang
- , Sankaran Sundaresan
- & Michael A. Webb
-
Article
| Open Access Direct visualization of stacking-selective self-intercalation in epitaxial Nb1+xSe2 films
Direct visualization of stacking-selective self-intercalation in epitaxial Nb1+xSe2 films
The interplay between stacking configurations and atom intercalation in van der Waals materials has been rarely characterized at the microscopic level. Here, the authors report an electron microscopy study of stacking-selective self-intercalation in Nb1+xSe2 films, showing potential for nanoscale engineering of electronic properties in van der Waals materials and devices.
- Hongguang Wang
- , Jiawei Zhang
- & Hidenori Takagi
-
Article
| Open Access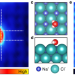 Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
The strong ionic bond in salt is broken by electrostatic interactions with water, but direct observation at the level of a single ion is challenging. Here, the authors have visualized the preferential dissolution of an anion by manipulating a single water molecule.
- Huijun Han
- , Yunjae Park
- & Hyung-Joon Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum spin liquid signatures in monolayer 1T-NbSe2
Quantum spin liquid signatures in monolayer 1T-NbSe2
Recently, signatures of quantum spin liquid have been reported in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Here the authors report evidence of such state in 1T-NbSe2 via the measurements of the Kondo effect in a 1T-1H heterostructure, further supported by measurements for magnetic molecules on 1T-NbSe2.
- Quanzhen Zhang
- , Wen-Yu He
- & Yeliang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access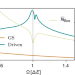 Theory of resonantly enhanced photo-induced superconductivity
Theory of resonantly enhanced photo-induced superconductivity
The authors theoretically propose a simple microscopic mechanism for light-induced superconductivity based on a boson coupled to an electronic interband transition. The electron-electron attraction needed for the superconductivity can be resonantly amplified when the boson’s frequency is close to the energy difference between the two electronic bands. The model can be engineered using a 2D heterostructure.
- Christian J. Eckhardt
- , Sambuddha Chattopadhyay
- & Marios H. Michael
-
Article
| Open Access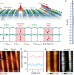 Unveiling diverse coordination-defined electronic structures of reconstructed anatase TiO2(001)-(1 × 4) surface
Unveiling diverse coordination-defined electronic structures of reconstructed anatase TiO2(001)-(1 × 4) surface
By measuring in energy, momentum and real space, the authors unveil diverse coordination environments and electronic structures on the reconstructed anatase TiO2(001), giving insights into its structure-property relationship with atomic precision.
- Xiaochuan Ma
- , Yongliang Shi
- & Bing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic potentials of atomic nanostructures at metal surfaces quantified by scanning quantum dot microscopy
Electrostatic potentials of atomic nanostructures at metal surfaces quantified by scanning quantum dot microscopy
Surface averaging techniques offer only limited access to the electrostatic potentials of nanostructures, which are determined by shape, material, and environment. Here, the authors quantify these potentials for gold and silver adatom chains, explaining the mechanisms of dipole formation.
- Rustem Bolat
- , Jose M. Guevara
- & Christian Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access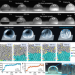 Interfacial ice sprouting during salty water droplet freezing
Interfacial ice sprouting during salty water droplet freezing
The understanding of salty water droplet freezing is limited. The authors examine the formation of brine film on top of frozen salty droplets and discover a new ice crystal growth pattern sprouting from the bottom of the brine film.
- Fuqiang Chu
- , Shuxin Li
- & Nenad Miljkovic
-
Article
| Open Access Pushing the thinness limit of silver films for flexible optoelectronic devices via ion-beam thinning-back process
Pushing the thinness limit of silver films for flexible optoelectronic devices via ion-beam thinning-back process
The use of thin silver films with nanometric thickness for optoelectronic devices is essential for high transparency, flexibility, and electrical properties. Ma et al. report a thinning-back process with a flood ion beam, to further reduce film thickness down to 4.5 nm.
- Dongxu Ma
- , Ming Ji
- & Huigao Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional magnetic nanotextures with high-order vorticity in soft magnetic wireframes
Three-dimensional magnetic nanotextures with high-order vorticity in soft magnetic wireframes
The spin texture of a magnetic system can host a variety of topological spin textures, the most famous of these being skyrmions. Here, Volkov et al demonstrate higher order vorticity in magnetic wireframe nanostructures and introduce a general protocol for the creation of arbitrary numbers of vortices and antivortices in such wireframe structures.
- Oleksii M. Volkov
- , Oleksandr V. Pylypovskyi
- & Denys Makarov
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of the nonanalytic behavior of optical phonons in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride
Observation of the nonanalytic behavior of optical phonons in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride
Here, the authors use high-resolution electron energy-loss spectroscopy to study the phonon dispersion of monolayer hexagonal boron nitride. They observe that the longitudinal optical (LO) and transverse optical (TO) phonons at the Brillouin zone centre exhibit no energy splitting, contrary to the conventional LO-TO splitting seen in bulk materials.
- Jiade Li
- , Li Wang
- & Xuetao Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access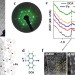 Ferromagnetism on an atom-thick & extended 2D metal-organic coordination network
Ferromagnetism on an atom-thick & extended 2D metal-organic coordination network
Despite having all the ingredients required for the formation of two-dimensional ferromagnetism, achieving such a magnetic state in atomically thin metal-organic coordination networks has proved to be a persistent challenge. Here, Lobo-Checa et al demonstrate 2Dferromagnetism in a self-assembled network, exhibiting coercive fields over 2 Tesla and a Curie temperature of 35K.
- Jorge Lobo-Checa
- , Leyre Hernández-López
- & Fernando Bartolomé
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
Disentangling the multiorbital contributions of excitons by photoemission exciton tomography
Understanding excitonic optical excitations is integral to improving optoelectronic and photovoltaic semiconductor devices. Here, Bennecke et al. use photoemission exciton tomography to unravel the multiorbital electron and hole contributions of entangled excitonic states in the prototypical organic semiconductor C60.
- Wiebke Bennecke
- , Andreas Windischbacher
- & Stefan Mathias
-
Article
| Open Access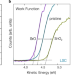 Engineering surface dipoles on mixed conducting oxides with ultra-thin oxide decoration layers
Engineering surface dipoles on mixed conducting oxides with ultra-thin oxide decoration layers
Improving materials for energy devices relates to an optimisation of their surfaces. Here authors show that surface modification with ultrathin oxide layers allows for a tailoring of the surface dipole and the work function of mixed ionic and electronic conducting oxides.
- Matthäus Siebenhofer
- , Andreas Nenning
- & Markus Kubicek
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable nanowrinkle-induced room-temperature exciton localization in monolayer WSe2
Programmable nanowrinkle-induced room-temperature exciton localization in monolayer WSe2
Here, the authors report on the fabrication of strained wrinkles in monolayer WSe2 by placing the material on Au nanoconical substrates. They investigate the correlation between topographical stress factors and localised, quantum-dot-like photoluminescence emission.
- Emanuil S. Yanev
- , Thomas P. Darlington
- & P. James Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access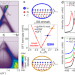 Achieving environmental stability in an atomically thin quantum spin Hall insulator via graphene intercalation
Achieving environmental stability in an atomically thin quantum spin Hall insulator via graphene intercalation
Topological states in atomically thin quantum spin Hall insulators suffer from instability against environmental factors. Here, the authors devise a strategy to preserve topologically protected states in monolayer indenene through graphene intercalation.
- Cedric Schmitt
- , Jonas Erhardt
- & Ralph Claessen
-
Article
| Open Access Endotaxial stabilization of 2D charge density waves with long-range order
Endotaxial stabilization of 2D charge density waves with long-range order
Stabilizing charge density wave states in low-dimensional systems is challenging. Here, the authors stabilize an ordered incommensurate charge density wave at elevated temperatures via endotaxial synthesis of TaS2 polytype heterostructures, where charge density wave layers are encapsulated within metallic layers.
- Suk Hyun Sung
- , Nishkarsh Agarwal
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access Surface triggered stabilization of metastable charge-ordered phase in SrTiO3
Surface triggered stabilization of metastable charge-ordered phase in SrTiO3
Charge order has been typically reported in doped systems with high d-electron occupancy. Here the authors demonstrate a charge-ordered insulating state in a La-doped SrTiO3 epitaxial film which has the lowest d-electron occupancy and attribute it to surface distortion that favours electron-phonon coupling.
- Kitae Eom
- , Bongwook Chung
- & Jaichan Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of large-area ultraflat chiral blue phosphorene
Realization of large-area ultraflat chiral blue phosphorene
Blue phosphorene (BlueP) is a 2D phosphorus allotrope predicted to host Dirac fermions and other interesting electronic properties. Here, the authors report the growth of large-area BlueP films with ordered chiral nanostructures on Cu(111) substrates, expanding the range of its potential applications.
- Ye-Heng Song
- , M. U. Muzaffar
- & Zhenyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic supercurrent non-reciprocity coupled to the crystal structure of a van der Waals Josephson barrier
Intrinsic supercurrent non-reciprocity coupled to the crystal structure of a van der Waals Josephson barrier
J.-K. Kim et al. study vertical Josephson junctions where the weak link is Td-WTe2 and the superconductor is NbSe2. The use of an inversion-symmetry-breaking Td-WTe2 weak link allows the authors to demonstrate the intrinsic origin of the observed Josephson non-reciprocity in these devices.
- Jae-Keun Kim
- , Kun-Rok Jeon
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Printed smart devices for anti-counterfeiting allowing precise identification with household equipment
Printed smart devices for anti-counterfeiting allowing precise identification with household equipment
The authors introduce a flexible laser printing method for synthesizing integrated optical and electric Physical Unclonable Functions (PUFs). The PUF devices can be read out by simple household equipment and show high uniqueness and stability.
- Junfang Zhang
- , Rong Tan
- & Felix F. Loeffler
-
Article
| Open Access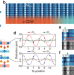 Dual Higgs modes entangled into a soliton lattice in CuTe
Dual Higgs modes entangled into a soliton lattice in CuTe
The Higgs mode in condensed matter physics refers to the oscillations of the amplitude of the order parameter, and single Higgs modes have been studies in various systems. Here the authors report real-space observation of two coupled Higgs modes in a 1D charge density wave phase of CuTe.
- SeongJin Kwon
- , Hyunjin Jung
- & Han Woong Yeom
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale manipulation of polar domain boundaries in monolayer ferroelectric In2Se3
Atomic-scale manipulation of polar domain boundaries in monolayer ferroelectric In2Se3
Here, the authors realize controllable manipulation of polar domain boundaries in a two-dimensional ferroelectric material In2Se3. It reveals the origin of distinct behaviors for different domain boundaries in combination with density functional theory calculations.
- Fan Zhang
- , Zhe Wang
- & Chenggang Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating the role of undercoordinated Pt sites at the surface of layered PtTe2 for methanol decomposition
Investigating the role of undercoordinated Pt sites at the surface of layered PtTe2 for methanol decomposition
Methanol on under-coordinated Pt sites at surface Te vacancies on layered PtTe2 decomposes at a probability >90 % which ultimately produces gaseous molecular hydrogen, methane, water and formaldehyde.
- Jing-Wen Hsueh
- , Lai-Hsiang Kuo
- & Meng-Fan Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Low-temperature grapho-epitaxial La-substituted BiFeO3 on metallic perovskite
Low-temperature grapho-epitaxial La-substituted BiFeO3 on metallic perovskite
In the field of multiferroic thin films, attaining low-temperature epitaxy has been a long-standing problem. In this work, authors propose a pathway to significantly reduce the BiFeO3 thin film growth temperature using the BaBiPbO3 template.
- Sajid Husain
- , Isaac Harris
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of strong surface reconstruction in partially reduced nickelate films
Direct observation of strong surface reconstruction in partially reduced nickelate films
Surface polarity affects the electronic and structural properties of oxide thin films through electrostatic effects, which is challenging to control. Here, the authors probe the tunable surface polarity at the atomic scale.
- Chao Yang
- , Rebecca Pons
- & Peter A. van Aken
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the light induced hydrophilicity of metal-oxide thin films
Understanding the light induced hydrophilicity of metal-oxide thin films
Light-induced hydrophilicity of TiO2 and ZnO surfaces rely on the same physics and involve excitation of electron-hole pairs. Here, the authors propose and test a model for the photowetting of TiO2 and ZnO thin films. The results suggest design rules for materials exhibiting photocatalytic wetting.
- Rucha Anil Deshpande
- , Jesper Navne
- & Rafael Taboryski
-
Article
| Open Access A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
Gas sensors typically detect only few specific gases; the authors show a broad-spectrum sensor based on correlated 2-dimensional electron gas (C-2DEG), which detects various gases quantitatively and measures partial pressures, through a purely physical mechanism.
- Yuhao Hong
- , Long Wei
- & Zhaoliang Liao
-
Article
| Open Access How frictional slip evolves
How frictional slip evolves
Conventionally, a continuous motion or “dynamic friction” is expected to take place after the initial rupture under friction. Here, the authors perform direct measurement of real contact and slip at the frictional interface and show that the secondary rupture takes place after each initial rupture.
- Songlin Shi
- , Meng Wang
- & Jay Fineberg
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip phonon-magnon reservoir for neuromorphic computing
On-chip phonon-magnon reservoir for neuromorphic computing
Developing efficient reservoir computing hardware that combines optically excited acoustic and spin waves with high spatial density remains a challenge. In this work, the authors propose a design capable of recognizing visual shapes drawn by a laser within remarkably confined spaces, down to 10 square microns.
- Dmytro D. Yaremkevich
- , Alexey V. Scherbakov
- & Manfred Bayer
-
Article
| Open Access Low-dimensional heat conduction in surface phonon polariton waveguide
Low-dimensional heat conduction in surface phonon polariton waveguide
Heat conduction in solids is known to be contributed by phonons and electrons. Here, authors observe enhanced and non-diffusive thermal conductance mediated by surface phonon polaritons in polar dielectric nanoribbon waveguides.
- Yu Pei
- , Li Chen
- & Renkun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Ferroelectric transistors are promising building blocks for developing energy-efficient memory and logic applications. Here, the authors report a record high 300 K resistance on-off ratio achieved in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors by exploiting a charge transfer layer to tailor the channel carrier density and mitigate the ferroelectric depolarization effect.
- Yifei Hao
- , Xuegang Chen
- & Xia Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Grain boundary atomic structures of crystalline materials have long been believed to be commensurate with the crystal periodicity of the adjacent crystals. Here, the authors discover an incommensurate grain boundary structure based on direct observations and theoretical calculations.
- Takehito Seki
- , Toshihiro Futazuka
- & Naoya Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional heavy fermion in a monoatomic-layer Kondo lattice YbCu2
Two-dimensional heavy fermion in a monoatomic-layer Kondo lattice YbCu2
Examples of 2D heavy-fermion materials are rare, and the details of their electronic structure have remained elusive. Here, Nakamura et al. report the synthesis and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy measurements of a monolayer Kondo lattice, YbCu2, on a Cu(111) surface with an estimated coherence temperature of 30 K.
- Takuto Nakamura
- , Hiroki Sugihara
- & Shin-ichi Kimura
-
Article
| Open Access Preferential ice growth on grooved surface for crisscross-aligned graphene aerogel with large negative Poisson’s ratio
Preferential ice growth on grooved surface for crisscross-aligned graphene aerogel with large negative Poisson’s ratio
Ice formation on grooved surfaces is ubiquitous, but controlling orientation is difficult due to lack of mechanistic insight. Here, the authors observed oriented growth using graphene oxide nanosheets as probes, revealing the effect of groove size, and programmed ice growth to fabricate freeze-cast metamaterials.
- Meng Li
- , Nifang Zhao
- & Hao Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Phonon polaritons are promising for infrared applications while it is difficult to tune the phonon polariton properties. Here, authors report a thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon polaritons in heterostructures of LaAlO3/SrTiO3.
- Yixi Zhou
- , Adrien Waelchli
- & Alexey B. Kuzmenko
-
Article
| Open Access Axion insulator state in hundred-nanometer-thick magnetic topological insulator sandwich heterostructures
Axion insulator state in hundred-nanometer-thick magnetic topological insulator sandwich heterostructures
A zero Hall conductance plateau has been taken as evidence of the axion insulator state in magnetically doped topological insulator heterostructures, but it can also originate from surface state hybridization. Here the authors establish such a state in a ~106 nm thick sample, where hybridization is negligible.
- Deyi Zhuo
- , Zi-Jie Yan
- & Cui-Zu Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Antiphase boundaries (APBs) have been considered major obstacles to optimizing the ionic conductivity of conductors. Here authors reveal that ionic conductivity can be enhanced through engineering APBs by topotactical transformation at the atomic scale.
- Kun Xu
- , Shih-Wei Hung
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Reentrance of interface superconductivity in a high-Tc cuprate heterostructure
Reentrance of interface superconductivity in a high-Tc cuprate heterostructure
The authors study interface superconductivity in over-doped La2-xSrxCuO4/La2CuO4 heterostructures. As x increases, the superconductivity is killed at x = 0.8 but fully recovers at x = 1.0, a “re-entrant” superconductivity.
- J. Y. Shen
- , C. Y. Shi
- & J. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Rotational symmetry breaking in superconducting nickelate Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 films
Rotational symmetry breaking in superconducting nickelate Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 films
The authors study transport in the superconducting state of infinite-layer nickelate Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 films using a Corbino-disk configuration, finding that the magnetoresistance changes from isotropic to four-fold anisotropic with increasing magnetic field. At even higher field, an additional two-fold component emerges, which coincides with an anomalous upturn of the critical field.
- Haoran Ji
- , Yi Liu
- & Jian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Dirac-fermion-assisted interfacial superconductivity in epitaxial topological-insulator/iron-chalcogenide heterostructures
Dirac-fermion-assisted interfacial superconductivity in epitaxial topological-insulator/iron-chalcogenide heterostructures
The authors study (Bi,Sb)2Te3/FeTe bilayers, which feature emergent superconductivity at the interface with Tc ~ 12 K. Through angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and electrical transport measurements, they argue that the Dirac-fermion-mediated Ruderman-Kittel-Kasuya-Yosida-type interaction weakens antiferromagnetic order in FeTe layer, allowing for superconductivity.
- Hemian Yi
- , Lun-Hui Hu
- & Cui-Zu Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Transport of bound quasiparticle states in a two-dimensional boundary superfluid
Transport of bound quasiparticle states in a two-dimensional boundary superfluid
Superfluid 3He appears to be composed of two independent superfluid subsystems. Here the authors discuss diffusion of quasiparticles in the two-dimensional boundary superfluid.
- Samuli Autti
- , Richard P. Haley
- & Dmitry E. Zmeev
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent superconductivity in topological-kagome-magnet/metal heterostructures
Emergent superconductivity in topological-kagome-magnet/metal heterostructures
The authors deposit non-superconducting metallic thin films on surfaces of the kagome Chern magnet TbMn6Sn6 and observe emergent superconductivity even though neither component is a superconductor. Furthermore, the superconducting state is quasi-two-dimensional and coexists with ferromagnetism, consistent with possible spin-triplet pairing and topological superconductivity.
- He Wang
- , Yanzhao Liu
- & Jian Wang

 Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers
Controlled condensation by liquid contact-induced adaptations of molecular conformations in self-assembled monolayers