Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
Quasicrystals possess long range order but no translational symmetry, and rotational symmetries that are forbidden in periodic crystals. Here, a fullerene overlayer deposited on a surface of an icosahedral intermetallic quasicrystal achieves a Fibonacci square grid structure, by selective adsorption at specific sites.
- Sam Coates
- , Joseph A. Smerdon
- & Hem Raj Sharma
-
Article
| Open Access Amplification of chirality in surface-confined supramolecular bilayers
Amplification of chirality in surface-confined supramolecular bilayers
One of the most dramatic effects of supramolecular assembly is the generation of homochirality in near-racemic systems. Here the authors rationalize the chiral amplification mechanism with a combined scanning tunneling microscopy and modelling study of surface-grown enantiomerically unbalanced supramolecular bilayers.
- Hai Cao
- & Steven De Feyter
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for auto-catalytic mineral dissolution from surface-specific vibrational spectroscopy
Evidence for auto-catalytic mineral dissolution from surface-specific vibrational spectroscopy
Although it is well known that silica can dissolve in water, the precise mechanism is unclear. Here, the authors employ sum frequency generation spectroscopy to probe the interfacial water structure reporting directly on the underlying dissolution mechanism, which appears to be auto-catalytic.
- Jan Schaefer
- , Ellen H. G. Backus
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article
| Open Access Monolayer surface chemistry enables 2-colour single molecule localisation microscopy of adhesive ligands and adhesion proteins
Monolayer surface chemistry enables 2-colour single molecule localisation microscopy of adhesive ligands and adhesion proteins
To date, the precise localisation of ligands and adhesion proteins are determined in two parallel characterization setups. Here, the authors report a self-assembled monolayer chemistry for indium tin oxide surfaces allowing single molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM) imaging of ligands and adhesion proteins in a single experiment.
- Xun Lu
- , Philip R. Nicovich
- & J. Justin Gooding
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry breakdown of 4,4″-diamino-p-terphenyl on a Cu(111) surface by lattice mismatch
Symmetry breakdown of 4,4″-diamino-p-terphenyl on a Cu(111) surface by lattice mismatch
In a symmetric molecule with identical functional groups, selective activation of only one site is challenging. Here, the authors show that 4,4″-diamino-p-terphenyl adsorbs asymmetrically to a metal surface, leading to a change in binding affinity of one of its amine groups.
- Qigang Zhong
- , Daniel Ebeling
- & André Schirmeisen
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly directed one-step synthesis of [4]radialene on Cu(100) surfaces
Self-assembly directed one-step synthesis of [4]radialene on Cu(100) surfaces
Radialenes have distinct structural, electronic and chemical properties from other hydrocarbons, but their synthesis remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a copper catalyzed one-step synthetic protocol of [4]radialene via the cyclotetramerization of phenylacetylene molecules upon thermal activation.
- Qing Li
- , Jianzhi Gao
- & Minghu Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space imaging with pattern recognition of a ligand-protected Ag374 nanocluster at sub-molecular resolution
Real-space imaging with pattern recognition of a ligand-protected Ag374 nanocluster at sub-molecular resolution
Translating high-resolution imaging methods to the curved organic surface of a nanoparticle has been challenging. Here, the authors are able to spatially resolve the sub-molecular surface details of a silver nanocluster by comparing scanning tunneling microscopy images and simulated topography data through a pattern recognition algorithm.
- Qin Zhou
- , Sami Kaappa
- & Lansun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Non-covalent control of spin-state in metal-organic complex by positioning on N-doped graphene
Non-covalent control of spin-state in metal-organic complex by positioning on N-doped graphene
Molecules can change their electronic properties when they are adsorbed on substrates, which can be useful for sensing and catalysis. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to show that the spin state of an iron complex can be changed upon displacing the molecule to different sites of a nitrogen-doped graphene
- Bruno de la Torre
- , Martin Švec
- & Pavel Jelínek
-
Article
| Open Access Water-dispersible PEG-curcumin/amine-functionalized covalent organic framework nanocomposites as smart carriers for in vivo drug delivery
Water-dispersible PEG-curcumin/amine-functionalized covalent organic framework nanocomposites as smart carriers for in vivo drug delivery
Despite their potential application as drug-delivery carriers, covalent organic frameworks (COF) have been only evaluated in vitro. Here the authors show by real time tracking in vivo the cell uptake of anticancer-drug loaded and water dispersible COFs.
- Guiyang Zhang
- , Xinle Li
- & Xudong Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Creating two self-assembly micro-environments to achieve supercrystals with dual structures using polyhedral nanoparticles
Creating two self-assembly micro-environments to achieve supercrystals with dual structures using polyhedral nanoparticles
Crystals with multiple structures often perform special functions in nature, inspiring the creation of synthetic analogues. Here, the authors subject polyhedral nanoparticles to two self-assembly micro-environments to realize supercrystals with dual structures, in which the order of the surface layer differs from the bulk structure.
- Yih Hong Lee
- , Chee Leng Lay
- & Xing Yi Ling
-
Article
| Open Access A biomimetic chiral-driven ionic gate constructed by pillar[6]arene-based host–guest systems
A biomimetic chiral-driven ionic gate constructed by pillar[6]arene-based host–guest systems
Uptake and release of glucose is regulated by glucose-sensitive ion channels, but complexity of the system impedes investigation of the gating behavior under physiological conditions. Here the authors use a pillararene based artificial ion channel to mimic and investigate chirality driven switching of a glucose ion channel.
- Yue Sun
- , Fan Zhang
- & Haibing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Deciphering absolute configuration of individual molecules directly by visual inspection remains a highly attractive goal. Here, the authors determine the absolute configuration and orientation of a single [123]tetramantane molecule adsorbed on Cu(111) using low temperature atomic force microscopy with a CO-functionalized tip.
- Daniel Ebeling
- , Marina Šekutor
- & Peter R. Schreiner
-
Article
| Open Access A photoelectrochemical platform for the capture and release of rare single cells
A photoelectrochemical platform for the capture and release of rare single cells
Many cell capture systems exist but the characterisation and controlled release of single cells is a challenge. Here, the authors report on the development of a duel trigger release system using a combination of photo and electro triggers to allow for light based analysis without unwanted release.
- Stephen G. Parker
- , Ying Yang
- & J. Justin Gooding
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting hot electron flux and catalytic activity at metal–oxide interfaces of PtCo bimetallic nanoparticles
Boosting hot electron flux and catalytic activity at metal–oxide interfaces of PtCo bimetallic nanoparticles
The real-time quantitative detection of hot electrons provides critical clues to understand the origin of the enhanced catalytic performance of bimetallic nanoparticles (NPs). Here, the authors investigate hot electrons generated on bimetallic PtCo NPs during H2 oxidation by measuring the chemicurrent on a catalytic nanodiode.
- Hyosun Lee
- , Juhyung Lim
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing hydrogen-induced reshaping and edge activation in MoS2 and Co-promoted MoS2 catalyst clusters
Visualizing hydrogen-induced reshaping and edge activation in MoS2 and Co-promoted MoS2 catalyst clusters
Rational design of a hydrodesulfurization catalyst relies on a fundamental understanding of its working principles. Here, the authors use scanning tunneling microscopy to directly visualize and quantify hydrogen-induced reshaping and edge activation in MoS2 and Co-promoted MoS2 catalyst clusters.
- Signe S. Grønborg
- , Norberto Salazar
- & Jeppe V. Lauritsen
-
Article
| Open Access Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers
Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers
While zeolites are industrially relevant as molecular sieves and catalysts, their growth mechanisms remain widely debated. Here, Rimer and colleagues probe the crystallization pathway of zeolite LTA with spatiotemporal resolution, identifying a distinctive nonclassical pathway, and demonstrating that growth is highly dependent on synthetic conditions.
- Manjesh Kumar
- , Madhuresh K. Choudhary
- & Jeffrey D. Rimer
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of a nitrogen-embedded buckybowl with inverse Stone–Thrower–Wales topology
On-surface synthesis of a nitrogen-embedded buckybowl with inverse Stone–Thrower–Wales topology
Heteroatom doping of buckybowls is a viable route to tune their intrinsic physico-chemical properties, but their synthesis remains challenging. Here, the authors report on a combined in-solution and on-surface synthetic strategy towards the fabrication of a buckybowl containing two fused nitrogen-doped pentagonal rings.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Maciej Krzeszewski
- & Daniel T. Gryko
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanisms of crystal growth inhibition by organic and inorganic inhibitors
The mechanisms of crystal growth inhibition by organic and inorganic inhibitors
Although trace compounds are known to inhibit crystal growth, the mechanisms by which they do so are unclear. Here, the authors use a microkinetic model to study the mechanisms of several inhibitors of calcite growth, finding that the processes are quite different for inorganic and organic inhibitors.
- S. Dobberschütz
- , M. R. Nielsen
- & M. P. Andersson
-
Article
| Open Access Self-cleaning and surface chemical reactions during hafnium dioxide atomic layer deposition on indium arsenide
Self-cleaning and surface chemical reactions during hafnium dioxide atomic layer deposition on indium arsenide
Atomic layer deposition of high-quality thin oxide layers is crucial for many modern semiconductor electronic devices. Here, the authors explore the surface chemistry during the initial deposition and observe a previously unknown two-step process, with promise for an improved self-cleaning effect.
- Rainer Timm
- , Ashley R. Head
- & Anders Mikkelsen
-
Article
| Open Access Optical characterization of surface adlayers and their compositional demixing at the nanoscale
Optical characterization of surface adlayers and their compositional demixing at the nanoscale
Characterization of adsorbed molecular layers on surfaces is the key to wide-ranging applications, but elucidating the structure and composition of such adlayers remains challenging. Here the authors develop an approach to unveil the nanoscale structure and composition of adlayers through spectrally resolved super-resolution microscopy.
- Limin Xiang
- , Michal Wojcik
- & Ke Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Experimentally quantifying anion polarizability at the air/water interface
Experimentally quantifying anion polarizability at the air/water interface
Understanding anion-specific interactions with hydrophobic interfaces is challenging due to an absence of local structural probes. Here, the authors experimentally quantify the anisotropy of perchlorate’s polarizability at the air/water interface, a window into anion and solvation shell structure.
- Yujin Tong
- , Igor Ying Zhang
- & R. Kramer Campen
-
Article
| Open Access Studying an antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon adsorbed on different surfaces
Studying an antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon adsorbed on different surfaces
Indeno[1,2-b]fluorene (IF) is an extremely reactive polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbon with antiaromatic character, thus it has not been detected to date. Here, the authors present the successful generation and characterisation of IF both on-surface and in-solution.
- Zsolt Majzik
- , Niko Pavliček
- & Leo Gross
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding and tailoring ligand interactions in the self-assembly of branched colloidal nanocrystals into planar superlattices
Understanding and tailoring ligand interactions in the self-assembly of branched colloidal nanocrystals into planar superlattices
The self-organization of nanocrystals into complex superlattices involves the interplay of different interactions. Here, the authors systematically reveal the effects of particle shape and ligand coverage on the assembly behavior of branched octapods into planar superlattices.
- Andrea Castelli
- , Joost de Graaf
- & Milena P. Arciniegas
-
Article
| Open Access Copper-surface-mediated synthesis of acetylenic carbon-rich nanofibers for active metal-free photocathodes
Copper-surface-mediated synthesis of acetylenic carbon-rich nanofibers for active metal-free photocathodes
While photoelectrochemical devices combine light-absorption with fuel and electricity generation, their implementation is hampered by high costs and low output. Here, the authors synthesized acetylene-rich carbon fibers by copper-mediated polymerization for high-activity, metal-free photocathodes.
- Tao Zhang
- , Yang Hou
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access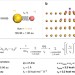 Insight into induced charges at metal surfaces and biointerfaces using a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential
Insight into induced charges at metal surfaces and biointerfaces using a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential
Molecular dynamics models for predicting the behavior of metallic nanostructures typically do not take into account polarization effects in metals. Here, the authors introduce a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential that provides quantitative insight into the role of induced charges at metal surfaces and related complex material interfaces.
- Isidro Lorenzo Geada
- , Hadi Ramezani-Dakhel
- & Hendrik Heinz
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing catalyst heterogeneity by a multifrequential oscillating reaction
Visualizing catalyst heterogeneity by a multifrequential oscillating reaction
The structurally different domains of a polycrystalline material may exhibit differing catalytic properties. Here, the authors directly visualize this phenomenon by observing the catalytic hydrogen oxidation that oscillates, simultaneously exhibiting different frequencies for structurally different rhodium domains.
- Yuri Suchorski
- , Martin Datler
- & Günther Rupprechter
-
Article
| Open Access Mössbauer spectroscopy of a monolayer of single molecule magnets
Mössbauer spectroscopy of a monolayer of single molecule magnets
Deposition of single molecule magnets onto surfaces is a key step for integration in devices exploiting their magnetic bistability and quantum properties. Here, Sessoli and colleagues exploit synchrotron Mössbauer spectroscopy to assess the effects of molecule-surface interactions on the magnetic properties of Fe(III) SMMs.
- Alberto Cini
- , Matteo Mannini
- & Roberta Sessoli
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ liquid cell transmission electron microscopy investigation on oriented attachment of gold nanoparticles
In-situ liquid cell transmission electron microscopy investigation on oriented attachment of gold nanoparticles
The non-classical oriented attachment crystallization pathway explains the growth of many nanocrystals. Here, the authors study citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles by in-situ liquid transmission electron microscopy to reveal that surface ligands are a critical driving force in the oriented attachment process.
- Chao Zhu
- , Suxia Liang
- & Litao Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Abnormal phase transition between two-dimensional high-density liquid crystal and low-density crystalline solid phases
Abnormal phase transition between two-dimensional high-density liquid crystal and low-density crystalline solid phases
Intermolecular interactions have a crucial role in the adsorption of molecules on a surface, however their role in promoting phase transitions is less well known. Here, the authors report an abnormal phase transition between a high-density liquid crystal and low-density solid in the case of carbon monoxide on Cu(111), driven by intermolecular interactions and entropy.
- Wenbin Li
- , Longjuan Kong
- & Lan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Raman enhancement on ultra-clean graphene quantum dots produced by quasi-equilibrium plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition
Raman enhancement on ultra-clean graphene quantum dots produced by quasi-equilibrium plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is a promising technology for sensitive optical sensors, generally using rough metal films. Here, Liu et al. synthesize high-quality graphene quantum dot films which offer a large SERS enhancement due to a strong light-matter interaction with Van Hove singularities.
- Donghua Liu
- , Xiaosong Chen
- & Dacheng Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Weakly perturbative imaging of interfacial water with submolecular resolution by atomic force microscopy
Weakly perturbative imaging of interfacial water with submolecular resolution by atomic force microscopy
Scanning probe microscopy has been extensively applied to probe interfacial water but the probes tend to disturb the structure of water easily. Here, the authors report submolecular-resolution imaging of water clusters within the nearly non-invasive region by qPlus noncontact atomic force microscopy.
- Jinbo Peng
- , Jing Guo
- & Ying Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin graphene oxide-based hollow fiber membranes with brush-like CO2-philic agent for highly efficient CO2 capture
Ultrathin graphene oxide-based hollow fiber membranes with brush-like CO2-philic agent for highly efficient CO2 capture
Membrane separation technologies show promise for CO2 capture, but typically suffer from a trade-off between permeance and selectivity. Here, the authors produce hollow fiber membranes coated with graphene oxide and a CO2-philic agent that can efficiently separate CO2 from flue gas under wet conditions.
- Fanglei Zhou
- , Huynh Ngoc Tien
- & Miao Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-resolution three-dimensional hydration structures on a heterogeneously charged surface
Atomic-resolution three-dimensional hydration structures on a heterogeneously charged surface
Local hydration structures at solid-liquid interfaces are important in catalytic, electrochemical, and biological processes. Here, the authors demonstrate atomic-scale 3D hydration structures around the boundary on a heterogeneous mineral surface using atomic force microscopy experiments and molecular dynamics simulations.
- Kenichi Umeda
- , Lidija Zivanovic
- & Hirofumi Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access Exploration of pyrazine-embedded antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbons generated by solution and on-surface azomethine ylide homocoupling
Exploration of pyrazine-embedded antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbons generated by solution and on-surface azomethine ylide homocoupling
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons can be precisely manipulated to yield ever more complex and discrete graphene analogs, such as nanographenes. Here, the authors use azomethine ylide homocoupling to insert an antiaromatic pyrazine ring into the core of a nanographene, and characterize the molecule’s unique electronic character.
- Xiao-Ye Wang
- , Marcus Richter
- & Klaus Müllen
-
Article
| Open Access Scaling relationships and theory for vibrational frequencies of adsorbates on transition metal surfaces
Scaling relationships and theory for vibrational frequencies of adsorbates on transition metal surfaces
Vibrational excitations are a fingerprint of molecule–surface interactions, but knowing how they scale across materials is tricky. Here, the authors discover correlations between the vibrational frequencies of adsorbates on transition metals, developing a predictive theory to allow interpretation of complex experimental spectra.
- Joshua L. Lansford
- , Alexander V. Mironenko
- & Dionisios G. Vlachos
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping microscale wetting variations on biological and synthetic water-repellent surfaces
Mapping microscale wetting variations on biological and synthetic water-repellent surfaces
Real-world surfaces exhibit spatially varying wettability, which affects water repellency and droplet behaviour on such surfaces. Here, the authors use scanning droplet adhesion microscopy to create wetting maps that visualize variations in wettability with a spatial resolution down to 10 μm.
- Ville Liimatainen
- , Maja Vuckovac
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
Article
| Open Access In situ detection of the protein corona in complex environments
In situ detection of the protein corona in complex environments
In situ detection of protein coronas is usually performed via optical methods, but light scattering may hamper these measurements. Here, the authors use diffusion NMR techniques to characterize protein corona formation on 19F-labeled nanoparticles in blood and other complex media.
- Monica Carril
- , Daniel Padro
- & Wolfgang J. Parak
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry control of nanorod superlattice driven by a governing force
Symmetry control of nanorod superlattice driven by a governing force
Shape complementarity is the primary way to control the symmetry of nanoparticle assemblies. Here, the authors introduce a governing force that dominates symmetry control of nanorod superlattices, using it to obtain an unexpected and highly thermostable tetragonal lattice.
- Yujia Liang
- , Yong Xie
- & Qian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access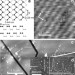 Supramolecular networks stabilise and functionalise black phosphorus
Supramolecular networks stabilise and functionalise black phosphorus
Few-layered black phosphorus has been exploited in transistors and other devices, but its poor stability under ambient conditions remains problematic. Here, a UK-Swiss collaboration show that a monolayer-thick supramolecular hydrogen-bonded network can protect a black phosphorus surface for over a month.
- Vladimir V. Korolkov
- , Ivan G. Timokhin
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article
| Open Access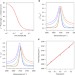 Second-order spectral lineshapes from charged interfaces
Second-order spectral lineshapes from charged interfaces
Charged interfaces are important in chemical systems, but the influence of charge on vibrational sum frequency spectra has only recently been considered. Here the authors show the importance of accounting for the interfacial potential-dependent χ(3) term in interpreting spectral lineshapes from charged interfaces.
- Paul E. Ohno
- , Hong-fei Wang
- & Franz M. Geiger
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time tracking of metal nucleation via local perturbation of hydration layers
Real-time tracking of metal nucleation via local perturbation of hydration layers
Electrochemical deposition is important for industrial processes however, tracking the early stages of metallic phase nucleation is challenging. Here, the authors visualize the birth and growth of metal nuclei at electrode surfaces in real time via high-speed non-contact lateral molecular force microscopy.
- Robert L. Harniman
- , Daniela Plana
- & David J. Fermín
-
Article
| Open Access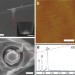 Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment
Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment
Crystal growth is a fundamental process, important in a wide range of fields, but the interparticle forces responsible for molecule alignment are not well understood. Here, the authors measure the alignment forces in ZnO using dynamic force spectroscopy, highlighting the role of intervening water molecules.
- X. Zhang
- , Z. Shen
- & K. M. Rosso
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping surface-modified titania nanoparticles with implications for activity and facet control
Mapping surface-modified titania nanoparticles with implications for activity and facet control
Metal oxide nanocrystals can be grown with different facets exposed to give variations in reactivity, but the chemical state of these surfaces is not clear. Here, the authors make use of a phosphine probe molecule allowing the differences in surface chemistry to be mapped by NMR spectroscopy.
- Yung-Kang Peng
- , Yichen Hu
- & Shik Chi Edman Tsang
-
Article
| Open Access Infused-liquid-switchable porous nanofibrous membranes for multiphase liquid separation
Infused-liquid-switchable porous nanofibrous membranes for multiphase liquid separation
Separating immiscible liquids with small surface energy differences remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a polarity-based strategy for the separation of multiphase mixtures of immiscible liquids, even those with surface energy differences as small as 2 mJ m-2.
- Yang Wang
- , Jiancheng Di
- & Jihong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling selectivities in CO2 reduction through mechanistic understanding
Controlling selectivities in CO2 reduction through mechanistic understanding
Understanding the mechanism of CO2 reduction on a catalyst surface is essential for achieving the desired product selectivity. Here, the authors show an operando kinetic analysis of CO2 hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst in order to address the factors governing the selectivity of the process.
- Xiang Wang
- , Hui Shi
- & János Szanyi
-
Article
| Open Access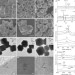 The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction
The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction
Nanocrystals display a variety of facets with different catalytic activity. Here the authors identify the most active facet of copper nanocrystals relevant to the low-temperature water gas shift reaction and further design zinc oxide-copper nanocubes with exceptionally high catalytic activity.
- Zhenhua Zhang
- , Sha-Sha Wang
- & Weixin Huang
-
Article
| Open Access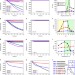 Hydrogen bond based smart polymer for highly selective and tunable capture of multiply phosphorylated peptides
Hydrogen bond based smart polymer for highly selective and tunable capture of multiply phosphorylated peptides
Capture of low-abundance multiply phosphorylated peptides (MPPs) is difficult due to limitation of enrichment materials and their interactions with phosphates. Here the authors show, a smart polymer driven by specific but tunable hydrogen bonding interactions can differentially complex with MPPs, singly phosphorylated and non-modified peptides.
- Guangyan Qing
- , Qi Lu
- & Taolei Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Observing the oxidation of platinum
Observing the oxidation of platinum
Improving platinum as an oxidation catalyst requires understanding its structure under catalytic conditions. Here, the authors discover that catalytically important surface oxides form only when Pt is exposed to high pressure and temperature, highlighting the need to study catalysts in realistic environments.
- Matthijs A. van Spronsen
- , Joost W. M. Frenken
- & Irene M. N. Groot
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-orbital charge transfer at highly oriented organic/metal interfaces
Multi-orbital charge transfer at highly oriented organic/metal interfaces
Charge transfer at molecule-metal interfaces affects the overall physical and magnetic properties of organic-based devices, and ultimately their performance. Here, the authors report evidence of a pronounced charge transfer involving nickel tetraphenyl porphyrin molecules adsorbed on copper.
- Giovanni Zamborlini
- , Daniel Lüftner
- & Claus Michael Schneider

 Reconfiguring surface functions using visible-light-controlled metal-ligand coordination
Reconfiguring surface functions using visible-light-controlled metal-ligand coordination