Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Quasiparticle tunnel electroresistance in superconducting junctions
Quasiparticle tunnel electroresistance in superconducting junctions
The non-volatile switching of tunnel electroresistance in ferroelectric junctions provides the basis for memory and neuromorphic computing devices. Rouco et al. show tunnel electroresistance in superconductor-based junctions that arises from a redox rather than ferroelectric mechanism and is enhanced by superconductivity.
- V. Rouco
- , R. El Hage
- & Javier E. Villegas
-
Article
| Open Access Disappearance of superconductivity due to vanishing coupling in the overdoped Bi\(_{2}\)Sr\(_{2}\)CaCu\(_{2}\)O\(_{8+\delta }\)
Disappearance of superconductivity due to vanishing coupling in the overdoped Bi\(_{2}\)Sr\(_{2}\)CaCu\(_{2}\)O\(_{8+\delta }\)
The pairing mechanism of cuprate superconductors is still under debate. Here, Valla et al. report that mass renormalization in Bi\(_{2}\)Sr\(_{2}\)CaCu\(_{2}\)O\(_{8+\delta }\) weakens with doping and disappears precisely where superconductivity disappears, eliminating phononic mechanism for pairing.
- T. Valla
- , I. K. Drozdov
- & G. D. Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Topological ultranodal pair states in iron-based superconductors
Topological ultranodal pair states in iron-based superconductors
Experiments indicate an abrupt change in the pairing gap near the nematic transition in the FeSe1−xSx iron-based superconductor. Here, Setty et al. propose to explain them via a novel spin-1/2 paired state with topologically protected zero-energy excitations over a finite area nodal surface.
- Chandan Setty
- , Shinibali Bhattacharyya
- & P. J. Hirschfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast transient liquid assisted growth of high current density superconducting films
Ultrafast transient liquid assisted growth of high current density superconducting films
High throughput manufacturing of long length coated conductors requires fast epitaxial growth of high-temperature superconducting films. Here, Soler et al. report an ultrafast growth rates and high critical current densities of YBa2Cu3O7 films using a transient liquid-assisted growth method.
- L. Soler
- , J. Jareño
- & T. Puig
-
Article
| Open Access Classification and characterization of nonequilibrium Higgs modes in unconventional superconductors
Classification and characterization of nonequilibrium Higgs modes in unconventional superconductors
The lately reported Higgs modes in unconventional superconductors require a classification and characterization allowed by nontrivial symmetry of the gap and the quench pulses. Here, the authors provide a classification scheme of Higgs oscillations with their excitation processes allowing them to distinguish between different symmetries of the superconducting condensate.
- L. Schwarz
- , B. Fauseweh
- & D. Manske
-
Article
| Open Access Direction and symmetry transition of the vector order parameter in topological superconductors CuxBi2Se3
Direction and symmetry transition of the vector order parameter in topological superconductors CuxBi2Se3
The understanding of the vector order parameter for Cu0.3Bi2Se3 topological superconductor remains unclear. Here, Kawai et al. report a surprising disappearance of the in-plane upper critical field anisotropy for CuxBi2Se3 single crystals with more carriers, indicating a transition from nematic to chiral superconducting gap symmetry.
- T. Kawai
- , C. G. Wang
- & Guo-qing Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Gate controlled anomalous phase shift in Al/InAs Josephson junctions
Gate controlled anomalous phase shift in Al/InAs Josephson junctions
The anomalous Josephson effect can be regarded as the hall-mark effect of superconducting spintronics. Here, the authors report the observation of a tunable anomalous Josephson effect in InAs/Al Josephson junctions measured via a superconducting quantum interference device.
- William Mayer
- , Matthieu C. Dartiailh
- & Javad Shabani
-
Article
| Open Access Conversion of a conventional superconductor into a topological superconductor by topological proximity effect
Conversion of a conventional superconductor into a topological superconductor by topological proximity effect
Realizing topological superconductivity is essential for applicable fault-tolerant quantum computation. Here, Trang et al. report migration of Dirac-cone from TlBiSe2 substrate to top surface of superconducting Pb film due to topological proximity effect, suggesting realization of topological superconductivity.
- C. X. Trang
- , N. Shimamura
- & T. Sato
-
Article
| Open Access A unified form of low-energy nodal electronic interactions in hole-doped cuprate superconductors
A unified form of low-energy nodal electronic interactions in hole-doped cuprate superconductors
The normal state of hole-doped, high-temperature superconductors is a currently-unexplained "strange metal" with exotic electronic behaviour. Here, the authors show that a doping-dependent power law ansatz for the electronic scattering phenomenologically captures ARPES, transport and optics observations.
- T. J. Reber
- , X. Zhou
- & D. S. Dessau
-
Article
| Open Access Theory of correlated insulating behaviour and spin-triplet superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene
Theory of correlated insulating behaviour and spin-triplet superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene
Twisted bilayer graphene exhibits correlated electronic phases and superconductivity, but its precise nature is under debate. Here, Lee and Khalaf et al. study a twisted double bilayer graphene, where ferromagnetic insulator and spin triplet superconducting phases can be stabilized.
- Jong Yeon Lee
- , Eslam Khalaf
- & Ashvin Vishwanath
-
Article
| Open Access Nematic fluctuations in the cuprate superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ
Nematic fluctuations in the cuprate superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ
Solid evidence of quantum fluctuations associated to a quantum critical point in cuprate superconductors remains elusive. Here, Auvray et al. report Raman scattering evidence of enhanced electronic nematic fluctuations near the endpoint of the pseudogap phase in Bi\({}_{2}\)Sr\({}_{2}\)CaCu\({}_{2}\)O\({}_{8+\delta }\).
- N. Auvray
- , B. Loret
- & Y. Gallais
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent honeycomb network of topological excitations in correlated charge density wave
Emergent honeycomb network of topological excitations in correlated charge density wave
The detailed structures of domain walls are important to determine macroscopic properties in charge density wave materials. Here, Park et al. report atomic and electronic structures of a honeycomb domain wall network in 1T-TaS2, which may help understand the enhanced superconductivity.
- Jae Whan Park
- , Gil Young Cho
- & Han Woong Yeom
-
Article
| Open Access Local Josephson vortex generation and manipulation with a Magnetic Force Microscope
Local Josephson vortex generation and manipulation with a Magnetic Force Microscope
Josephson vortices (JVs) play an important role in superconducting quantum devices, but they remain difficult to be observed and manipulated. Here, Dremov et al. report magnetic fingerprint of JVs in magnetic force microscopy experiments, which paves a way to generate and control JVs.
- Viacheslav V. Dremov
- , Sergey Yu. Grebenchuk
- & Vasily S. Stolyarov
-
Article
| Open Access Ballistic superconductivity and tunable π–junctions in InSb quantum wells
Ballistic superconductivity and tunable π–junctions in InSb quantum wells
Hybrid superconductor-semiconductor devices offer a promising platform for topological superconductivity. Here, Ke and Moehle et al. create ballistic Josephson junctions in InSb quantum wells and use magnetic and electric fields to control their free energy landscape.
- Chung Ting Ke
- , Christian M. Moehle
- & Srijit Goswami
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous quantum Griffiths singularity in ultrathin crystalline lead films
Anomalous quantum Griffiths singularity in ultrathin crystalline lead films
Evidence of quantum phase transitions is normally difficult to be detected. Here, Liu and Wang et al. report divergent critical exponent in ultrathin Pb films with superconducting fluctuations and spin-orbit interaction, indicating an anomalous quantum Griffiths singularity of superconductor-metal transition.
- Yi Liu
- , Ziqiao Wang
- & Jian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved XUV ARPES with tunable 24–33 eV laser pulses at 30 meV resolution
Time-resolved XUV ARPES with tunable 24–33 eV laser pulses at 30 meV resolution
Currently, it is difficult to reach high momenta with narrow energy resolution via laser-based angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). Here, Sie et al. develop a time-resolved XUV based ARPES setup which can access the first Brillouin zone of all materials with narrow energy resolution.
- Edbert J. Sie
- , Timm Rohwer
- & Nuh Gedik
-
Article
| Open Access Diagonal nematicity in the pseudogap phase of HgBa2CuO4+δ
Diagonal nematicity in the pseudogap phase of HgBa2CuO4+δ
One of the proposed explanations for the unusual pseudogap behaviour of cuprate superconductors is the formation of an electron nematic phase. Murayama et al. find magnetic anisotropy in the pseudogap regime of HgBa2CuO4+δ, providing evidence for anomalous nematic ordering.
- H. Murayama
- , Y. Sato
- & Y. Matsuda
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of two types of charge-density-wave orders in superconducting La2-xSrxCuO4
Observation of two types of charge-density-wave orders in superconducting La2-xSrxCuO4
To fully elucidate the relationship between density wave orders and superconductivity in high-Tc cuprates remains difficult. Here, the authors reveal two types of charge-density-wave orders and their intertwined relationship with spin-density-wave order and superconductivity in La2-xSrxCuO4.
- J.-J. Wen
- , H. Huang
- & J.-S. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access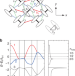 Mechanism of superconductivity and electron-hole doping asymmetry in κ-type molecular conductors
Mechanism of superconductivity and electron-hole doping asymmetry in κ-type molecular conductors
The mechanism of unconventional superconductivity in molecular conductors remains controversial. Here, Watanabe et al. theoretically study and report electron-hole doping asymmetry and competing orders with superconductivity in a doped molecular Mott system.
- Hiroshi Watanabe
- , Hitoshi Seo
- & Seiji Yunoki
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for singular-phonon-induced nematic superconductivity in a topological superconductor candidate Sr0.1Bi2Se3
Evidence for singular-phonon-induced nematic superconductivity in a topological superconductor candidate Sr0.1Bi2Se3
Superconductivity mediated by phonons is usually conventional due to isotropic electron-phonon coupling. Here, Wang et al. report highly anisotropic phonons only along [001] direction in Sr0.1Bi2Se3, indicating a singular electron-phonon coupling which favors a p-wave nematic superconductivity scenario.
- Jinghui Wang
- , Kejing Ran
- & Jinsheng Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Nonreciprocal charge transport at topological insulator/superconductor interface
Nonreciprocal charge transport at topological insulator/superconductor interface
The superconducting proximity effect on the surface state of a topological insulator is promising to generate topological superconductivity. Here, Yasuda et al. reported enhanced nonreciprocal charge transport in a Bi2Te3/FeTe heterostructure with an emerging superconducting order parameter.
- Kenji Yasuda
- , Hironori Yasuda
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Universal superconducting precursor in three classes of unconventional superconductors
Universal superconducting precursor in three classes of unconventional superconductors
The understanding of how superconductivity emerges from a complex normal state remains elusive in unconventional superconductors. Here, Pelc et al. report exponential temperature dependence of the diamagnetic response in the normal state with a characteristic temperature scale, universally existing in three classes of oxide superconductors.
- D. Pelc
- , Z. Anderson
- & M. Greven
-
Article
| Open Access Isolated pairs of Majorana zero modes in a disordered superconducting lead monolayer
Isolated pairs of Majorana zero modes in a disordered superconducting lead monolayer
It is predicted that Majorana zero modes can appear locally around topological defects in a two-dimensional system. Here, the authors observe pairs of zero modes stabilized in the middle and around the magnetic domains in a disordered superconducting Pb monolayer.
- Gerbold C. Ménard
- , Andrej Mesaros
- & Tristan Cren
-
Article
| Open Access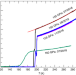 Superconducting phase diagram of H3S under high magnetic fields
Superconducting phase diagram of H3S under high magnetic fields
The discovery of over 200 K superconductivity excites the community to search for room temperature superconductivity. Here, Mozaffari et al. report the temperature dependence of the upper critical fields of superconducting H3S under a record-high combination of pressures up to 160 GPa and magnetic fields up to 65 T.
- Shirin Mozaffari
- , Dan Sun
- & Fedor F. Balakirev
-
Article
| Open Access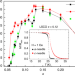 Phase transition in the cuprates from a magnetic-field-free stiffness meter viewpoint
Phase transition in the cuprates from a magnetic-field-free stiffness meter viewpoint
Precise measurements of the superconducting stiffness tensor can give detailed insights into the superconductor-normal phase transition. Kapon et al. introduce the Stiffnessometer approach for sensitive magnetic-field-free measurements and find two transition temperatures in LSCO rings.
- Itzik Kapon
- , Zaher Salman
- & Amit Keren
-
Article
| Open Access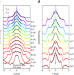 Proximity-induced surface superconductivity in Dirac semimetal Cd3As2
Proximity-induced surface superconductivity in Dirac semimetal Cd3As2
Surface superconductivity in a Dirac semimetal remains rarely studied. Here, Huang and Zhou et al. report the evidence of proximity-induced surface superconductivity in a superconductor/Dirac semimetal hybrid system Nb/Cd3As2.
- Ce Huang
- , Benjamin T. Zhou
- & Faxian Xiu
-
Article
| Open Access Transport evidence of asymmetric spin–orbit coupling in few-layer superconducting 1Td-MoTe2
Transport evidence of asymmetric spin–orbit coupling in few-layer superconducting 1Td-MoTe2
Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides with peculiar spin–orbit coupling may lead to exotic phenomena. Here, the authors report a large in-plane upper critical field with a two-fold symmetry, suggesting a novel asymmetric spin–orbit coupling in few-layer 1Td-MoTe2.
- Jian Cui
- , Peiling Li
- & Guangtong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Concomitant opening of a bulk-gap with an emerging possible Majorana zero mode
Concomitant opening of a bulk-gap with an emerging possible Majorana zero mode
A quantized zero-bias conductance peak (ZBCP) is potentially a signature of Majorana edge mode provided that a topological gap opens in the bulk. Here, Grivnin et al. observe ZBCP at the edge both with and without a superconducting bulk-gap in an InAs nanowire coated with epitaxial Al.
- Anna Grivnin
- , Ella Bor
- & Hadas Shtrikman
-
Article
| Open Access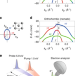 Ultrafast nematic-orbital excitation in FeSe
Ultrafast nematic-orbital excitation in FeSe
Several experiments have shown evidence for unusual nematic electronic behaviour in unconventional superconductors. Here the authors use pump-probe spectroscopy to observe out-of-equilibrium behaviour of coupled nematic-orbital excitations in iron selenide.
- T. Shimojima
- , Y. Suzuki
- & K. Ishizaka
-
Article
| Open Access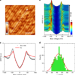 Directly visualizing the sign change of d-wave superconducting gap in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ by phase-referenced quasiparticle interference
Directly visualizing the sign change of d-wave superconducting gap in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ by phase-referenced quasiparticle interference
The superconducting gap structure contains important information to understand the pairing mechanism of unconventional superconductivity. Here, by using a newly established phase-referenced quasiparticle interference technique, the authors visualize the sign change of the d-wave superconducting gap directly in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ.
- Qiangqiang Gu
- , Siyuan Wan
- & Hai-Hu Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Charge density wave memory in a cuprate superconductor
Charge density wave memory in a cuprate superconductor
The understanding of charge density wave (CDW) correlations in cuprate superconductors remains hampered due to the lack of scattering phase information. Here, Chen et al. discover a reproducible CDW domain memory effect upon repeated cycling to temperatures well above the CDW ordering temperature.
- X. M. Chen
- , C. Mazzoli
- & I. K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of nematic order and nodal superconducting gap along [110] direction in RbFe2As2
Evidence of nematic order and nodal superconducting gap along [110] direction in RbFe2As2
Exotic electronic order may emerge and intertwine with superconductivity in iron-based superconductors. Here, the authors observe asymmetric electronic and superconducting gap structure in heavily hole-doped RbFe2As2 along the (π, π) and (π, -π) directions in reciprocal space, suggesting a novel (π, π) nematic phase emerging.
- Xi Liu
- , Ran Tao
- & Donglai Feng
-
Article
| Open Access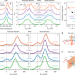 Strain-engineering Mott-insulating La2CuO4
Strain-engineering Mott-insulating La2CuO4
The optimal condition for superconductivity is a long-sought issue but remains challenging. Here, Ivashko et al. demonstrate that the compressive strain to La2CuO4 films enhances the Coulomb and magnetic-exchange interactions relevant for superconductivity, providing a strategy to optimise the parent Mott state for superconductivity.
- O. Ivashko
- , M. Horio
- & J. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access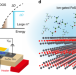 Giant thermoelectric power factor in ultrathin FeSe superconductor
Giant thermoelectric power factor in ultrathin FeSe superconductor
In an effort to optimize the performance of two-dimensional materials for thermoelectric generation, compounds with advantageous intrinsic properties must be identified. Here, the authors report large thermoelectric effect in ultrathin FeSe thin films with high Tc superconductivity.
- Sunao Shimizu
- , Junichi Shiogai
- & Yoshihiro Iwasa
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of cooperative effect on the enhanced superconducting transition temperature at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
Evidence of cooperative effect on the enhanced superconducting transition temperature at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
The mechanism of enhanced superconducting transition temperature (Tc) at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface remains enigmatic. Here, Song and Yu et al. reveal the evidence of cooperation between intrinsic pairing interaction in FeSe and interfacial electron–phonon coupling to enhance the Tc at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface.
- Q. Song
- , T. L. Yu
- & D. L. Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced superconductivity close to a non-magnetic quantum critical point in electron-doped strontium titanate
Enhanced superconductivity close to a non-magnetic quantum critical point in electron-doped strontium titanate
Among its interesting properties, SrTiO3 can show both superconductivity and ferroelectric quantum criticality at low temperatures. Tomioka et al. use La and oxygen-isotope doping to tune electron-doped SrTiO3 to the critical region and observe enhanced superconductivity, suggesting a link between them.
- Yasuhide Tomioka
- , Naoki Shirakawa
- & Isao H. Inoue
-
Article
| Open Access Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
Noisy defects in the high-Tc superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
The effects of dopants in high-temperature superconductors on the surrounding electronic structure give insights into their unconventional microscopic behaviour. Here the authors find a new class of defects that they identify as oxygen dopants whose ionization and local environment induce unusual atomic-scale charge dynamics.
- F. Massee
- , Y. K. Huang
- & M. Aprili
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of the 4π-periodic Josephson effect in indium arsenide nanowires
Observation of the 4π-periodic Josephson effect in indium arsenide nanowires
The interplay of induced superconductivity and magnetic fields should drive InAs nanowires into a topological superconducting phase. Laroche et al. use the microwave radiation emitted by an InAs nanowire Josephson junction to observe the 4π-periodic Josephson effect, a hallmark of the topological phase.
- Dominique Laroche
- , Daniël Bouman
- & Attila Geresdi
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-Orbit induced phase-shift in Bi2Se3 Josephson junctions
Spin-Orbit induced phase-shift in Bi2Se3 Josephson junctions
An anomalous phase shift in a topological insulator based Josephson junction is expected but never been observed. Here, Assouline et al. observe an anomalous phase shift in a Bi2Se3 based Josephson junction in presence of an in-plane magnetic field, opening opportunities for phase-controlled Josephson devices.
- Alexandre Assouline
- , Cheryl Feuillet-Palma
- & Hervé Aubin
-
Article
| Open Access Light induced non-volatile switching of superconductivity in single layer FeSe on SrTiO3 substrate
Light induced non-volatile switching of superconductivity in single layer FeSe on SrTiO3 substrate
How photoexcitations influence superconductivity at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface remains elusive. Here, the authors report fast optical generation of a metastable superconducting state and its reversal by voltage pulses at the FeSe monolayer/SrTiO3 interface.
- Ming Yang
- , Chenhui Yan
- & Cheng Cen
-
Article
| Open Access Geometric quenching of orbital pair breaking in a single crystalline superconducting nanomesh network
Geometric quenching of orbital pair breaking in a single crystalline superconducting nanomesh network
It is highly desired to maintain superconductivity in presence of magnetic fields but it is by far difficult. Here, Nam et al. create a single crystalline superconducting Pb nanowire network, where critical temperatures are maintained and critical fields are enhanced in either parallel or perpendicular fields.
- Hyoungdo Nam
- , Hua Chen
- & Chih-Kang Shih
-
Article
| Open Access Creation of equal-spin triplet superconductivity at the Al/EuS interface
Creation of equal-spin triplet superconductivity at the Al/EuS interface
Spectroscopic evidence of equal-spin triplet Cooper pairs is still missing so far. Here, Diesch et al. propose a unique signature for the presence of equal-spin triplet pairs and experimentally reveal the spin configuration of triplet pairs at the Al/EuS interface.
- S. Diesch
- , P. Machon
- & E. Scheer
-
Article
| Open Access Phase diagram of Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ revisited
Phase diagram of Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ revisited
The doping level of cuprate superconductors is usually difficult to determine. Here, Drozdov et al. report spectroscopic studies of in-situ modified Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ, exploring not only the superconducting dome but also the previously inaccessible, non-superconducting regime of the phase diagram, with absolute determination of the doping level.
- I. K. Drozdov
- , I. Pletikosić
- & T. Valla
-
Article
| Open Access Vortex rectenna powered by environmental fluctuations
Vortex rectenna powered by environmental fluctuations
Devices that generate electricity from electric fluctuations are promising for wireless power transmission as well as energy harvesting from environmental radio waves. Here the authors report the electric power generation from environmental fluctuations by using superconducting vortex strings in MoGe/YIG bilayer system.
- J. Lustikova
- , Y. Shiomi
- & E. Saitoh
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave emission from superconducting vortices in Mo/Si superlattices
Microwave emission from superconducting vortices in Mo/Si superlattices
Emission of electromagnetic waves is expected when superconducting vortices cross sample edges, but such a radiation has not been observed so far. Here, Dobrovolskiy et al. evidence the electromagnetic radiation from vortices crossing the layers of a Mo/Si superlattice, where the emission spectra can be tuned by dc bias current and coarsely by the in-plane magnetic field.
- O. V. Dobrovolskiy
- , V. M. Bevz
- & M. Huth
-
Article
| Open Access Parity transitions in the superconducting ground state of hybrid InSb–Al Coulomb islands
Parity transitions in the superconducting ground state of hybrid InSb–Al Coulomb islands
Understanding the ground state (GS) phase transitions in the quantum tunneling regime of a superconducting system is important for future qubit devices. Here, Shen, Heedt and Borsoi et al. report distinct types of fermion parity GS transitions as a function of magnetic field and gate voltages in a Coulomb-blockaded InSb–Al island.
- Jie Shen
- , Sebastian Heedt
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Signature of quantum Griffiths singularity state in a layered quasi-one-dimensional superconductor
Signature of quantum Griffiths singularity state in a layered quasi-one-dimensional superconductor
Whether the quantum Griffiths singularity state exists in one-dimensional (1D) systems remains elusive. Here, Zhang et al. report violation of the Pauli limit in the superconducting critical field and multiple phase transitions in the current-voltage hysteresis loops in a Ta2PdS5 nanowire, suggesting signatures of quasi-1D quantum Griffith singularity.
- Enze Zhang
- , Jinhua Zhi
- & Faxian Xiu
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic field compatible circuit quantum electrodynamics with graphene Josephson junctions
Magnetic field compatible circuit quantum electrodynamics with graphene Josephson junctions
A transmon qubit insensitive to magnetic fields is a crucial element in topological quantum computing. Here, Kroll et al. create graphene transmons by integrating monolayer graphene Josephson junctions into microwave frequency superconducting circuits, allowing them to operate in a parallel magnetic field of 1 T.
- J. G. Kroll
- , W. Uilhoorn
- & L. P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of superconductivity in the cuprates via a universal percolation process
Emergence of superconductivity in the cuprates via a universal percolation process
The emergence of superconductivity from the normal state in the cuprates above the transition temperature (Tc) has been controversial. Here, Pelc et al. report nonlinear conductivity, resulting from superconducting precursors only, vanishing exponentially above Tc both with temperature and with magnetic field.
- Damjan Pelc
- , Marija Vučković
- & Neven Barišić

 Energy-level quantization and single-photon control of phase slips in YBa2Cu3O7–x nanowires
Energy-level quantization and single-photon control of phase slips in YBa2Cu3O7–x nanowires