Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling structural ambiguities in lithium- and manganese-rich transition metal oxides
Unravelling structural ambiguities in lithium- and manganese-rich transition metal oxides
Lithium and manganese-rich transition metal oxides are a class of promising battery electrodes but their structures are a subject of a controversial debate. Here, the authors use a variety of materials characterization tools to unravel the structural ambiguities in these materials.
- Alpesh Khushalchand Shukla
- , Quentin M. Ramasse
- & Guoying Chen
-
Review Article
| Open Access Structural analysis of hierarchically organized zeolites
Structural analysis of hierarchically organized zeolites
Hierarchically organized zeolites are materials retaining the crystalline order and associated functionality of bulk zeolites while also integrating a multilevel pore network. Here, the authors review the raft of techniques applied to characterize their crystal, pore and active site structures.
- Sharon Mitchell
- , Ana B. Pinar
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Article
| Open Access Strong frequency dependence of vibrational relaxation in bulk and surface water reveals sub-picosecond structural heterogeneity
Strong frequency dependence of vibrational relaxation in bulk and surface water reveals sub-picosecond structural heterogeneity
The structural heterogeneity in liquid water is commonly believed to disappear beyond 50 fs due to the strong intermolecular interaction. Here, the authors show frequency-dependent vibrational relaxation, which indicates the persistence of structural heterogeneity on a picosecond timescale.
- Sietse T. van der Post
- , Cho-Shuen Hsieh
- & Johannes Hunger
-
Article
| Open Access A predictive structural model for bulk metallic glasses
A predictive structural model for bulk metallic glasses
The atomic structure of metallic glasses is related to their properties such as the ability of materials to form glasses. Here, the authors develop a new approach to model the atomic structure of metallic glasses, to enable a better connection between atomic structure and glass properties.
- K. J. Laws
- , D. B. Miracle
- & M. Ferry
-
Article |
 Imaging of alignment and structural changes of carbon disulfide molecules using ultrafast electron diffraction
Imaging of alignment and structural changes of carbon disulfide molecules using ultrafast electron diffraction
Imaging the structure of molecules in transient excited states remains a challenge due to the extreme requirements for spatial and temporal resolution. Here, the authors probe the dynamics in CS2using ultrafast electron diffraction and femtosecond laser mass spectrometery.
- Jie Yang
- , Joshua Beck
- & Martin Centurion
-
Article
| Open Access Flash Joule heating for ductilization of metallic glasses
Flash Joule heating for ductilization of metallic glasses
Metallic glasses (MG) have higher yield strengths than crystalline alloys but at the same time are very brittle, which has hampered practical applications. Here, the authors use flash Joule heating to design a MG-matrix composite with a uniform distribution of ductile crystals, improving mechanical properties.
- I. V. Okulov
- , I. V. Soldatov
- & J. Eckert
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual fast secondary relaxation in metallic glass
Unusual fast secondary relaxation in metallic glass
Mechanical relaxation processes in glasses can provide information on the structural and mechanical properties of glasses. Here, the authors observe a fast secondary relaxation process in La-based metallic glasses, providing information on the inelasticity of metallic glasses.
- Q. Wang
- , S.T. Zhang
- & J. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental differences between glassy dynamics in two and three dimensions
Fundamental differences between glassy dynamics in two and three dimensions
The existing glass transition theories show little dimensional dependence. Here Flenner et al. disprove this general consensus by finding that, for instance, the bond-orientational relaxation is decoupled from the translational relaxation in two dimensions, but not in three dimensions.
- Elijah Flenner
- & Grzegorz Szamel
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave spectroscopy of the low-filling-factor bilayer electron solid in a wide quantum well
Microwave spectroscopy of the low-filling-factor bilayer electron solid in a wide quantum well
In 2D electron gases, insulating behaviour at low fractional quantum Hall filling factors is understood by the formation of an electronic Wigner solid. Here, the authors use microwave spectroscopy to evidence an electron liquid–solid mixed phase in bilayer states of GaAs/AlGaAs wide quantum wells.
- A. T. Hatke
- , Y. Liu
- & K. W. Baldwin
-
Article |
 Ultrasonic hammer produces hot spots in solids
Ultrasonic hammer produces hot spots in solids
The initiation of explosions is thought to result from ‘hot spot’ generation at localized microstructures in energetic material, although experimental evidence has been limited. Here, the authors show controllable hot spot formation in solid composites using an ultrasonic hammer, introducing a new method of study.
- Sizhu You
- , Ming-Wei Chen
- & Kenneth S. Suslick
-
Article |
 Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Degrees of freedom can be frozen in glassy material, which results in a hysteresis in heat capacity under cooling or heating. Here, the authors show that the hysteresis can be minimized at selected thermodynamic conditions, leading to thermally reversible glasses that are isostatically rigid.
- M. Bauchy
- & M. Micoulaut
-
Article
| Open Access Misfit accommodation mechanism at the heterointerface between diamond and cubic boron nitride
Misfit accommodation mechanism at the heterointerface between diamond and cubic boron nitride
Interfaces between two materials often show interesting properties. Here, the authors demonstrate that diamond and cubic boron nitride, the hardest materials known, can be grown on top of each other through a novel misfit accommodation mechanism, forming a two-dimensional electron gas at the interface.
- Chunlin Chen
- , Zhongchang Wang
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article |
 Hierarchical densification and negative thermal expansion in Ce-based metallic glass under high pressure
Hierarchical densification and negative thermal expansion in Ce-based metallic glass under high pressure
Metallic glasses show polyamorphous features, while the nature of the transformation between those amorphous structures is still unclear. Here, Luo et al.propose a pressure-induced hierarchical densification to explain a transformation in Ce-based metallic glass near glass transition temperature.
- Qiang Luo
- , Gaston Garbarino
- & Jun Shen
-
Article |
 Carrier density modulation in a germanium heterostructure by ferroelectric switching
Carrier density modulation in a germanium heterostructure by ferroelectric switching
The control of electrical charges through an electronic field is the basis of modern electronic devices such as the transistor. Here, the authors achieve charge density modulation through a ferroelectric field effect in germanium and barium titanate thin-film heterostructures.
- Patrick Ponath
- , Kurt Fredrickson
- & Alexander A. Demkov
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality-selected phase behaviour in ionic polypeptide complexes
Chirality-selected phase behaviour in ionic polypeptide complexes
Complexes that form between oppositely charged polyelectrolytes may be solid or liquid. Here, Perry et al.show that chirality in polypeptides can determine the state of those complexes based on a propensity for hydrogen-bond formation.
- Sarah L. Perry
- , Lorraine Leon
- & Matthew Tirrell
-
Article
| Open Access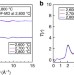 Atomic and electronic structures of an extremely fragile liquid
Atomic and electronic structures of an extremely fragile liquid
ZrO2 is known to be a very poor glass former, namely an extremely fragile liquid, while its high melting temperature impedes a mechanistic understanding. Here, Kohara et al. show the absence of intermediate-range ordering beyond the correlation between oxide polyhedron units in ZrO2upon melting.
- Shinji Kohara
- , Jaakko Akola
- & Takeshi Usuki
-
Article
| Open Access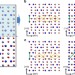 Atomic-scale structure and properties of highly stable antiphase boundary defects in Fe3O4
Atomic-scale structure and properties of highly stable antiphase boundary defects in Fe3O4
Although Fe3O4is widely investigated for a variety of applications, the relation between some defects and its properties remains poorly understood. Here, the authors use high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and simulations to determine the atomic structure of the common antiphase boundary defects.
- Keith P. McKenna
- , Florian Hofer
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article |
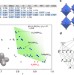 Structure and properties of complex hydride perovskite materials
Structure and properties of complex hydride perovskite materials
Complex metal hydrides are of interest for applications such as hydrogen storage, solid-state phosphors and solid electrolytes. Here the authors present the synthesis and properties of 30 complex hydride compounds with a perovskite crystal structure, based on the BH4−anion and new synthesis protocols involving rare-earth elements.
- Pascal Schouwink
- , Morten B. Ley
- & Radovan Černý
-
Article |
 Supercooled liquids with enhanced orientational order
Supercooled liquids with enhanced orientational order
Medium-range structural ordering is expected to exist in supercooled liquids yet direct probes of this are difficult to achieve. Capponi et al.report a new metastable phase of organic molecular glasses exhibiting long-living, highly enhanced orientational order above its glass transition temperature.
- Simona Capponi
- , Simone Napolitano
- & Michael Wübbenhorst
-
Article
| Open Access Roles of icosahedral and crystal-like order in the hard spheres glass transition
Roles of icosahedral and crystal-like order in the hard spheres glass transition
The dynamics and structure of the glass transition in liquids is still debated. Using particle-level confocal microscopy, Leocmach and Tanaka investigate supercooled colloidal liquids and distinguish different scenarios for glassy slow dynamics, suggesting that local ordering may only play a minor role.
- Mathieu Leocmach
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article |
 Ultrafast changes in lattice symmetry probed by coherent phonons
Ultrafast changes in lattice symmetry probed by coherent phonons
Ultrafast excitation offers new routes to controlling material properties on short timescales, but probes are needed to better understand the changes. By studying the phonon spectrum of VO2 in the time domain, Wall et al. find a prompt change in lattice potential after a photoinduced structural transition.
- S. Wall
- , D. Wegkamp
- & M. Wolf

 Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor