Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access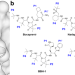 Covalent narlaprevir- and boceprevir-derived hybrid inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Covalent narlaprevir- and boceprevir-derived hybrid inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Three covalent hybrid inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) have been designed and compared to Pfizer’s nirmatrelvir (PF-07321332), providing atomic and thermodynamic details of their binding to the enzyme, and antiviral potency.
- Daniel W. Kneller
- , Hui Li
- & Andrey Kovalevsky
-
Article
| Open Access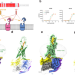 A distinctive ligand recognition mechanism by the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 2
A distinctive ligand recognition mechanism by the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 2
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 2 (VIP2R) is involved in immunity. Here, the authors report two cryo-EM structures of the VIP2R–Gs in complex with the endogenous peptide ligand PACAP27, revealing a unique interaction mode between PACAP27 and the receptor, stabilized by the N-terminal α-helix of VIP2R.
- Yingna Xu
- , Wenbo Feng
- & Ming-Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A structural exposé of noncanonical molecular reactivity within the protein tyrosine phosphatase WPD loop
A structural exposé of noncanonical molecular reactivity within the protein tyrosine phosphatase WPD loop
Inositol pyrophosphates (PP-IPs) regulate immunity and phosphate homeostasis. Here, the authors’ structural dissection of an Arabidopsis thaliana PP-IP phosphatase reveals that substrates drive their own hydrolysis and identifies a highly elusive metaphosphate-like reaction intermediate.
- Huanchen Wang
- , Lalith Perera
- & Stephen B. Shears
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of ATP synthase under strain during catalysis
Structure of ATP synthase under strain during catalysis
CryoEM of mitochondrial ATP synthase frozen during rotary catalysis reveals dramatic conformational changes in the peripheral stalk subcomplex, which enable the enzyme’s efficient synthesis of ATP.
- Hui Guo
- & John L. Rubinstein
-
Article
| Open Access Magic angle spinning NMR structure of human cofilin-2 assembled on actin filaments reveals isoform-specific conformation and binding mode
Magic angle spinning NMR structure of human cofilin-2 assembled on actin filaments reveals isoform-specific conformation and binding mode
Despite their relevance as regulators of actin severing and filament disassembly, few structural insights into the mechanism of cofilin-isoform-specific severing activity are reported. Here, the authors provide structural insights towards actin severing activity by human cofilin-2 obtained by MAS NMR and all-atom MD simulations. The results reveal an isoform-specific binding mode unique to CFL2 that may be related to its potent severing properties in-vivo.
- Jodi Kraus
- , Ryan W. Russell
- & Tatyana Polenova
-
Article
| Open Access Structure, gating, and pharmacology of human CaV3.3 channel
Structure, gating, and pharmacology of human CaV3.3 channel
T-type calcium channels are implicated in many diseases. Here, multiple structures of CaV3.3 channel elucidate molecular mechanisms of T-type CaV channels activation at low voltage and interaction with different clinically used channel blockers.
- Lingli He
- , Zhuoya Yu
- & Yan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into the peptide selectivity and activation of human neuromedin U receptors
Structural insights into the peptide selectivity and activation of human neuromedin U receptors
Neuromedin U receptors (NMURs) are potential drug targets for obesity and inflammatory disorders. Here, the authors report structural basis for neuromedin recognition and activation mechanism of NMURs.
- Chongzhao You
- , Yumu Zhang
- & Yi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the assembly and quinone transport mechanisms of the dimeric photosynthetic RC–LH1 supercomplex
Structural basis for the assembly and quinone transport mechanisms of the dimeric photosynthetic RC–LH1 supercomplex
Bacterial photosynthesis reflects the early stages of the evolution of photosynthesis. Here, the authors present a systematic study of the cryo-EM structures of the dimeric light harvesting–reaction center complexes and assembly variants from Rhodobacter sphaeroides, which delineated a hierarchical assembly pathway and quinone transport routes of the dimeric photosynthetic RC–LH1 core complex.
- Peng Cao
- , Laura Bracun
- & Lu-Ning Liu
-
Article
| Open Access The crystal structure of iC3b-CR3 αI reveals a modular recognition of the main opsonin iC3b by the CR3 integrin receptor
The crystal structure of iC3b-CR3 αI reveals a modular recognition of the main opsonin iC3b by the CR3 integrin receptor
Complement activation on foreign cell surfaces leads to the generation of complement opsonins, which activate complement receptor type 3 (CR3) and pathogen clearance by macrophages. Here, the authors reveal structural basis of the interaction between human opsonin iC3b and the von Willebrand A inserted domain of the α chain of CR3.
- Francisco J. Fernández
- , Jorge Santos-López
- & M. Cristina Vega
-
Article
| Open Access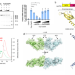 Insights into the inhibition of type I-F CRISPR-Cas system by a multifunctional anti-CRISPR protein AcrIF24
Insights into the inhibition of type I-F CRISPR-Cas system by a multifunctional anti-CRISPR protein AcrIF24
Phages use anti-CRISPR proteins (Acrs) to counteract the bacterial CRISPR-Cas systems. Here, the authors characterize AcrIF24, which functions as an Aca (Acr-associated) to repress and regulate its own transcription, dimerizes the Csy complex, blocks the hybridization of target DNA, and tethers non-sequence-specific DNA to the Csy complex.
- Lingguang Yang
- , Laixing Zhang
- & Yue Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Functional control of a 0.5 MDa TET aminopeptidase by a flexible loop revealed by MAS NMR
Functional control of a 0.5 MDa TET aminopeptidase by a flexible loop revealed by MAS NMR
Motion is key to enzymatic catalysis. Gauto et al. show that a flexible loop region is crucial for the function of an aminopeptidase and show that magic-angle spinning NMR provides atomic-level quantitative insights in this very large complex.
- Diego F. Gauto
- , Pavel Macek
- & Paul Schanda
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric structure of the native Rhodobacter sphaeroides dimeric LH1–RC complex
Asymmetric structure of the native Rhodobacter sphaeroides dimeric LH1–RC complex
Rhodobacter sphaeroides is a model organism for studying bacterial photosynthesis. Here, the authors present structures of its native dimeric and a protein-U-lacking monomeric light-harvesting-reaction center complexes, which reveal asymmetric features for the dimer and an altered shape for the monomer.
- Kazutoshi Tani
- , Ryo Kanno
- & Zheng-Yu Wang-Otomo
-
Article
| Open Access Waffle Method: A general and flexible approach for improving throughput in FIB-milling
Waffle Method: A general and flexible approach for improving throughput in FIB-milling
Here the authors describe the Waffle Method, aimed at increasing the throughput of and solves several challenges present in cryo-FIB/SEM sample preparation for cryo-ET analysis — the highest-resolution method for obtaining 3D views of native biological specimens in-situ.
- Kotaro Kelley
- , Ashleigh M. Raczkowski
- & Alex J. Noble
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of the essential kinase PDK1 by phosphoinositide-driven trans-autophosphorylation
Activation of the essential kinase PDK1 by phosphoinositide-driven trans-autophosphorylation
The essential protein kinase PDK1 is activated by phospoinositide-mediated dimerization and trans-autophosphorylation. Here, the authors show that in the absence of PIP3 or PI(3,4)P2 phosphoinositides, PDK1 is maintained in an inactive, autoinhibited conformation in the cytosol.
- Aleksandra Levina
- , Kaelin D. Fleming
- & Thomas A. Leonard
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for PoxtA-mediated resistance to phenicol and oxazolidinone antibiotics
Structural basis for PoxtA-mediated resistance to phenicol and oxazolidinone antibiotics
PoxtA confers resistance to ribosome-targeting oxazolidinone (linezolid) and chloramphenicol antibiotics. Here, Crowe-McAuliffe et al. provide structural insights into how binding of PoxtA to the ribosome indirectly promotes drug dissociation.
- Caillan Crowe-McAuliffe
- , Victoriia Murina
- & Vasili Hauryliuk
-
Article
| Open Access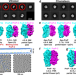 Structural basis for the mechanisms of human presequence protease conformational switch and substrate recognition
Structural basis for the mechanisms of human presequence protease conformational switch and substrate recognition
Presequence protease (PreP) is essential to mitochondrial proteostasis. This study leverages advanced vitrification techniques to solve cryoEM structures of apo- and substrate-bound PreP and integrates these data with other analysis to reveal key stages and mechanistic insights of the PreP catalytic cycle.
- Wenguang G. Liang
- , Juwina Wijaya
- & Wei-Jen Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based design of stabilized recombinant influenza neuraminidase tetramers
Structure-based design of stabilized recombinant influenza neuraminidase tetramers
Influenza virus neuraminidase (NA) is a drug target and a potential vaccine antigen. Here, the authors provide a detailed analysis of the conformational stability of NA, and show how expression and stability of recombinant NA antigens can be strengthened through structure-based design.
- Daniel Ellis
- , Julia Lederhofer
- & Masaru Kanekiyo
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of a LptDE transporter in complex with Pro-macrobodies offer insight into lipopolysaccharide translocation
Cryo-EM structures of a LptDE transporter in complex with Pro-macrobodies offer insight into lipopolysaccharide translocation
Lateral opening of the LptDE transporter in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria is necessary for insertion of lipopolysaccharides. Here, Botte et al. report a cryo-EM structure of a partially opened LptDE transporter, in complex with rigid chaperones derived from nanobodies.
- Mathieu Botte
- , Dongchun Ni
- & Michael Hennig
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the SUMO protease activity of the atypical ubiquitin-specific protease USPL1
Structural basis for the SUMO protease activity of the atypical ubiquitin-specific protease USPL1
USPL1 is a non-canonical member of the ubiquitin-specific protease (USP) family with activity toward SUMO instead of ubiquitin. Here, the authors present a crystal structure of USPL1 bound to SUMO2, revealing how this enzyme has evolved to bind SUMO as an example of divergent evolution in the USP family.
- Ying Li
- , Nathalia Varejão
- & David Reverter
-
Article
| Open Access Exploration of the dynamic interplay between lipids and membrane proteins by hydrostatic pressure
Exploration of the dynamic interplay between lipids and membrane proteins by hydrostatic pressure
Direct information on the dynamic interplay between membrane proteins and lipids is scarce. Here the authors report a detailed description of these close relationships by combining lipid nanodiscs and high-pressure NMR. They report the link between pressure and lipid compositions to the conformational landscape of the β-barrel OmpX and the α-helical BLT2 G Protein-Coupled Receptor in nanodiscs.
- Alexandre Pozza
- , François Giraud
- & Laurent J. Catoire
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of FPR2 in recognition of Aβ42 and neuroprotection by humanin
Structural basis of FPR2 in recognition of Aβ42 and neuroprotection by humanin
The formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) is involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Structures of FPR2 bound to Aβ42, humanin, or formyl peptides offer insight into Aβ42 neurotoxicity, humanin neuroprotection, and FPR ligand selectivity
- Ya Zhu
- , Xiaowen Lin
- & Beili Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Assembly mechanism of the pleomorphic immature poxvirus scaffold
Assembly mechanism of the pleomorphic immature poxvirus scaffold
Immature poxviruses are characterized by nonicosahedral semiordered protein scaffolds critical for morphogenesis. Here, the authors use cryo-EM structures of Vaccinia virus D13 scaffold intermediates to explain their assembly mechanism.
- Jaekyung Hyun
- , Hideyuki Matsunami
- & Matthias Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure and cellular functions of uPAR dimer
Crystal structure and cellular functions of uPAR dimer
The structural basis for urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) dimerization is not understood. Here, the authors solve the crystal structure of soluble uPAR dimers, identifying substantial structural changes compared to the monomer.
- Shujuan Yu
- , Yaqun Sui
- & Mingdong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of R-loop recognition by the S9.6 monoclonal antibody
Structural basis of R-loop recognition by the S9.6 monoclonal antibody
The S9.6 monoclonal antibody is widely used to map R-loops genome wide. Here, Bou-Nader et al., define the nucleic acid-binding specificity of S9.6 and report its crystal structures free and bound to a hybrid, which reveal the asymmetric recognition of the RNA and DNA strands and its A-form conformation.
- Charles Bou-Nader
- , Ankur Bothra
- & Jinwei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access MERS-CoV ORF4b employs an unusual binding mechanism to target IMPα and block innate immunity
MERS-CoV ORF4b employs an unusual binding mechanism to target IMPα and block innate immunity
MERS-CoV ORF4b antagonizes host innate immune response, partially via blocking nuclear import adapter IMPα activity and preventing nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Here, Munasinghe and Edwards et al. biochemically and structurally define the interaction between ORF4b and IMPα-family members and find a non-canonical interaction between ORF4b NLS and IMPα2 and IMPα3.
- Thilini S. Munasinghe
- , Megan R. Edwards
- & Jade K. Forwood
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal Structures of Wolbachia CidA and CidB Reveal Determinants of Bacteria-induced Cytoplasmic Incompatibility and Rescue
Crystal Structures of Wolbachia CidA and CidB Reveal Determinants of Bacteria-induced Cytoplasmic Incompatibility and Rescue
Wolbachia induced cytoplasmic incompatibility (CI) is caused by linked pairs of genes named cifA and cifB. Here, authors show that the residues at interfaces of the CidA-CidB complex is crucial for their binding and contribute to the diversity of CI.
- Haofeng Wang
- , Yunjie Xiao
- & Haitao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic insights into the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis by the rice SPX2 – PHR2 complex
Mechanistic insights into the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis by the rice SPX2 – PHR2 complex
SPX receptors regulate plant phosphate response via PHR transcription factors. Here, based on crystal structure analysis of rice PHR2 complexes, the authors propose that SPX2 regulates PHR2 by preventing DNA binding and oligomerisation of the PHR2 CC domain.
- Zeyuan Guan
- , Qunxia Zhang
- & Zhu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A distinct mechanism of C-type inactivation in the Kv-like KcsA mutant E71V
A distinct mechanism of C-type inactivation in the Kv-like KcsA mutant E71V
Constriction of the selectivity filter is assumed to be a hallmark of C-type inactivation in K+ channels. Using different high-resolution methods, this study shows a distinct C-type inactivation mechanism in a KcsA mutant that emulates Kv-channels.
- Ahmed Rohaim
- , Bram J. A. Vermeulen
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of pseudorabies virus capsids
Structures of pseudorabies virus capsids
Pseudorabies virus (PRV) is a major etiological agent of swine infectious diseases responsible for significant economic losses in the swine industry. The authors report the structures of the PRV A-capsid and C-capsid, shedding light on PRV’s assembly mechanism.
- Guosong Wang
- , Zhenghui Zha
- & Ningshao Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription factors modulate RNA polymerase conformational equilibrium
Transcription factors modulate RNA polymerase conformational equilibrium
Pausing of RNA polymerase (RNAP) and transcription is regulated by the NusA and NusG transcription factors in bacteria. Here the authors provide structural evidence for how they interact with RNAP to carry out their pausing roles and also reveal functions for NusA and NusG in transcription termination.
- Chengjin Zhu
- , Xieyang Guo
- & Albert Weixlbaumer
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of hairpin RNA excited states reveals multi-step transitions
Rational design of hairpin RNA excited states reveals multi-step transitions
RNA molecules exhibit conformational fluctuations between ground states and excited states. Here the authors designed and verified small hairpin RNAs with predefined secondary structure reshufflings. In light of Van’t Hoff analysis and accelerated molecular dynamics simulation, a mechanism of multistep sequential transition has been revealed.
- Ge Han
- & Yi Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Inorganic phosphate in growing calcium carbonate abalone shell suggests a shared mineral ancestral precursor
Inorganic phosphate in growing calcium carbonate abalone shell suggests a shared mineral ancestral precursor
Phosphate involvement in calcium carbonate biominerals raises questions on biomineralisation pathways. Here, the authors explore the presence of phosphate in the growing shell of the European abalone and suggest a shared mixed mineral ancestral precursor with final crystal phase being selected by mineral-associated proteins.
- Widad Ajili
- , Camila B. Tovani
- & Nadine Nassif
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of a deltacoronavirus spike protein bound to porcine and human receptors
Structures of a deltacoronavirus spike protein bound to porcine and human receptors
As a potential zoonotic pathogen, porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) has been shown to cause febrile illness in humans. Here, Ji et al. report the structures of PDCoV spike protein bound to porcine and human aminopeptidase receptors, pointing to the likely underlying mechanism of PDCoV zoonotic transmission.
- Weiwei Ji
- , Qi Peng
- & Shuijun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of protein unfolding by fast cross-linking mass spectrometry using di-ortho-phthalaldehyde cross-linkers
Characterization of protein unfolding by fast cross-linking mass spectrometry using di-ortho-phthalaldehyde cross-linkers
Conformations sampled by a protein while it unfolds are difficult to visualize. Here, the authors develop di-ortho-phthalaldehyde cross-linkers for rapid chemical cross-linking mass spectrometry analysis and demonstrate that this method captures the conformations of protein unfolding intermediates.
- Jian-Hua Wang
- , Yu-Liang Tang
- & Xiaoguang Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism and biomass association of glucuronoyl esterase: an α/β hydrolase with potential in biomass conversion
Mechanism and biomass association of glucuronoyl esterase: an α/β hydrolase with potential in biomass conversion
Zong and coworkers combine computational and experimental methods to decipher in detail the mechanism of action of glucuronoyl esterases, enzymes with significant biotechnological potential for decoupling lignin from polysaccharides in biomass.
- Zhiyou Zong
- , Scott Mazurkewich
- & Leila Lo Leggio
-
Article
| Open Access Flagellin outer domain dimerization modulates motility in pathogenic and soil bacteria from viscous environments
Flagellin outer domain dimerization modulates motility in pathogenic and soil bacteria from viscous environments
It has been suggested that the outer domains of bacterial flagellins are not needed for motility. Here, the authors show that flagellar filament outer domains from some bacteria have unique structures which can alter the motility of the bacteria.
- Mark A. B. Kreutzberger
- , Richard C. Sobe
- & Edward H. Egelman
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided unlocking of NaX reveals a non-selective tetrodotoxin-sensitive cation channel
Structure-guided unlocking of NaX reveals a non-selective tetrodotoxin-sensitive cation channel
NaX is an atypical member of the voltage-gated sodium channel family that may contribute to Na+ homeostasis. Here, the authors describe the structural and functional attributes of the human NaX channel to reveal new insights into its physiology.
- Cameron L. Noland
- , Han Chow Chua
- & Jian Payandeh
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for activation and gating of IP3 receptors
Structural basis for activation and gating of IP3 receptors
IP3 receptors are intracellular calcium channels involved in numerous signaling pathways. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of type-3 IP3 receptors in multiple gating conformations, including the active state revealing the molecular mechanism of the receptor activation.
- Emily A. Schmitz
- , Hirohide Takahashi
- & Erkan Karakas
-
Article
| Open Access Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway
Global profiling of regulatory elements in the histone benzoylation pathway
Lysine benzoylation (Kbz) is a recently discovered histone modification. Here, the authors characterize writers, erasers and readers of histone Kbz in S. cerevisiae and identify non-histone proteins bearing Kbz, laying foundations to dissect the roles of Kbz in diverse cellular processes.
- Duo Wang
- , Fuxiang Yan
- & Yong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural Insight into the MCM double hexamer activation by Dbf4-Cdc7 kinase
Structural Insight into the MCM double hexamer activation by Dbf4-Cdc7 kinase
The Dbf4-dependent kinase Cdc7 (DDK) is essential for eukaryotic DNA replication. Here, the authors present a series of cryo-EM structures elucidating the versatility of this kinase in exerting an ordered phosphorylation of its essential target to promote replication initiation.
- Jiaxuan Cheng
- , Ningning Li
- & Yuanliang Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers
Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers
In this work, Louros et al. uncover a rule book for interactions of amyloids with other proteins. This grammar was shown to promote cellular spreading of tau aggregates in cells, but can also be harvested to develop structure-based aggregation blockers.
- Nikolaos Louros
- , Meine Ramakers
- & Joost Schymkowitz
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for allosteric agonism and G protein subtype selectivity of galanin receptors
Molecular basis for allosteric agonism and G protein subtype selectivity of galanin receptors
The basis for the diverse peptide-binding modes and the G protein selectivity of peptide GPCRs remains elusive. Here, the authors offer a structural basis for allosteric-like agonism and G protein selectivity of a neuropeptide GPCR, galanin receptor.
- Jia Duan
- , Dan-Dan Shen
- & Yi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized human metapneumovirus fusion proteins
Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized human metapneumovirus fusion proteins
The degree to which the conformation of the human metapneumovirus fusion (F) protein affects immunogenicity has been debated. Here, Hsieh et al. engineer prefusion-stabilized F variants with enhanced thermostability that elicit higher neutralizing antibody titers in mice than postfusion F.
- Ching-Lin Hsieh
- , Scott A. Rush
- & Jason S. McLellan
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying and comparing radiation damage in the Protein Data Bank
Quantifying and comparing radiation damage in the Protein Data Bank
Radiation damage hampers protein structure determination by X-ray crystallography. Here, the AUs introduce the Bnet metric, a single value summarising the extent of radiation damage of a protein crystal structure, and use Bnet to detect radiation damage in structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank.
- Kathryn L. Shelley
- & Elspeth F. Garman
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis for regulation of the glutathione transporter Ycf1 by regulatory domain phosphorylation
The structural basis for regulation of the glutathione transporter Ycf1 by regulatory domain phosphorylation
Ycf1, a C-family member ATP Binding Cassette (ABC) transporter, transports glutathione and glutathione-metal complexes in yeast. Here the authors use cryo-EM and biochemical analysis to show how an intrinsically-disordered regulatory domain (R-domain) controls activity upon phosphorylation by engaging with a Nucleotide Binding Domain.
- Nitesh Kumar Khandelwal
- , Cinthia R. Millan
- & Thomas M. Tomasiak
-
Article
| Open Access Secondary structure prediction for RNA sequences including N6-methyladenosine
Secondary structure prediction for RNA sequences including N6-methyladenosine
RNA folding free energy nearest neighbor parameters were determined for sequences with the nucleotide m6A. The RNAstructure software package can accommodate modified nucleotides, enabling secondary structure prediction of sequences with m6A.
- Elzbieta Kierzek
- , Xiaoju Zhang
- & David H. Mathews
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for modulation of human NaV1.3 by clinical drug and selective antagonist
Structural basis for modulation of human NaV1.3 by clinical drug and selective antagonist
NaV1.3 is involved in neuronal development, hormone secretion and pain perception. Here, the authors elucidate the molecular mechanism for modulation of NaV1.3 by a site-2 neurotoxin bulleyaconitine A and a subtype selective antagonist ICA121431.
- Xiaojing Li
- , Feng Xu
- & Daohua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic structure of the predominant GII.4 human norovirus capsid reveals novel stability and plasticity
Atomic structure of the predominant GII.4 human norovirus capsid reveals novel stability and plasticity
GII.4 variants of human noroviruses cause pandemic viral gastroenteritis. The atomic structure of GII.4 virus-like particles reveal novel insights into capsid stability, dynamics and antigenic presentation potentially useful for ongoing vaccine development.
- Liya Hu
- , Wilhelm Salmen
- & B. V. Venkataram Prasad
-
Article
| Open Access An open-like conformation of the sigma-1 receptor reveals its ligand entry pathway
An open-like conformation of the sigma-1 receptor reveals its ligand entry pathway
The nonopioid sigma-1 receptor (σ1R) is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), interacts with multiple effector proteins and various synthetic ligands, and is implicated in many diseases. Here, authors provide structural and functional evidence to reveal the likely ligand entry pathway for σ1R.
- Fuhui Meng
- , Yang Xiao
- & Xiaoming Zhou

 L-tyrosine-bound ThiH structure reveals C–C bond break differences within radical SAM aromatic amino acid lyases
L-tyrosine-bound ThiH structure reveals C–C bond break differences within radical SAM aromatic amino acid lyases