Article |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Explaining why simple liquids are quasi-universal
Explaining why simple liquids are quasi-universal
Researchers refer to the approximate invariance in the structure and dynamics of simple liquids among different pair models as quasi-universality, while little is known about its origin. Here, Becher et al.show that the pair potential as a sum of exponential terms fulfils the quasuniversality.
- Andreas K. Bacher
- , Thomas B. Schrøder
- & Jeppe C. Dyre
-
Article
| Open Access Target control of complex networks
Target control of complex networks
Network controllability has numerous applications in natural and technological systems. Here, Gao et al.develop a theoretical approach and a greedy algorithm to study target control—the ability to efficiently control a preselected subset of nodes—in complex networks.
- Jianxi Gao
- , Yang-Yu Liu
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article |
 Vanadium dioxide nanowire-based microthermometer for quantitative evaluation of electron beam heating
Vanadium dioxide nanowire-based microthermometer for quantitative evaluation of electron beam heating
Understanding localized heating of a material by a beam of electrons is important in electron microscopy, but measuring temperature at the nanoscale is difficult. Here, the authors show that a vanadium dioxide nanowire can act as a microthermometer and measure electron beam heating in silicon nanowires.
- H. Guo
- , M. I. Khan
- & A. M. Minor
-
Article
| Open Access Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis for compound thermoelectrics and new criterion for combustion processing
Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis for compound thermoelectrics and new criterion for combustion processing
The existing methods to synthesize thermoelectric materials remain constrained to multi-step processes that are usually time and energy consuming. Here, Su et al.use a fast, one-step combustion approach to synthesize various compounds, which holds promise for scalable industrial processing.
- Xianli Su
- , Fan Fu
- & Ctirad Uher
-
Article |
 Nonlinear phononics using atomically thin membranes
Nonlinear phononics using atomically thin membranes
Analogous to photonic crystals, phononic crystals can be used to engineer the acoustic properties of a system, however, creating nonlinear phononic crystals or nonlinear acoustic metamaterial is challenging. Here, Midtvedt et al.propose periodically pinned, atomically thin membranes as a nonlinear phononics platform.
- Daniel Midtvedt
- , Andreas Isacsson
- & Alexander Croy
-
Article |
 Memory in network flows and its effects on spreading dynamics and community detection
Memory in network flows and its effects on spreading dynamics and community detection
Random walks are standard tools for modelling dynamics in networks but usually neglect the possibility that the next step may depend on the previous ones. Rosvall et al. study the paths taken in various systems and show that memory effects play an important role and can uncover informative organization.
- Martin Rosvall
- , Alcides V. Esquivel
- & Renaud Lambiotte
-
Article |
 Work extraction and thermodynamics for individual quantum systems
Work extraction and thermodynamics for individual quantum systems
Traditionally, thermodynamics deals with the study of macroscopic systems comprised of a large number of particles. Skrzypczyk et al. present a framework—including a thermal bath and work-storage device—to extract the optimal amount of work from individual quantum systems.
- Paul Skrzypczyk
- , Anthony J. Short
- & Sandu Popescu
-
Article |
 A quantum diffractor for thermal flux
A quantum diffractor for thermal flux
The Josephson effect produces a supercurrent between two superconductors separated by an insulator, but it also leads to more exotic effects like electric quantum diffraction. Here, the authors show the appearance of Fraunhofer diffraction for thermal currents in a thermally biased Josephson junction.
- Maria José Martínez-Pérez
- & Francesco Giazotto
-
Article |
 Understanding water’s anomalies with locally favoured structures
Understanding water’s anomalies with locally favoured structures
Water shows various anomalies, but an understanding of their microscopic origin is still missing. Russo and Tanaka introduce a new structural order parameter in simulations and identify locally favoured structures whose formation is responsible for the anomalies and supercooled water's stability against ice crystallization.
- John Russo
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Glassiness and exotic entropy scaling induced by quantum fluctuations in a disorder-free frustrated magnet
Glassiness and exotic entropy scaling induced by quantum fluctuations in a disorder-free frustrated magnet
Spin liquids and spin ices arise when spins arranged on a lattice have several states that are close in energy, a phenomenon referred to as frustration. Here, Klich et al.show that quantum fluctuations can induce a spin liquid to freeze into a glassy state.
- I. Klich
- , S.-H. Lee
- & K. Iida
-
Article
| Open Access Restoration of the third law in spin ice thin films
Restoration of the third law in spin ice thin films
In bulk, the spin ice Dy2Ti2O7 has posed an enigma because – due to its slow dynamics – it is unclear whether and how the material will reach a zero entropy state at zero temperature. Here, the authors show that in thin films of Dy2Ti2O7a zero entropy state is induced at 0.4 K, plausibly by lattice strain.
- L. Bovo
- , X. Moya
- & S.T. Bramwell
-
Article
| Open Access Direct measurement of the upper critical field in cuprate superconductors
Direct measurement of the upper critical field in cuprate superconductors
The point at which a magnetic field kills superconductivity in the cuprates has been difficult to measure. Grissonnanche et al. use thermal conductivity measurements to reliably determine this field and find that it drops suddenly below some critical doping, suggesting the onset of a new competing phase.
- G. Grissonnanche
- , O. Cyr-Choinière
- & Louis Taillefer
-
Article |
 Thermotropic phase boundaries in classic ferroelectrics
Thermotropic phase boundaries in classic ferroelectrics
Morphotropic phase boundaries, which separate two competing phases of different chemical composition, are the crucial ingredient for lead-based piezoelectrics. Here, the authors show that similar enhanced properties and analogous thermotropic phase boundaries can occur in simple, lead-free ferroelectrics.
- Tom T.A. Lummen
- , Yijia Gu
- & Venkatraman Gopalan
-
Article |
 Co-operativity in a nanocrystalline solid-state transition
Co-operativity in a nanocrystalline solid-state transition
Co-operativity is an effect where initial reaction events influence later events. Here, White et al.find evidence for co-operativity in the cation exchange process of nanocrystals, as cadmium selenide transforms into the copper selenide phase.
- Sarah L. White
- , Jeremy G. Smith
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article |
 Stabilization of a linear nanomechanical oscillator to its thermodynamic limit
Stabilization of a linear nanomechanical oscillator to its thermodynamic limit
Micro- and nano-scale oscillators are finding usage in novel sensors, but their performance is limited by their sensitivity to external perturbations. Here, the authors report an optomechanical technique to stabilize a nanomechanical beam to its thermodynamic limit.
- Emanuel Gavartin
- , Pierre Verlot
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Exact controllability of complex networks
Exact controllability of complex networks
Although it has been possible to calculate the conditions for exerting complete control over a directed complex network, for undirected and weighted networks this calculation is inexact. Yuan et al. develop a general framework for determining the controllability of any complex network.
- Zhengzhong Yuan
- , Chen Zhao
- & Ying-Cheng Lai
-
Article |
 Inducing effect on the percolation transition in complex networks
Inducing effect on the percolation transition in complex networks
A K-core of a complex network is a cluster of nodes that are connected to at least K other nodes of the cluster. Zhao et al. show that the influence of nodes outside a percolating K-core of protected nodes determines the size of the core and may cause an abrupt breakdown of the core.
- Jin-Hua Zhao
- , Hai-Jun Zhou
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Article |
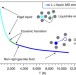 Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
A physical description of supercritical fluids remains challenging because common approximations for solids and gases do not apply to liquids. Bolmatov et al. identify a liquid/gas dynamic crossover of specific heat above the critical point, and formulate a theory to shed light on its nature.
- Dima Bolmatov
- , V. V. Brazhkin
- & K. Trachenko
-
Article |
 Crackling noise in fractional percolation
Crackling noise in fractional percolation
Crackling noise is commonly observed in various physical systems. Schröderet al.demonstrate that crackling noise can be attributed to the concept of fractional percolation, which is found to be applicable to the known Barkhausen effect in ferromagnets.
- Malte Schröder
- , S. H. Ebrahimnazhad Rahbari
- & Jan Nagler
-
Article |
 Liquid–liquid transition in a strong bulk metallic glass-forming liquid
Liquid–liquid transition in a strong bulk metallic glass-forming liquid
The nature of liquid–liquid phase transitions remains inconclusive, because direct experimental evidence is limited by crystallization. Wei et al.observe it in a bulk metallic glass former, which is characterized by heat capacity maxima and sudden changes in both viscosity and local structures.
- Shuai Wei
- , Fan Yang
- & Ralf Busch
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum simulation of low-temperature metallic liquid hydrogen
Quantum simulation of low-temperature metallic liquid hydrogen
The melting temperature of hydrogen drops at high pressures, which suggests the possible emergence of a low-temperature liquid state of metallic hydrogen. Chen et al.confirm the existence of this phase in simulations and show how the quantum motion of the protons has a critical role in its stabilization.
- Ji Chen
- , Xin-Zheng Li
- & Enge Wang
-
Article |
 Truly work-like work extraction via a single-shot analysis
Truly work-like work extraction via a single-shot analysis
Thermodynamics and information theory are closely related but the fundamental limitations of this relation are difficult to determine. Combining concepts from one-shot information theory, probability theory and statistical mechanics, the author quantifies extractable work in a non-equilibrium system.
- Johan Åberg
-
Article |
 Fundamental limitations for quantum and nanoscale thermodynamics
Fundamental limitations for quantum and nanoscale thermodynamics
The usual laws of thermodynamics that are valid for macroscopic systems do not necessarily apply to the nanoscale, where quantum effects become important. Here, the authors develop a theoretical framework based on quantum information theory to properly treat thermodynamics at the nanoscale.
- Michał Horodecki
- & Jonathan Oppenheim
-
Article |
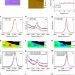 Molecular adsorption induces the transformation of rhombohedral- to Bernal-stacking order in trilayer graphene
Molecular adsorption induces the transformation of rhombohedral- to Bernal-stacking order in trilayer graphene
Although Bernal stacked trilayer graphene is believed to be the stable packing type, at temperatures below 1,000 °C the transformation from rhombohedral packing does not occur. Zhang et al.show that rhombohedral stacking can be converted to Bernal type by evaporating triazine onto graphene at 150 °C.
- Wenjing Zhang
- , Jiaxu Yan
- & Lain-Jong Li
-
Article |
 Dipolar-energy-activated magnetic domain pattern transformation driven by thermal fluctuations
Dipolar-energy-activated magnetic domain pattern transformation driven by thermal fluctuations
Magnetic domain patterns and the capability to control them is important for applications such as information storage. Here, Kronseder and colleagues find a metastable magnetic domain state with a domain width larger than the thermodynamically stable one as a result of reduced thermal fluctuations.
- M. Kronseder
- , M. Buchner
- & C.H. Back
-
Article |
 Emergence of bimodality in controlling complex networks
Emergence of bimodality in controlling complex networks
The control of a complex network can be achieved by different combinations of relatively few driver nodes. Tao Jia and colleagues show that this can lead to two distinct control modes—centralized or distributed—that determine the number of nodes that can act as driver node.
- Tao Jia
- , Yang-Yu Liu
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article |
 Spectral non-uniform temperature and non-local heat transfer in the spin Seebeck effect
Spectral non-uniform temperature and non-local heat transfer in the spin Seebeck effect
The spin Seebeck effect, which refers to a spin current induced by a temperature gradient, is experimentally well established but a comprehensive theoretical framework is still missing. Here the authors succeed in explaining the non-locality and in predicting a non-magnon origin of the effect.
- Konstantin S. Tikhonov
- , Jairo Sinova
- & Alexander M. Finkel’stein
-
Article |
 Ballistic to diffusive crossover of heat flow in graphene ribbons
Ballistic to diffusive crossover of heat flow in graphene ribbons
Understanding heat flow in two-dimensional nanomaterials has wide-ranging implications. Here, the authors show that the thermal conductance of quarter-micron graphene samples is quasi-ballistic, but patterning the graphene into nanoribbons leads to diffusive heat flow strongly limited by edge scattering.
- Myung-Ho Bae
- , Zuanyi Li
- & Eric Pop
-
Article |
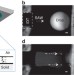 Unique fingering instabilities and soliton-like wave propagation in thin acoustowetting films
Unique fingering instabilities and soliton-like wave propagation in thin acoustowetting films
The study of dynamic fingering in liquid films has a long and storied history dating back to the discovery of wine tears. Rezket al.report novel fingering patterns driven by sound waves, above which peculiar wave pulses akin to solitary waves are formed.
- Amgad R. Rezk
- , Ofer Manor
- & Leslie Y. Yeo
-
Article |
 First-order coil-globule transition driven by vibrational entropy
First-order coil-globule transition driven by vibrational entropy
The coil-globule transition undergone by polymers in solution delineates a transition from expanded coils to collapsed globules, depending on the polarity of the solvent. This study examines the influence of vibrational entropy on the transition, and finds it can induce a crossover from a second-order to a first-order transition.
- Carlo Maffi
- , Marco Baiesi
- & Paolo De Los Rios
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dome structure in electron-doped iron arsenide superconductors
Two-dome structure in electron-doped iron arsenide superconductors
The iron pnictides are a class of superconductors that have received widespread interest in recent years. By doping the prototypical material LaFeAsO with hydrogen, this study reveals the existence of a second superconducting dome at higher doping ranges, which arises due to orbital fluctuations.
- Soshi Iimura
- , Satoru Matsuishi
- & Hideo Hosono

 A photon thermal diode
A photon thermal diode