Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Elasticity-controlled jamming criticality in soft composite solids
Elasticity-controlled jamming criticality in soft composite solids
Soft composite solids are building blocks for many functional and biological materials, yet it remains challenging to predict their mechanical properties. Zhao et al. propose a criticality framework to connect the mechanics to the critical behaviour near the shear-jamming transition of the dispersed inclusions.
- Yiqiu Zhao
- , Haitao Hu
- & Qin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access How to steer active colloids up a vertical wall
How to steer active colloids up a vertical wall
It has been demonstrated theoretically earlier that a dense phase made of repulsive active particles, in phase-separating regime, exhibit wetting-like behaviors: wall-meniscus or capillary rise in channels. Here authors experimentally investigate a non-phase separating assembly of active colloids under gravity and show that a wetting-like phenomenology persists against a vertical wall, and they evidence a counter-gravity wall climbing.
- Adérito Fins Carreira
- , Adam Wysocki
- & Cécile Cottin-Bizonne
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasound-activated piezo-hot carriers trigger tandem catalysis coordinating cuproptosis-like bacterial death against implant infections
Ultrasound-activated piezo-hot carriers trigger tandem catalysis coordinating cuproptosis-like bacterial death against implant infections
Implantation-associated infections often lead to infections. Here, the authors propose a piezo-based nanoreactor to achieve US-excited tandem catalysis, endowing the polyetherketoneketone bone scaffold with on-demand antibacterial and osteogenic capacities.
- Yanli Huang
- , Xufeng Wan
- & Duan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the role of vaporization momentum in self-jumping dynamics of freezing supercooled droplets at reduced pressures
Unraveling the role of vaporization momentum in self-jumping dynamics of freezing supercooled droplets at reduced pressures
The momentum transport dynamics of a vaporizing droplet under low pressures remain undiscovered. Here authors report the vaporization momentum resulting from the intensive vaporization on the free surface of the water droplet contributes to the self-detachment of freezing droplets.
- Xiao Yan
- , Samuel C. Y. Au
- & Shuhuai Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable afterglow for mechanical self-monitoring 3D printing structures
Tunable afterglow for mechanical self-monitoring 3D printing structures
Organic afterglow materials have potential in self-monitoring applications but it is challenging to design materials with desired properties. Here, the authors report the development of a lifetime tunable organic afterglow system for use in mechanical self-monitoring 3D printed structures.
- Rongjuan Huang
- , Yunfei He
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access 4D printed hydrogel scaffold with swelling-stiffening properties and programmable deformation for minimally invasive implantation
4D printed hydrogel scaffold with swelling-stiffening properties and programmable deformation for minimally invasive implantation
3D printing has potential in designing personalised scaffolds, but minimally invasive implantation is still challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a polyurethane material with temperature triggered shape memory and water triggered deformation that allows for transcatheter delivery.
- Bo Liu
- , Hui Li
- & Xiaoli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart sensors are important components in the development of touchless human-machine interaction systems. Here, the authors describe a smart 3D porous crystalline organic cage-based system that exhibits remarkable responsiveness to fingertip humidity, contributing to the advancement of touchless human-machine interaction technology.
- Jinrong Wang
- , Weibin Lin
- & Niveen M. Khashab
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed nanotrap structures for efficient separation of rare earth elements over a single step
Rationally designed nanotrap structures for efficient separation of rare earth elements over a single step
Extracting rare earth elements (REEs) from wastewater is essential for the growth of an eco-friendly sustainable economy but separating individual rare earth elements remains challenging. Here, the authors report a REE nanotrap that features dense uncoordinated carboxyl groups and triazole N atoms in a two-fold interpenetrated metalorganic framework which is highly responsive to the size variation of rareearth ions.
- Qing-Hua Hu
- , An-Min Song
- & Jian-Ding Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Relating the degree of network crosslinking as a descriptor to the desalination performance of crosslinked polymer membranes remains challenging. Here, the authors introduce a parameter based on distinct amide bonds per unit mass of polyamide, to unravel the relationship between the crosslinked networks of polyamide membranes and their desalination performance.
- Yu-Ren Xue
- , Chang Liu
- & Zhi-Kang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
Mechanoelectric energy conversion is a potential solution for the power supply of soft devices, but the low current output for low frequency motions limits its applicability. Here, the authors report a hydrogel generator with mechanoionic current generation amplified by orders of magnitudes and its application as controlled drug-releasing system for wound healing.
- Hongzhen Liu
- , Xianglin Ji
- & Lizhi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Stable water splitting using photoelectrodes with a cryogelated overlayer
Stable water splitting using photoelectrodes with a cryogelated overlayer
Photoelectrodes made of earth-abundant materials can contribute to low-cost and carbon-free hydrogen production, but suffer from a short lifetime. Here the authors report cryogel overlayer to increase the operation time of the device by regulating evolving hydrogen bubble dynamics.
- Byungjun Kang
- , Jeiwan Tan
- & Hyungsuk Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Complexation-driven assembly of imine-linked helical receptors showing adaptive folding and temperature-dependent guest selection
Complexation-driven assembly of imine-linked helical receptors showing adaptive folding and temperature-dependent guest selection
The development of synthetic receptors capable of selectively binding monosaccharides is highly challenging. Here, authors present the efficient synthesis of these receptors based on foldamers, achieved through complexation-induced equilibrium shifting.
- Geunmoo Song
- , Seungwon Lee
- & Kyu-Sung Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Stenus-inspired, swift, and agile untethered insect-scale soft propulsors
Stenus-inspired, swift, and agile untethered insect-scale soft propulsors
Inspired by the swift swingable abdomen, conducting canals, and body setae of Stenus comma, the authors present a swift, agile untethered insect-scale soft propulsor, offering new insights into systematically bio-inspired artificial soft robots.
- Xingxing Ke
- , Haochen Yong
- & Zhigang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Circular olefin copolymers made de novo from ethylene and α-olefins
Circular olefin copolymers made de novo from ethylene and α-olefins
Although several advances have been made in chemical Polyethylene (PE) re- and upcycling, energy-efficient and selective catalytic processes are still lacking. Here, the authors show coupling of an industrially relevant coordination copolymerization olefins with a functionalized chain-transfer agent, followed by modular assembly of the resulting telechelic polyolefin building blocks by polycondensation to afford ester-linked PE-based random and block copolymers which exhibit full chemical circularity.
- Xing-Wang Han
- , Xun Zhang
- & Yong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Functional features in the spatiotemporal regulation of blood chemistry are not much explored. Here authors show vascular network-inspired fluidics, functionalizable for different region-specific trans-wall transport to regulate fluids over space and time.
- Yafeng Yu
- , Yi Pan
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access Low-frequency vibrational density of states of ordinary and ultra-stable glasses
Low-frequency vibrational density of states of ordinary and ultra-stable glasses
Power-law scaling of low-frequency vibrational density of states is widely observed in glassy materials, yet the value of scaling exponents remains controversial. Here, Xu et al. identify two scaling exponents by separating stable from unstable glass to reconcile the debate in the literature.
- Ding Xu
- , Shiyun Zhang
- & Ning Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Durable Janus membrane with on-demand mode switching fabricated by femtosecond laser
Durable Janus membrane with on-demand mode switching fabricated by femtosecond laser
Janus membranes are highly valued for their unique water unidirectional transportation capabilities. Here, authors report an on-demand mode-switching strategy that significantly enhances the durability of the Janus membrane.
- Zehang Cui
- , Yachao Zhang
- & Yanlei Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable templating of photonic microparticles via liquid crystal order-guided adsorption of amphiphilic polymers in emulsions
Tunable templating of photonic microparticles via liquid crystal order-guided adsorption of amphiphilic polymers in emulsions
The role of polymers in stabilizing liquid crystal (LC)-water interfaces is well studied but how the LC affects stabilizers is not fully explored yet. Here, Ma et al. show that amphiphilic polymers change their behavior when the LC is heated towards its transition to the isotropic state, and propose that this is due to an entropic repulsion active at low temperatures where the orientationally ordered LC restricts the mobility of the flexible polymer chains.
- Xu Ma
- , Yucen Han
- & Jan P. F. Lagerwall
-
Article
| Open Access Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Injectable pro-regenerative biomaterials are vital for developing minimally invasive regenerative treatment, but impeded by brittleness and lack of biological functions. Here the authors address these issues by engineering injectable functionalized composites that facilitate the sequential release of IL-4 and IGF-1 to regulate macrophages and stem cell behavior for enhanced in situ regeneration.
- Yi Li
- , Siyang Liu
- & Meifeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ formatting donor-acceptor polymer with giant dipole moment and ultrafast exciton separation
In-situ formatting donor-acceptor polymer with giant dipole moment and ultrafast exciton separation
Donor-acceptor polymers have potential for application in photocatalysis, but often harsh synthetic conditions are required. Here, the authors report a post-synthetic method for conversion to donor-acceptor states, to give a polymer capable of enhancing photocatalytic hydrogen peroxide synthesis.
- Chang Cheng
- , Jiaguo Yu
- & Mietek Jaroniec
-
Article
| Open Access Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks
Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks
Tough hydrogels commonly utilise energy dissipation mechanisms, but this can lead to challenges in achieving low hysteresis. Here, the authors report a hydrogel with a highly entangled double network that allows reversibility following stretching.
- Ruixin Zhu
- , Dandan Zhu
- & Xinling Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Miniaturized and untethered McKibben muscles based on photothermal-induced gas-liquid transformation
Miniaturized and untethered McKibben muscles based on photothermal-induced gas-liquid transformation
Traditional McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles are limited by connecting devices, preventing remote control and miniaturization. Here, Ai et all., report a miniaturized McKibben artificial muscle, filled by a low-boiling liquid actuated by light.
- Wenfei Ai
- , Kai Hou
- & Kai Song
-
Article
| Open Access Twofold rigidity activates ultralong organic high-temperature phosphorescence
Twofold rigidity activates ultralong organic high-temperature phosphorescence
Obtaining high-temperature phosphorescence in organic materials can potentially lead to broader applications, but can be challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of rigid molecules as both host and guest to give temperature resistance and therefore high-temperature phosphorescence.
- Kaijun Chen
- , Yongfeng Zhang
- & Xiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Robust links in photoactive covalent organic frameworks enable effective photocatalytic reactions under harsh conditions
Robust links in photoactive covalent organic frameworks enable effective photocatalytic reactions under harsh conditions
The development of heterogeneous photocatalysts applicable under harsh conditions is challenging. Here the authors report the conversion of imine linkages into quinoline groups in triphenylamine incorporated photosensitive covalent organic frameworks to develop robust heterogeneous photocatalysts for photocatalytic applications in harsh conditions.
- Jia-Rui Wang
- , Kepeng Song
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralight crystalline hybrid composite material for highly efficient sequestration of radioiodine
Ultralight crystalline hybrid composite material for highly efficient sequestration of radioiodine
The development of effective adsorbents of radioiodine nuclear waste remains difficult due to the lack of proper material design strategies. Here the authors report an ultralight hierarchically porous crystalline multifunctional hybrid nanocomposite for ultrafast entrapment of iodine and polyiodide species under both static and dynamic condition.
- Sahel Fajal
- , Writakshi Mandal
- & Sujit K. Ghosh
-
Article
| Open Access A 3D printable tissue adhesive
A 3D printable tissue adhesive
Tissue adhesives have received significant interest for their clinical utility but are typically incompatible with advanced manufacturing methods. Here, the authors introduce a 3D printable tissue adhesive for the fabrication of patches and devices for diverse biomedical applications.
- Sarah J. Wu
- , Jingjing Wu
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetrically pulsating bubbles swim in an anisotropic fluid by nematodynamics
Symmetrically pulsating bubbles swim in an anisotropic fluid by nematodynamics
For an active particle to be able to swim in a low-Reynolds number flow, breaking of time-reversal symmetry and centrosymmetry is required. Typically, this is achieved through asymmetric characteristics of the swimmer. Now, swimming of centrosymmetric pulsating bubbles in an anisotropic fluid is reported.
- Sung-Jo Kim
- , Žiga Kos
- & Joonwoo Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Hydraulic-driven adaptable morphing active-cooling elastomer with bioinspired bicontinuous phases
Hydraulic-driven adaptable morphing active-cooling elastomer with bioinspired bicontinuous phases
Low thermal conduction and conformability of traditional rigid heat sinks limit their adoption in flexible electronics and soft robotics. Here, authors report a liquid metal skeleton-based active-cooling elastomer with high thermal conductivity, stretchability, and hydraulic-driven adaptable morphing.
- Dehai Yu
- , Zhonghao Wang
- & Zhizhu He
-
Article
| Open Access Water-stable boroxine structure with dynamic covalent bonds
Water-stable boroxine structure with dynamic covalent bonds
Despite the structural significance of boroxines in different classes of materials, their applicability in aqueous media is limited by their hydrolytic instability. Here, the authors discovered a water-stable boroxine structure with excellent pH stability and water-compatible dynamic covalent bonds.
- Xiaopei Li
- , Yongjie Zhang
- & Guangyan Qing
-
Article
| Open Access Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Coacervate-based compartments are attractive as potential protocells, but formation and control of the compartments can be challenging. Here, the authors report the spontaneous formation of core-shell, cell-sized coacervate compartments driven by droplet evaporation.
- Cheng Qi
- , Xudong Ma
- & Zhou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-friction gold-based stretchable electronics enabled by interfacial diffusion-induced cohesion
Anti-friction gold-based stretchable electronics enabled by interfacial diffusion-induced cohesion
Stretchable electronics require high interfacial strength between the inert metal and elastomer components for durable interconnection applications. Cao et al. show a chemical modification-free interfacial diffusion-induced cohesion strategy, using hydrophilic polyurethane to induce hydrogen bonding of gold grains.
- Jie Cao
- , Xusheng Liu
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Logical rotation of non-separable states via uniformly self-assembled chiral superstructures
Logical rotation of non-separable states via uniformly self-assembled chiral superstructures
The logical rotation of non-separable states with a large tunable range is demonstrated by the uniformly self-assembled chiral superstructures, which enables a set of logic gates, proof-of-principle logic network, and angular motion tracking.
- Yi-Heng Zhang
- , Si-Jia Liu
- & Yan-Qing Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable droplet networks
Reconfigurable droplet networks
Earlier methods for droplet network stabilization require extremely precise control and manipulation with considerable energy consumption, making them difficult to implement. Here, the authors present 2D interfacial networks, formed by irreversible interfacial interactions between polymer chains dissolved in one liquid and ligands dissolved in a second immiscible liquid at random points along the chains.
- Shuyi Sun
- , Shuailong Li
- & Shaowei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation
Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation
The structures and properties of membranes depend strongly on their preparation methods. Here, the authors present a plasma-assisted nonsolvent-induced phase separation method that allows to tailor the physicochemical and electrical characteristics of PVDF membranes for various applications.
- Yueh-Han Huang
- , Meng-Jiy Wang
- & Tai-Shung Chung
-
Article
| Open Access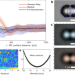 Determining intrinsic potentials and validating optical binding forces between colloidal particles using optical tweezers
Determining intrinsic potentials and validating optical binding forces between colloidal particles using optical tweezers
Understanding the interactions between submicrometer-sized colloidal particles is of interest to scientists in numerous disciplines. Here, the authors use optical tweezers alongside a full image reconstruction technique to investigate these interactions on the nanometer scale.
- Chi Zhang
- , José Muñetón Díaz
- & Frank Scheffold
-
Article
| Open Access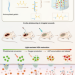 Programmed microalgae-gel promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes
Programmed microalgae-gel promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes
The treatment of infected diabetic wounds faces obstacles of bacterial infection, hypoxia, hyperexpression of reactive oxygen species, and inflammation. Here, the authors address these issues by developing a programmed treatment strategy that utilizes live Haematococcus to promote healing of diabetic wounds in a comprehensive manner.
- Yong Kang
- , Lingling Xu
- & Xiaoyuan Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
“Understanding the structure-property relationship of organic molecules which exhibit different properties upon aggregation is important for the field of material science. Here, the authors prepare nonconjugated rhodamine-based molecules without aggregation-induced emission building blocks yet displaying typical aggregation-induced emission behavior.”
- Lin-Lin Yang
- , Haoran Wang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Dressings for aiding in chronic wound healing can be beneficial, but often involve additional processes or leave residue. Here, the authors report a hydrogel dressing with antibiofilm and antioxidative properties for the treatment of infected diabetic wounds.
- Dicky Pranantyo
- , Chun Kiat Yeo
- & Mary B. Chan-Park
-
Article
| Open Access Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Multifunctional composite hydrogels are promising candidates to develop smart and recyclable electronic components. Here, the authors report a reversible on-demand liquefication and solidification conductive gel formed by the self-assembly of photoresponsive host-guest complexes and MXene nanosheets which can be integrated into traditional solid-state circuits.
- Yu-Liang Lin
- , Sheng Zheng
- & Jiun-Tai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Ionic skins have potential in long-term physiological monitoring, but do not always achieve a desirable balance of viscosity and elasticity. Here, the authors report a material with hierarchical topological entanglements allowing desirable viscoelastic properties.
- Huating Ye
- , Baohu Wu
- & Peiyi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired polymeric supramolecular columns as efficient yet controllable artificial light-harvesting platform
Bioinspired polymeric supramolecular columns as efficient yet controllable artificial light-harvesting platform
The formation of artificial light-harvesting systems with high donor/acceptor ratios for efficient energy transfer remains challenging. Here, the authors describe a polymeric supramolecular column-based light-harvesting system by modular columnar assembly of donor/acceptor chromophores, enabling superior light-harvesting efficiency and dynamic full-color tunable emission.
- Bin Mu
- , Xiangnan Hao
- & Wei Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing synthetic active particles for physical reservoir computing
Harnessing synthetic active particles for physical reservoir computing
The ability of living systems to process signals and information is of vital importance. Inspired by nature, Wang and Cichos show an experimental realization of a physical reservoir computer using self-propelled active microparticles to predict chaotic time series such as the Mackey–Glass and Lorenz series.
- Xiangzun Wang
- & Frank Cichos
-
Article
| Open Access Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
It is desirable to be able to mimic the properties of skin with hydrogels, but challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of functionalised extracellular vesicles as crosslinkers for skin-mimicking hydrogels with good mechanical strength.
- Feng Wu
- , Yusheng Ren
- & Yan Pang
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Artificial ion channels have potential in a range of applications, but achieving performance comparable to biological channels has been challenging. Here, the authors report an artificial, light-driven chloride pump, inspired by halorhodopsin, with a helical porphyrin channel array.
- Chao Li
- , Yi Zhai
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access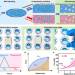 Self-poled piezoelectric polymer composites via melt-state energy implantation
Self-poled piezoelectric polymer composites via melt-state energy implantation
Lightweight flexible piezoelectric polymers are demanded for various applications, but restricted by the low instinctively piezoelectric coefficient and complex poling process. Here, the authors develop a high performance lightweight, flexible self-poled piezoelectric polymer composite towards sustainable self-powered sensing and energy harvesting.
- Zhao-Xia Huang
- , Lan-Wei Li
- & Jin-Ping Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with nia nets for efficient separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures
Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with nia nets for efficient separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures
The synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with highly connected building blocks presents a significant challenge. Here, the authors report the synthesis of two 3D COFs with the nia topology, by introducing planar hexagonal and triangular prism nodes.
- Jianhong Chang
- , Fengqian Chen
- & Qianrong Fang
-
Article
| Open Access A wearable electrostimulation-augmented ionic-gel photothermal patch doped with MXene for skin tumor treatment
A wearable electrostimulation-augmented ionic-gel photothermal patch doped with MXene for skin tumor treatment
A wearable biological patch capable of producing multiple responses to light and electricity without interfering with daily activities is desired for skin cancer treatment but remains elusive. Herein, the authors report a skin-mountable and dual-responsive electrothermal patch for melanoma treatment by the co-therapy of photothermal and electrical stimulations.
- Xingkai Ju
- , Jiao Kong
- & Yongdong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access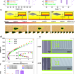 An energy-free strategy to elevate anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic materials through interfacial airflow manipulation
An energy-free strategy to elevate anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic materials through interfacial airflow manipulation
Currently, the anti-icing performance limitation of superhydrophobic materials is gradually approached without the assistance of an external field. Here, the authors propose a strategy of microdroplet movement manipulation induced by interfacial airflow for further improving the anti-icing performance.
- Jiawei Jiang
- , Yizhou Shen
- & Haifeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial decomposition of biodegradable plastics on the deep-sea floor
Microbial decomposition of biodegradable plastics on the deep-sea floor
It is unclear whether microbes can efficiently degrade biodegradable plastics in the extreme environmental conditions of the seafloor. Here, Omura et al. show that biodegradable plastics can be degraded by the action of microorganisms on the deep-sea floor, although with much less efficiency than in coastal settings.
- Taku Omura
- , Noriyuki Isobe
- & Tadahisa Iwata

 Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials