Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Intelligent perceptual textiles based on ionic-conductive and strong silk fibers
Intelligent perceptual textiles based on ionic-conductive and strong silk fibers
Perception plays a pivotal role in advancing future intelligent textiles. Here, the authors develop smart perceptual textiles using natural-derived ionic-conductive silk fibers. These textiles can electrically detect external hazards and precisely pinpointing human touch, making them suitable for smart protective clothing and soft human-machine interfaces.
- Haojie Lu
- , Yong Zhang
- & Yingying Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A facile one step route that introduces functionality to polymer powders for laser sintering
A facile one step route that introduces functionality to polymer powders for laser sintering
Polyamide-12 is the main polymer employed to produce 3D objects by laser sintering constraining the functionality of the items produced. Here, the authors report a clean and scalable approach for the functionalization of polyamide-12 particles, yielding materials that can be printed using commercial apparatus.
- Eduards Krumins
- , Liam A. Crawford
- & Steven M. Howdle
-
Article
| Open Access Vapor-induced phase-separation-enabled versatile direct ink writing
Vapor-induced phase-separation-enabled versatile direct ink writing
The extrusion-based three-dimensional printing of polymers, metals, and composites requires elevated temperatures and may lead to diverse undesirable defects on printed parts. Here, the authors develop a vapor-induced phase separation printing technique to construct polymeric, metallic, and composite parts by using a polymer as a binder.
- Marc Sole-Gras
- , Bing Ren
- & Yong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling robust blue circularly polarized organic afterglow through self-confining isolated chiral chromophore
Enabling robust blue circularly polarized organic afterglow through self-confining isolated chiral chromophore
The preparation of systems that give blue circularly polarised organic afterglow is desirable but challenging. Here, the authors confine a chiral chromophore within a polymer matrix to limit non-radiative transitions and give blue circularly polarised organic afterglow.
- Mingjian Zeng
- , Weiguang Wang
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Fine-tuning the pore environment of ultramicroporous three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for efficient one-step ethylene purification
Fine-tuning the pore environment of ultramicroporous three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for efficient one-step ethylene purification
The construction of three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for gas separation is challenging due to the similar physicochemical properties of the gas mixture. Here, the authors report functional three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks by fine-tunning the pore environment with pyridine units to achieve effective separation of ethane from ethylene.
- Yang Xie
- , Wenjing Wang
- & Cheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial kagome lattices of Shockley surface states patterned by halogen hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks
Artificial kagome lattices of Shockley surface states patterned by halogen hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks
By utilizing the templating effect of a halogen hydrogen-bonded organic framework, the authors show that the Shockley surface states of coinage metals can be patterned into artificial kagome lattices with high tunability.
- Ruoting Yin
- , Xiang Zhu
- & Bing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A Janus carbaporphyrin pseudo-dimer
A Janus carbaporphyrin pseudo-dimer
Carbaporphyrin dimers, known for their interesting photophysical properties and application in metal-organic chemistry, generally contain two identical subunits. Here, the authors highlight the benefits that can accrue from breaking the inherent symmetry of carbaporphyrin dimers and details a new approach to creating heterobimetallic complexes.
- Haodan He
- , Jiyeon Lee
- & Xian-Sheng Ke
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion-rate sieving of propylene and propane mixtures in a cooperatively dynamic porous crystal
Diffusion-rate sieving of propylene and propane mixtures in a cooperatively dynamic porous crystal
Porous coordination polymers (PCPs) are commonly used in gas separation processes but developing PCPs that work at high temperatures and feature both high uptake capacity and selectivity remains challenging. Here, the authors report diffusion-rate sieving of propylene/propane at 300 K by constructing a PCP whose global and local dynamics cooperatively govern the adsorption process via gate opening for propylene and diffusion regulation for propane.
- Yan Su
- , Ken-ichi Otake
- & Cheng Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic polymer self-cleavage for CO2 generation before combustion empowers materials with fire safety
Catalytic polymer self-cleavage for CO2 generation before combustion empowers materials with fire safety
Overcoming this challenge of fire hazards by carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen rich materials remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstarte that catalytic polymer auto-pyrolysis before combustion releases CO2, equipping the material with fire retardant properties.
- Wei Luo
- , Ming-Jun Chen
- & Hai-Bo Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous anti-Kasha excited-state luminescence from symmetry-breaking heterogeneous carbon bisnanohoops
Anomalous anti-Kasha excited-state luminescence from symmetry-breaking heterogeneous carbon bisnanohoops
It is a long-standing scientific controversy to achieve anti-Kasha emissions by tuning structures at a molecular level. Herein, the authors constructed two symmetry-breaking heterogeneous carbon bisnanohoops with unusual anti-Kasha characteristics.
- Xinyu Zhang
- , Cheng Chen
- & Pingwu Du
-
Article
| Open Access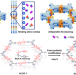 Engineering the pore environment of antiparallel stacked covalent organic frameworks for capture of iodine pollutants
Engineering the pore environment of antiparallel stacked covalent organic frameworks for capture of iodine pollutants
Radioiodine capture from nuclear fuel waste and contaminated water sources is of environmental importance but technically challenging. Here, the authors report covalent organic frameworks with antiparallel eclipsed stacked structures with dynamic adsorption performance for iodine pollutants under various conditions.
- Yinghui Xie
- , Qiuyu Rong
- & Xiangke Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleic-acid-base photofunctional cocrystal for information security and antimicrobial applications
Nucleic-acid-base photofunctional cocrystal for information security and antimicrobial applications
Cocrystal engineering is a promising strategy for constructing multifunctional materials. Here, the authors describe nucleic-acid-base cocrystal systems with different colors of phosphorescence from their monomeric counterparts and high-temperature phosphorescence with antimicrobial effects and data encryption applications.
- Wenqing Xu
- , Guanheng Huang
- & David Lee Phillips
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-8 nm networked cage nanofilm with tunable nanofluidic channels for adaptive sieving
Sub-8 nm networked cage nanofilm with tunable nanofluidic channels for adaptive sieving
Drawing inspiration from biological cell membranes, here, the authors create sub-8 nm membranes with adaptive nanofluidic channels, mimicking the cell membrane properties, by interconnecting 0D nanoporous molecules at the oil/water interface.
- Si-Hua Liu
- , Jun-Hao Zhou
- & Jian-Ke Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Encoding ordered structural complexity to covalent organic frameworks
Encoding ordered structural complexity to covalent organic frameworks
Starting from simple building blocks with specific molecular packing geometries, here, the authors synthesized structurally complex covalent organic framework COF-305 with nine different stereoisomers of its constituents showing specific sequences on topologically equivalent sites.
- Lei Wei
- , Xinyue Hai
- & Yingbo Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printing by stereolithography using thermal initiators
3D printing by stereolithography using thermal initiators
Common stereolithography-based 3D printing relies on photopolymerization using photoinitiators. Here, the authors replace the conventional photoinitiators with low-cost, widely used thermal initiators to achieve 3D-printed objects.
- Doron Kam
- , Omri Rulf
- & Shlomo Magdassi
-
Article
| Open Access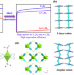 Molecular sieving of iso-butene from C4 olefins with simultaneous high 1,3-butadiene and n-butene uptakes
Molecular sieving of iso-butene from C4 olefins with simultaneous high 1,3-butadiene and n-butene uptakes
The efficient separation of iso-butene, an important raw material in chemical industry, remains challenging due to similar molecular properties of C4 olefins. Here, the authors report a sulfate-pillared adsorbent for the molecular sieving of iso-C4H8 from C4H6 and n-C4H8 with good benchmark uptake ratios and Henry’s selectivities.
- Junhui Liu
- , Hanting Xiong
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Complete separation of benzene-cyclohexene-cyclohexane mixtures via temperature-dependent molecular sieving by a flexible chain-like coordination polymer
Complete separation of benzene-cyclohexene-cyclohexane mixtures via temperature-dependent molecular sieving by a flexible chain-like coordination polymer
The separation and purification of C6 cyclic hydrocarbons by thermal distillation is an energy intensive process which may be replaced by alternative energy-efficient adsorptive techniques. Here, the authors report a chain-like coordination polymer which facilitates complete separation of benzene, cyclohexene, and cyclohexane via an ideal molecular sieving mechanism.
- Feng Xie
- , Lihang Chen
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Abnormal thermally-stimulated dynamic organic phosphorescence
Abnormal thermally-stimulated dynamic organic phosphorescence
In thermally stimulated phosphorescent materials a thermal stimulus inevitably quenches the emission due to intensive non radiative transition. Here, the authors report an abnormal thermally stimulated phosphorescence behavior in organic phosphors and show enhancement of phosphorescence and change of the emission color upon temperature increase.
- He Wang
- , Huili Ma
- & Zhongfu An
-
Article
| Open Access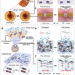 Ultrafast underwater self-healing piezo-ionic elastomer via dynamic hydrophobic-hydrolytic domains
Ultrafast underwater self-healing piezo-ionic elastomer via dynamic hydrophobic-hydrolytic domains
Elastomers capable of autonomous self-healing and mechanical stimulus sensing in aquatic environments are interesting for applications in underwater soft electronics. Here, the authors present a hydrophobic-hydrolytic molecularly engineered self-healing piezo-ionic elastomer with underwater self-healing properties and mechanosensitive ion channels.
- Zhengyang Kong
- , Elvis K. Boahen
- & Do Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
By virtue of the rotational motions of interlocked macrocycles, the authors describe a chameleon-like catenane host that can adjust its co-conformation for selective binding to copper(I) or sulfate ion. While the cationic copper(I) complex is achiral, the interlocked rings in the catenane host rotate and re-orient into a chiral co-conformation upon forming the anionic sulfate complex.
- Yueliang Yao
- , Yuen Cheong Tse
- & Ho Yu Au-Yeung
-
Article
| Open Access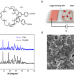 Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart sensors are important components in the development of touchless human-machine interaction systems. Here, the authors describe a smart 3D porous crystalline organic cage-based system that exhibits remarkable responsiveness to fingertip humidity, contributing to the advancement of touchless human-machine interaction technology.
- Jinrong Wang
- , Weibin Lin
- & Niveen M. Khashab
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed nanotrap structures for efficient separation of rare earth elements over a single step
Rationally designed nanotrap structures for efficient separation of rare earth elements over a single step
Extracting rare earth elements (REEs) from wastewater is essential for the growth of an eco-friendly sustainable economy but separating individual rare earth elements remains challenging. Here, the authors report a REE nanotrap that features dense uncoordinated carboxyl groups and triazole N atoms in a two-fold interpenetrated metalorganic framework which is highly responsive to the size variation of rareearth ions.
- Qing-Hua Hu
- , An-Min Song
- & Jian-Ding Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Complexation-driven assembly of imine-linked helical receptors showing adaptive folding and temperature-dependent guest selection
Complexation-driven assembly of imine-linked helical receptors showing adaptive folding and temperature-dependent guest selection
The development of synthetic receptors capable of selectively binding monosaccharides is highly challenging. Here, authors present the efficient synthesis of these receptors based on foldamers, achieved through complexation-induced equilibrium shifting.
- Geunmoo Song
- , Seungwon Lee
- & Kyu-Sung Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
Mechanoelectric energy conversion is a potential solution for the power supply of soft devices, but the low current output for low frequency motions limits its applicability. Here, the authors report a hydrogel generator with mechanoionic current generation amplified by orders of magnitudes and its application as controlled drug-releasing system for wound healing.
- Hongzhen Liu
- , Xianglin Ji
- & Lizhi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralight crystalline hybrid composite material for highly efficient sequestration of radioiodine
Ultralight crystalline hybrid composite material for highly efficient sequestration of radioiodine
The development of effective adsorbents of radioiodine nuclear waste remains difficult due to the lack of proper material design strategies. Here the authors report an ultralight hierarchically porous crystalline multifunctional hybrid nanocomposite for ultrafast entrapment of iodine and polyiodide species under both static and dynamic condition.
- Sahel Fajal
- , Writakshi Mandal
- & Sujit K. Ghosh
-
Article
| Open Access Robust links in photoactive covalent organic frameworks enable effective photocatalytic reactions under harsh conditions
Robust links in photoactive covalent organic frameworks enable effective photocatalytic reactions under harsh conditions
The development of heterogeneous photocatalysts applicable under harsh conditions is challenging. Here the authors report the conversion of imine linkages into quinoline groups in triphenylamine incorporated photosensitive covalent organic frameworks to develop robust heterogeneous photocatalysts for photocatalytic applications in harsh conditions.
- Jia-Rui Wang
- , Kepeng Song
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Water-stable boroxine structure with dynamic covalent bonds
Water-stable boroxine structure with dynamic covalent bonds
Despite the structural significance of boroxines in different classes of materials, their applicability in aqueous media is limited by their hydrolytic instability. Here, the authors discovered a water-stable boroxine structure with excellent pH stability and water-compatible dynamic covalent bonds.
- Xiaopei Li
- , Yongjie Zhang
- & Guangyan Qing
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
“Understanding the structure-property relationship of organic molecules which exhibit different properties upon aggregation is important for the field of material science. Here, the authors prepare nonconjugated rhodamine-based molecules without aggregation-induced emission building blocks yet displaying typical aggregation-induced emission behavior.”
- Lin-Lin Yang
- , Haoran Wang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Multifunctional composite hydrogels are promising candidates to develop smart and recyclable electronic components. Here, the authors report a reversible on-demand liquefication and solidification conductive gel formed by the self-assembly of photoresponsive host-guest complexes and MXene nanosheets which can be integrated into traditional solid-state circuits.
- Yu-Liang Lin
- , Sheng Zheng
- & Jiun-Tai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Upcycling poly(succinates) with amines to N-substituted succinimides over succinimide anion-based ionic liquids
Upcycling poly(succinates) with amines to N-substituted succinimides over succinimide anion-based ionic liquids
Ionic liquids have been employed in dissolution and chemical degradation of waste polymers. Here the authors report a cation-anion confined hydrogen-bonding catalysis strategy to deconstruct poly(succinates) into N-substituted succinimides over ionic liquids.
- Fengtian Wu
- , Yuepeng Wang
- & Zhimin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Robust hydrogels offer a promising solution for the development of artificial skin for bionic robots, yet few hydrogels have a comprehensive performance comparable to real human skin. Here, the authors present a general method to convert traditional elastomers into tough hydrogels via a unique radiation-induced penetrating polymerization method.
- Yuan Tian
- , Zhihao Wang
- & Yunlong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the crucial role of trace oxygen in organic semiconductors
Unraveling the crucial role of trace oxygen in organic semiconductors
Conventional deoxygenation methods typically result in inevitable trace oxygen residue in organic semiconductors. Here, Huang et al. reports a non-destructive soft-plasma treatment for deoxygenation and that removal of trace oxygen can be used to modulate p-type characteristics.
- Yinan Huang
- , Kunjie Wu
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled dendrimer polyamide nanofilms with enhanced effective pore area for ion separation
Self-assembled dendrimer polyamide nanofilms with enhanced effective pore area for ion separation
Membrane technology using well-defined pore structure enables high ion purity and recovery but achieving uniform pore structure and effective pore area is challenging. Here the authors introduce dendrimers that self-assemble, facilitating the formation of polyamide nanofilms with well-defined effective pore ranges and uniform pore structures.
- Bingbing Yuan
- , Yuhang Zhang
- & Q. Jason Niu
-
Article
| Open Access Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
The design of multifunctional platforms with tunable spectroscopic and fluorescent properties that span the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared spectral regions remains challenging. Here, the authors report an actuator-type system that leverages a readily-prepared, easily-processable, and exceptionally-stable nonacene-like molecule to achieve multiple complementary dynamic operating modes.
- Preeta Pratakshya
- , Chengyi Xu
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article
| Open Access Stoichiometry validation of supramolecular complexes with a hydrocarbon cage host by van ’t Hoff analyses
Stoichiometry validation of supramolecular complexes with a hydrocarbon cage host by van ’t Hoff analyses
“van ’t Hoff, the first Nobel laureate, invented a double-arrow formalism to define equilibria in 1884. Here, the authors apply his accompanying method, the van ’t Hoff plot, to a modern problem to decide the stoichiometry of supramolecular complexes.”
- Toshiya M. Fukunaga
- , Yuzuka Onaka
- & Hiroyuki Isobe
-
Article
| Open Access Folk arts-inspired twice-coagulated configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors
Folk arts-inspired twice-coagulated configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors
Aerogels attract considerable attention in various emerging fields in recent decades, but low density and weak mechanical performance make their configuration-editing capability challenging. Here the authors establish an efficient twice-coagulated strategy to fabricate configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors.
- Lishan Li
- , Guandu Yang
- & Xuetong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Site-selective chemical reactions by on-water surface sequential assembly
Site-selective chemical reactions by on-water surface sequential assembly
Controlling site-selectivity and reactivity in chemical reactions continues to be a key challenge in modern synthetic chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate the assembly of amino-substituted porphyrins on a water surface into J-aggregate structures in the presence of charged surfactants.
- Anupam Prasoon
- , Xiaoqing Yu
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen-bonding and π-π interaction promoted solution-processable covalent organic frameworks
Hydrogen-bonding and π-π interaction promoted solution-processable covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks are generally not dispersible in common solvents resulting in the poor processability which limits their practical application. Here, the authors develop a top-down process to produce solution-processable covalent organic frameworks based on the assistance of ionic liquids by means of intermolecular hydrogen bonding and π-π interactions.
- Lei Zhang
- , Qiu-Hong Zhu
- & Ling He
-
Article
| Open Access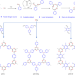 A highly proton conductive perfluorinated covalent triazine framework via low-temperature synthesis
A highly proton conductive perfluorinated covalent triazine framework via low-temperature synthesis
Perfluorinated covalent triazine frameworks are promising proton-conducting materials with high content of phosphoric acid anchor sites to enhance proton conductivity but their synthesis is challenging. Here, the authors report a mild method to produce perfluorinated covalent triazine frameworks displaying high proton conductivity.
- Lijiang Guan
- , Zhaoqi Guo
- & Shangbin Jin
-
Article
| Open Access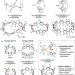 A dodecamethoxy[6]cycloparaphenylene consisting entirely of hydroquinone ethers: unveiling in-plane aromaticity through a rotaxane structure
A dodecamethoxy[6]cycloparaphenylene consisting entirely of hydroquinone ethers: unveiling in-plane aromaticity through a rotaxane structure
“Cycloparaphenylenes consisting of are cyclic π-conjugated structures presetting interesting physical properties upon functionalization. However, the ring strain and steric hindrance of the substituents hamper the functionalization of small sized cycloparaphenylenes. Here, the authors describe a [6]cycloparaphenylene with twelve methoxy units employed to form a rotaxane with in-plane aromaticity upon oxidation.”
- Naoki Narita
- , Yusuke Kurita
- & Yoshitaka Tsuchido
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraflexible, cost-effective and scalable polymer-based phase change composites via chemical cross-linking for wearable thermal management
Ultraflexible, cost-effective and scalable polymer-based phase change composites via chemical cross-linking for wearable thermal management
Jing et al. report a cost-effective chemical cross-linking method for synthesizing ultraflexible polymer-based phase change composites with 3D crosslinked networks and further demonstrate portable applications for wearable thermal management.
- Yaoge Jing
- , Zhengchuang Zhao
- & Tingxian Li
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition
Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition
Strategies to construct circularly polarized luminescence (CPL)-active materials with color modulation and handedness of CPL are desirable for the synthesis of chiral photo-responsive devices. Here the authors develop a CPL system based on styrylpyrenes. Benefiting from CH-π interactions between chromophores, the styrylpyrene aggregates show color-dependent CPL property and photo-responsive behavior.
- Wei Yuan
- , Letian Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access In situ observation of a stepwise [2 + 2] photocycloaddition process using fluorescence spectroscopy
In situ observation of a stepwise [2 + 2] photocycloaddition process using fluorescence spectroscopy
Using highly sensitive and selective in situ techniques to investigate the dynamics of intermediates formation is key to better understand reaction mechanisms but investigating the early stages of solid-state reactions or transformations is still challenging. Here the authors use in situ fluorescence spectroscopy to observe the evolution of intermediates during a two-step [2 + 2] photocycloaddition process in a coordination polymer.
- Meng-Fan Wang
- , Yun-Hu Deng
- & Jian-Ping Lang
-
Article
| Open Access Woven organic crystals
Woven organic crystals
The entanglement of fibrous elements produces flexible structures with enhanced strength and resilience to abrasion. Here, the authors report the weaving of organic crystals into flexible and robust patches with plain, twill, and satin topologies of arbitrary porosity, expanding one-dimensional crystals into flexible, two-dimensional planar structures with potential for future applications in flexible electronics.
- Linfeng Lan
- , Liang Li
- & Hongyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of aligned dipoles and angular chromism of exciplexes in organic molecular heterostructures
Observation of aligned dipoles and angular chromism of exciplexes in organic molecular heterostructures
The directional features of dipole moments of Frenkel excitons and exciplexes are important for optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors study photo- and electro-luminescence emissions of organic heterostructures and observe angular chromism of exciplexes, indicating possible delocalization.
- Sang-hun Lee
- , Taek Joon Kim
- & Jinsoo Joo
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired thermadapt shape-memory polymer with light-induced reversible fluorescence for rewritable 2D/3D-encoding information carriers
Bioinspired thermadapt shape-memory polymer with light-induced reversible fluorescence for rewritable 2D/3D-encoding information carriers
The stimuli responsive color-shifting properties of fluorescent materials have been used for 2D encoding for information encryption applications but possessing a risk of information leakage. Here, the authors develop shape-memory fluorescent films with reversible fluorescence-shifting and thermadapt shape-memory properties for integrating rewritable 2D/3D encoding in one system.
- Jinhui Huang
- , Yue Jiang
- & Shaobing Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access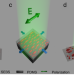 Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Light-responsive polymers with polarization-dependent deformation are promising material to develop tunable devices usually limited by irreversible dynamic control. Here, the authors use controlled polarization of visible light to produce arbitrary deformations into amorphous composites containing azopolymer microdomains to unlock the next level of complex actuation in soft lightdriven robots.
- David Urban
- , Niccolò Marcucci
- & Emiliano Descrovi
-
Article
| Open Access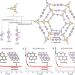 Twistedly hydrophobic basis with suitable aromatic metrics in covalent organic networks govern micropollutant decontamination
Twistedly hydrophobic basis with suitable aromatic metrics in covalent organic networks govern micropollutant decontamination
The synergetic regulation of the electronic structure and interfacial reaction of covalent organic frameworks (COF) for water purification remains a challenge. Here the authors propose that COFs materials possessing molecular interfaces with ordered π skeletons, suitable pore size, and hydrophilic/hydrophobic channels synergically break through the adsorption energy barrier achieving high removal rates for micropollutants.
- Chencheng Qin
- , Yi Yang
- & Hou Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Aromatized liposomes for sustained drug delivery
Aromatized liposomes for sustained drug delivery
The development of liposome-based drug delivery systems has been hindered by the systemic toxicity and limited duration of effect due to insufficient drug loading and leakage of payload. Here the authors address these issues by designing aromatized liposomes that feature increased drug loading and slowed release compared to conventional liposomes.
- Yang Li
- , Tianjiao Ji
- & Daniel S. Kohane

 An organic proton cage that is ultra-resistant to hydroxide-promoted degradation
An organic proton cage that is ultra-resistant to hydroxide-promoted degradation