Featured
-
-
-
News & Views |
Chemoradiation superior in muscle-invasive bladder cancer
Multimodal organ-sparing treatment strategies have shown similar survival rates when compared to radical surgery for muscle-invasive bladder cancer; however, up to 80% of surviving patients retained their own, well-functioning bladder. Within an interdisciplinary bladder-preserving treatment protocol, concurrent chemoradiotherapy was superior to radiotherapy alone—supporting its use as an alternative to radical cystectomy.
- Christian Weiss
- & Claus Rödel
-
-
In Brief |
Good old acupuncture
-
News & Views |
 Localized non-bulky Hodgkin lymphoma—future questions
Localized non-bulky Hodgkin lymphoma—future questions
Late toxicities from radiation therapy are frequent in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma and can hamper survival. These late toxicities should decrease with modern radiation therapy but results are not mature and so the importance of this decrease is still unknown. Hence, all studies in Hodgkin lymphoma must report long-term outcome.
- Bertrand Coiffier
- & Olivier Casasnovas
-
News & Views |
The importance of local control in pancreatic cancer
The ECOG E4201 study adds another piece of information to a growing body of evidence pointing strongly to the importance of local control and the role of radiotherapy in unresectable pancreatic cancer. Based on this evidence, we believe radiotherapy should be used routinely in this setting.
boxed-text - Edgar Ben-Josef
- & Theodore S. Lawrence
-
Review Article |
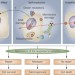 Clinical radioimmunotherapy—the role of radiobiology
Clinical radioimmunotherapy—the role of radiobiology
Radioimmunotherapy is being used successfully for the treatment of patients with hematological malignancies, however similar efficacy is lacking in patients with solid tumors. Pouget and colleagues explain basic concepts of radiobiology, review the results of clinical radioimmunotherapy trials, and highlight potential strategies to improve the efficacy of radioimmunotherapy in patients with solid tumors.
- Jean-Pierre Pouget
- , Isabelle Navarro-Teulon
- & David Azria
-
-
Opinion |
Nipple-sparing mastectomy—is it worth the risk?
The advent of prophylactic mastectomy and the new surgical techniques that are available has encouraged the use of nipple-sparing mastectomy. This Perspectives article examines this technique in terms of aesthetics, contraindications, side effects and recurrence, and outlines why, in the authors' opinion, nipple-sparing mastectomy should be offered to patients with breast cancer and those at high risk.
- Jean-Yves Petit
- , Umberto Veronesi
- & Mario Rietjens
-
News & Views |
An important piece of the localized prostate cancer puzzle?
A recent trial randomly allocated 1,979 men with localized prostate cancer to radiation therapy with or without neoadjuvant androgen deprivation. Despite the combination reducing prostate cancer-specific mortality by approximately 60% and producing a modest overall survival benefit in men with intermediate-risk cancers, the authors did not recommend changing the standard of care—why?
- James W. Denham
-
Review Article |
The current landscape of locally advanced rectal cancer
Current treatments for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) consist of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, followed by total mesorectal excision and adjuvant chemotherapy. Aklilu and Eng review the pivotal trials that have led to this treatment paradigm and discuss novel therapies that are being developed for patients with LARC.
- Mebea Aklilu
- & Cathy Eng
-
-
Review Article |
 Organ-sparing radiation therapy for head and neck cancer
Organ-sparing radiation therapy for head and neck cancer
Radiation therapy techniques have made great strides over the past decade, both in terms of efficacy and in the avoidance of the associated toxic effects. This Review highlights the particular areas of concern for patients with head and neck cancer and outlines how to avoid toxic effects, while maintaining the optimal treatment efficacy.
- XiaoShen Wang
- , ChaoSu Hu
- & Avraham Eisbruch
-
Research Highlight |
 Radiopeptide therapy improves outcomes for neuroendocrine cancers
Radiopeptide therapy improves outcomes for neuroendocrine cancers
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
-
Research Highlight |
 IMRT reduces incidence of xerostomia in patients with head and neck cancer
IMRT reduces incidence of xerostomia in patients with head and neck cancer
- Christoph A. Schmitt
-
News & Views |
Has the role of WBRT in primary CNS lymphoma been settled?
The use of whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in the treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma is controversial. A recent randomized study addressing the use of this therapy was flawed and questions remain about the use of WBRT in these patients.
- Lisa M. DeAngelis
-
News & Views |
 Hypoxia modification with radiotherapy for bladder cancer
Hypoxia modification with radiotherapy for bladder cancer
The outcomes in bladder cancer treated with radiotherapy are suboptimal. Recently, Hoskin et al. reported improved survival in patients with bladder cancer treated with radiation therapy with concurrent hypoxia-modification therapy. These results are promising but must be viewed in the context of previous studies and alternative treatment approaches.
- Mary Gospodarowicz
-
Year in Review |
Maximizing survival and minimizing toxicity
Outcomes for patients with oropharyngeal cancer are determined by their tumor characteristics and associated demographics. The role of human papilloma virus-related disease for prognosis and outcomes with chemoradiotherapy is being more clearly defined. EGFR inhibitors are used in conjunction with radiotherapy, and the importance of optimizing radiation quality and minimizing toxicity is the focus of ongoing studies.
- Bruce E. Brockstein
- & Everett E. Vokes
-
Year in Review |
 New therapies and standard of care in oncology
New therapies and standard of care in oncology
2010 was not a year of survival breakthroughs in hematologic malignancies. However, in Hodgkin's disease and multiple myeloma new therapies emerged as the standard of care and nilotinib may be considered the treatment choice for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia.
- Vincent T. DeVita Jr
- & George P. Canellos
-
Review Article |
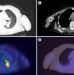 PET–CT for radiotherapy treatment planning and response monitoring in solid tumors
PET–CT for radiotherapy treatment planning and response monitoring in solid tumors
PET–CT is important for the staging of disease, but also in detecting mechanisms of resistance at the molecular level. In combination with tracers, these imaging modalities can delineate the underlying processes of resistance, such as tumor-cell proliferation, hypoxia, and vascular density. The authors of this Review discuss how the use of various tracers makes it possible to predict outcome and monitor response to treatment. By selecting patients on the basis of their mechanism of resistance, it should be possible to avoid the rejection of treatment options by assessing individuals rather than a population as a whole.
- Johan Bussink
- , Johannes H. A. M. Kaanders
- & Wim J. G. Oyen
-
Review Article |
 Neoadjuvant radiotherapy for locally advanced and high-risk prostate cancer
Neoadjuvant radiotherapy for locally advanced and high-risk prostate cancer
Men with locally advanced or high-risk prostate cancer may benefit from combined modality strategies. This Review discusses the approaches and rational for preoperative and intraoperative radiotherapy and compares them with the utility of postoperative radiotherapy. The urgent need for novel biomarkers for selection purposes is highlighted.
- John Thoms
- , Jayant S. Goda
- & Robert G. Bristow
-
News & Views |
 Chemoradiotherapy for NSCLC—does a 'standard' exist?
Chemoradiotherapy for NSCLC—does a 'standard' exist?
The optimal chemotherapy regimen to be used concurrently with thoracic radiation for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer remains uncertain. Studies investigating this question are ongoing.
- Allen M. Chen
- & Primo N. Lara Jr
-
News & Views |
Ultra-targeted APBI using TARGIT—a cautionary note
One of the seven ongoing trials of accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) has concluded that single-dose intraoperative radiotherapy should be considered as an alternative to protracted whole-breast irradiation. With a median follow up of 2 years, such conclusions seem premature. Until the risk and pattern of breast recurrence is reported at longer follow up, TARGIT APBI should remain an experimental approach.
- Rajiv Sarin
-
-
News & Views |
Accelerated radiotherapy for HNSCC in developing countries
The IAEA-ACC study compared accelerated radiotherapy with standard radiotherapy in a multicenter trial conducted in developing countries. Advantages were most notable in patients with early-stage disease, which may limit the utility of this therapy. In countries where resources are limited, however, this strategy may be a cost-effective approach to improving outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer.
- Bruce Brockstein
- & Everett E. Vokes
-
Opinion |
 Intra-arterial brachytherapy of hepatic malignancies: watch the flow
Intra-arterial brachytherapy of hepatic malignancies: watch the flow
Radio-embolization using radioactive microspheres allows the delivery of high-dose internal radiotherapy to malignant tumors of the liver. The surrogate for measuring flow dynamics for radio-embolization planning does not best represent treatment efficacy. Therefore, Morgan et al. propose that imaging protocols sensitive to changes in vasculature are likely to represent useful predictive markers of malignant lesions that could benefit from radio-embolization.
- Bruno Morgan
- , Andrew S. Kennedy
- & Ricky A. Sharma
-
News & Views |
 Intermediate-risk endometrial cancer—adjuvant treatment
Intermediate-risk endometrial cancer—adjuvant treatment
Adjuvant vaginal brachytherapy was compared with adjuvant pelvic radiation therapy in patients with high-intermediate-risk uterine cancers in the PORTEC-2 trial. The results suggest that vaginal brachytherapy is the treatment of choice; however, the inclusion of very few patients with grade 2 or 3 disease limits generalizability of the results to these subgroups.
- Patricia J. Eifel
-
Review Article |
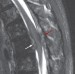 The role of radiotherapy for metastatic epidural spinal cord compression
The role of radiotherapy for metastatic epidural spinal cord compression
Radiotherapy has an important role in the treatment of metastatic epidural spinal cord compression; when used alone, it is important to select the most suitable radiotherapy regimen. In this Review, Rades and Abrahm report that longer-course radiotherapy is associated with better local control than short-course radiotherapy. However, short-course radiotherapy is more suitable than longer-course treatment in patients with a poor prognosis.
- Dirk Rades
- & Janet L. Abrahm
-
Review Article |
 Treating prostate cancer with radiotherapy
Treating prostate cancer with radiotherapy
This Review focuses on the adverse effects of radical radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. The authors discuss the methodological issues that make comparison between the different treatment modalities problematic, and describe the pattern of adverse effects that occur over time after radiotherapy. Recent technical advances, such as intensity modulation and image guidance, will hopefully further improve the toxicity profile of prostate radiotherapy.
- Anna Wilkins
- & Chris Parker
-
News & Views |
Optimizing chemotherapy and radiotherapy for anaplastic glioma
The optimum approach for the treatment of rare anaplastic gliomas following surgical resection is uncertain. A recent study has now provided a greater understanding of the heterogeneous tumor biology of these tumors and has emphasized the prognostic importance of chromosome 1p19q deletion, IDH mutation and MGMT promoter methylation. The importance of radiotherapy and chemotherapy for treating these heterogeneous tumors is being elucidated for subgroups of patients.
- Patrick G. Morris
- & Andrew B. Lassman
-
Review Article |
Whole-brain radiation therapy in breast cancer patients with brain metastases
Brain metastases are a frequent complication in patients with advanced breast cancer. Whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) is the standard treatment for these patients, but it can cause neurocognitive damage, and results are suboptimal. Therapies that reduce toxic effects, improve local control, and prevent recurrences are needed. The authors of this Review outline the current strategies and novel developments in WBRT, and discuss new irradiation modalities that are improving outcomes in breast cancer patients with brain metastases.
- Cyrus Chargari
- , François Campana
- & Youlia M. Kirova
-
Correspondence |
Author reply: Radioembolization for colorectal liver metastases
- Nils H. Nicolay
- , David P. Berry
- & Ricky A. Sharma
-
Correspondence |
Radioembolization for colorectal liver metastases
- Maarten A. D. Vente
- , Maurice A. A. J. van den Bosch
- & Johannes F. W. Nijsen
-
News & Views |
 Hypofractionation for breast cancer—clinical implications
Hypofractionation for breast cancer—clinical implications
A recent landmark study reported the long-term results that compared a standard course of whole-breast irradiation (25 treatments over 5 weeks) with a hypofractionated course of radiation (16 treatments over 3.5 weeks) in patients with early-stage, node-negative breast cancer. The trial demonstrated equivalence of results with respect to overall survival, local control, toxicity and cosmetic outcomes.
- Bruce G. Haffty
-
News & Views |
 Secondary malignancies after prostate cancer treatment
Secondary malignancies after prostate cancer treatment
The 5-year follow up data from a study on localized prostate cancer has shown high rates of bladder, lung, and rectal cancers in men treated with external beam radiotherapy compared with radical prostatectomy. At 10 years of follow-up, only excess lung cancer risk was significant, and the authors conclude that increased secondary malignancy risk with radiation should be included in initial treatment decisions and counseling. In my opinion, younger men subjected to radiation might suffer more in the long-term than if they had undergone surgery.
- Judd W. Moul
-
News & Views |
Neurocognitive considerations in the treatment of brain metastases
The results of a randomized, controlled trial investigating the neurocognitive effects of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), with or without whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT), to treat brain metastases demonstrated a significant reduction in learning and memory, associated with the addition of WBRT to SRS. The results indicate that SRS monotherapy is an effective and safe initial management strategy for brain metastases.
- Nicholas F. Marko
- & Robert J. Weil
-
News & Views |
 PSA nadir predicts long-term mortality
PSA nadir predicts long-term mortality
The effect of PSA level on distant metastases and cause-specific mortality was assessed in a recent study, and showed a nadir PSA level 1.5 ng/ml within 2 years of radiotherapy treatment predicts distant metastases and death from prostate cancer.
- Mark K. Buyyounouski
-
Review Article |
 Treatment of painful bone metastases
Treatment of painful bone metastases
Painful bone metastases can be treated with radiotherapy, and single-fraction radiotherapy with 1 × 8 Gy has been shown to be as effective for pain relief as multi-fraction regimens. The authors discuss why single-fraction radiotherapy is considered the standard regimen for uncomplicated painful bone metastases without pathological fractures or spinal cord compression, and highlight the reasons why long-course multi-fraction radiotherapy should be reserved for patients with a relatively favorable survival prognosis.
- Dirk Rades
- , Steven E. Schild
- & Janet L. Abrahm
-
News & Views |
 ADT for prostate cancer: true love or heartbreak?
ADT for prostate cancer: true love or heartbreak?
The addition of hormonal therapy to radiation therapy improves survival in men with unfavorable risk prostate cancer. Yet, men with prostate cancer have higher rates of non-cancer death than the general population and most will die from causes other than their index malignancy. Co-morbid cardiovascular disease is strongly associated with cause of death and this raises the possibility that prostate cancer or its treatment increases cardiovascular disease risk and possibly mortality.
- Jason A. Efstathiou
- , William U. Shipley
- & Matthew R. Smith
-
News & Views |
 Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer
Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer
Chemoradiotherapy and surgical resection are important elements of multimodality treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. The optimum sequence of these modalities has been addressed in several randomized trials and preoperative chemoradiotherapy has been shown to be superior to postoperative treatment for a variety of end points.
- Claus Rödel

 For localized prostate cancer, does technology equal progress?
For localized prostate cancer, does technology equal progress? Stop recurring breast cancer nightmares
Stop recurring breast cancer nightmares Repopulating tumor cells—dying for caspase 3
Repopulating tumor cells—dying for caspase 3 Avoiding EBRT for those without high-risk endometrial cancer
Avoiding EBRT for those without high-risk endometrial cancer NSCLC treatment—reducing costs and improving outcomes
NSCLC treatment—reducing costs and improving outcomes