Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Vibronic origin of long-lived coherence in an artificial molecular light harvester
Vibronic origin of long-lived coherence in an artificial molecular light harvester
Two-dimensional spectroscopy revealed oscillatory signals in photosynthesis’ exciton dynamics, but crowded spectra impede the identification of what sustains the oscillations. Here the authors probe an J-aggregate, whose uncongested response shows that vibronic coupling is responsible for the sustained coherence.
- James Lim
- , David Paleček
- & Jürgen Hauer
-
Article
| Open Access Digital quantum simulation of fermionic models with a superconducting circuit
Digital quantum simulation of fermionic models with a superconducting circuit
Quantum simulation offers an unparalleled computational resource, but realizing it for fermionic systems is challenging due to their particle statistics. Here the authors report on the time evolutions of fermionic interactions implemented with digital techniques on a nine-qubit superconducting circuit.
- R. Barends
- , L. Lamata
- & John M. Martinis
-
Article
| Open Access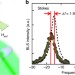 Thickness dependence of the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in inversion symmetry broken systems
Thickness dependence of the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in inversion symmetry broken systems
Spin-orbit effects at heavy metal/ferromagnet interfaces can give rise to the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, promoting chiral magnetization textures applicable in thin film devices. Here, the authors use Brillouin light scattering to study the dependence of this interaction on film thickness.
- Jaehun Cho
- , Nam-Hui Kim
- & Chun-Yeol You
-
Article |
 Constant-intensity waves and their modulation instability in non-Hermitian potentials
Constant-intensity waves and their modulation instability in non-Hermitian potentials
In the presence of a Hermitian potential, a plane wave propagating in free space cannot maintain a constant intensity due to scattering. Here, Makriset al. show that in non-Hermitian potential, waves can propagate with constant intensity through linear and nonlinear inhomogeneous media with gain and loss.
- K. G. Makris
- , Z. H. Musslimani
- & S. Rotter
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional magnetotransport in a black phosphorus naked quantum well
Two-dimensional magnetotransport in a black phosphorus naked quantum well
The two-dimensional atomic layers of black phosphorus may be exfoliated to create devices with desirable electronic transport properties. Here, the authors observe two-dimensional quantum transport in black phosphorus quantum wells, protected from oxidation by encapsulation in a polymer layer.
- V. Tayari
- , N. Hemsworth
- & T. Szkopek
-
Article
| Open Access The minimal work cost of information processing
The minimal work cost of information processing
Irreversible computation cannot be performed without a work cost, and energy dissipation imposes limitations on devices' performances. Here the authors show that the minimal work requirement of logical operations is given by the amount of discarded information, measured by entropy.
- Philippe Faist
- , Frédéric Dupuis
- & Renato Renner
-
Article
| Open Access Heat capacity peak at the quantum critical point of the transverse Ising magnet CoNb2O6
Heat capacity peak at the quantum critical point of the transverse Ising magnet CoNb2O6
The archetypal transverse Ising magnet CoNb2O6possesses a set of collective spin modes near its quantum critical point. Here, the authors use heat capacity measurements to evidence the existence of Fermionic gapless spin excitations at the critical point.
- Tian Liang
- , S. M. Koohpayeh
- & N. P. Ong
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic polymers and soft-matter-like broken symmetries in underdoped cuprates
Electronic polymers and soft-matter-like broken symmetries in underdoped cuprates
High-Tc superconductivity is thought to be associated with spatial electronic ordering, which for cuprates is not well understood yet. Here the authors use Monte Carlo simulations to show the emergence of a soft-matter-like electronic phase between the antiferromagnetic and the superconducting states.
- M. Capati
- , S. Caprara
- & J. Lorenzana
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum simulation of 2D topological physics in a 1D array of optical cavities
Quantum simulation of 2D topological physics in a 1D array of optical cavities
A wide variety of interesting phenomena arise in 2D systems subject to external gauge fields, but these are sometimes challenging to verify experimentally. Here the authors propose a setup to simulate 2D physics with a 1D arrangement of cavities, by exploiting the orbital angular momentum of trapped photons.
- Xi-Wang Luo
- , Xingxiang Zhou
- & Zheng-Wei Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Low-temperature thermodynamics with quantum coherence
Low-temperature thermodynamics with quantum coherence
Thermal operations, a model of thermodynamic processes for small quantum systems out of equilibrium, are well-understood in absence of coherence. Here the authors introduce cooling processes, a generalization of thermal operations and find necessary and sufficient conditions for coherent state transitions via cooling processes.
- Varun Narasimhachar
- & Gilad Gour
-
Article
| Open Access Towards experimental quantum-field tomography with ultracold atoms
Towards experimental quantum-field tomography with ultracold atoms
Full tomography of the quantum state of a many-body system becomes harder as more and more atoms are included. Here the authors borrow a concept from condensed-matter physics, continuous matrix-product states, and present an efficient approach for experimental quantum-field tomography.
- A. Steffens
- , M. Friesdorf
- & J. Eisert
-
Article |
 Vertical twinning of the Dirac cone at the interface between topological insulators and semiconductors
Vertical twinning of the Dirac cone at the interface between topological insulators and semiconductors
The discovery of topological insulators has presented the prospect of the technological application of their spin-momentum locked surface states. Here, the authors demonstrate theoretically how band hybridization can transfer such spin texture to an interfaced topologically trivial semiconductor.
- L. Seixas
- , D. West
- & S. B. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Navigable networks as Nash equilibria of navigation games
Navigable networks as Nash equilibria of navigation games
Connections in networks are organized to fulfil a function, and a common one is targeted transport or navigation. Here the authors use game theory to show how networks designed to maximize navigation efficiency at minimal cost share basic structural properties, which are also found in real cases.
- András Gulyás
- , József J. Bíró
- & Dmitri Krioukov
-
Article
| Open Access A low pre-infall mass for the Carina dwarf galaxy from disequilibrium modelling
A low pre-infall mass for the Carina dwarf galaxy from disequilibrium modelling
The cold dark matter paradigm predicts that Milky Way-like galaxies should have dwarf galaxies with dark matter halos as satellites. Ural et al.present a new model, independent of cosmological simulations, that constrains the pre-infall mass of the Milky Way satellite Carina to a value lower than expected.
- Uğur Ural
- , Mark I. Wilkinson
- & Matthew G. Walker
-
Article
| Open Access The free energy of mechanically unstable phases
The free energy of mechanically unstable phases
Phase diagrams are useful to describe the different states of matter, although for mechanically instable system the derivation of a free energy and thus of phase diagrams has been a challenge. Here, the authors propose a computational method to define the free energy of mechanically unstable phases.
- A. van de Walle
- , Q. Hong
- & R. Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Adiabatic elimination-based coupling control in densely packed subwavelength waveguides
Adiabatic elimination-based coupling control in densely packed subwavelength waveguides
Optical communications and quantum operations require active coupling control in closely packed integrated photonic circuits. Here, Mrejen et al.exploit adiabatic elimination to demonstrate active coupling control between two closely packed waveguides by tuning the mode index of an in-between decoupled waveguide.
- Michael Mrejen
- , Haim Suchowski
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article |
 Thermal transport in phononic crystals and the observation of coherent phonon scattering at room temperature
Thermal transport in phononic crystals and the observation of coherent phonon scattering at room temperature
Silicon-based semiconductors are attractive for thermoelectric devices, but their phonon-dominated thermal conductivity is preventing their use. Here, Alaie et al.observe coherent phonon boundary scattering in phononic crystals at room temperature by introducing large (=100 nm) air holes in the Si matrix.
- Seyedhamidreza Alaie
- , Drew F. Goettler
- & Ihab El-Kady
-
Article |
 Universal far-from-equilibrium dynamics of a holographic superconductor
Universal far-from-equilibrium dynamics of a holographic superconductor
In strongly coupled systems lacking long-lived quasiparticles, conventional methods are inadequate to study the dynamics of phase transitions. Here, the authors use holographic duality to investigate the superconducting transition and show that critical dynamics and formation of topological defects are universal.
- Julian Sonner
- , Adolfo del Campo
- & Wojciech H. Zurek
-
Article
| Open Access Maxwell’s demon in biochemical signal transduction with feedback loop
Maxwell’s demon in biochemical signal transduction with feedback loop
The connection between information and thermodynamics is embodied in the figure of Maxwell’s demon, a feedback controller. Here, the authors apply thermodynamics of information to signal transduction in chemotaxis of E. coli, predicting that its robustness is quantified by transfer entropy.
- Sosuke Ito
- & Takahiro Sagawa
-
Article |
 A two-dimensional spin liquid in quantum kagome ice
A two-dimensional spin liquid in quantum kagome ice
Two-dimensional quantum spin liquid states, which retain spin disorder down to low temperatures, have never been realized experimentally. Here, the authors use quantum Monte Carlo methods to predict a new route to this state in rare-earth pyrochlore quantum spin ices under an applied (111) magnetic field.
- Juan Carrasquilla
- , Zhihao Hao
- & Roger G. Melko
-
Article
| Open Access Probing deformed commutators with macroscopic harmonic oscillators
Probing deformed commutators with macroscopic harmonic oscillators
A minimal observable length leading to deformed commutation relations is a common feature of theories that aim to merge quantum physics and gravity. Here, the authors analyse the free evolution of micro- and nano-oscillators to lower the limits on the parameters quantifying commutator deformation.
- Mateusz Bawaj
- , Ciro Biancofiore
- & Francesco Marin
-
Article
| Open Access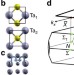 A Weyl Fermion semimetal with surface Fermi arcs in the transition metal monopnictide TaAs class
A Weyl Fermion semimetal with surface Fermi arcs in the transition metal monopnictide TaAs class
Proposals for the realization of Weyl semimetals, topologically non-trivial materials which host Weyl fermion quasiparticles, have faced demanding experimental requirements. Here, the authors predict such a state in stoichiometric TaAs, arising due to the breaking of inversion symmetry.
- Shin-Ming Huang
- , Su-Yang Xu
- & M. Zahid Hasan
-
Article
| Open Access Macroscopic quantum tunnelling in spin filter ferromagnetic Josephson junctions
Macroscopic quantum tunnelling in spin filter ferromagnetic Josephson junctions
Spin triplet superconductivity may benefit spintronics, providing dissipation-free spin-polarized currents. Here, the authors demonstrate macroscopic quantum tunnelling in spin filter Josephson junctions containing a ferromagnetic insulator barrier of GdN, evidencing unconventional superconductivity below 100 mK.
- D. Massarotti
- , A. Pal
- & F. Tafuri
-
Article |
 Diffusion on networked systems is a question of time or structure
Diffusion on networked systems is a question of time or structure
Structural patterns such as communities are used to understand the architecture of complex networks, but this is typically obtained for a purely static case. Here the authors introduce a generalized formalism that includes the statistical properties of the event timings.
- Jean-Charles Delvenne
- , Renaud Lambiotte
- & Luis E. C. Rocha
-
Article |
 Robust quantum metrological schemes based on protection of quantum Fisher information
Robust quantum metrological schemes based on protection of quantum Fisher information
Quantum features such as entanglement can be used to improve metrological precision, but noise affects their performances. Here the authors construct schemes for exploiting quantum error correction to preserve the quantum Fisher information, thereby shielding quantum gain efficiently.
- Xiao-Ming Lu
- , Sixia Yu
- & C. H. Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Theory and computation of hot carriers generated by surface plasmon polaritons in noble metals
Theory and computation of hot carriers generated by surface plasmon polaritons in noble metals
Hot carriers generated by surface plasmons in metal structures are garnering interest for their use in optoelectronics or photocatalysis. Bernardi et al. present a quantum mechanical framework to study their properties and find the optimalyconditions for their generation and extraction.
- Marco Bernardi
- , Jamal Mustafa
- & Steven G. Louie
-
Article
| Open Access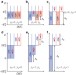 Valley polarization assisted spin polarization in two dimensions
Valley polarization assisted spin polarization in two dimensions
In the emerging field of valleytronics, the valley degree of freedom of electrons is exploited in addition to charge and spin for novel functionalities. Here, Renard et al.show how valley polarization can facilitate spin-polarization in a silicon-on-insulator quantum well.
- V. T. Renard
- , B. A. Piot
- & K. Takashina
-
Article
| Open Access Superdense teleportation using hyperentangled photons
Superdense teleportation using hyperentangled photons
Implementations of known quantum teleportation techniques suffer from a number of technical limitations, most notably the scaling of the required classical resources. Here, the authors implement a new protocol, superdense teleportation, which requires fewer resources than the conventional approaches.
- Trent M. Graham
- , Herbert J. Bernstein
- & Paul G Kwiat
-
Article |
 Resonance shifts and spill-out effects in self-consistent hydrodynamic nanoplasmonics
Resonance shifts and spill-out effects in self-consistent hydrodynamic nanoplasmonics
Recent experiments with plasmonic nanostructures have found phenomena that cannot be explained classically, necessitating new theoretical models. Toscano et al. present a self-consistent hydrodynamic theory that describes both the nonlocal response and the electronic spill-out for noble and simple metals.
- Giuseppe Toscano
- , Jakob Straubel
- & Martijn Wubs
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected edge conduction in mercury telluride quantum wells under broken time-reversal symmetry
Unexpected edge conduction in mercury telluride quantum wells under broken time-reversal symmetry
Quantum spin Hall edge states are protected by time-reversal symmetry and are expected to disappear in a strong magnetic field. Here, the authors use microwave impedance microscopy and find, surprisingly, edge conduction in mercury telluride quantum wells that survives up to 9 T with little change.
- Eric Yue Ma
- , M. Reyes Calvo
- & Zhi-Xun Shen
-
Article |
 Constructing minimal models for complex system dynamics
Constructing minimal models for complex system dynamics
In statistical physics, the observable macroscopic behaviour of a system is obtained from a microscopic model of its components. Here, the authors extend this approach to systems with no known microscopic dynamics, by looking at the system’s response to external perturbations.
- Baruch Barzel
- , Yang-Yu Liu
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the quantum critical behaviour in a driven Tavis–Cummings circuit
Exploring the quantum critical behaviour in a driven Tavis–Cummings circuit
Quantum phase transitions are a discontinuous change in a property of the ground state or the structure of the excited states as a system parameter traverses a critical point. Here, the authors recreate analogous effects with laboratory-achievable light-matter coupling in an on-chip superconducting circuit
- M. Feng
- , Y.P. Zhong
- & H. Wang
-
Article |
 Theory of Floquet band formation and local pseudospin textures in pump-probe photoemission of graphene
Theory of Floquet band formation and local pseudospin textures in pump-probe photoemission of graphene
Condensed matter research has seen prominent recent advances in ultrafast optical manipulation and topological materials. Here, Sentef et al. simulate the development of the photoemission-measured band structure of Floquet states in graphene excited by low-frequency circularly-polarized laser pulses.
- M.A. Sentef
- , M. Claassen
- & T.P. Devereaux
-
Article |
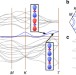 Charge order from orbital-dependent coupling evidenced by NbSe2
Charge order from orbital-dependent coupling evidenced by NbSe2
Two-dimensional charge ordering cannot be fully described by Peierls-like weak coupling mechanisms appropriate for one-dimensional materials. Here, the authors show how strong orbital-dependent electron–phonon coupling drives two-dimensional charge ordering in archetypal niobium diselenide.
- Felix Flicker
- & Jasper van Wezel
-
Article
| Open Access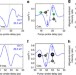 Observation of laser-induced electronic structure in oriented polyatomic molecules
Observation of laser-induced electronic structure in oriented polyatomic molecules
Although expected to have an influence, the effect of strong laser fields on molecules in high-harmonic generation in gases is rarely explored. Kraus et al.show that the laser modifies the electronic structure of large polyatomic molecules and present a new theoretical framework to model this.
- P. M. Kraus
- , O. I. Tolstikhin
- & H. J. Wörner
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting bit-flip errors in a logical qubit using stabilizer measurements
Detecting bit-flip errors in a logical qubit using stabilizer measurements
Future quantum computers will employ error correction to protect quantum data from decoherence and faulty hardware. Here, using a quantum processor with five superconducting qubits, the authors demonstrate how to protect one logical qubit from bitflip errors using multi-qubit, stabilizer measurements.
- D. Ristè
- , S. Poletto
- & L. DiCarlo
-
Article
| Open Access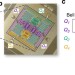 Demonstration of a quantum error detection code using a square lattice of four superconducting qubits
Demonstration of a quantum error detection code using a square lattice of four superconducting qubits
The physical realization of a quantum computer requires built-in error-correcting codes that compensate the disruption of quantum information arising from noise. Here, the authors demonstrate a quantum error detection scheme for arbitrary single-qubit errors on a four superconducting qubit lattice.
- A.D. Córcoles
- , Easwar Magesan
- & Jerry M. Chow
-
Article
| Open Access Multifractality of random eigenfunctions and generalization of Jarzynski equality
Multifractality of random eigenfunctions and generalization of Jarzynski equality
The work fluctuations of systems driven out of equilibrium are governed by the same large-deviation theory as wavefunction amplitudes close to the Anderson localization transition. Exploiting this analogy, the authors generalize the Jarzynski equality, verifying their relation on a single-electron box.
- I.M. Khaymovich
- , J.V. Koski
- & J.P. Pekola
-
Article
| Open Access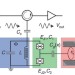 Cavity optomechanics mediated by a quantum two-level system
Cavity optomechanics mediated by a quantum two-level system
Radiation pressure can control the motion of a nanoscale resonator, but pushing this to the quantum limit is difficult because the influence of a single photon is tiny. Here, the authors boost the radiation–pressure interaction by six orders of magnitude using a Josephson junction qubit
- J.-M. Pirkkalainen
- , S.U. Cho
- & M.A. Sillanpää
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary games of condensates in coupled birth–death processes
Evolutionary games of condensates in coupled birth–death processes
A driven-dissipative system of non-interacting bosons may form multiple condensates—a dynamics described by birth–death processes that also occur in evolutionary game theory. Here, the authors apply game theory to show how the vanishing of relative entropy production governs condensate selection.
- Johannes Knebel
- , Markus F. Weber
- & Erwin Frey
-
Article |
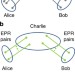 Limitations on quantum key repeaters
Limitations on quantum key repeaters
Quantum repeaters have been conceived as a means to extend the range of quantum secure communications, but can handle only distillable entangled states. Here, the authors introduce and study quantum key repeaters, devices which may allow long-distance quantum key distribution with non-distillable states.
- Stefan Bäuml
- , Matthias Christandl
- & Andreas Winter
-
Article |
 Ranking in interconnected multilayer networks reveals versatile nodes
Ranking in interconnected multilayer networks reveals versatile nodes
A challenging problem is to identify the most central agents in interconnected multilayer networks. Here, De Domenico et al. present a mathematical framework to calculate centrality in such networks—versatility—and rank nodes accordingly.
- Manlio De Domenico
- , Albert Solé-Ribalta
- & Alex Arenas
-
Article |
 Structural reducibility of multilayer networks
Structural reducibility of multilayer networks
Multilayer networks have been used to capture the structure of complex systems with different types of interactions, but often contain redundant information. Here, De Domenico et al. present a method based on quantum information, to identify the minimal configuration of layers to retain.
- Manlio De Domenico
- , Vincenzo Nicosia
- & Vito Latora
-
Article |
 Phase nucleation in curved space
Phase nucleation in curved space
Nucleation is the fundamental relaxation mechanism that leads to the emergence of a new phase or structure via first-order phase transitions. Here, the authors study nucleation and growth of two-dimensional phases on curved surfaces, and show how the curvature influences its inhomogeneity and speed.
- Leopoldo R. Gómez
- , Nicolás A. García
- & Daniel A. Vega
-
Article
| Open Access Universal structure of transmission eigenchannels inside opaque media
Universal structure of transmission eigenchannels inside opaque media
The transmission of light through opaque media is a complex process, owing to the many scattering processes of light. Here, the authors develop a method to determine the transmission eigenchannels through an opaque medium as a solution of diffusion equations.
- Matthieu Davy
- , Zhou Shi
- & Azriel Z. Genack
-
Article
| Open Access Separation and conversion dynamics of nuclear-spin isomers of gaseous methanol
Separation and conversion dynamics of nuclear-spin isomers of gaseous methanol
The conversion dynamics of nuclear-spin isomers has only been observed for a small number of molecules, generally with rotational symmetry. Here, the authors observe the separation of nuclear-spin isomers of gaseous methanol and show a decreased interconversion at higher pressures.
- Zhen-Dong Sun
- , Meihua Ge
- & Yujun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access All-photonic quantum repeaters
All-photonic quantum repeaters
Quantum repeaters are needed for long-distance quantum communication but it is thought that they require matter quantum memories. Azuma et al. introduce an all-photonic quantum repeater based on flying qubits that scales polynomially with the channel distance without the need for matter quantum memories.
- Koji Azuma
- , Kiyoshi Tamaki
- & Hoi-Kwong Lo
-
Article |
 Twisting phonons in complex crystals with quasi-one-dimensional substructures
Twisting phonons in complex crystals with quasi-one-dimensional substructures
Quasi-one-dimensional substructures have distinctive properties, but the lattice dynamics are poorly understood. Here, Chen et al.use inelastic neutron scattering and density functional theory to discover that numerous low-energy optical vibrational modes including a twisting polarization are present in higher manganese silicides.
- Xi Chen
- , Annie Weathers
- & Li Shi
-
Article
| Open Access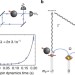 Interaction-free measurements by quantum Zeno stabilization of ultracold atoms
Interaction-free measurements by quantum Zeno stabilization of ultracold atoms
The inherent strangeness of quantum mechanics means it is possible to detect objects using single-quantum particles even if they do not interact directly. Peise et al. realize such an ‘interaction-free measurement’ by exploiting the quantum Zeno effect in a BEC, obviating the need for single-particle sources.
- J. Peise
- , B. Lücke
- & C. Klempt

 Aharonov–Bohm oscillations in a quasi-ballistic three-dimensional topological insulator nanowire
Aharonov–Bohm oscillations in a quasi-ballistic three-dimensional topological insulator nanowire