Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access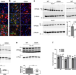 Retromer stabilization results in neuroprotection in a model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Retromer stabilization results in neuroprotection in a model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
ALS is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by loss of motor neurons. Here, the authors showed that reduced levels of the VSP35 subunit in the retromer complex is a conserved ALS feature and identified a new lead compound increasing retromer stability ameliorating the disease phenotype.
- Luca Muzio
- , Riccardo Sirtori
- & Gianvito Martino
-
Article
| Open Access The SecA motor generates mechanical force during protein translocation
The SecA motor generates mechanical force during protein translocation
The ATPase SecA drives Sec-dependent protein translocation across the bacterial plasma membrane. Here, the authors combine kinetic translocation measurements with single-molecule force spectroscopy and demonstrate that the SecA motor generates mechanical force to unfold and translocate preproteins.
- Riti Gupta
- , Dmitri Toptygin
- & Christian M. Kaiser
-
Article
| Open Access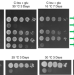 Coupling of 5S RNP rotation with maturation of functional centers during large ribosomal subunit assembly
Coupling of 5S RNP rotation with maturation of functional centers during large ribosomal subunit assembly
As assembling 60S subunits transit from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm, they undergo significant changes in protein composition and structure. Here, the authors provide a structural view of interconnected events during the middle steps of assembly that include the maturation of the central protuberance, the peptidyltransferase center and the nascent polypeptide exit tunnel.
- Jelena Micic
- , Yu Li
- & John L. Woolford Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access Fast three-color single-molecule FRET using statistical inference
Fast three-color single-molecule FRET using statistical inference
Three-colour FRET is a powerful tool to study macromolecular conformational dynamics, but is temporally limited due to the experimental complexity. Here the authors develop experimental and analytical methods for probing submillisecond-time scale dynamics using single continuous-wave excitation.
- Janghyun Yoo
- , Jae-Yeol Kim
- & Hoi Sung Chung
-
Article
| Open Access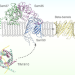 Structural insight into mitochondrial β-barrel outer membrane protein biogenesis
Structural insight into mitochondrial β-barrel outer membrane protein biogenesis
The Sorting and Assembly Machinery (SAM) complex folds beta-barrel proteins and inserts them into the mitochondrial outer membrane. Here authors report cryoEM structures of the SAM complex from Myceliophthora thermophila, which reveals a GST-like fold for Sam35 and Sam37 and sheds light on how the Sam50 beta-barrel opens a lateral gate to accommodate its substrates.
- Kathryn A. Diederichs
- , Xiaodan Ni
- & Susan K. Buchanan
-
Article
| Open Access NSs amyloid formation is associated with the virulence of Rift Valley fever virus in mice
NSs amyloid formation is associated with the virulence of Rift Valley fever virus in mice
Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV) can cause severe diseases in humans, including encephalitis. Here the authors show that NSs, the major virulence factor of RVFV, is an amyloidogenic protein forming fibrils in infected mouse brains and causing increased mortality in mice.
- Psylvia Léger
- , Eliana Nachman
- & Pierre-Yves Lozach
-
Article
| Open Access Non-cooperative 4E-BP2 folding with exchange between eIF4E-binding and binding-incompatible states tunes cap-dependent translation inhibition
Non-cooperative 4E-BP2 folding with exchange between eIF4E-binding and binding-incompatible states tunes cap-dependent translation inhibition
Phosphorylation of eIF4E binding proteins (4E-BPs) controls their folding and regulates cap-dependent translation. Here, the authors show that phosphorylation of the C-terminal disordered region stabilizes the non-cooperatively folded 4E-BP domain to an eIF4E binding-incompatible state to control translation.
- Jennifer E. Dawson
- , Alaji Bah
- & Julie D. Forman-Kay
-
Article
| Open Access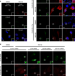 Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor UPF1 promotes aggresome formation
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor UPF1 promotes aggresome formation
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a translation-coupled process that eliminates mRNAs containing premature translation-termination codons. Here the authors identify a role for the NMD factor UPF1 in protein quality control, whereby truncated misfolded polypeptides are cleared through autophagy.
- Yeonkyoung Park
- , Joori Park
- & Yoon Ki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct metabolic states of a cell guide alternate fates of mutational buffering through altered proteostasis
Distinct metabolic states of a cell guide alternate fates of mutational buffering through altered proteostasis
Changes in osmotic homeostasis alter metabolites and therefore chemical milieu of the cells. Here, the authors show that altering metabolites in E. coli also change the cellular capacity for buffering mutations that impair protein folding and influences proteostasis irrespective of molecular chaperones
- Kanika Verma
- , Kanika Saxena
- & Kausik Chakraborty
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-omics analysis reveals the unfolded protein response regulon and stress-induced resistance to folate-based antimetabolites
A multi-omics analysis reveals the unfolded protein response regulon and stress-induced resistance to folate-based antimetabolites
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a stress response pathway implicated in numerous diseases and chemotherapy resistance. Here, the authors define the UPR regulon with a multi-omics strategy, uncovering changes to mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism and concomitant resistance to folate-based therapeutics.
- Stefan Reich
- , Chi D. L. Nguyen
- & Jan Medenbach
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-liquid phase separation induces pathogenic tau conformations in vitro
Liquid-liquid phase separation induces pathogenic tau conformations in vitro
Tau plays an important role in tauopathies and undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). The authors show that disease-related P301L mutant and phosphomimic (S199E/S202E/T205E) tau enhance LLPS in vitro at physiological levels, and using specific antibodies, that tau LLPS leads to pathological conformations such as N-terminal exposure and oligomeric species.
- Nicholas M. Kanaan
- , Chelsey Hamel
- & Benjamin Combs
-
Article
| Open Access Polyamine regulation of ion channel assembly and implications for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor pharmacology
Polyamine regulation of ion channel assembly and implications for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor pharmacology
Small molecule polyamines participate in diverse aspects of cell growth and differentiation and are known to regulate ion channel gating. Here authors reveal that cellular polyamines control nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) biogenesis, and either catabolic degradation or inhibition of polyamine production augments nAChR assembly.
- Madhurima Dhara
- , Jose A. Matta
- & David S. Bredt
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of light-driven sodium pumping
Molecular mechanism of light-driven sodium pumping
The Na+-pumping KR2 rhodopsin from Krokinobacter eikastus is a light-driven non-proton cation pump whose mechanism of pumping remains to be understood. Here authors solved crystal structures of the O-intermediate state of the pentameric form of KR2 and its D116N and H30A mutants, which sheds light on the mechanism of non-proton cation light-driven pumping.
- Kirill Kovalev
- , Roman Astashkin
- & Valentin Gordeliy
-
Article
| Open Access Inter-domain dynamics in the chaperone SurA and multi-site binding to its outer membrane protein clients
Inter-domain dynamics in the chaperone SurA and multi-site binding to its outer membrane protein clients
The chaperone SurA is involved in outer membrane protein (OMP) biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria, but its mechanism of action is not fully understood. Combining mass spectrometric, biophysical and computational approaches, the authors here show how the conformational dynamics of SurA facilitate OMP binding.
- Antonio N. Calabrese
- , Bob Schiffrin
- & Sheena E. Radford
-
Article
| Open Access An in vivo platform to select and evolve aggregation-resistant proteins
An in vivo platform to select and evolve aggregation-resistant proteins
Protein aggregation remains a significant challenge for manufacturing of protein biopharmaceuticals. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of directed evolution and an assay for in vivo innate protein aggregation-propensity to generate aggregation-resistant scFv fragments.
- Jessica S. Ebo
- , Janet C. Saunders
- & David J. Brockwell
-
Article
| Open Access The ribosome-associated complex RAC serves in a relay that directs nascent chains to Ssb
The ribosome-associated complex RAC serves in a relay that directs nascent chains to Ssb
The ribosome-associated complex (RAC), which contains the Hsp40 protein Zuo1 and the non-canonical Hsp70 protein Ssz1 forms a chaperone triad with the fungal-specific Hsp70 protein Ssb. Here the authors combine X-ray crystallography, crosslinking and biochemical experiments and present the structure of the Zuo1 N-terminus bound to Ssz1 and demonstrate that Ssz1 is an active chaperone for nascent chains.
- Ying Zhang
- , Genís Valentín Gesé
- & Irmgard Sinning
-
Article
| Open Access Pharmacological induction of selective endoplasmic reticulum retention as a strategy for cancer therapy
Pharmacological induction of selective endoplasmic reticulum retention as a strategy for cancer therapy
Inhibition of PERK, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) unfolded protein response (UPR) protein, is a potential pharmacological target for cancer treatment. Here, the authors show that inhibition of PERK under ER stress affects trafficking from the ER to the surface of several key receptor tyrosine kinases, suggesting a selective ER retention.
- Mohamed Mahameed
- , Shatha Boukeileh
- & Boaz Tirosh
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-liquid phase separation and extracellular multivalent interactions in the tale of galectin-3
Liquid-liquid phase separation and extracellular multivalent interactions in the tale of galectin-3
Galectin-3 consists of an unstructured N-terminal domain (NTD) and a structured carbohydrate-recognition domain and agglutinates neutrophils and glycosylated molecules in the extracellular milieu. Here the authors combine biophysical and biochemical experiments with NMR measurements and show that the galectin-3 NTD undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) and agglutinates other molecules through this process.
- Yi-Ping Chiu
- , Yung-Chen Sun
- & Jie-rong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A methylated lysine is a switch point for conformational communication in the chaperone Hsp90
A methylated lysine is a switch point for conformational communication in the chaperone Hsp90
Methylation of a lysine residue in Hsp90 is a recently discovered post-translational modification but the mechanistic effects of this modification have remained unknown so far. Here the authors combine biochemical and biophysical approaches, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and functional experiments with yeast and show that this lysine is a switch point, which specifically modulates conserved Hsp90 functions including co-chaperone regulation and client activation.
- Alexandra Rehn
- , Jannis Lawatscheck
- & Johannes Buchner
-
Article
| Open Access Cerebellum-enriched protein INPP5A contributes to selective neuropathology in mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxias type 17
Cerebellum-enriched protein INPP5A contributes to selective neuropathology in mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxias type 17
It is not yet clear how ubiquitously-expressed proteins can cause the selective degeneration of particular populations of neurons, such as in spinocerebellar ataxia type 17, SCA17, which results from a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor TBP. Here, the authors show that mutant TBP suppresses the cerebellum-enriched transcription of Inpp5a and link altered levels of INPP5A to the selective degeneration of cerebellar neurons.
- Qiong Liu
- , Shanshan Huang
- & Shihua Li
-
Article
| Open Access FMN reduces Amyloid-β toxicity in yeast by regulating redox status and cellular metabolism
FMN reduces Amyloid-β toxicity in yeast by regulating redox status and cellular metabolism
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a model organism to study proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Here, the authors performed a yeast genome-wide synthetic genetic interaction array (SGA) to screen for toxicity modifiers of Aβ42 and identify riboflavin kinase and its metabolic product flavin mononucleotide as modulators that alleviate cellular Aβ42 toxicity, which is supported by further experimental analyses.
- Xin Chen
- , Boyang Ji
- & Dina Petranovic
-
Article
| Open Access Arginine π-stacking drives binding to fibrils of the Alzheimer protein Tau
Arginine π-stacking drives binding to fibrils of the Alzheimer protein Tau
Tau fibril formation is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. Here the authors reveal an aggregation-dependent protein interaction pattern of Tau and further show that π-stacking of the arginine side-chains drives aberrant protein binding to Tau fibrils.
- Luca Ferrari
- , Riccardo Stucchi
- & Stefan G. D. Rüdiger
-
Article
| Open Access Studying biomolecular folding and binding using temperature-jump mass spectrometry
Studying biomolecular folding and binding using temperature-jump mass spectrometry
Native mass spectrometry allows monitoring the folding and interactions of multiple coexisting species but its temporal resolution is traditionally limited. Here, the authors develop a temperature-jump electrospray source for mass spectrometry that enables fast kinetics experiments at different temperatures.
- Adrien Marchand
- , Martin F. Czar
- & Renato Zenobi
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial Hsp70 resolves misfolded states and accelerates productive folding of a multi-domain protein
Bacterial Hsp70 resolves misfolded states and accelerates productive folding of a multi-domain protein
The Hsp70 system prevents protein aggregation and increases folding yields, but it is unknown whether it also enhances the rate of folding. Here the authors combine refolding assays, FRET and hydrogen/deuterium exchange-mass spectrometry measurements to study the folding of firefly luciferase and find that the bacterial Hsp70 actively promotes the folding of this multi-domain protein.
- Rahmi Imamoglu
- , David Balchin
- & F. Ulrich Hartl
-
Article
| Open Access Melanoblast transcriptome analysis reveals pathways promoting melanoma metastasis
Melanoblast transcriptome analysis reveals pathways promoting melanoma metastasis
Metastatic cells can mimic many of the phenotypic behaviors of embryonic cells. Here, the authors generate a melanoblast-specific transcriptome using a genetically engineered mouse model and identify KDELR3 as a pro-metastasis gene in melanoma.
- Kerrie L. Marie
- , Antonella Sassano
- & Pravin J. Mishra
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering protein assemblies with allosteric control via monomer fold-switching
Engineering protein assemblies with allosteric control via monomer fold-switching
The design of protein assemblies is a major thrust for biomolecular engineering and nanobiotechnology. Here the authors demonstrate a general mechanism for designing allosteric macromolecular assemblies and showcase a proof of concept for engineered allosteric protein assembly.
- Luis A. Campos
- , Rajendra Sharma
- & Victor Muñoz
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule detection on a portable 3D-printed microscope
Single-molecule detection on a portable 3D-printed microscope
Single-molecule in vitro assays require dedicated confocal microscopes equipped with fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) modules. Here the authors present a compact, cheap and open-source 3D-printed confocal microscope for single photon counting and FCS measurements, and use it to detect α-synuclein aggregation.
- James W. P. Brown
- , Arnaud Bauer
- & Yann Gambin
-
Article
| Open Access The autophagy receptor p62/SQST-1 promotes proteostasis and longevity in C. elegans by inducing autophagy
The autophagy receptor p62/SQST-1 promotes proteostasis and longevity in C. elegans by inducing autophagy
While the cellular recycling process autophagy has been linked to aging, the impact of selective autophagy on lifespan remains unclear. Here Kumsta et al. show that the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1 is required for hormetic benefits and p62/SQSTM1 overexpression is sufficient to extend C. elegans lifespan and improve proteostasis.
- Caroline Kumsta
- , Jessica T. Chang
- & Malene Hansen
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for chirality-regulated Aβ self-assembly and receptor recognition revealed by ion mobility-mass spectrometry
Molecular basis for chirality-regulated Aβ self-assembly and receptor recognition revealed by ion mobility-mass spectrometry
Chiral inversion of amino acids is thought to modulate the structure and function of amyloid beta (Aβ) but these processes are poorly understood. Here, the authors develop an ion mobility-mass spectrometry based approach to study chirality-regulated structural features of Aβ fragments and their influence on receptor recognition.
- Gongyu Li
- , Kellen DeLaney
- & Lingjun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of a transthyretin-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis
Cryo-EM structure of a transthyretin-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis
Systemic amyloidosis of the ATTR is one of the most abundant forms of systemic amyloidosis and caused by misfolding of the circulating blood protein transthyretin (TTR). Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of patient-derived Val30Met ATTR amyloid fibrils which reveals that the protofilament consists of an N-terminal and a C-terminal TTR fragment and discuss implications for the mechanism of misfolding.
- Matthias Schmidt
- , Sebastian Wiese
- & Marcus Fändrich
-
Article
| Open Access Tau deposition is associated with functional isolation of the hippocampus in aging
Tau deposition is associated with functional isolation of the hippocampus in aging
Deposition of tau protein aggregates occurs during aging and Alzheimer disease. Here, the authors show that tau burden in the anterior-temporal memory network is associated with disrupted fMRI connectivity and functional isolation of the hippocampus from other memory network components.
- Theresa M. Harrison
- , Anne Maass
- & William J. Jagust
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular sequestrases maintain basal Hsp70 capacity ensuring balanced proteostasis
Cellular sequestrases maintain basal Hsp70 capacity ensuring balanced proteostasis
The sequestration of misfolded proteins into large assemblies by sequestrases is now considered as the third pillar in protein quality control besides chaperones and proteases. Here the authors characterise the functions of the sequestrases Hsp42 and Btn2 in the proteostasis network of S. cerevisiae and find that they protect cells from too exhaustive depletion of the Hsp70 system.
- Chi-ting Ho
- , Tomas Grousl
- & Axel Mogk
-
Article
| Open Access Protein folding while chaperone bound is dependent on weak interactions
Protein folding while chaperone bound is dependent on weak interactions
Spy is an ATP independent chaperone that allows folding of its client protein Im7 while continuously bound to Spy. Here the authors employ kinetics measurements to study the folding of another Spy client protein SH3 and find that Spy’s ability to allow a client to fold while bound is inversely related to how strongly it interacts with that client.
- Kevin Wu
- , Frederick Stull
- & James C. A. Bardwell
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular features of the UNC-45 chaperone critical for binding and folding muscle myosin
Molecular features of the UNC-45 chaperone critical for binding and folding muscle myosin
Myosin, a motor protein essential for intracellular transport to muscle contraction, requires a chaperone UNC-45 for folding and assembly. Here authors use in vitro reconstitution and structural biology to characterize the interplay between UNC-45 and muscle myosin MHC-B.
- Doris Hellerschmied
- , Anita Lehner
- & Tim Clausen
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level insight into mRNA processing bodies by combining solid and solution-state NMR spectroscopy
Atomic-level insight into mRNA processing bodies by combining solid and solution-state NMR spectroscopy
Processing bodies are membrane less organelles that contain enzymes involved in mRNA turnover, among them enhancer of decapping 3 (Edc3). Here the authors use solid- and solution-state NMR spectroscopy to characterize the structural organization and dynamics of Edc3 and find that its interactions with RNA and between the different Edc3 domains are largely preserved in the phase-separated state.
- Reinier Damman
- , Stefan Schütz
- & Marc Baldus
-
Article
| Open Access Constitutive XBP-1s-mediated activation of the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response protects against pathological tau
Constitutive XBP-1s-mediated activation of the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response protects against pathological tau
Accumulation of abnormal tau protein drives neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia disorders. Here, the authors demonstrate the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response mediator XBP-1 controls pathological tau accumulation and the resultant neurodegeneration in a transgenic C. elegans model.
- Sarah M. Waldherr
- , Timothy J. Strovas
- & Brian C. Kraemer
-
Article
| Open Access Methionine in a protein hydrophobic core drives tight interactions required for assembly of spider silk
Methionine in a protein hydrophobic core drives tight interactions required for assembly of spider silk
Spider silk is of interest in material science research. Here the authors show that the tight binding of a spider silk protein domain relies on the amino acid methionine, which is abundant in the domain core where it facilitates dynamic shape adaption of the binding interface.
- Julia C. Heiby
- , Benedikt Goretzki
- & Hannes Neuweiler
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular basis of chaperone-mediated interleukin 23 assembly control
The molecular basis of chaperone-mediated interleukin 23 assembly control
It is unclear how unassembled secretory pathway proteins are discriminated from misfolded ones. Here the authors combine biophysical and cellular experiments to study the folding of heterodimeric interleukin 23 and describe how ER chaperones recognize unassembled proteins and aid their assembly into protein complexes while preventing the premature degradation of unassembled units.
- Susanne Meier
- , Sina Bohnacker
- & Matthias J. Feige
-
Article
| Open Access Solid-state NMR spectroscopy based atomistic view of a membrane protein unfolding pathway
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy based atomistic view of a membrane protein unfolding pathway
Studying the unfolding of membrane proteins in a native-like lipid environment is challenging. Here the authors describe a method combining hydrogen-deuterium exchange and solid-state NMR measurements that allows the characterization of unfolding events in lipid-embedded membrane proteins and use the photoreceptor Anabaena Sensory Rhodopsin as a test case.
- Peng Xiao
- , David Bolton
- & Vladimir Ladizhansky
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic structure of PI3-kinase SH3 amyloid fibrils by cryo-electron microscopy
Atomic structure of PI3-kinase SH3 amyloid fibrils by cryo-electron microscopy
The Src-homology 3 domain of phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K-SH3) is a model system for studying amyloid fibril formation. Here the authors present the 3.4 Å cryo-EM structure of the PI3K-SH3 amyloid fibril, which allows them to rationalize the effects of mutations on the kinetics of fibril formation.
- Christine Röder
- , Nicola Vettore
- & Gunnar F. Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Cytoplasmic DAXX drives SQSTM1/p62 phase condensation to activate Nrf2-mediated stress response
Cytoplasmic DAXX drives SQSTM1/p62 phase condensation to activate Nrf2-mediated stress response
The autophagy protein p62 undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation but how this is regulated is unclear. Here, the authors report that the histone chaperone DAXX interacts with p62 in the cytoplasm to drive its phase separation.
- Yi Yang
- , Thea L. Willis
- & Shouqing Luo
-
Article
| Open Access The prion-like protein kinase Sky1 is required for efficient stress granule disassembly
The prion-like protein kinase Sky1 is required for efficient stress granule disassembly
The factors regulating stress granule dissolution are not fully understood. Here, the authors identify Sky1 as a stress granule component in yeast, and show that Sky1 kinase activity is required for timely stress granule disassembly during stress recovery.
- Jenifer E. Shattuck
- , Kacy R. Paul
- & Eric D. Ross
-
Article
| Open Access The Hsp90 isoforms from S. cerevisiae differ in structure, function and client range
The Hsp90 isoforms from S. cerevisiae differ in structure, function and client range
S. cerevisiae encodes two Hsp90 isoforms, the constitutively expressed Hsc82 and stress-inducible Hsp82 that are 97% identical. Here, the authors combine a range of biophysical methods and show that they differ in their enzymatic properties, resilience to stress and client range, which suggests that they evolved to provide fine-tuned chaperone assistance under physiological and stress conditions.
- Hannah Girstmair
- , Franziska Tippel
- & Johannes Buchner
-
Article
| Open Access Hsp70 and Hsp40 inhibit an inter-domain interaction necessary for transcriptional activity in the androgen receptor
Hsp70 and Hsp40 inhibit an inter-domain interaction necessary for transcriptional activity in the androgen receptor
Hsp chaperones stabilize the inactive conformation of androgen receptor (AR) and are released upon hormone-induced AR activation. Here, the authors locate the Hsp binding region on AR, and show that Hsp70 reduces AR aggregation and promotes AR degradation in cellular and mouse models of a neuromuscular disorder.
- Bahareh Eftekharzadeh
- , Varuna C. Banduseela
- & Xavier Salvatella
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial coiled coil biomineralisation protein for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Artificial coiled coil biomineralisation protein for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Proteins have been used in the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles but issues with aggregation limit this application. Here, the authors report on the synthesis of coiled proteins that display the active loop of the natural proteins to avoid aggregation and investigate the application in nanoparticle synthesis.
- Andrea E. Rawlings
- , Lori A. Somner
- & Sarah S. Staniland
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional analysis of the role of the chaperonin CCT in mTOR complex assembly
Structural and functional analysis of the role of the chaperonin CCT in mTOR complex assembly
β-propeller domains are an important class of folding substrates for the eukaryotic cytosolic chaperonin CTT. Here the authors find that CTT contributes to the folding and assembly of two β-propeller proteins from mTOR complexes, mLST8 and Raptor, and determine the 4.0 Å cryoEM structure of a human mLST8-CCT intermediate that shows mLST8 in a near-native state.
- Jorge Cuéllar
- , W. Grant Ludlam
- & José M. Valpuesta
-
Article
| Open Access Non-equilibrium dynamics of a nascent polypeptide during translation suppress its misfolding
Non-equilibrium dynamics of a nascent polypeptide during translation suppress its misfolding
Co-translational protein folding is thought to occur at equilibrium for fast-folding domains. Here authors use optical tweezers to show that the folding kinetics of stalled ribosome-bound nascent chains do not match the folding of nascent chains in real time.
- Lisa M. Alexander
- , Daniel H. Goldman
- & Carlos Bustamante
-
Article
| Open Access Hsp90 middle domain phosphorylation initiates a complex conformational program to recruit the ATPase-stimulating cochaperone Aha1
Hsp90 middle domain phosphorylation initiates a complex conformational program to recruit the ATPase-stimulating cochaperone Aha1
Phosphorylation of Tyr313 in Hsp90 enhances the binding to its activator Aha1, but the underlying mechanism is unknown. Here, the authors study the structural consequences of Tyr313 phosphorylation, showing that it serves as a conformational switch in Hsp90 that enables Aha1 recruitment.
- Wanping Xu
- , Kristin Beebe
- & Len Neckers
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for substrate gripping and translocation by the ClpB AAA+ disaggregase
Structural basis for substrate gripping and translocation by the ClpB AAA+ disaggregase
Bacterial ClpB is a disaggregase that solubilizes protein aggregates. Here the authors present the 2.9 Å cryo-EM structure of a hyperactive variant of ClpB bound to the substrate casein in active translocation states and discuss its polypeptide translocation mechanism.
- Alexandrea N. Rizo
- , JiaBei Lin
- & Daniel R. Southworth

 Turn-on chemiluminescence probes and dual-amplification of signal for detection of amyloid beta species in vivo
Turn-on chemiluminescence probes and dual-amplification of signal for detection of amyloid beta species in vivo