Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen receptor-mediated depletion of FOXP3 in induced regulatory T-lymphocytes via PTPN2 and FOXO1
Antigen receptor-mediated depletion of FOXP3 in induced regulatory T-lymphocytes via PTPN2 and FOXO1
Antigen stimulation in vivocan reprogram T regulatory cells to lose the expression of Foxp3 and become effector cells. Here the authors show that the mechanism involves dephosphorylation of STAT5 by PTPN2 and downregulation of Foxo1 by miR-182.
- Evita Bothur
- , Hartmann Raifer
- & Michael Lohoff
-
Article
| Open Access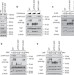 MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway
MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway
A variety of signals have been reported to either activate or inhibit the Hippo kinase cascade. Here, Meng et al. show that mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase (MAP4K) family members function in parallel to and are partially redundant with MST1/2 in regulating LATS in response to upstream signals.
- Zhipeng Meng
- , Toshiro Moroishi
- & Kun-Liang Guan
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between arginine methylation and ubiquitylation regulates KLF4-mediated genome stability and carcinogenesis
Interplay between arginine methylation and ubiquitylation regulates KLF4-mediated genome stability and carcinogenesis
Krüppel-like factor 4 plays an important role in regulating responses to DNA damage, cell-fate decision and apoptosis. Here the authors show that aberrant regulation by methyltransferase PRMT5 results in failure to arrest the cell cycle and genome instability, pointing to a role in carcinogenesis.
- Dong Hu
- , Mert Gur
- & Yong Wan
-
Article
| Open Access O-GlcNAcylation of G6PD promotes the pentose phosphate pathway and tumor growth
O-GlcNAcylation of G6PD promotes the pentose phosphate pathway and tumor growth
The pentose phosphate pathway is aberrantly activated in cancer cells but the mechanism is unclear. Here, the authors show that G6PD, the rate-limiting enzyme in the pathway, is post-translationally modified with a sugar moiety under hypoxic conditions leading to increased production of precursors for macromolecular synthesis and antioxidants.
- Xiongjian Rao
- , Xiaotao Duan
- & Wen Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Bub1 autophosphorylation feeds back to regulate kinetochore docking and promote localized substrate phosphorylation
Bub1 autophosphorylation feeds back to regulate kinetochore docking and promote localized substrate phosphorylation
Bub1 kinase phosphorylates histone H2A-T120 at the centromere to recruit shugoshin proteins and promote sister chromatid cohesion during mitosis. Here the authors show that Bub1 autophosphorylation on T589 influences Bub1 dynamics at the kinetochore and restricts H2A-T120 phosphorylation to centromeres.
- Adeel Asghar
- , Audrey Lajeunesse
- & Sabine Elowe
-
Article
| Open Access Hypothalamic PKA regulates leptin sensitivity and adiposity
Hypothalamic PKA regulates leptin sensitivity and adiposity
Mice lacking RIIβ, a regulatory subunit of protein kinase A, are lean and resistant to diet-induced obesity. Here, the authors show that RIIβ regulates leptin sensitivity, acting as a physiological brake on leptin responsiveness and the duration of leptin signalling in the hypothalamus.
- Linghai Yang
- & G. Stanley McKnight
-
Article
| Open Access LRRK2 G2019S mutation attenuates microglial motility by inhibiting focal adhesion kinase
LRRK2 G2019S mutation attenuates microglial motility by inhibiting focal adhesion kinase
In response to brain injury, microglia extend processes to isolate the lesion. Here Choi et al. show that microglia expressing a pathogenic mutation in the Parkinson’s disease-associated LRRK2 gene show reduced motility and delayed lesion isolation in vitro and in vivodue to attenuated focal adhesion kinase activity.
- Insup Choi
- , Beomsue Kim
- & Eun-Hye Joe
-
Article
| Open Access GITR subverts Foxp3+ Tregs to boost Th9 immunity through regulation of histone acetylation
GITR subverts Foxp3+ Tregs to boost Th9 immunity through regulation of histone acetylation
Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR), a costimulatory protein expressed by T cells, has immunostimulatory effect but the underlying mechanism is not clear. Here the authors show that GITR ligation inhibits the induction of Foxp3 expression and diverts CD4 T cells towards Th9 differentiation instead of iTreg.
- Xiang Xiao
- , Xiaomin Shi
- & Xian Chang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale models of signal propagation in human cells derived from discovery phosphoproteomic data
Large-scale models of signal propagation in human cells derived from discovery phosphoproteomic data
Phosphoproteomics can offer significant insight into cell signalling and how signalling is modified in response to perturbations. Here the authors develop a new tool for the analysis of high-content phosphoproteomics in the context of kinase/phosphatase-substrate knowledge, which is used to train logic models.
- Camille D. A. Terfve
- , Edmund H. Wilkes
- & Julio Saez-Rodriguez
-
Article
| Open Access TORC1 controls G1–S cell cycle transition in yeast via Mpk1 and the greatwall kinase pathway
TORC1 controls G1–S cell cycle transition in yeast via Mpk1 and the greatwall kinase pathway
The target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) pathway couples nutrient availability with cell growth and division by destabilizing the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor Sic1. Here the authors show that TORC1 downregulation leads to stabilization of Sic1 via phosphorylation by the MAP kinase Mpk1 and inhibition of dephosphorylation via the greatwall kinase pathway.
- Marta Moreno-Torres
- , Malika Jaquenoud
- & Claudio De Virgilio
-
Article
| Open Access A flexible codon in genomically recoded Escherichia coli permits programmable protein phosphorylation
A flexible codon in genomically recoded Escherichia coli permits programmable protein phosphorylation
The effects of protein phosphorylation, a common post-translational modification, are difficult to study using recombinant proteins. Here the authors use genomically engineered E. colito enhance translation systems that express phosphor-serine containing proteins, and use these systems to produce phosphorylated MEK1 kinase.
- Natasha L. Pirman
- , Karl W. Barber
- & Jesse Rinehart
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in SLC12A5 in epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures
Mutations in SLC12A5 in epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures
The potassium-chloride co-transporter, KCC2 is an essential component in maintaining a gradient for chloride ions in neurons. Here Stodberg and colleagues identify loss-of-function mutations in the encoding geneSLC12A5, which impair normal synaptic function associated with early-onset epilepsy.
- Tommy Stödberg
- , Amy McTague
- & Manju A. Kurian
-
Article
| Open Access Activity-regulated trafficking of the palmitoyl-acyl transferase DHHC5
Activity-regulated trafficking of the palmitoyl-acyl transferase DHHC5
Synaptic plasticity is mediated by the dynamic localization of proteins at synapses, which is partly controlled via palmitoylation of synaptic proteins. Here, the authors show how neuronal activity regulates the palmitoylation reaction through the translocation of the palmitoyl-acyl transferase DHHC5.
- G. Stefano Brigidi
- , Brendan Santyr
- & Shernaz X. Bamji
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquitination switches EphA2 vesicular traffic from a continuous safeguard to a finite signalling mode
Ubiquitination switches EphA2 vesicular traffic from a continuous safeguard to a finite signalling mode
Receptor tyrosine kinases can be auto-activated independent of ligand. Sabet et al.show that on ligand stimulation, ephrin receptor EphA2 switches from auto-activation suppression by vesicular recycling to ligand-dependent signalling limited by directional trafficking to late endosomes/lysosomes.
- Ola Sabet
- , Rabea Stockert
- & Philippe I. H. Bastiaens
-
Article |
 Myristoylation confers noncanonical AMPK functions in autophagy selectivity and mitochondrial surveillance
Myristoylation confers noncanonical AMPK functions in autophagy selectivity and mitochondrial surveillance
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a role in starvation-induced autophagy, but a role in mitochondrial damage-induced mitophagy is not known. Here, Liang et al. show that AMPK is recruited to damaged mitochondria in an N-myristoylation-dependent manner and in turn recruits the ATG16 autophagy complex.
- Jiyong Liang
- , Zhi-Xiang Xu
- & Gordon B. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative analysis reveals how EGFR activation and downregulation are coupled in normal but not in cancer cells
Quantitative analysis reveals how EGFR activation and downregulation are coupled in normal but not in cancer cells
Cells respond to increasing concentrations of EGF by altering the balance between EGFR phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Here the authors show that the establishment of an EGFR signaling threshold requires both a multiplicity of binding sites and cooperative binding of Cbl and Grb2 to the EGFR.
- Fabrizio Capuani
- , Alexia Conte
- & Andrea Ciliberto
-
Article
| Open Access Pannexin 1 channels regulate leukocyte emigration through the venous endothelium during acute inflammation
Pannexin 1 channels regulate leukocyte emigration through the venous endothelium during acute inflammation
Endothelial cell activation by inflammation requires extracellular ATP release. Here the authors show that TNF-α induces Src-family kinase-dependent ATP release by Pannexin1 channels in endothelial cells, and that Pannexin1 is required for leukocyte adhesion and emigration into the inflamed tissue.
- Alexander W. Lohman
- , Igor L. Leskov
- & Brant E. Isakson
-
Article
| Open Access Mto2 multisite phosphorylation inactivates non-spindle microtubule nucleation complexes during mitosis
Mto2 multisite phosphorylation inactivates non-spindle microtubule nucleation complexes during mitosis
In S. pombe, cytoplasmic microtubule nucleation, which depends on the Mto1/2 complex, ceases during mitosis. Here, Borek et al., show that multisite phosphorylation of Mto1/2 during mitosis disassembles the Mto1/2 complex and prevents microtubule nucleation activity.
- Weronika E. Borek
- , Lynda M. Groocock
- & Kenneth E. Sawin
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative interactome analysis reveals a chemoresistant edgotype
Quantitative interactome analysis reveals a chemoresistant edgotype
Changes in protein–protein interactions result in changes to cellular phenotype. Here the authors use crosslinking mass spectrometry to derive a quantitative protein interaction network in drug-sensitive and -resistant HeLa cells, and uncover a chemoresistant ‘edgotype’.
- Juan D. Chavez
- , Devin K. Schweppe
- & James E. Bruce
-
Article
| Open Access Highly condensed chromatins are formed adjacent to subtelomeric and decondensed silent chromatin in fission yeast
Highly condensed chromatins are formed adjacent to subtelomeric and decondensed silent chromatin in fission yeast
The level of chromatin condensation and gene expression is believed to be inversely correlated. Here the authors show that the transcriptionally silent telomere regions are flanked by highly condensed chromatin, and are less condensed than euchromatin in the interphase of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
- Atsushi Matsuda
- , Yuji Chikashige
- & Yasushi Hiraoka
-
Article
| Open Access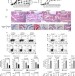 Phosphorylation status determines the opposing functions of Smad2/Smad3 as STAT3 cofactors in TH17 differentiation
Phosphorylation status determines the opposing functions of Smad2/Smad3 as STAT3 cofactors in TH17 differentiation
TGF-ß and IL-6 are the essential cytokines for mediating the differentiation of IL-17-producing CD4+ T helper cells (TH17). Here, Yoon et al. provide more insights into this process and describe the opposing roles of TGFß-signalling intermediates Smad2 and Smad3 as STAT3 cofactors in Th17 differentiation.
- Jeong-Hwan Yoon
- , Katsuko Sudo
- & Mizuko Mamura
-
Article
| Open Access Tyrosine glycosylation of Rho by Yersinia toxin impairs blastomere cell behaviour in zebrafish embryos
Tyrosine glycosylation of Rho by Yersinia toxin impairs blastomere cell behaviour in zebrafish embryos
Yersinia ruckeri is the source of redmouth disease in fish. Here the authors analysed the Yersiniatoxin Afp18 and show that it acts to inhibit RhoA activation by glycosylating a distinct tyrosine residue inducing a signalling incompetent structural conformation.
- Thomas Jank
- , Stephanie Eckerle
- & Klaus Aktories
-
Article
| Open Access PI3K/AKT activation induces PTEN ubiquitination and destabilization accelerating tumourigenesis
PI3K/AKT activation induces PTEN ubiquitination and destabilization accelerating tumourigenesis
Mutations and post-translational modifications of the PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor PTEN are a feature of many cancers, but these have not been associated with cervical cancer. Here, the authors identify a PI3K/AKT-mediated ubiquitination degradation pathway of PTEN that occurs in patients with cervical cancer.
- Min-Sik Lee
- , Man-Hyung Jeong
- & Jaewhan Song
-
Article
| Open Access Downregulation of N-terminal acetylation triggers ABA-mediated drought responses in Arabidopsis
Downregulation of N-terminal acetylation triggers ABA-mediated drought responses in Arabidopsis
N-terminal acetylation is a common protein modification in eukaryotes. Here the authors show that in Arabidopsis, N-terminal acetylation is decreased by drought stress, that abundance of an N-terminal acetyltransferase is reduced by abscisic acid and that constitutive downregulation can confer drought resistance.
- Eric Linster
- , Iwona Stephan
- & Markus Wirtz
-
Article
| Open Access Interneuron- and GABAA receptor-specific inhibitory synaptic plasticity in cerebellar Purkinje cells
Interneuron- and GABAA receptor-specific inhibitory synaptic plasticity in cerebellar Purkinje cells
Rebound potentiation (RP), a form of inhibitory plasticity in the cerebellum, is characterized by an increase in GABAergic synaptic currents. Here the authors demonstrate that RP is both interneuron input-specific and GABAAreceptor subunit-specific and serves to regulate Purkinje cell firing patterns.
- Qionger He
- , Ian Duguid
- & Trevor G. Smart
-
Article |
 Arginylation regulates purine nucleotide biosynthesis by enhancing the activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthase
Arginylation regulates purine nucleotide biosynthesis by enhancing the activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthase
The phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthase PRPS2 catalyses the first step ofde novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis, and has recently been shown to couple protein and nucleotide metabolism. Zhang et al. demonstrate that PRPS2 activity is regulated by tRNA-dependent post-translational addition of arginine.
- Fangliang Zhang
- , Devang M. Patel
- & Anna Kashina
-
Article
| Open Access SUMOylation of synapsin Ia maintains synaptic vesicle availability and is reduced in an autism mutation
SUMOylation of synapsin Ia maintains synaptic vesicle availability and is reduced in an autism mutation
Synapsins anchor synaptic vesicles (SVs) to the actin cytoskeleton to establish the reserve vesicle pool. Here Tanget al. show that SUMOylation of synapsin 1a enhances its interaction with SVs to promote efficient reclustering following stimulation, and a mutation linked to autism and epilepsy leads to defective SUMOylation.
- Leo T. -H. Tang
- , Tim J. Craig
- & Jeremy M. Henley
-
Article
| Open Access 9-O-Acetylation of sialic acids is catalysed by CASD1 via a covalent acetyl-enzyme intermediate
9-O-Acetylation of sialic acids is catalysed by CASD1 via a covalent acetyl-enzyme intermediate
9-O-Acetylation is one of the most common modifications of sialic acids, implicated in sialoglycan recognition and ganglioside biology. Here, the authors show that the key enzyme for the biosynthesis of 9-O-acetylated sialoglycans is CASD1, which uses CMP-activated sialic acid as acceptor substrate.
- Anna-Maria T. Baumann
- , Mark J. G. Bakkers
- & Martina Mühlenhoff
-
Article
| Open Access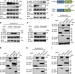 A phosphorylation switch controls the spatiotemporal activation of Rho GTPases in directional cell migration
A phosphorylation switch controls the spatiotemporal activation of Rho GTPases in directional cell migration
Directed cell migration requires spatially regulated activity of GTPases Rac1 and RhoA. Here Cao et al. show that growth factor stimulation promotes phosphorylation of tensin-3 and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) and their association with PI 3-kinase and deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1) to regulate GTPase activity.
- Xuan Cao
- , Tomonori Kaneko
- & Shawn S. C. Li
-
Article
| Open Access Biotin starvation causes mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation and partial rescue by the SIRT3-like deacetylase Hst4p
Biotin starvation causes mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation and partial rescue by the SIRT3-like deacetylase Hst4p
Biotin is an essential vitamin in the regulation of energy metabolism. Here Madsen et al.show that biotin deficiency in yeast leads to hyperacetylation of mitochondrial proteins that is compensated for by the SIRT-like deacetylase Hst4p.
- Christian T. Madsen
- , Kathrine B. Sylvestersen
- & Michael L. Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Crucial roles of RSK in cell motility by catalysing serine phosphorylation of EphA2
Crucial roles of RSK in cell motility by catalysing serine phosphorylation of EphA2
The EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed in many cancers and is reported to be phosphorylated by Akt. Here, Zhou et al.show that RSK, rather than Akt, phosphorylates EphA2 on Ser-897, and this regulates cell migration and invasion of metastatic cancer cells.
- Yue Zhou
- , Naoki Yamada
- & Hiroaki Sakurai
-
Article
| Open Access SUMO and ubiquitin-dependent XPC exchange drives nucleotide excision repair
SUMO and ubiquitin-dependent XPC exchange drives nucleotide excision repair
The SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase RNF111 promotes K63-linked ubiquitylation of SUMOylated XPC after DNA damage. Here the authors show that RNF111 is responsible for sequential XPC ubiquitylation, and RNF111-mediated ubiquitylation promotes the release of XPC from damaged DNA after NER initiation.
- Loes van Cuijk
- , Gijsbert J. van Belle
- & Jurgen A. Marteijn
-
Article
| Open Access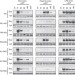 Caspase-8 scaffolding function and MLKL regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of TLR3
Caspase-8 scaffolding function and MLKL regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of TLR3
Inflammasome activation requires a complex and incompletely understood network of signalling events. Here the authors characterize step-by-step contributions of TLR3, caspase-8, RIPK3 and MLKL to the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in response to double-stranded RNA.
- Seokwon Kang
- , Teresa Fernandes-Alnemri
- & Emad S. Alnemri
-
Article |
 Glycan clustering stabilizes the mannose patch of HIV-1 and preserves vulnerability to broadly neutralizing antibodies
Glycan clustering stabilizes the mannose patch of HIV-1 and preserves vulnerability to broadly neutralizing antibodies
The glycan patch that covers the HIV-1 envelope protein gp120 can be targeted by broadly neutralizing antibodies. Here, Pritchard et al.show that structural changes in the glycans do not significantly hamper antibody recognition, supporting the glycan patch as a stable target for vaccine design.
- Laura K. Pritchard
- , Daniel I.R. Spencer
- & Max Crispin
-
Article
| Open Access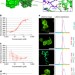 Grb2 monomer–dimer equilibrium determines normal versus oncogenic function
Grb2 monomer–dimer equilibrium determines normal versus oncogenic function
Grb2 is an adaptor protein that can exist as a dimer that dissociates on phosphorylation of Y160. Here, the authors show that only the monomeric protein is capable of activating mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction and hence control oncogenic outcome.
- Zamal Ahmed
- , Zahra Timsah
- & John E. Ladbury
-
Article |
 mRNA 3′-UTR shortening is a molecular signature of mTORC1 activation
mRNA 3′-UTR shortening is a molecular signature of mTORC1 activation
mTOR signalling regulates protein synthesis in response to changes in nutrient availability. Chang et al.demonstrate that mTOR can stimulate translation by promoting the shortening of mRNA 3′-untranslated regions, and that expression of ubiquitin ligases is selectively enhanced by this mechanism.
- Jae-Woong Chang
- , Wei Zhang
- & Jeongsik Yong
-
Article
| Open Access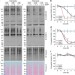 System-wide identification of wild-type SUMO-2 conjugation sites
System-wide identification of wild-type SUMO-2 conjugation sites
Tryptic digestion of SUMOylated proteins generates large peptides, rendering proteomic characterisation of this post-translational modification particularly challenging unless mutant SUMO is used. Hendriks et al.present a method that allows the quantitative identification of wild-type SUMO sites.
- Ivo A. Hendriks
- , Rochelle C. D’Souza
- & Alfred C. O. Vertegaal
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of asymmetric DNA methylation and ATP-triggered long-range diffusion by EcoP15I
Structural basis of asymmetric DNA methylation and ATP-triggered long-range diffusion by EcoP15I
Type III restriction–modification enzymes consists of two methylation and one or two restriction subunits. Here the authors report the structure of the full EcoP15I complex bound to DNA, which suggests mechanisms for ATP hydrolysis dependent diffusion along DNA and how a dimeric methyltransferase modifies only one DNA strand.
- Yogesh K. Gupta
- , Siu-Hong Chan
- & Aneel K. Aggarwal
-
Article
| Open Access Proximity-dependent initiation of hybridization chain reaction
Proximity-dependent initiation of hybridization chain reaction
Proximity ligation assays are a sensitive method for detecting protein interactions, but require the addition of enzymes. Here the authors introduce proxHCR, an enzyme-free method of detecting interactions in close proximity by inducing a hybribization chain reaction (HCR) of fluorescently labelled oligonucleotides.
- Björn Koos
- , Gaëlle Cane
- & Ola Söderberg
-
Article
| Open Access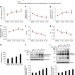 Small-molecule activation of SERCA2a SUMOylation for the treatment of heart failure
Small-molecule activation of SERCA2a SUMOylation for the treatment of heart failure
SUMOylation of the cardiac calcium pump SERCA2a affects its activity and promotes cardiomyocyte contractility. Here the authors identify a small molecule N106 that increases SERCA2 SUMOylation and improves heart function in mice, and propose a promising therapeutic strategy for treatment of heart failure.
- Changwon Kho
- , Ahyoung Lee
- & Roger J. Hajjar
-
Article |
 Cdk5 controls lymphatic vessel development and function by phosphorylation of Foxc2
Cdk5 controls lymphatic vessel development and function by phosphorylation of Foxc2
The mechanisms regulating lymphatic vessel development and function are still largely unknown. Here, the authors show that the protein kinase Cdk5 is required for lymphatic vessel development by regulating the activity of the transcription factor Foxc2 and its target genes.
- Johanna Liebl
- , Siwei Zhang
- & Stefan Zahler
-
Article
| Open Access Acetylation of Beclin 1 inhibits autophagosome maturation and promotes tumour growth
Acetylation of Beclin 1 inhibits autophagosome maturation and promotes tumour growth
Beclin 1 is an essential autophagy effector, necessary to form the autophagosome. Here Sun et al. show that Beclin 1 acetylation regulated by p300 and SIRT1 inhibits autophagosome maturation, and mutation of the acetylation sites leads to tumour growth suppression in vivo.
- Ting Sun
- , Xuan Li
- & Xiao-Feng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access PI3K/mTORC2 regulates TGF-β/Activin signalling by modulating Smad2/3 activity via linker phosphorylation
PI3K/mTORC2 regulates TGF-β/Activin signalling by modulating Smad2/3 activity via linker phosphorylation
Although crosstalk between the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and transforming growth factor-β pathways is important, the mechanism is obscure. Here, Yu et al. show that activation of mTORC2 downstream of PI3K leads to the linker phosphorylation of Smad2/3 and their ubiquitin-dependent degradation.
- Jason S. L. Yu
- , Thamil Selvee Ramasamy
- & Wei Cui
-
Article |
 Stk38 protein kinase preferentially inhibits TLR9-activated inflammatory responses by promoting MEKK2 ubiquitination in macrophages
Stk38 protein kinase preferentially inhibits TLR9-activated inflammatory responses by promoting MEKK2 ubiquitination in macrophages
Activation of innate immune responses is subject to versatile regulation. Here the authors show that a conserved LATS family kinase Stk38 limits proinflammatory signalling downstream of TLR9 in macrophages and protects mice from lethal sepsis by MEKK2 ubiquitination and degradation.
- Mingyue Wen
- , Xianwei Ma
- & Huazhang An
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism for USP7-mediated DNMT1 stabilization by acetylation
Molecular mechanism for USP7-mediated DNMT1 stabilization by acetylation
DNMT1 is a methyl-transferase involved in maintaining tissue-specific patterns of DNA methylation. Here the authors solve the structure of a DNMT1-USP7 complex and demonstrate the mechanism by which DNMT1 stability is regulated through acetylation by preventing association with the deubiquitinase USP7.
- Jingdong Cheng
- , Huirong Yang
- & Yanhui Xu
-
Article |
 Clk post-transcriptional control denoises circadian transcription both temporally and spatially
Clk post-transcriptional control denoises circadian transcription both temporally and spatially
CLOCK (CLK) is essential for the development and maintenance of circadian rhythms in Drosophila. Here, the authors show that Clk mRNA is regulated by miRNA bantam, and deletion of bantambinding site leads to stochastic CLK-driven transcription and development of the circadian neurons.
- Immanuel Lerner
- , Osnat Bartok
- & Sebastian Kadener
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic interplay between catalytic and lectin domains of GalNAc-transferases modulates protein O-glycosylation
Dynamic interplay between catalytic and lectin domains of GalNAc-transferases modulates protein O-glycosylation
Polypeptide GalNAc-transferases decorate proteins with dense arrays of O-glycans, which in the case of mucins are essential for their barrier functions. Here the authors present comprehensive structural studies that shed light on the molecular attributes that allow GalNAc-T2 to efficiently carry out dense O-glycosylation.
- Erandi Lira-Navarrete
- , Matilde de las Rivas
- & Ramon Hurtado-Guerrero
-
Article
| Open Access Acetylation of MAT IIα represses tumour cell growth and is decreased in human hepatocellular cancer
Acetylation of MAT IIα represses tumour cell growth and is decreased in human hepatocellular cancer
Folate plays an essential role in dividing cells and is regulated by methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), where a switch from MAT Iα to MAT IIα expression seems to promote liver cancer progression. Here the authors demonstrate that MAT IIα stability is regulated by acetylation and this regulation is important for tumour growth.
- Hong-Bin Yang
- , Ying-Ying Xu
- & Qun-Ying Lei
-
Article |
 dDsk2 regulates H2Bub1 and RNA polymerase II pausing at dHP1c complex target genes
dDsk2 regulates H2Bub1 and RNA polymerase II pausing at dHP1c complex target genes
dDsk2 is a conserved extraproteasomal ubiquitin receptor that targets ubiquitylated proteins for degradation. Here the authors report that dDsk2 regulates RNA polymerase II pausing by preventing H2Bub1 deubiquitylation, suggesting a nonproteolytic function of dDsk2.
- Roman Kessler
- , Johan Tisserand
- & Fernando Azorín

 Discovery of protein acetylation patterns by deconvolution of peptide isomer mass spectra
Discovery of protein acetylation patterns by deconvolution of peptide isomer mass spectra