Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The Shc1 adaptor simultaneously balances Stat1 and Stat3 activity to promote breast cancer immune suppression
The Shc1 adaptor simultaneously balances Stat1 and Stat3 activity to promote breast cancer immune suppression
Tyrosine kinase signalling in cancer cells promotes immune evasion. Here, the authors show that tyrosine kinases engage scaffold protein Shc1 to promote immunosuppression in breast cancer by simultaneously activating STAT3 immunosuppressive signals and impairing STAT1-driven anti-tumour immune responses.
- Ryuhjin Ahn
- , Valérie Sabourin
- & Josie Ursini-Siegel
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided mutagenesis reveals a hierarchical mechanism of Parkin activation
Structure-guided mutagenesis reveals a hierarchical mechanism of Parkin activation
Parkin and PINK1 are involved in damaged mitochondria clearance; however the sequence of events of Parkin activation is not clear. Here, the authors show that binding to phospho-ubiquitin on mitochondria enables Parkin phosphorylation, which allows Repressor Element of Parkin removal, E3 ligase activation and mitophagy.
- Matthew Y. Tang
- , Marta Vranas
- & Edward A. Fon
-
Article
| Open Access PARP1 promotes gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by modulating the RNA-binding protein HuR
PARP1 promotes gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by modulating the RNA-binding protein HuR
PARP1, in addition to its role in DNA repair, has a role in regulating gene transcription via PARylation of target proteins. Here the authors show that HuR is targeted after lipopolysaccharide exposure to regulate the inflammatory gene expression at post-transcriptional level.
- Yueshuang Ke
- , Yanlong Han
- & Xianlu Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Nur77 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via switching glucose metabolism toward gluconeogenesis through attenuating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase sumoylation
Nur77 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via switching glucose metabolism toward gluconeogenesis through attenuating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase sumoylation
Gluconeogenesis is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Here, the authors show that nuclear receptor Nur77 acts as a tumour suppressor sustaining gluconeogenesis by enhancing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK1) stability via regulating its interaction with the SUMO-conjugating enzyme Ubc9.
- Xue-li Bian
- , Hang-zi Chen
- & Qiao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding the genetic code of Mus musculus
Expanding the genetic code of Mus musculus
Expanding the genetic code with unnatural amino acids in model organisms is a powerful tool for investigatingin vivocellular proteins and processes. Here the authors re-engineer the amber stop codon in laboratory mice to allow site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids in target proteins.
- Songmi Han
- , Aerin Yang
- & Hee-Sung Park
-
Article
| Open Access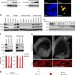 Dub3 inhibition suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by promoting Snail1 degradation
Dub3 inhibition suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by promoting Snail1 degradation
Snail1 is a key factor controlling epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. While the E3 ligases responsible for Snail1 ubiquitination and degradation have been defined, the deubiquitinating enzyme is unknown. Here Zhou and colleagues show that Dub3 stabilizes Snail1 by removing ubiquitin, thus impacting breast cancer cell metastasis.
- Yadi Wu
- , Yu Wang
- & Binhua P. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access RIP1 autophosphorylation is promoted by mitochondrial ROS and is essential for RIP3 recruitment into necrosome
RIP1 autophosphorylation is promoted by mitochondrial ROS and is essential for RIP3 recruitment into necrosome
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) promote necroptosis and the receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1) is a key player in this form of cell death. Here, the authors show that cysteine residues in RIP1 sense ROS and oxidation of the cysteines triggers RIP1 autophosphorylation, which promotes functional necrosome formation.
- Yingying Zhang
- , Sheng Sean Su
- & Jiahuai Han
-
Article
| Open Access Erythrocytes retain hypoxic adenosine response for faster acclimatization upon re-ascent
Erythrocytes retain hypoxic adenosine response for faster acclimatization upon re-ascent
Humans that reach high altitude soon after the first ascent show faster adaptation to hypoxia. Songet al. show that this adaptive response relies on decreased red blood cell uptake of plasma adenosine due to reduced levels of nucleoside transporter ENT1 resulting from coordinated adenosine generation by ectonucleotidase CD73 and activation of A2B receptors.
- Anren Song
- , Yujin Zhang
- & Yang Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Ufd2p synthesizes branched ubiquitin chains to promote the degradation of substrates modified with atypical chains
Ufd2p synthesizes branched ubiquitin chains to promote the degradation of substrates modified with atypical chains
How ubiquitination affects the proteins it modifies varies according to the type of linkage between ubiquitin moieties. Here, Liuet al. show how yeast Udf2p promotes K48 linkage formation onto K29-linked chains to generate branched K29-K48 ubiquitin chains that target its substrate to the proteasome.
- Chao Liu
- , Weixiao Liu
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal ubiquitin transfer identifies ubiquitination substrates under differential control by the two ubiquitin activating enzymes
Orthogonal ubiquitin transfer identifies ubiquitination substrates under differential control by the two ubiquitin activating enzymes
The transfer of ubiquitin (UB) to cellular targets is mediated sequentially by three groups of enzymes, UB activating enzyme (E1), UB conjugating enzyme (E2) and UB ligase (E3). Here the authors provide evidence that the two mammalian E1 enzymes, Uba1 and Uba6, exert biologically distinct functions.
- Xianpeng Liu
- , Bo Zhao
- & Hiroaki Kiyokawa
-
Article
| Open Access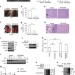 CDK4/6-dependent activation of DUB3 regulates cancer metastasis through SNAIL1
CDK4/6-dependent activation of DUB3 regulates cancer metastasis through SNAIL1
Overexpression of SNAIL confers tumour cells with cancer stem-like characteristics associated with tumour progression. Here the authors show that inhibition of CDK4/6 blocks tumour metastasis in triple negative breast cancer by targeting DUB3 which in turns deubiquitinates and stabilises SNAIL1.
- Tongzheng Liu
- , Jia Yu
- & Zhenkun Lou
-
Article
| Open Access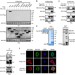 c-Src phosphorylation and activation of hexokinase promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis
c-Src phosphorylation and activation of hexokinase promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis
The protein tyrosine kinase c-Src is a renowned proto-oncogene with pleiotropic effects. Here, the authors show that c-Src induces the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells by phosphorylating hexokinases HK1 and HK2, which in turns lead to increased HK catalytic activity and consequent enhancement of glycolysis.
- Jia Zhang
- , Suili Wang
- & Qinxi Li
-
Article
| Open Access K63-polyubiquitinated HAUSP deubiquitinates HIF-1α and dictates H3K56 acetylation promoting hypoxia-induced tumour progression
K63-polyubiquitinated HAUSP deubiquitinates HIF-1α and dictates H3K56 acetylation promoting hypoxia-induced tumour progression
Hypoxia-induced transcriptional responses mediated by HIF-1a are regulated through the ubiquitin-dependent pathway to control HIF-1a stability. Here the authors show that the deubiquitinase HAUSP modulates the stability of HIF-1a and K63-polyubiquitinated HAUSP serves as an anchor for HIF-1a-induced gene transcription.
- Han-Tsang Wu
- , Yi-Chih Kuo
- & Kou-Juey Wu
-
Article
| Open Access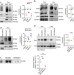 ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins
ISGylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of MVB proteins
Multivesicular bodies (MVB) are endosomal compartments that can either fuse with the plasma membrane for the secretion of exosomes, or fuse with the lysosome and be degraded along with their contents. Here, the authors show that ISGylation of the MVB protein TSG101 impairs exosome secretion and acts as a regulator of MVB fate.
- Carolina Villarroya-Beltri
- , Francesc Baixauli
- & Francisco Sánchez-Madrid
-
Article
| Open Access The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a cAMP-induced substrate switch
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a cAMP-induced substrate switch
GCN5 inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis through acetylation of PGC-1α. Here the authors show that GCN5 also activates hepatic gluconeogenesis by acetylating histone H3K9, and that the affinity of GCN5 for its different substrates is regulated via phosphorylation at S275 by PKA in a CITED2-dependent manner.
- Mashito Sakai
- , Tomoko Tujimura-Hayakawa
- & Michihiro Matsumoto
-
Article
| Open Access Rad18-dependent SUMOylation of human specialized DNA polymerase eta is required to prevent under-replicated DNA
Rad18-dependent SUMOylation of human specialized DNA polymerase eta is required to prevent under-replicated DNA
Translesion synthesis polymerase eta has a well characterized role in replicating past UV-induced DNA lesions and has recently been shown to act at difficult to replicate sequences. Here the authors show that its SUMOylation is required to recruit pol eta at the replication fork and to prevent under-replicated DNA.
- Emmanuelle Despras
- , Méghane Sittewelle
- & Patricia L Kannouche
-
Article
| Open Access KAT2A/KAT2B-targeted acetylome reveals a role for PLK4 acetylation in preventing centrosome amplification
KAT2A/KAT2B-targeted acetylome reveals a role for PLK4 acetylation in preventing centrosome amplification
The acetyltransferases KAT2A and KAT2B are essential regulators of transcription, cell cycle progression and DNA repair. Here the authors describe a KAT2A/2B-dependent acetylome, and show that acetylation of the protein kinase PLK4 contributes to the regulation of centrosome number.
- Marjorie Fournier
- , Meritxell Orpinell
- & László Tora
-
Article
| Open Access Bimodal antagonism of PKA signalling by ARHGAP36
Bimodal antagonism of PKA signalling by ARHGAP36
Protein kinase A (PKA) is a key mediator of cyclic AMP signalling. Here, Eccles et al. show that ARHGAP36 antagonizes PKA by acting as a kinase inhibitor and targeting the catalytic subunit for endolysosomal degradation, thus reducing sensitivity of cells to cAMP and promoting Hedgehog signalling.
- Rebecca L. Eccles
- , Maciej T. Czajkowski
- & Oliver Rocks
-
Article
| Open Access ARD1-mediated Hsp70 acetylation balances stress-induced protein refolding and degradation
ARD1-mediated Hsp70 acetylation balances stress-induced protein refolding and degradation
The chaperone Hsp70 has a dual role, promoting both protein refolding and protein degradation. Seo and Park et al. show that Hsp70 acetylation enhances protein refolding after stress, and that subsequent deacetylation progressively promotes ubiquitin ligase binding and protein degradation.
- Ji Hae Seo
- , Ji-Hyeon Park
- & Kyu-Won Kim
-
Article
| Open Access SUMOylated NKAP is essential for chromosome alignment by anchoring CENP-E to kinetochores
SUMOylated NKAP is essential for chromosome alignment by anchoring CENP-E to kinetochores
The kinetochore-bound motor CENP-E plays a critical role in chromosome alignment. Here, the authors show that NF-κB activating protein (NKAP) dynamically localises to kinetochores, is SUMOylated during mitosis, and this modification is required for NKAP to bind CENP-E and localise CENP-E to the kinetochore.
- Teng Li
- , Liang Chen
- & Qing Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-wide identification of the endogenous ADP-ribosylome of mammalian cells and tissue
Proteome-wide identification of the endogenous ADP-ribosylome of mammalian cells and tissue
ADP-ribosylation is a reversible post-translational protein modification involved in many cellular processes. Here the authors describe a sensitive approach for the analysis of ADP-ribosylation sites under physiologic conditions and identify lysine residues as in vivotargets of ADP-ribosylation.
- Rita Martello
- , Mario Leutert
- & Michael L. Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Aromatic thiol-mediated cleavage of N–O bonds enables chemical ubiquitylation of folded proteins
Aromatic thiol-mediated cleavage of N–O bonds enables chemical ubiquitylation of folded proteins
Chemical approaches to site-specifically ubiquitylate a target protein allow investigation of the biochemical effects of this modification, but they often destabilize the protein. Here, the authors report on a synthetic conjugation strategy that leads to protein ubiquitylation in non-denaturing conditions.
- Caroline E. Weller
- , Abhinav Dhall
- & Champak Chatterjee
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoselective synthesis and analysis of naturally occurring phosphorylated cysteine peptides
Chemoselective synthesis and analysis of naturally occurring phosphorylated cysteine peptides
Protein phosphorylation mediates signalling and other important cellular processes, but the specific effect of cysteine phosphorylation is unclear. Here, the authors present a chemical strategy to selectively phosphorylate cysteine residues and a mass spectrometry approach to detect and characterize endogenous pCys sites.
- Jordi Bertran-Vicente
- , Martin Penkert
- & Christian P. R. Hackenberger
-
Article
| Open Access MARCH1 regulates insulin sensitivity by controlling cell surface insulin receptor levels
MARCH1 regulates insulin sensitivity by controlling cell surface insulin receptor levels
Insulin receptor levels at the cell surface are reduced in insulin resistance, for reasons that are not fully understood. Here, the authors identify the E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH1 as a direct regulator of basal insulin receptor surface levels and, therefore, insulin signalling.
- Arvindhan Nagarajan
- , Max C. Petersen
- & Narendra Wajapeyee
-
Article
| Open Access Insulin post-transcriptionally modulates Bmal1 protein to affect the hepatic circadian clock
Insulin post-transcriptionally modulates Bmal1 protein to affect the hepatic circadian clock
The effect of the liver clock is modified by food entrainment via Bmal1/Clock core machinery. Here the authors show that insulin promotes postprandial Akt-dependent phosphorylation of Bmal1, resulting in association with 14-3-3 and Bmal1 shuttling out of the nucleus, thereby disrupting Bmal1 transcriptional effects on the clock.
- Fabin Dang
- , Xiujie Sun
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Glycosylation and stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell activity
Glycosylation and stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell activity
Programmed Death ligand-1 (PD-L1) protein mediates immune suppression in cancer. Here, the authors show that in breast cancer, PD-L1 expression can be up regulated post-translationally by glycosylation, which in turn acts through inhibiting GSK3β-mediated PD-L1 degradation.
- Chia-Wei Li
- , Seung-Oe Lim
- & Mien-Chie Hung
-
Article
| Open Access Cullin3-KLHL15 ubiquitin ligase mediates CtIP protein turnover to fine-tune DNA-end resection
Cullin3-KLHL15 ubiquitin ligase mediates CtIP protein turnover to fine-tune DNA-end resection
CtIP has a key role in DNA double-strand break repair as its role in resecting DNA at the break commits a cell to homologous recombination. Here the authors show that KLHL15 interacts with CtIP and regulates repair by controlling protein turnover.
- Lorenza P. Ferretti
- , Sarah-Felicitas Himmels
- & Alessandro A. Sartori
-
Article
| Open Access The tumour suppressor CYLD regulates the p53 DNA damage response
The tumour suppressor CYLD regulates the p53 DNA damage response
CYLD is a deubiquitinase known to act as a tumour suppressor in different models of carcinogenesis. Here, the authors show that CYLD suppresses carcinogen-induced tumorigenesis by deubiquitinating p53 and promoting its stabilization and activation in response to DNA damage.
- Vanesa Fernández-Majada
- , Patrick-Simon Welz
- & Manolis Pasparakis
-
Article
| Open Access A MUB E2 structure reveals E1 selectivity between cognate ubiquitin E2s in eukaryotes
A MUB E2 structure reveals E1 selectivity between cognate ubiquitin E2s in eukaryotes
Regulators of the important ubiquitylation cascade are not well studied. Here, the authors report the crystal structure of a prenylated membrane-anchored ubiquitin-fold protein from Arabidopsisbound to an E2 protein and conclude that it is an example of selective activation between E2 enzymes.
- Xiaolong Lu
- , Konstantin R. Malley
- & Brian P. Downes
-
Article
| Open Access Positive feedback regulation of p53 transactivity by DNA damage-induced ISG15 modification
Positive feedback regulation of p53 transactivity by DNA damage-induced ISG15 modification
The ‘genome guardian’ p53 has a well-established role in suppressing tumour development after DNA damage. Here the authors show that expression of the ubiquitin-like protein ISG15 is regulated by p53 which in turn is modified by ISG15 to enhance binding to target gene promoters.
- Jong Ho Park
- , Seung Wook Yang
- & Chin Ha Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperphosphorylation amplifies UPF1 activity to resolve stalls in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Hyperphosphorylation amplifies UPF1 activity to resolve stalls in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Gene expression is regulated by a range of mechanisms, including post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation. Here the authors present evidence for a feedback mechanism whereby hyperphosphorylation of UPF1 in response to delays in nonsense-mediated decay enhances recruitment of mRNA decay machinery.
- Sébastien Durand
- , Tobias M. Franks
- & Jens Lykke-Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of energy homeostasis by the ubiquitin-independent REGγ proteasome
Regulation of energy homeostasis by the ubiquitin-independent REGγ proteasome
In conditions of energy stress cells reduce transcription of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) to maintain cell survival. Here, the authors show that energy stress induces an AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of Sirt7, which promotes its ubiquitin-independent degradation by REGγ, resulting in the down-regulation of rRNA transcription and cell survival.
- Lianhui Sun
- , Guangjian Fan
- & Chuangui Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Protein kinase A modulation of CaV1.4 calcium channels
Protein kinase A modulation of CaV1.4 calcium channels
Phosphorylation of L-type calcium CaV channels by protein kinase A is essential for several physiological events. Here, the authors show how this kinase regulates CaV1.4 activity, suggesting a general regulatory mechanism for all L-type calcium channels.
- Lingjie Sang
- , Ivy E. Dick
- & David T. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Target-dependent biogenesis of cognate microRNAs in human cells
Target-dependent biogenesis of cognate microRNAs in human cells
MicroRNAs are a widespread regulatory mechanism and are themselves extensively regulated. Here the authors show regulated miRNA biogenesis by the target mRNA, a layer of regulation that modulates miRNA levels dependent on target availability.
- Mainak Bose
- & Suvendra N. Bhattacharyya
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of post-Golgi LH3 trafficking is essential for collagen homeostasis
Regulation of post-Golgi LH3 trafficking is essential for collagen homeostasis
Lysine hydroxylation of procollagen precursors by LH3 is required for collagen fibril crosslinking and stabilization. Here the authors show that the trafficking protein VIPAR is required for correct sorting of LH3 into post-Golgi collagen carriers and for correct collagen modification and structure.
- Blerida Banushi
- , Federico Forneris
- & Paul Gissen
-
Article
| Open Access The methyltransferase Suv39h1 links the SUMO pathway to HP1α marking at pericentric heterochromatin
The methyltransferase Suv39h1 links the SUMO pathway to HP1α marking at pericentric heterochromatin
The Suv39h histone methyltransferases promote trimethylation of histone H3 on lysine 9 (H3K9me3). Here, in the Suv39h1 paralog, the authors identify an enhancer of HP1a sumoylation activity that impacts heterochromatin.
- Christèle Maison
- , Delphine Bailly
- & Geneviève Almouzni
-
Article
| Open Access Critical role of RanBP2-mediated SUMOylation of Small Heterodimer Partner in maintaining bile acid homeostasis
Critical role of RanBP2-mediated SUMOylation of Small Heterodimer Partner in maintaining bile acid homeostasis
As signalling molecules, bile acids (BAs) can affect metabolism, but due to detergent-like properties, BA levels must be tightly regulated. Here, Kim et al.show that RanBP2, a nucleoporin, maintains BA homoeostasis through SUMOylation of Small Heterodimer Partner (SHP), an orphan nuclear receptor.
- Dong-Hyun Kim
- , Sanghoon Kwon
- & Jongsook Kim Kemper
-
Article
| Open Access Claspin recruits Cdc7 kinase for initiation of DNA replication in human cells
Claspin recruits Cdc7 kinase for initiation of DNA replication in human cells
Claspin mediates the transmission of a replication-stress signal from ATR to Chk1 and is necessary for efficient fork progression. Here the authors demonstrate that the C-terminal acidic patch is important for this role due to its interaction with Cdc7.
- Chi-Chun Yang
- , Masahiro Suzuki
- & Hisao Masai
-
Article
| Open Access Essential role of autoactivation circuitry on Aurora B-mediated H2AX-pS121 in mitosis
Essential role of autoactivation circuitry on Aurora B-mediated H2AX-pS121 in mitosis
Aurora B activation at the centromere is critical for faithful chromosome segregation in mammals. Here the authors show that Aurora B-mediated phosphorylation of histone H2AX at serine 121 is essential for Aurora B auto-activation circuitry at centromeres, ensuring proper chromosome segregation.
- Midori Shimada
- , Takahiro Goshima
- & Makoto Nakanishi
-
Article
| Open Access NEDDylation promotes stress granule assembly
NEDDylation promotes stress granule assembly
Stress granules that form in response to stress contain translationally stalled mRNPs and play important roles in cellular homeostasis. Here the authors implicate SRSF3 neddylation as an important factor in the formation of stress granules in response to arsenite exposure.
- Aravinth Kumar Jayabalan
- , Anthony Sanchez
- & Takbum Ohn
-
Article
| Open Access A combined cryo-EM and molecular dynamics approach reveals the mechanism of ErmBL-mediated translation arrest
A combined cryo-EM and molecular dynamics approach reveals the mechanism of ErmBL-mediated translation arrest
When the antibiotic erythromycin is bound to the ribosomal exit tunnel, ErmBL peptide translation stalls and allows translation of the downstream methyltransferase ErmB. Here the authors combine cryo-EM and molecular dynamics simulations to identify the underlying basis for the inhibition of peptide bond formation that results in ribosome stalling.
- Stefan Arenz
- , Lars V. Bock
- & Daniel N. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Deficient methylation and formylation of mt-tRNAMet wobble cytosine in a patient carrying mutations in NSUN3
Deficient methylation and formylation of mt-tRNAMet wobble cytosine in a patient carrying mutations in NSUN3
The post-transcriptional 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification occurs in a wide range of nuclear-encoded RNAs. Here the authors identify the mitochondrial tRNA-Met as a target for the m5C methyltransferase NSun3—found mutated in a mitochondrial disease patient—and link mitochondrial tRNA modifications with energy metabolism.
- Lindsey Van Haute
- , Sabine Dietmann
- & Michal Minczuk
-
Article
| Open Access MLP and CARP are linked to chronic PKCα signalling in dilated cardiomyopathy
MLP and CARP are linked to chronic PKCα signalling in dilated cardiomyopathy
Altered function of the muscle LIM protein (MLP) causes dilated cardiomyopathy in mice and humans. Lange et al. explain the molecular role of MLP in the heart by showing that it affects the signalling complex at the intercalated discs of failing hearts that consists of PKCα, PLCβ1 and CARP by inhibiting PKCα auto-phosphorylation and function.
- Stephan Lange
- , Katja Gehmlich
- & Elisabeth Ehler
-
Article
| Open Access p62/Sqstm1 promotes malignancy of HCV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma through Nrf2-dependent metabolic reprogramming
p62/Sqstm1 promotes malignancy of HCV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma through Nrf2-dependent metabolic reprogramming
Dysregulation of p62 has been implicated in tumorigenesis. Here, the authors show that p62 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by reprogramming glucose and glutamine metabolism through Nrf2 and present a novel compound that can inhibit p62 action thus sensitizing cancer cells to chemotherapy.
- Tetsuya Saito
- , Yoshinobu Ichimura
- & Masaaki Komatsu
-
Article
| Open Access Arginine demethylation is catalysed by a subset of JmjC histone lysine demethylases
Arginine demethylation is catalysed by a subset of JmjC histone lysine demethylases
While reversal of lysine methylation on histone tails is a well-established mechanism to tune gene expression, the existence of a similar arginine demethylation process is controversial. Here, the authors show that some jumonji enzymes possess both lysine and arginine demethylase activity in vitro.
- Louise J. Walport
- , Richard J. Hopkinson
- & Christopher J. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access Cardiac sodium channel palmitoylation regulates channel availability and myocyte excitability with implications for arrhythmia generation
Cardiac sodium channel palmitoylation regulates channel availability and myocyte excitability with implications for arrhythmia generation
Cardiac voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav1.5) are crucial regulators of heart electric activity. Here the authors show that palmitoylation, a process of lipid modification of cysteine residues, modulates Nav1.5 function and affects cardiomyocyte excitability, representing a potential target in treating cardiac diseases.
- Zifan Pei
- , Yucheng Xiao
- & Theodore R. Cummins
-
Article
| Open Access Counteracting H3K4 methylation modulators Set1 and Jhd2 co-regulate chromatin dynamics and gene transcription
Counteracting H3K4 methylation modulators Set1 and Jhd2 co-regulate chromatin dynamics and gene transcription
Histone H3K4 methylation affects gene transcription from yeast to humans. Here, the authors show that Set1 and Jhd2, the only H3K4 methyltransferase and H3K4 demethylase, respectively, in budding yeast, co-regulate both positive and negative transcription mediated by nucleosomal turnover and occupancy.
- Saravanan Ramakrishnan
- , Srijana Pokhrel
- & Mahesh B. Chandrasekharan
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of STING requires palmitoylation at the Golgi
Activation of STING requires palmitoylation at the Golgi
STING is essential for the type I interferon immune response to foreign DNA. Here, the authors show that palmitoylation of STING at the Golgi is required for activating downstream signalling, and increased Golgi localization of certain STING variants may cause autoimmune disease in some cases.
- Kojiro Mukai
- , Hiroyasu Konno
- & Tomohiko Taguchi
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: On the enzymology and significance of HSPA1 lysine methylation
Correspondence: On the enzymology and significance of HSPA1 lysine methylation
- Magnus E. Jakobsson
- , Anders Moen
- & Pål Ø Falnes

 H3 ubiquitination by NEDD4 regulates H3 acetylation and tumorigenesis
H3 ubiquitination by NEDD4 regulates H3 acetylation and tumorigenesis