Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Raman fingerprint of two terahertz spin wave branches in a two-dimensional honeycomb Ising ferromagnet
Raman fingerprint of two terahertz spin wave branches in a two-dimensional honeycomb Ising ferromagnet
Characteristics of spin waves in recently discovered two-dimensional (2D) Ising ferromagnets are still lacking. Here, Jin and Kim et al. report Raman resonance evidence of two sets of surface spin waves in the 2D honeycomb ferromagnet CrI3.
- Wencan Jin
- , Hyun Ho Kim
- & Rui He
-
Article
| Open Access Determining molecular properties with differential mobility spectrometry and machine learning
Determining molecular properties with differential mobility spectrometry and machine learning
The fast and accurate determination of molecular properties is particularly crucial in drug discovery. Here, the authors employ supervised machine learning to treat differential mobility spectrometry – mass spectrometry data for ten classes of drug candidates and predict several condensed-phase properties.
- Stephen W. C. Walker
- , Ahdia Anwar
- & W. Scott Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access Fast kinetics of multivalent intercalation chemistry enabled by solvated magnesium-ions into self-established metallic layered materials
Fast kinetics of multivalent intercalation chemistry enabled by solvated magnesium-ions into self-established metallic layered materials
While magnesium rechargeable batteries could combine high energy density with low cost and good safety, the extremely sluggish reaction kinetics remains to be overcome. Here, the authors show that by using solvated Mg2+ intercalation, the high charge density of bare Mg2+ may be effectively mitigated.
- Zhenyou Li
- , Xiaoke Mu
- & Maximilian Fichtner
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the role of vacancies in lead halide perovskite through electrical switching of photoluminescence
Unravelling the role of vacancies in lead halide perovskite through electrical switching of photoluminescence
Methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite based solar cells have attracted lots of attention but many physical characteristics of this material remain elusive. Here Li et al. reveal the role of defects in the carrier recombination dynamics in photoluminescence experiments and present a model to describe it.
- Cheng Li
- , Antonio Guerrero
- & Juan Bisquert
-
Article
| Open Access A monoclinic polymorph of sodium birnessite for ultrafast and ultrastable sodium ion storage
A monoclinic polymorph of sodium birnessite for ultrafast and ultrastable sodium ion storage
Layered NaxMnO2 cathode suffers from structural instability and sluggish kinetics. Here the authors show a method to yield monoclinic NaMn2−y−δ(OH)2y, a new polymorph of Na-birnessite with maximum Na occupancy and enlarged interlayer spacing, enabling outstanding cyclability and rate performance.
- Hui Xia
- , Xiaohui Zhu
- & Ying Shirley Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial optic-neural synapse for colored and color-mixed pattern recognition
Artificial optic-neural synapse for colored and color-mixed pattern recognition
Artificial neural networks can emulate the human vision because of their spike-based operation by employing memristors as synapses. Here, Seo et al. integrate synaptic and optical sensing functions in a single heterostructure, which enables accurate and energy-efficient recognition of colored patterns.
- Seunghwan Seo
- , Seo-Hyeon Jo
- & Jin-Hong Park
-
Article
| Open Access Biocatalytic production of adiponitrile and related aliphatic linear α,ω-dinitriles
Biocatalytic production of adiponitrile and related aliphatic linear α,ω-dinitriles
Typically, preparation of the polymer precursors α,ω-dinitriles requires hydrogen cyanide. Here, the authors use aldoxime hydratase to produce adiponitrile and related aliphatic linear dinitriles under ambient conditions starting from readily available substrates without needing hydrogen cyanide.
- Tobias Betke
- , Manuel Maier
- & Harald Gröger
-
Review Article
| Open Access Immediate neurophysiological effects of transcranial electrical stimulation
Immediate neurophysiological effects of transcranial electrical stimulation
Transcranial electrical stimulation techniques, such as tDCS and tACS, are popular tools for neuroscience and clinical therapy, but how low-intensity current might modulate brain activity remains unclear. In this review, the authors review the evidence on mechanisms of transcranial electrical stimulation.
- Anli Liu
- , Mihály Vöröslakos
- & György Buzsáki
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of electron radiation belts at Saturn by Z-mode wave acceleration
Formation of electron radiation belts at Saturn by Z-mode wave acceleration
Radial diffusion is the only mechanism considered to accelerate trapped electrons to relativistic energies in Saturn’s magnetic field, forming radiation belts. Here the authors show another mechanism, electron acceleration via Doppler shifted cyclotron resonant interaction with Z-mode waves, which can form radiation belts inside the orbit of Enceladus.
- E. E. Woodfield
- , R. B. Horne
- & W. S. Kurth
-
Article
| Open Access Melt-driven erosion in microparticle impact
Melt-driven erosion in microparticle impact
Supersonic particle impacts can cause permanent damage to space vehicles and satellites, but how exactly remains unclear. Here, the authors visualise for the first time the high impact of single tin microparticles on a tin substrate and show erosion of ductile metallic materials is melt-driven.
- Mostafa Hassani-Gangaraj
- , David Veysset
- & Christopher A. Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access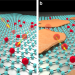 Silicon as a ubiquitous contaminant in graphene derivatives with significant impact on device performance
Silicon as a ubiquitous contaminant in graphene derivatives with significant impact on device performance
Silicon-based contaminants are ubiquitous in natural graphite, and they are thus expected to be present in exfoliated graphene. Here, the authors show that such impurities play a non-negligible role in graphene-based devices, and use high-purity parent graphite to boost the performance of graphene sensors and supercapacitor microelectrodes.
- Rouhollah Jalili
- , Dorna Esrafilzadeh
- & Gordon G. Wallace
-
Article
| Open Access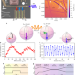 A fast quantum interface between different spin qubit encodings
A fast quantum interface between different spin qubit encodings
The race to produce a quantum computer has driven the development of many different qubit designs with different benefits and drawbacks. Noiri et al. demonstrate a hybrid device with two coupled semiconductor spin qubits of different designs, which should allow each qubit’s advantages to be exploited.
- A. Noiri
- , T. Nakajima
- & S. Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access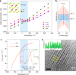 Charge transfer drives anomalous phase transition in ceria
Charge transfer drives anomalous phase transition in ceria
Nanosized ceria has conventionally been thought to have a cubic fluorite structure. Here, the authors use a combination of experiments and simulations to show that oxygen vacancies in ceria promote a charge-transfer induced phase transition from tetragonal to cubic.
- He Zhu
- , Chao Yang
- & Xianran Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Antibiotic sensitivity reveals that wall teichoic acids mediate DNA binding during competence in Bacillus subtilis
Antibiotic sensitivity reveals that wall teichoic acids mediate DNA binding during competence in Bacillus subtilis
Natural genetic transformation in bacteria requires DNA binding at the surface of competent cells. Here, Mirouze et al. show that wall teichoic acids are specifically produced or modified during competence in Bacillus subtilis and promote (directly or indirectly) DNA binding at the cell surface.
- Nicolas Mirouze
- , Cécile Ferret
- & Rut Carballido-López
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and non-contact 3D sample rotation for microscopy
Dynamic and non-contact 3D sample rotation for microscopy
Sample orientation is crucial to ensure optimal image quality in light microscopy. Here the authors enable multi-axis orientation of fixed mouse embryos and shrimp, and live zebrafish embryos and larvae by introducing magnetic beads and rotating the sample with a magnetic field in a microscope.
- Frederic Berndt
- , Gopi Shah
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-organic framework glasses with permanent accessible porosity
Metal-organic framework glasses with permanent accessible porosity
Metal–organic framework glasses have emerged as a new family of melt-quenched glass, but have yet to display the accessible porosity of their crystalline counterparts. Here, Bennett and colleagues report that glasses derived from ZIF-76 parent materials possess 4 – 8 Å pores and exhibit reversible gas adsorption.
- Chao Zhou
- , Louis Longley
- & Thomas D. Bennett
-
Review Article
| Open Access Dimensionality engineering of hybrid halide perovskite light absorbers
Dimensionality engineering of hybrid halide perovskite light absorbers
Organic−inorganic metal halide perovskite solar cells possess high efficiency and low processing cost but suffer poor stability. Here Gao et al. review the recent progress on the 2D–3D mixed perovskites and suggest that greatly improved stability can be achieved without compromising the efficiency.
- Peng Gao
- , Abd Rashid Bin Mohd Yusoff
- & Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin
-
Article
| Open Access 39Ar dating with small samples provides new key constraints on ocean ventilation
39Ar dating with small samples provides new key constraints on ocean ventilation
The rare noble gas isotope 39Ar is the ideal tracer to investigate the ventilation of the deep ocean in the time range of 50 to 1000 years. Here the authors constrain transit time distributions in the eastern Tropical Atlantic with 39Ar-measurements done on a sample size of 5 L of water utilising modern atom-optical techniques.
- Sven Ebser
- , Arne Kersting
- & Markus K. Oberthaler
-
Article
| Open Access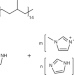 Tuning anhydrous proton conduction in single-ion polymers by crystalline ion channels
Tuning anhydrous proton conduction in single-ion polymers by crystalline ion channels
High-conductivity solid-state electrolyte materials with minimal polarization loss are difficult to synthesize. Here the authors show single-ion block copolymers with crystalline protogenic channels having a promising potential to be used as efficient proton conductors.
- Onnuri Kim
- , Kyoungwook Kim
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled nematic colloidal motors powered by light
Self-assembled nematic colloidal motors powered by light
Biological motors which convert energy into mechanical work inspire the fabrication of synthetic motors. Here the authors demonstrate self-assembled colloidal motors which are driven to a range of responses controlled by the feedback between light polarization and deformation of a liquid crystal.
- Ye Yuan
- , Ghaneema N. Abuhaimed
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article
| Open Access A new look at effective interactions between microgel particles
A new look at effective interactions between microgel particles
Changing temperature of thermoresponsive microgels is typically used as a proxy for modifying volume fraction based on the assumption that doing so does not alter the interaction potential. Bergman et al. shows that this picture is oversimplified and microgels are better described by a multi-Hertzian model.
- Maxime J. Bergman
- , Nicoletta Gnan
- & Peter Schurtenberger
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic phases in two-dimensional active matter
Thermodynamic phases in two-dimensional active matter
Adapting statistical physics tools to study active systems is challenging due to their non-equilibrium nature. Here the authors use simulations to present a phase diagram of a 2D active system, showing a two-step melting scenario far from equilibrium along with gas-liquid motility-induced phase separation.
- Juliane U. Klamser
- , Sebastian C. Kapfer
- & Werner Krauth
-
Article
| Open Access A biomimetic nanoreactor for synergistic chemiexcited photodynamic therapy and starvation therapy against tumor metastasis
A biomimetic nanoreactor for synergistic chemiexcited photodynamic therapy and starvation therapy against tumor metastasis
Photodynamic therapy is usually ineffective against deeply seated metastatic tumors due to poor penetration of the excitation light. Here, the authors design a biomimetic nanoreactor which can convert nutriment glucose into toxic singlet oxygen via chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer with no light excitation and demonstrate its high efficacy in a mouse lung metastatic model.
- Zhengze Yu
- , Ping Zhou
- & Bo Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Communication and quorum sensing in non-living mimics of eukaryotic cells
Communication and quorum sensing in non-living mimics of eukaryotic cells
Cells communicate through chemical and mechanical signals but emulating these in non-living mimics has been challenging. Here the authors present a porous mimic with a DNA-hydrogel ‘nucleus’ that can communicate through diffusive protein signals.
- Henrike Niederholtmeyer
- , Cynthia Chaggan
- & Neal K. Devaraj
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and stable sky-blue delayed fluorescence organic light-emitting diodes with CIEy below 0.4
Efficient and stable sky-blue delayed fluorescence organic light-emitting diodes with CIEy below 0.4
The potential of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) for display and lighting applications is limited by the need for blue emitters that show efficient and stable operation. Here, the authors report stable and efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence OLEDs based on a sky-blue emitter.
- Chin-Yiu Chan
- , Masaki Tanaka
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access Free-space creation of ultralong anti-diffracting beam with multiple energy oscillations adjusted using optical pen
Free-space creation of ultralong anti-diffracting beam with multiple energy oscillations adjusted using optical pen
Anti-diffracting propagation of light beams over infinite distance requires infinite power. Here, the authors develop an approach that uses multiple energy oscillation mechanisms to overcome this limitation, developing a versatile optical pen.
- Xiaoyu Weng
- , Qiang Song
- & Songlin Zhuang
-
Article
| Open Access Pd(OAc)2-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of sterically hindered N-tosylimines
Pd(OAc)2-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of sterically hindered N-tosylimines
Sterically hindered unsaturated compounds are challenging substrates for asymmetric hydrogenation. Here, the authors report a palladium/chiral (bis)phosphine catalytic system that hydrogenates a number of hindered N-tosylimines with excellent enantioselectivitites.
- Jianzhong Chen
- , Zhenfeng Zhang
- & Wanbin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient solar-driven electrocatalytic CO2 reduction in a redox-medium-assisted system
Efficient solar-driven electrocatalytic CO2 reduction in a redox-medium-assisted system
Generating high-energy fuels from sunlight, water, and CO2 using synthetic materials requires, among many things, the careful separation of reduced and oxidized products. Here, authors employ a zinc-based redox pair to spatially and temporally separate light-driven water oxidation and CO2 reduction.
- Yuhang Wang
- , Junlang Liu
- & Gengfeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Double dative bond between divalent carbon(0) and uranium
Double dative bond between divalent carbon(0) and uranium
While chemical bonding between carbon and the d- and p-block elements is relatively well-studied, that between carbon and the f-block elements remains comparatively poorly understood. Here, the authors synthesize a series of uranium−carbone complexes in which carbon forms an unprecedented double dative bond to uranium.
- Wei Su
- , Sudip Pan
- & Congqing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Geometric phase magnetometry using a solid-state spin
Geometric phase magnetometry using a solid-state spin
When performing interferometry-based magnetometry, there is generally a trade-off between sensitivity and range. Here, instead, the authors demonstrate a geometric-phase-based protocol which allows a 400-fold enhancement in static magnetic field range with a single NV-centre without reducing sensitivity.
- K. Arai
- , J. Lee
- & R. L. Walsworth
-
Article
| Open Access Differentiation between enamines and tautomerizable imines in the oxidation reaction with TEMPO
Differentiation between enamines and tautomerizable imines in the oxidation reaction with TEMPO
Tautomerization of imines into enamines is the basis of their similar reactivity; however, minor structural changes may lead to different outcomes. Here, the authors show that the reaction of cyclohexanone and amines in presence of TEMPO affords either α-amino-enones or arylamines depending on the intermediate imine structure.
- Xiaoming Jie
- , Yaping Shang
- & Weiping Su
-
Article
| Open Access Passive directional sub-ambient daytime radiative cooling
Passive directional sub-ambient daytime radiative cooling
Passive daytime radiative cooling presents a promising low-cost refrigeration solution but has thus far relied on specialized nanophotonic structures. Here Bhatia et al. show a directional approach that decouples solar reflectance and infrared emission to achieve superior cooling performance.
- Bikram Bhatia
- , Arny Leroy
- & Evelyn N. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Colossal tunability in high frequency magnetoelectric voltage tunable inductors
Colossal tunability in high frequency magnetoelectric voltage tunable inductors
Voltage tunable inductors (VTIs) with high working frequency and tunability are desired for new design of energy efficient electronics. Here the authors demonstrate magnetoelectric VTIs operating up to 10 MHz with tunability over 750% via strain mediated magnetoelectric effect and magnetocrystalline anisotropy cancellation strategy.
- Yongke Yan
- , Liwei D. Geng
- & Shashank Priya
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging antiferromagnetic antiphase domain boundaries using magnetic Bragg diffraction phase contrast
Imaging antiferromagnetic antiphase domain boundaries using magnetic Bragg diffraction phase contrast
Imaging the antiferromagnetic (AFM) domains facilitates the understanding and design of AFM spintronics but is still challenging. Here the authors show an imaging approach for antiphase domains in AFM Fe2Mo3O8 by resonantly scattered coherent soft X-rays, which is also applicable to collinear antiferromagnets.
- Min Gyu Kim
- , Hu Miao
- & V. Kiryukhin
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding dynamics of coherent Ising machines through simulation of large-scale 2D Ising models
Understanding dynamics of coherent Ising machines through simulation of large-scale 2D Ising models
Coherent Ising machines constitute a possible way to solve Ising models, but there are still open questions about their dynamics. In this work, the authors simulate regular and frustrated 2D lattices, highlighting the role of optical pump power and freeze-out effects for solving optimization problems.
- Fabian Böhm
- , Takahiro Inagaki
- & Hiroki Takesue
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the effect of charge dynamics at the plasmonic metal/semiconductor interface for CO2 photoreduction
Unravelling the effect of charge dynamics at the plasmonic metal/semiconductor interface for CO2 photoreduction
Light-driven CO2 reduction provides a way to limit greenhouse gas concentrations, but understanding how materials accomplish this transformation is challenging. Here, authors examine the reaction over plasmonic silver-titanium dioxide using time-resolved, in situ techniques to follow the mechanism.
- Laura Collado
- , Anna Reynal
- & Víctor A. de la Peña O’Shea
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral interferometry with waveform-dependent relativistic high-order harmonics from plasma surfaces
Spectral interferometry with waveform-dependent relativistic high-order harmonics from plasma surfaces
High-order harmonic generation is explored in gases, solids and plasmas with moderate to high intensity lasers. Here the authors show spectral interferometry of HHG from relativistic plasma and its potential as a source of intense isolated attosecond pulses.
- Dmitrii Kormin
- , Antonin Borot
- & Laszlo Veisz
-
Article
| Open Access Competition between proton transfer and intermolecular Coulombic decay in water
Competition between proton transfer and intermolecular Coulombic decay in water
Interatomic or intermolecular Coulombic decay is responsible for the generation of slow electrons in clusters and biological samples. Here the authors use electron–electron coincidence detection to find the competitive roles of proton transfer and ICD that occur on similar time scales in water clusters.
- Clemens Richter
- , Daniel Hollas
- & Uwe Hergenhahn
-
Article
| Open Access High-entropy high-hardness metal carbides discovered by entropy descriptors
High-entropy high-hardness metal carbides discovered by entropy descriptors
The overwhelming number of possible high-entropy materials represents a big challenge for predicting their existence. Here, the authors introduce an entropy-forming-ability descriptor capturing the synthesizability of these systems, and apply the model to the discovery of new refractory metal carbides.
- Pranab Sarker
- , Tyler Harrington
- & Stefano Curtarolo
-
Article
| Open Access Multidirectional desymmetrization of pluripotent building block en route to diastereoselective synthesis of complex nature-inspired scaffolds
Multidirectional desymmetrization of pluripotent building block en route to diastereoselective synthesis of complex nature-inspired scaffolds
Methods enabling the synthesis of diverse collections of nature-inspired compounds with potential medicinal use are sought after in drug design. Here, the authors report a build/couple/pair strategy to efficiently construct chiral polycyclic scaffolds and show their diversification for drug discovery screening.
- Vunnam Srinivasulu
- , Paul Schilf
- & Taleb H. Al-Tel
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting natural language descriptions of mono-molecular odorants
Predicting natural language descriptions of mono-molecular odorants
It is now possible to predict what a chemical smells like based on its chemical structure, however to date, this has only been done for a small number of odor descriptors. Here, using natural-language semantic representations, the authors demonstrate prediction of a much wider range of descriptors.
- E. Darío Gutiérrez
- , Amit Dhurandhar
- & Guillermo A. Cecchi
-
Article
| Open Access Exchange coupling torque in ferrimagnetic Co/Gd bilayer maximized near angular momentum compensation temperature
Exchange coupling torque in ferrimagnetic Co/Gd bilayer maximized near angular momentum compensation temperature
High speed current induced domain wall motion is key to various spintronic applications, such as memory-storage. Here the authors show that the motion of chiral domain walls in Co/Gd bilayer structures is controlled by an exchange coupling torque that is maximized at the temperature where the Co and Gd angular momenta exactly balance each other
- Robin Bläsing
- , Tianping Ma
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Unicolored phosphor-sensitized fluorescence for efficient and stable blue OLEDs
Unicolored phosphor-sensitized fluorescence for efficient and stable blue OLEDs
The potential of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) for solid-state lighting applications is limited by the need to develop efficient blue emitters. Here, the authors utilize a unicolored phosphor-sensitized fluorescence strategy to demonstrate efficient sky-blue OLEDs with enhanced lifetime.
- Paul Heimel
- , Anirban Mondal
- & Robert Lovrincic
-
Article
| Open Access Excess charge-carrier induced instability of hybrid perovskites
Excess charge-carrier induced instability of hybrid perovskites
Optoelectronic devices based on organic–inorganic halide perovskites show promising performance, but their poor stability impedes the commercialization. Here Lin et al. show that excess free charges are detrimental and efficient charge-carrier extraction is necessary for improved device stability.
- Yuze Lin
- , Bo Chen
- & Jinsong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed AFM height spectroscopy reveals µs-dynamics of unlabeled biomolecules
High-speed AFM height spectroscopy reveals µs-dynamics of unlabeled biomolecules
The dynamics of biomolecules can occur over a wide range of time and length scales. Here the authors develop a high-speed AFM height spectroscopy method to directly detect the motion of unlabeled molecules at Angstrom spatial and microsecond temporal resolution.
- George R. Heath
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating water dissociation kinetics by isolating cobalt atoms into ruthenium lattice
Accelerating water dissociation kinetics by isolating cobalt atoms into ruthenium lattice
Water splitting provides an appealing route to generating carbon-neutral fuel, however the scarcity and cost of platinum, often used as a catalyst, necessitates a search for alternatives. Here, authors show cobalt atoms in ruthenium nanosheets to afford excellent hydrogen production activities.
- Junjie Mao
- , Chun-Ting He
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Cobalt-catalyzed difluoroalkylation of tertiary aryl ketones for facile synthesis of quaternary alkyl difluorides
Cobalt-catalyzed difluoroalkylation of tertiary aryl ketones for facile synthesis of quaternary alkyl difluorides
The catalytic C(sp3)-CF2 bond formation is of high interest in drug design and discovery. Here, the authors report a cobalt-catalyzed difluoroalkylation of tertiary α-C-H bonds of aryl ketones for facile synthesis of quaternary alkyl difluorides and show the late-stage functionalization of marketed drugs.
- Chao Li
- , Yi-Xuan Cao
- & Xi-Sheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding structure-activity relationships in linear polymer photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution
Understanding structure-activity relationships in linear polymer photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution
While inorganic semiconductors are well-studied for their solar-to-fuel energy conversion abilities, organic materials receive far less attention. Here, authors prepare linear conjugated polymers as H2 evolution photocatalysts and rationalize photocatalytic activities with fundamental properties.
- Michael Sachs
- , Reiner Sebastian Sprick
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Pulsed axial epitaxy of colloidal quantum dots in nanowires enables facet-selective passivation
Pulsed axial epitaxy of colloidal quantum dots in nanowires enables facet-selective passivation
The precise control over nanoscale structures is crucial in developing new, functional nanomaterials. Here, authors demonstrate a controllable method to epitaxially stack CdS quantum dots into ZnS nanowires and show improved photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activities.
- Yi Li
- , Tao-Tao Zhuang
- & Shu-Hong Yu

 X-ray rheography uncovers planar granular flows despite non-planar walls
X-ray rheography uncovers planar granular flows despite non-planar walls