Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access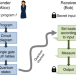 Quantum advantage for probabilistic one-time programs
Quantum advantage for probabilistic one-time programs
Information Theoretically-secure deterministic programs that self-destruct after a single use are known to be impossible to implement. Here, the authors use quantum states to implement a probabilistic version of this fundamental cryptographic primitive, and provide a proof-of-principle implementation with single photons.
- Marie-Christine Roehsner
- , Joshua A. Kettlewell
- & Philip Walther
-
Article
| Open Access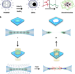 Manipulating and monitoring nanoparticles in micellar thin film superstructures
Manipulating and monitoring nanoparticles in micellar thin film superstructures
Understanding how nanoparticle superstructures respond to external stimuli is of importance to their potential application. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of cryo-transmission electron microscopy for monitoring and manipulating movement within nanoparticle-loaded dendrimicelle superstructure thin films upon irradiation with an electron beam.
- Jan Bart ten Hove
- , Fijs W. B. van Leeuwen
- & Aldrik H. Velders
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical and programmable one-pot synthesis of oligosaccharides
Hierarchical and programmable one-pot synthesis of oligosaccharides
The software Optimer has aided the programmable one-pot oligosaccharide synthesis with a library of 50 Building BLocks (BBLs). Here, the authors expanded Optimer's validated and virtual libraries of BBLs and developed Auto-CHO, a software which allows the one-pot programmable synthesis of more complex glycans.
- Cheng-Wei Cheng
- , Yixuan Zhou
- & Chi-Huey Wong
-
Article
| Open Access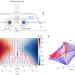 The two-fluid dynamics and energetics of the asymmetric magnetic reconnection in laboratory and space plasmas
The two-fluid dynamics and energetics of the asymmetric magnetic reconnection in laboratory and space plasmas
Magnetic energy in the plasma is transferred into particle energy by magnetic reconnection. Here the authors show the two-fluid dynamics of asymmetric magnetic reconnection in two different spatial scales of plasma, namely laboratory and astrophysical plasma.
- M. Yamada
- , L.-J. Chen
- & R. Torbert
-
Article
| Open Access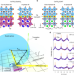 Three-dimensional atomic scale electron density reconstruction of octahedral tilt epitaxy in functional perovskites
Three-dimensional atomic scale electron density reconstruction of octahedral tilt epitaxy in functional perovskites
In complex oxides, oxygen octahedra are major structural motifs and their tilts sensitively determine the material’s physical properties. Exploiting Coherent Bragg Rod Analysis enables 3D mapping of complex tilt patterns and reveals the means to control polarization through them in CaTiO3 thin films.
- Yakun Yuan
- , Yanfu Lu
- & Venkatraman Gopalan
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of the strength and timing of sunspot cycle 25 reveal decadal-scale space environmental conditions
Prediction of the strength and timing of sunspot cycle 25 reveal decadal-scale space environmental conditions
The Sun’s activity cycle impacts space-reliant technologies and the Earth’s climate, but predicting this is challenging. An ensemble forecast based on an innovative combination of two solar magnetic field evolution models indicates a weak, but not insignificant sunspot cycle 25 peaking in 2024.
- Prantika Bhowmik
- & Dibyendu Nandy
-
Article
| Open Access Layer-edge device of two-dimensional hybrid perovskites
Layer-edge device of two-dimensional hybrid perovskites
The edge of the thin sheets of two dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite crystals shows exotic physical properties that remain unexplored. Here Cheng et al. make electronic devices and study their transport properties, photoresponses and humid sensitivities which show large anisotropy.
- Bin Cheng
- , Ting-You Li
- & Jr-Hau He
-
Article
| Open Access Selective production of phase-separable product from a mixture of biomass-derived aqueous oxygenates
Selective production of phase-separable product from a mixture of biomass-derived aqueous oxygenates
The efficiency and selectivity of the transformation process for an aqueous solution of mixed oxygenates produced by biomass fermentation remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a simple reaction for the conversion of aqueous biomass fermentation broth to a water-immiscible product efficiently and selectively.
- Yehong Wang
- , Mi Peng
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Wavepacket insights into the photoprotection mechanism of the UV filter methyl anthranilate
Wavepacket insights into the photoprotection mechanism of the UV filter methyl anthranilate
Here, the authors explore the ultrafast photodynamics of methyl anthranilate. From the quantum beat behavior, the authors find evidence for ultrafast energy redistribution processes which hinder excited state relaxation, making methyl anthranilate a poor choice for a sunscreen chemical filter.
- Natércia d. N. Rodrigues
- , Neil C. Cole-Filipiak
- & Vasilios G. Stavros
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable production of highly conductive multilayer graphene ink for wireless connectivity and IoT applications
Sustainable production of highly conductive multilayer graphene ink for wireless connectivity and IoT applications
Printed conductive inks show promise for future electronic device applications. Here, the authors report synthesis of graphene inks with conductivity of 7.13 × 10^4 S/m by Cyrene assisted liquid phase exfoliation, and their applications in data communication and RF energy harvesting.
- Kewen Pan
- , Yangyang Fan
- & Zhirun Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Seamless lateral graphene p–n junctions formed by selective in situ doping for high-performance photodetectors
Seamless lateral graphene p–n junctions formed by selective in situ doping for high-performance photodetectors
Fabricating lateral graphene p–n junctions with controlled doping levels is instrumental to realize ultrafast and efficient optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors report a seamless graphene based photodetector doped by selective ion implantation and in-situ chemical vapour deposition.
- Gang Wang
- , Miao Zhang
- & Xi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access H2 roaming chemistry and the formation of H3+ from organic molecules in strong laser fields
H2 roaming chemistry and the formation of H3+ from organic molecules in strong laser fields
H2 roaming is associated with H3+ formation when certain organic molecules are exposed to strong laser fields. Here, the mechanistic details and time-resolved dynamics of H3+ formation from a series of alcohols were obtained and found that the product yield decreases as the carbon chain length increases.
- Nagitha Ekanayake
- , Travis Severt
- & Marcos Dantus
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon induced thermoelectric effect in graphene
Plasmon induced thermoelectric effect in graphene
The photoresponse of graphene-based photodetectors is dominated by photovoltaic and photothermoelectric effects. Here, the authors leverage strongly localised plasmonic heating of graphene carriers to detect a second photothermoelectric effect occurring across a homogeneous channel in the presence of an electronic temperature gradient.
- Viktoryia Shautsova
- , Themistoklis Sidiropoulos
- & Rupert F. Oulton
-
Article
| Open Access Aqueous thermogalvanic cells with a high Seebeck coefficient for low-grade heat harvest
Aqueous thermogalvanic cells with a high Seebeck coefficient for low-grade heat harvest
Achieving high thermopower in liquid-state thermogalvanic cells is vital to realize a low-cost technology solution for thermal-to-electrical energy conversion. Here, the authors present aqueous thermogalvanic cells based on modified electrolyte with enhanced Seebeck coefficient and thermopower.
- Jiangjiang Duan
- , Guang Feng
- & Jun Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired and bristled microparticles for ultrasensitive pressure and strain sensors
Bioinspired and bristled microparticles for ultrasensitive pressure and strain sensors
The potential of electromechanical sensors has been limited by low volumetric density in sensing sites. Here, the authors demonstrate ultrasensitive pressure and strain sensors using ZnO microparticles that have high-aspect ratio and high-density nanostructured spines mimicking bristles in insects.
- Bing Yin
- , Xiaomeng Liu
- & Jun Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Minimizing the electrosorption of water from humid ionic liquids on electrodes
Minimizing the electrosorption of water from humid ionic liquids on electrodes
Ionic liquid electrolytes can impart increased operational voltage and energy density in supercapacitors, but water may diminish performance. Here the authors show that the hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of ionic liquids can influence electrosorption of water and ultimately the supercapacitor performance.
- Sheng Bi
- , Runxi Wang
- & Guang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Coincident molecular auxeticity and negative order parameter in a liquid crystal elastomer
Coincident molecular auxeticity and negative order parameter in a liquid crystal elastomer
Auxeticity in synthetic materials is realised by geometrical design of porous structures rather than on a molecular level. Here the authors demonstrate auxeticity in a non-porous liquid crystal elastomer overcoming porosity related weakening of the material and opening a pathway to designed molecular auxetic materials.
- D. Mistry
- , S. D. Connell
- & H. F. Gleeson
-
Article
| Open Access Self-limited single nanowire systems combining all-in-one memristive and neuromorphic functionalities
Self-limited single nanowire systems combining all-in-one memristive and neuromorphic functionalities
Memristors have become an emerging technology capable in emulating human brain information processing, but understanding and controlling the switching mechanism remains elusive. Here, Milano et al. combine memristive and neuromorphic functionalities in a single crystalline nanowire model system.
- Gianluca Milano
- , Michael Luebben
- & Ilia Valov
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance reconstruction of microscopic force fields from Brownian trajectories
High-performance reconstruction of microscopic force fields from Brownian trajectories
The measure of microscopic forces is currently dominated by optical methods requiring parameter-based analyses and long data acquisitions. This work describes a fast and parameter-free method that can characterize both the conservative and non-conservative force fields acting on Brownian particles.
- Laura Pérez García
- , Jaime Donlucas Pérez
- & Giovanni Volpe
-
Article
| Open Access Long distance electron transfer through the aqueous solution between redox partner proteins
Long distance electron transfer through the aqueous solution between redox partner proteins
Electron transport chains rely on interactions between redox proteins, but the distance-dependence of the electron transfer rate through the solution is unknown. Here, the authors show that the current between two redox protein partners occurs at long distances and is electrochemically gated.
- Anna Lagunas
- , Alejandra Guerra-Castellano
- & Pau Gorostiza
-
Article
| Open Access Inertial delay of self-propelled particles
Inertial delay of self-propelled particles
Active matter describes a group of interacting units showing collective motions by constantly consuming energy from the environment, but inertia has largely been overlooked in this context. Scholz et al. show how important it can be by characterizing the dynamics of self-propelled particles in a model system.
- Christian Scholz
- , Soudeh Jahanshahi
- & Hartmut Löwen
-
Article
| Open Access The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration
The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration
Diversity is believed to raise effectiveness and performance but it contains many aspects. Here the authors studied the relationship between research impact and five classes of diversity and found that ethnic diversity had the strongest correlation with scientific impact.
- Bedoor K. AlShebli
- , Talal Rahwan
- & Wei Lee Woon
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive particle representation of fluorescence microscopy images
Adaptive particle representation of fluorescence microscopy images
Modern microscopes can generate high volumes of 3D images, driving difficulties in data handling and processing. Here, the authors present a content-adaptive image representation as an alternative to standard pixels that goes beyond data compression to overcome storage, memory, and processing bottlenecks.
- Bevan L. Cheeseman
- , Ulrik Günther
- & Ivo F. Sbalzarini
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative adsorption of carbon disulfide in diamine-appended metal–organic frameworks
Cooperative adsorption of carbon disulfide in diamine-appended metal–organic frameworks
The large-scale production of CS2 presents both environmental and biological hazards, yet adsorbents capable of CS2 capture remain scarcely explored. Here, Long and colleagues demonstrate that CS2 is adsorbed in diamine-appended metal–organic frameworks through a cooperative and chemically specific insertion process.
- C. Michael McGuirk
- , Rebecca L. Siegelman
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical field-free three-dimensional orientation of asymmetric-top molecules
All-optical field-free three-dimensional orientation of asymmetric-top molecules
Alignment and orientation of the molecules allows studying the photon-molecule interactions in greater detail. Here the authors demonstrate the three-dimensional orientation of SO2 molecules in using COLTRIMS and orthogonally polarized laser pulses but in the absence of DC field.
- Kang Lin
- , Ilia Tutunnikov
- & Jian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A simple and robust approach to reducing contact resistance in organic transistors
A simple and robust approach to reducing contact resistance in organic transistors
Minimizing contact effects in organic semiconductor-based devices is a key step toward the development of a low-cost technology for next-generation electronics. Here, the authors reduce contact resistance in organic devices by engineering electrodes with high work function surface domains.
- Zachary A. Lamport
- , Katrina J. Barth
- & Oana D. Jurchescu
-
Article
| Open Access Solar cell designs by maximizing energy production based on machine learning clustering of spectral variations
Solar cell designs by maximizing energy production based on machine learning clustering of spectral variations
Though multijunction solar cells can exceed silicon technology in terms of standard efficiency, the uncertainty in solar spectral changes impacts its energy production. Here, the authors use machine learning techniques to predict the optimal solar cell designs in terms of yearly averaged efficiency.
- J. M. Ripalda
- , J. Buencuerpo
- & I. García
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic reconnection driven by electron dynamics
Magnetic reconnection driven by electron dynamics
Magnetic reconnection is the process of releasing energy by magnetized and space plasma. Here the authors report experimental observation of magnetic reconnection in laser-produced plasma and the role of electron scaling on reconnection.
- Y. Kuramitsu
- , T. Moritaka
- & M. Hoshino
-
Article
| Open Access Entangled polymer dynamics beyond reptation
Entangled polymer dynamics beyond reptation
Polymer dynamics at entangled conditions has generally been simplified as motions governed by the two ends of each polymer chain. Abadi et al. characterize linear and cyclic dsDNA molecules with high resolution, revealing position-dependent chain motions which cannot be described by the reptation theory.
- Maram Abadi
- , Maged F. Serag
- & Satoshi Habuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Dissymmetry enhancement in enantioselective synthesis of helical polydiacetylene by application of superchiral light
Dissymmetry enhancement in enantioselective synthesis of helical polydiacetylene by application of superchiral light
Superchiral light can be utilized to promote asymmetric photochemical reactions. Here the authors show that superchiral light imparts greater chiral bias to trigger asymmetric photo-polymerization reactions from initially achiral diacetylene monomers and enhanced optical dissymmetry in polydiacetylene films.
- Chenlu He
- , Guang Yang
- & Gang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoribbons self-assembled from short peptides demonstrate the formation of polar zippers between β-sheets
Nanoribbons self-assembled from short peptides demonstrate the formation of polar zippers between β-sheets
Peptide self-assembly is a hierarchical process which includes forming β-sheets but the formation of high ordered structures remains largely unexplored. Here the authors report on a super-secondary structural template, based on well-defined hydrogen bonds by rational design and assembly of short peptides
- Meng Wang
- , Jiqian Wang
- & Hai Xu
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray rheography uncovers planar granular flows despite non-planar walls
X-ray rheography uncovers planar granular flows despite non-planar walls
Tracking the deformation of opaque materials under their surfaces is fascinating, yet a challenging task, which has been constrained to static conditions or model materials to date. Here, Baker et al. develop X-ray rheography to reconstruct three-dimensional velocity fields in general granular media.
- James Baker
- , François Guillard
- & Itai Einav
-
Article
| Open Access Raman fingerprint of two terahertz spin wave branches in a two-dimensional honeycomb Ising ferromagnet
Raman fingerprint of two terahertz spin wave branches in a two-dimensional honeycomb Ising ferromagnet
Characteristics of spin waves in recently discovered two-dimensional (2D) Ising ferromagnets are still lacking. Here, Jin and Kim et al. report Raman resonance evidence of two sets of surface spin waves in the 2D honeycomb ferromagnet CrI3.
- Wencan Jin
- , Hyun Ho Kim
- & Rui He
-
Article
| Open Access Determining molecular properties with differential mobility spectrometry and machine learning
Determining molecular properties with differential mobility spectrometry and machine learning
The fast and accurate determination of molecular properties is particularly crucial in drug discovery. Here, the authors employ supervised machine learning to treat differential mobility spectrometry – mass spectrometry data for ten classes of drug candidates and predict several condensed-phase properties.
- Stephen W. C. Walker
- , Ahdia Anwar
- & W. Scott Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access Fast kinetics of multivalent intercalation chemistry enabled by solvated magnesium-ions into self-established metallic layered materials
Fast kinetics of multivalent intercalation chemistry enabled by solvated magnesium-ions into self-established metallic layered materials
While magnesium rechargeable batteries could combine high energy density with low cost and good safety, the extremely sluggish reaction kinetics remains to be overcome. Here, the authors show that by using solvated Mg2+ intercalation, the high charge density of bare Mg2+ may be effectively mitigated.
- Zhenyou Li
- , Xiaoke Mu
- & Maximilian Fichtner
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the role of vacancies in lead halide perovskite through electrical switching of photoluminescence
Unravelling the role of vacancies in lead halide perovskite through electrical switching of photoluminescence
Methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite based solar cells have attracted lots of attention but many physical characteristics of this material remain elusive. Here Li et al. reveal the role of defects in the carrier recombination dynamics in photoluminescence experiments and present a model to describe it.
- Cheng Li
- , Antonio Guerrero
- & Juan Bisquert
-
Article
| Open Access A monoclinic polymorph of sodium birnessite for ultrafast and ultrastable sodium ion storage
A monoclinic polymorph of sodium birnessite for ultrafast and ultrastable sodium ion storage
Layered NaxMnO2 cathode suffers from structural instability and sluggish kinetics. Here the authors show a method to yield monoclinic NaMn2−y−δ(OH)2y, a new polymorph of Na-birnessite with maximum Na occupancy and enlarged interlayer spacing, enabling outstanding cyclability and rate performance.
- Hui Xia
- , Xiaohui Zhu
- & Ying Shirley Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial optic-neural synapse for colored and color-mixed pattern recognition
Artificial optic-neural synapse for colored and color-mixed pattern recognition
Artificial neural networks can emulate the human vision because of their spike-based operation by employing memristors as synapses. Here, Seo et al. integrate synaptic and optical sensing functions in a single heterostructure, which enables accurate and energy-efficient recognition of colored patterns.
- Seunghwan Seo
- , Seo-Hyeon Jo
- & Jin-Hong Park
-
Article
| Open Access Biocatalytic production of adiponitrile and related aliphatic linear α,ω-dinitriles
Biocatalytic production of adiponitrile and related aliphatic linear α,ω-dinitriles
Typically, preparation of the polymer precursors α,ω-dinitriles requires hydrogen cyanide. Here, the authors use aldoxime hydratase to produce adiponitrile and related aliphatic linear dinitriles under ambient conditions starting from readily available substrates without needing hydrogen cyanide.
- Tobias Betke
- , Manuel Maier
- & Harald Gröger
-
Review Article
| Open Access Immediate neurophysiological effects of transcranial electrical stimulation
Immediate neurophysiological effects of transcranial electrical stimulation
Transcranial electrical stimulation techniques, such as tDCS and tACS, are popular tools for neuroscience and clinical therapy, but how low-intensity current might modulate brain activity remains unclear. In this review, the authors review the evidence on mechanisms of transcranial electrical stimulation.
- Anli Liu
- , Mihály Vöröslakos
- & György Buzsáki
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of electron radiation belts at Saturn by Z-mode wave acceleration
Formation of electron radiation belts at Saturn by Z-mode wave acceleration
Radial diffusion is the only mechanism considered to accelerate trapped electrons to relativistic energies in Saturn’s magnetic field, forming radiation belts. Here the authors show another mechanism, electron acceleration via Doppler shifted cyclotron resonant interaction with Z-mode waves, which can form radiation belts inside the orbit of Enceladus.
- E. E. Woodfield
- , R. B. Horne
- & W. S. Kurth
-
Article
| Open Access Melt-driven erosion in microparticle impact
Melt-driven erosion in microparticle impact
Supersonic particle impacts can cause permanent damage to space vehicles and satellites, but how exactly remains unclear. Here, the authors visualise for the first time the high impact of single tin microparticles on a tin substrate and show erosion of ductile metallic materials is melt-driven.
- Mostafa Hassani-Gangaraj
- , David Veysset
- & Christopher A. Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon as a ubiquitous contaminant in graphene derivatives with significant impact on device performance
Silicon as a ubiquitous contaminant in graphene derivatives with significant impact on device performance
Silicon-based contaminants are ubiquitous in natural graphite, and they are thus expected to be present in exfoliated graphene. Here, the authors show that such impurities play a non-negligible role in graphene-based devices, and use high-purity parent graphite to boost the performance of graphene sensors and supercapacitor microelectrodes.
- Rouhollah Jalili
- , Dorna Esrafilzadeh
- & Gordon G. Wallace
-
Article
| Open Access A fast quantum interface between different spin qubit encodings
A fast quantum interface between different spin qubit encodings
The race to produce a quantum computer has driven the development of many different qubit designs with different benefits and drawbacks. Noiri et al. demonstrate a hybrid device with two coupled semiconductor spin qubits of different designs, which should allow each qubit’s advantages to be exploited.
- A. Noiri
- , T. Nakajima
- & S. Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access Charge transfer drives anomalous phase transition in ceria
Charge transfer drives anomalous phase transition in ceria
Nanosized ceria has conventionally been thought to have a cubic fluorite structure. Here, the authors use a combination of experiments and simulations to show that oxygen vacancies in ceria promote a charge-transfer induced phase transition from tetragonal to cubic.
- He Zhu
- , Chao Yang
- & Xianran Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Antibiotic sensitivity reveals that wall teichoic acids mediate DNA binding during competence in Bacillus subtilis
Antibiotic sensitivity reveals that wall teichoic acids mediate DNA binding during competence in Bacillus subtilis
Natural genetic transformation in bacteria requires DNA binding at the surface of competent cells. Here, Mirouze et al. show that wall teichoic acids are specifically produced or modified during competence in Bacillus subtilis and promote (directly or indirectly) DNA binding at the cell surface.
- Nicolas Mirouze
- , Cécile Ferret
- & Rut Carballido-López
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and non-contact 3D sample rotation for microscopy
Dynamic and non-contact 3D sample rotation for microscopy
Sample orientation is crucial to ensure optimal image quality in light microscopy. Here the authors enable multi-axis orientation of fixed mouse embryos and shrimp, and live zebrafish embryos and larvae by introducing magnetic beads and rotating the sample with a magnetic field in a microscope.
- Frederic Berndt
- , Gopi Shah
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-organic framework glasses with permanent accessible porosity
Metal-organic framework glasses with permanent accessible porosity
Metal–organic framework glasses have emerged as a new family of melt-quenched glass, but have yet to display the accessible porosity of their crystalline counterparts. Here, Bennett and colleagues report that glasses derived from ZIF-76 parent materials possess 4 – 8 Å pores and exhibit reversible gas adsorption.
- Chao Zhou
- , Louis Longley
- & Thomas D. Bennett
-
Review Article
| Open Access Dimensionality engineering of hybrid halide perovskite light absorbers
Dimensionality engineering of hybrid halide perovskite light absorbers
Organic−inorganic metal halide perovskite solar cells possess high efficiency and low processing cost but suffer poor stability. Here Gao et al. review the recent progress on the 2D–3D mixed perovskites and suggest that greatly improved stability can be achieved without compromising the efficiency.
- Peng Gao
- , Abd Rashid Bin Mohd Yusoff
- & Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin

 Real-time determination of enantiomeric and isomeric content using photoelectron elliptical dichroism
Real-time determination of enantiomeric and isomeric content using photoelectron elliptical dichroism