Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Onset of meso-scale turbulence in active nematics
Onset of meso-scale turbulence in active nematics
Bacteria continuously inject energy into their surroundings and thus induce chaotic like flows, namely meso-scale turbulence. Here, the authors show that transition to meso-scale turbulence and inertial turbulence observed in pipes share the same scaling behavior that belongs to the directed percolation universality class.
- Amin Doostmohammadi
- , Tyler N. Shendruk
- & Julia M. Yeomans
-
Article
| Open Access High precision hyperfine measurements in Bismuth challenge bound-state strong-field QED
High precision hyperfine measurements in Bismuth challenge bound-state strong-field QED
Precision measurements provide a sensitive test of fundamental constants and their uncertainties. Here the authors precisely measure the hyperfine structure splitting in bismuth ions, and report significant discrepancy with the theoretical prediction of quantum electrodynamics.
- Johannes Ullmann
- , Zoran Andelkovic
- & Wilfried Nörtershäuser
-
Article
| Open Access Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics
Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics
Self-powered nanogenerators by harvesting energy from the environment are desirable for future portable and wearable electronics. Liet al. show the use of ferroelectret nanogenerators to build microphone or loudspeaker, which convert electrical signals to mechanical motions in a reversible manner.
- Wei Li
- , David Torres
- & Nelson Sepúlveda
-
Article
| Open Access An in-plane magnetic chiral dichroism approach for measurement of intrinsic magnetic signals using transmitted electrons
An in-plane magnetic chiral dichroism approach for measurement of intrinsic magnetic signals using transmitted electrons
Electron energy-loss magnetic chiral dichroism enables the measurement of the local magnetic properties of a material using a transmission electron microscope, but is limited to signals in the electron-beam direction. Here, the authors demonstrate a method to extend this to in-plane magnetic signals too.
- Dongsheng Song
- , Amir H. Tavabi
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access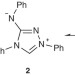 New Blatter-type radicals from a bench-stable carbene
New Blatter-type radicals from a bench-stable carbene
Blatter’s radicals are highly valuable stable organic free radicals, comprising a heterocyclic ring system functionalized with a heteroaryl or alkyl group at the C-3 position. Here, the authors report a synthetic strategy to obtain Blatter’s radical substituted with an amine and amide group.
- Jacob A. Grant
- , Zhou Lu
- & AnnMarie C. O’Donoghue
-
Article
| Open Access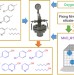 Controllable cyanation of carbon-hydrogen bonds by zeolite crystals over manganese oxide catalyst
Controllable cyanation of carbon-hydrogen bonds by zeolite crystals over manganese oxide catalyst
Sustainable strategies for nitrile synthesis are needed. Here, the authors report an environmentally benign, selective heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of nitriles by the oxidative cyanation of carbon and hydrogen (C-H) bonds, which comprises nanoscale manganese oxide catalysts fixed inside a zeolite crystal.
- Liang Wang
- , Guoxiong Wang
- & Feng-Shou Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Absorptive pinhole collimators for ballistic Dirac fermions in graphene
Absorptive pinhole collimators for ballistic Dirac fermions in graphene
Shaping and guiding the flow of ballistic electrons is at the core of electron optics; however in graphene this is hindered by chiral tunneling. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate an electron collimator based on hBN-encapsulated ballistic graphene, capable of emitting narrow electron beams.
- Arthur W. Barnard
- , Alex Hughes
- & David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Article
| Open Access Mid-infrared coincidence measurements on twin photons at room temperature
Mid-infrared coincidence measurements on twin photons at room temperature
Quantum optics in the mid-infrared is difficult due to the lack of suitable detectors. Here the authors show that by spectral translation it is possible to develop a room temperature mid-infrared detector suitable for coincidence measurements on non-degenerate twin photons.
- M. Mancinelli
- , A. Trenti
- & L. Pavesi
-
Article
| Open Access Probing nanofriction and Aubry-type signatures in a finite self-organized system
Probing nanofriction and Aubry-type signatures in a finite self-organized system
Superlubricity has been predicted and observed at an atomistic level, yet its dynamics is not well understood due to the lack ofin situ characterization of contact surfaces. Kiethe et al. use a trapped two-dimensional ion crystal as a model for the study of nanofriction in self-organized structures.
- J. Kiethe
- , R. Nigmatullin
- & T. E. Mehlstäubler
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of the universal magnetoelectric effect in a 3D topological insulator
Observation of the universal magnetoelectric effect in a 3D topological insulator
The electrodynamics of topological insulators has been predicted to show a new magnetoelectric term, but this hasn’t been observed. Here, Dziomet al. observe a universal Faraday rotation angle equal to the fine structure constant, evidencing the so-called topological magnetoelectric effect.
- V. Dziom
- , A. Shuvaev
- & L. W. Molenkamp
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic diversity of synthetic supramolecular polymers in water as revealed by hydrogen/deuterium exchange
Dynamic diversity of synthetic supramolecular polymers in water as revealed by hydrogen/deuterium exchange
Understanding the dynamics of supramolecular architectures without using labels is crucial for developing advanced biosystems. Here, the authors show kinetic hydrogen/deuterium exchange profiles for a series of water-soluble supramolecular polymers.
- Xianwen Lou
- , René P. M. Lafleur
- & E W Meijer
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusive and martensitic nucleation kinetics in solid-solid transitions of colloidal crystals
Diffusive and martensitic nucleation kinetics in solid-solid transitions of colloidal crystals
Solid-solid transitions between different crystalline structures have broad implications in earth science, steel and ceramic materials. Penget al. show a transformation pathway that starts off as being martensitic then switches to diffusive at the single particle level in a colloidal system under pressure.
- Yi Peng
- , Wei Li
- & Yilong Han
-
Article
| Open Access Energy efficiency to reduce residential electricity and natural gas use under climate change
Energy efficiency to reduce residential electricity and natural gas use under climate change
Climate change may alter building energy demand. Here, the authors quantify changes in residential electricity and natural gas demand in Los Angeles County and find that rising temperatures may increase electricity demand by 41–87% between 2020 and 2060, but improved efficiency could lower this increase to 28%.
- Janet L. Reyna
- & Mikhail V. Chester
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser
An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser
The breaking of parity-time symmetric gain and loss profiles can be used to achieve single-mode lasing in coupled microring resonators. Here, Liuet al. show that this effect can be electrically controlled with a tunable lasing wavelength and strong sidemode suppression.
- Weilin Liu
- , Ming Li
- & Jianping Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Underwater Leidenfrost nanochemistry for creation of size-tailored zinc peroxide cancer nanotherapeutics
Underwater Leidenfrost nanochemistry for creation of size-tailored zinc peroxide cancer nanotherapeutics
Water can function as a sustainable reactor for the synthesis of size-controlled, functional nanoparticles. Here, the authors introduce an underwater Leidenfrost synthesis that reproduces the dynamic chemistry of the deep ocean, in which anticancer therapeutic ZnO2nanoclusters form in an overheated zone and migrate to colder water to continue growth.
- Mady Elbahri
- , Ramzy Abdelaziz
- & Moheb Abdelaziz
-
Article
| Open Access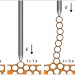 Formation of printable granular and colloidal chains through capillary effects and dielectrophoresis
Formation of printable granular and colloidal chains through capillary effects and dielectrophoresis
Conductive colloidal chains are promising for electronics but difficult to synthesize outside of a liquid environment. Here, the authors use field-directed assembly and capillary effects to pull conductive particle chains out of a suspension, which remain held together by flexible liquid bridges even after the external field is turned off.
- Zbigniew Rozynek
- , Ming Han
- & Erik Luijten
-
Article
| Open Access Pore configuration landscape of granular crystallization
Pore configuration landscape of granular crystallization
Emergence and growth of crystalline domains in granular media remains under-explored. Here, the authors analyse tomographic snapshots from partially recrystallized packings of spheres using persistent homology and find agreement with proposed transitions based on continuous deformation of octahedral and tetrahedral voids.
- M. Saadatfar
- , H. Takeuchi
- & Y. Hiraoka
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum vertex model for reversible classical computing
Quantum vertex model for reversible classical computing
Solutions of computations can be encoded in the ground state of many-body spin models. Here the authors show that solutions to generic reversible classical computations can be encoded in the ground state of a vertex model, which can be reached without finite temperature phase transitions.
- C. Chamon
- , E. R. Mucciolo
- & Z.-C. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Using shape to turn off blinking for two-colour multiexciton emission in CdSe/CdS tetrapods
Using shape to turn off blinking for two-colour multiexciton emission in CdSe/CdS tetrapods
CdSe/CdS tetrapods exhibit the unusual trait of two-colour multiexcitonic emission. Here Mishraet al. study this type of dual emission at the single-nanocrystal level. By tuning arm diameter and length they seek to understand shape-dependent evolution of the emission and of blinking behaviour.
- Nimai Mishra
- , Noah J. Orfield
- & Jennifer A. Hollingsworth
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time atomistic observation of structural phase transformations in individual hafnia nanorods
Real-time atomistic observation of structural phase transformations in individual hafnia nanorods
The high-temperature tetragonal phase of HfO2 is technologically useful but difficult to stabilize at room temperature. Here, the authors observe in real-time the transformation of a HfO2nanorod from its room temperature to tetragonal phase, at 1000° less than its bulk temperature, suggesting that size confinement may kinetically trap this phase.
- Bethany M. Hudak
- , Sean W. Depner
- & Beth S. Guiton
-
Article
| Open Access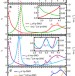 Tunable and low-loss correlated plasmons in Mott-like insulating oxides
Tunable and low-loss correlated plasmons in Mott-like insulating oxides
Conventional plasmons in metals often suffer from high plasmonic loss in the optical range. Here, the authors report a distinct form of tunable correlated plasmons in Mott-like insulating Sr1−xNbO3+δfilms, with multiple plasmon frequencies and low loss in the visible-ultraviolet range.
- Teguh Citra Asmara
- , Dongyang Wan
- & Andrivo Rusydi
-
Article
| Open Access Giant five-photon absorption from multidimensional core-shell halide perovskite colloidal nanocrystals
Giant five-photon absorption from multidimensional core-shell halide perovskite colloidal nanocrystals
The small high-order multi-photon action cross-section of traditional biological imaging media presents a fundamental limitation for deep-tissue nonlinear optical imaging. Here the authors overcome this limitation by employing multidimensional core–shell perovskite nanocrystals.
- Weiqiang Chen
- , Saikat Bhaumik
- & Tze Chien Sum
-
Article
| Open Access Face classification using electronic synapses
Face classification using electronic synapses
Using chips that mimic the human brain to perform cognitive tasks, namely neuromorphic computing, calls for low power and high efficiency hardware. Here, Yaoet al. show on-chip analogue weight storage by integrating non-volatile resistive memory into a CMOS platform and test it in facial recognition.
- Peng Yao
- , Huaqiang Wu
- & He Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast all-optical tuning of direct-gap semiconductor metasurfaces
Ultrafast all-optical tuning of direct-gap semiconductor metasurfaces
Metasurfaces are not adjustable after fabrication, and a critical challenge is to realise a technique of tuning their optical properties that is both fast and efficient. Here, Shcherbakov et al. realise an ultrafast tunable metasurface with picosecond-scale large absolute reflectance modulation at low pump fluences.
- Maxim R. Shcherbakov
- , Sheng Liu
- & Andrey A. Fedyanin
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and interstitial iodide migration in hybrid perovskite methylammonium lead iodide
Structure and interstitial iodide migration in hybrid perovskite methylammonium lead iodide
The mechanism underpinning the photovoltaic effect in hybrid perovskite solar cells has remained unclear. Here, Green and co-workers suggest that iodide ions in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite migrate via interstitial sites and undergo a redox reaction to form molecular iodine and free electrons.
- J. L. Minns
- , P. Zajdel
- & M. A. Green
-
Article
| Open Access Super-diffusion of excited carriers in semiconductors
Super-diffusion of excited carriers in semiconductors
Determining the spatial dynamics of excited carriers will provide a more complete understanding of ultrafast carrier dynamics in materials. Using scanning ultrafast electron microscopy, Najafiet al. are able to observe the spatiotemporal dynamics of excited electron and hole carriers in silicon.
- Ebrahim Najafi
- , Vsevolod Ivanov
- & Marco Bernardi
-
Article
| Open Access Fast oxygen diffusion and iodide defects mediate oxygen-induced degradation of perovskite solar cells
Fast oxygen diffusion and iodide defects mediate oxygen-induced degradation of perovskite solar cells
Determining the degradation pathways in lead halide perovskites is key to its development as a viable solar technology. Aristidouet al. identify iodide vacancies as the preferred sites in mediating the photo-induced formation of superoxide species from intercalated oxygen.
- Nicholas Aristidou
- , Christopher Eames
- & Saif A. Haque
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning the effective spin-orbit coupling in molecular semiconductors
Tuning the effective spin-orbit coupling in molecular semiconductors
Organic semiconductors with long spin lifetime hold promise for future spintronics devices that can process and store information. Here, Schottet al. perform a systematic study of the strength of spin-orbit coupling and its effect on spin lifetime over 32 promising molecules with high charge mobility.
- Sam Schott
- , Erik R. McNellis
- & Henning Sirringhaus
-
Article
| Open Access Kondo blockade due to quantum interference in single-molecule junctions
Kondo blockade due to quantum interference in single-molecule junctions
Exploring the interplay of quantum effects enriches the scientific and technological understanding in nanoscale devices. The authors find that two apparently different quantum effects, quantum interference and the Kondo effect, can be unified to describe electron transport in single-molecule junctions.
- Andrew K. Mitchell
- , Kim G. L. Pedersen
- & Jens Paaske
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency and high-power rechargeable lithium–sulfur dioxide batteries exploiting conventional carbonate-based electrolytes
High-efficiency and high-power rechargeable lithium–sulfur dioxide batteries exploiting conventional carbonate-based electrolytes
Commercial electrolytes for lithium ion batteries cannot be used for current metal-gas batteries due to the instability despite various merits. Here, the authors successfully exploit a widely used carbonate-based electrolyte to boost the electrochemical performance of lithium-sulfur dioxide batteries for the first time.
- Hyeokjun Park
- , Hee-Dae Lim
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental test of photonic entanglement in accelerated reference frames
Experimental test of photonic entanglement in accelerated reference frames
The unification of the theory of relativity and quantum mechanics is a long-standing challenge in physics. Here the authors investigate the effects of a wide range of accelerations on an entangled photon pair, providing an upper bound for the effects of non-inertial frames on quantum systems.
- Matthias Fink
- , Ana Rodriguez-Aramendia
- & Rupert Ursin
-
Article
| Open Access Large polarization gradients and temperature-stable responses in compositionally-graded ferroelectrics
Large polarization gradients and temperature-stable responses in compositionally-graded ferroelectrics
Future technologies based on ferroelectric materials will require new routes to control the nature of polar order. Through a combined experimental and theoretical study of compositionally and strain-graded Ba1-xSrxTiO3 heterostructures, Damodaranet al. demonstrate the ability to engineer large polarization gradients and temperature-stable susceptibilities.
- Anoop R. Damodaran
- , Shishir Pandya
- & Lane W. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access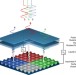 Actively addressed single pixel full-colour plasmonic display
Actively addressed single pixel full-colour plasmonic display
Tuning of plasmonic nanostructures has yet to cover a full colour basis set with a single nanostructure. Franklinet al. demonstrate a liquid crystal-plasmonic system that covers the full red-green-blue colour basis set as a function of voltage and which can be actively addressed with thin-film-transistor technology.
- Daniel Franklin
- , Russell Frank
- & Debashis Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid supercapacitors for reversible control of magnetism
Hybrid supercapacitors for reversible control of magnetism
The ability to electrically control magnetism could enable a new generation of low-power electronic devices. Here the authors show that charging and discharging of supercapacitors are powerful tools to achieve reversible above-room-temperature magnetoelectric effects.
- Alan Molinari
- , Philipp M. Leufke
- & Horst Hahn
-
Article
| Open Access Lipoprotein-biomimetic nanostructure enables efficient targeting delivery of siRNA to Ras-activated glioblastoma cells via macropinocytosis
Lipoprotein-biomimetic nanostructure enables efficient targeting delivery of siRNA to Ras-activated glioblastoma cells via macropinocytosis
Drug delivery in brain tumours is still a significant clinical concern. In this study, the authors develop a biomimetic lipoprotein nanoparticle for the efficient delivery of ATF5 siRNA inRas-activated brain cancer cells, where the nanoparticle is internalized by macropinocytosis in a Ras-dependent manner.
- Jia-Lin Huang
- , Gan Jiang
- & Xiao-Ling Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced unfolding and refolding of supramolecular polymer nanofibres
Light-induced unfolding and refolding of supramolecular polymer nanofibres
Dynamically controlling the conformations of 1D elongated supramolecular polymers can induce functions comparable to protein folding/unfolding. Here the authors show light-induced conformational changes of azobenzene-based supramolecular polymers from helically coiled to extended/randomly coiled conformations.
- Bimalendu Adhikari
- , Yuki Yamada
- & Shiki Yagai
-
Article
| Open Access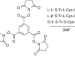 Selective C70 encapsulation by a robust octameric nanospheroid held together by 48 cooperative hydrogen bonds
Selective C70 encapsulation by a robust octameric nanospheroid held together by 48 cooperative hydrogen bonds
Individual hydrogen bonds are weak, so self-assembling multiple components via hydrogen bonding is a significant challenge. Here the authors report a robust, enantiopure nanocapsule held together by 48 cooperative hydrogen bonds, and use it for the selective binding of C70.
- Grzegorz Markiewicz
- , Anna Jenczak
- & Artur R Stefankiewicz
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable and efficient separation of hydrogen isotopes using graphene-based electrochemical pumping
Scalable and efficient separation of hydrogen isotopes using graphene-based electrochemical pumping
Thousands of tons of water are processed every year for hydrogen isotope separation, using extremely costly technology. Here the authors demonstrate a fully-scalable graphene electrochemical pump, which promises to dramatically reduce the energy and capital costs.
- M. Lozada-Hidalgo
- , S. Zhang
- & A. K. Geim
-
Article
| Open Access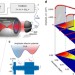 Optically levitated nanoparticle as a model system for stochastic bistable dynamics
Optically levitated nanoparticle as a model system for stochastic bistable dynamics
Nano-mechanical resonators improve with high-Q factor and light mass, but this leads to the onset of nonlinear behaviour. Here the authors demonstrate precise control of the non-linear and bistable dynamics of a levitated nanoparticle in vacuum, using it as model system to study stochastic bistable phenomena.
- F. Ricci
- , R. A. Rica
- & R. Quidant
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional double-bended saturation of carrier occupation in optically excited graphene due to many-particle interactions
Unconventional double-bended saturation of carrier occupation in optically excited graphene due to many-particle interactions
Saturable absorption, a technologically relevant property of graphene, is usually explained with Pauli blocking of optically driven carriers in the strong-excitation regime. Here, Winzeret al. reveal a new saturation regime at low excitations, resulting in a double-bended saturation behaviour.
- Torben Winzer
- , Martin Mittendorff
- & Andreas Knorr
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-large supramolecular coordination cages composed of endohedral Archimedean and Platonic bodies
Ultra-large supramolecular coordination cages composed of endohedral Archimedean and Platonic bodies
Host–guest chemistry in hollow coordination cages can be exploited for a range of applications, but is often limited by inner cavity dimensions. Here, Schmitt and co-workers fabricate supramolecular keplerates that possess ultra-large cross-sectional diameters and are composed of multiple sub-cages.
- Kevin Byrne
- , Muhammad Zubair
- & Wolfgang Schmitt
-
Article
| Open Access Remote detection of radioactive material using high-power pulsed electromagnetic radiation
Remote detection of radioactive material using high-power pulsed electromagnetic radiation
Detection of hazardous radioactive material far from its source is challenging. Here the authors demonstrate a method with higher sensitivity by utilizing high-power pulsed electromagnetic-wave-induced plasma breakdown, which has potential uses in security and defence.
- Dongsung Kim
- , Dongho Yu
- & EunMi Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum-coherent mixtures of causal relations
Quantum-coherent mixtures of causal relations
The set of causal relations that can connect two systems is much richer in the quantum world. Here the authors show that it is possible to have a coherent mixture of a cause-effect and a common-cause mechanism between two systems, realizing this in a quantum optics experiment.
- Jean-Philippe W. MacLean
- , Katja Ried
- & Kevin J. Resch
-
Article
| Open Access Amorphous nickel-cobalt complexes hybridized with 1T-phase molybdenum disulfide via hydrazine-induced phase transformation for water splitting
Amorphous nickel-cobalt complexes hybridized with 1T-phase molybdenum disulfide via hydrazine-induced phase transformation for water splitting
Electrocatalysts based on earth-abundant elements have emerged as promising candidates to replace noble metal materials. Here, the authors develop porous hybrid nanostructures combining amorphous Ni-Co complexes with 1T phase MoS2for enhanced electrocatalytic activity for overall water splitting.
- Haoyi Li
- , Shuangming Chen
- & Xun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line
Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line
The formation mechanisms of ice-shelf channels remain poorly understood. Here, using ice-penetrating radar data, the authors propose that ice-shelf channel morphology in the Roi Baudouin Ice Shelf, East Antarctica, is seeded by esker ridges, indenting the ice from below.
- R. Drews
- , F. Pattyn
- & N. Neckel
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental realization of a multiplexed quantum memory with 225 individually accessible memory cells
Experimental realization of a multiplexed quantum memory with 225 individually accessible memory cells
To realize long-distance quantum communication it is required to have individually addressable quantum memories with programmable access to many cells. Here the authors report DLCZ-type quantum memories with 225 individually accessible memory cells in a macroscopic atomic ensemble
- Y-F Pu
- , N. Jiang
- & L-M Duan
-
Article
| Open Access A general method for controlling and resolving rotational orientation of molecules in molecule-surface collisions
A general method for controlling and resolving rotational orientation of molecules in molecule-surface collisions
The rotational orientation of a molecule plays a fundamental role in molecule-surface collisions, yet is difficult to study. Here, the authors present a general approach for controlling and resolving molecular rotational orientation and apply it to study H2scattering from flat and stepped copper surfaces.
- Oded Godsi
- , Gefen Corem
- & Gil Alexandrowicz
-
Article
| Open Access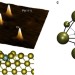 Mapping the orbital structure of impurity bound states in a superconductor
Mapping the orbital structure of impurity bound states in a superconductor
The complex internal structure of magnetic impurities, which locally distort superconductivity, is usually neglected. Here, Choiet al. report that the number and shape of Shiba states are correlated to the spin-polarized atomic orbitals of the impurity, valuable to design atomic-scale superconducting devices.
- Deung-Jang Choi
- , Carmen Rubio-Verdú
- & Jose Ignacio Pascual
-
Article
| Open Access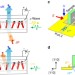 Magnetoelectrical control of nonreciprocal microwave response in a multiferroic helimagnet
Magnetoelectrical control of nonreciprocal microwave response in a multiferroic helimagnet
Control of microwave propagation is important for future communication technology. Here, Iguchiet al. report the reversal of microwave nonreciprocity by an external electric field in a multiferroic helimagnet Ba2Mg2Fe12O22.
- Y. Iguchi
- , Y. Nii
- & Y. Onose

 Voltage-controlled interlayer coupling in perpendicularly magnetized magnetic tunnel junctions
Voltage-controlled interlayer coupling in perpendicularly magnetized magnetic tunnel junctions