Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access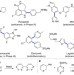 Asymmetric Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of heterocycles via Rhodium-catalysed allylic arylation of racemates
Asymmetric Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of heterocycles via Rhodium-catalysed allylic arylation of racemates
Asymmetric Suzuki-Miyaura procedures often have difficulty incorporating heterocyclic reagents, despite the importance of these in the pharmaceutical industry. Here the authors report a rhodium catalysed cross-coupling that tolerates a wide variety of nucleophiles including a range of heterocycles.
- Philipp Schäfer
- , Thomas Palacin
- & Stephen P. Fletcher
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence of Willis coupling in a one-dimensional effective material element
Experimental evidence of Willis coupling in a one-dimensional effective material element
Metamaterials enable the realization of unique material properties such as coupling between strain and momentum in a fluid—known as Willis coupling. Here, Muhlesteinet al. use homogenization theory to better understand Willis coupling in acoustic metamaterials and demonstrate the unusual material response.
- Michael B. Muhlestein
- , Caleb F. Sieck
- & Michael R. Haberman
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental study of thermal rectification in suspended monolayer graphene
Experimental study of thermal rectification in suspended monolayer graphene
Thermal rectification is instrumental to achieving active heat flow control and energy harvesting in nanoscale devices. Here, the authors demonstrate thermal rectification in asymmetric graphene nanostructures, achieving a large rectification factor up to 26%.
- Haidong Wang
- , Shiqian Hu
- & Jie Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Mutual synchronization of spin torque nano-oscillators through a long-range and tunable electrical coupling scheme
Mutual synchronization of spin torque nano-oscillators through a long-range and tunable electrical coupling scheme
The spintronics based complex network is promising for next generation computing systems but hampered by short-range spin-wave coupling. The authors make progress by achieving long range and tunable mutual synchronization of two spin-torque oscillators with improved emission power and signal linewidth.
- R. Lebrun
- , S. Tsunegi
- & V. Cros
-
Article
| Open Access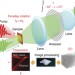 All-optical observation and reconstruction of spin wave dispersion
All-optical observation and reconstruction of spin wave dispersion
Observation of the entire dispersion relation for spin waves remains a challenge which prevents the full understanding of many intriguing magnetic properties. Here, the authors develop a table-top all-optical approach to map out the dispersion curve of pure-magnetostatic waves in magnetic films.
- Yusuke Hashimoto
- , Shunsuke Daimon
- & Eiji Saitoh
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
2D nanomaterials are promising capacitive energy storage materials, but their tendency to restack hinders electrolyte transport. Here, Yamauchi and colleagues introduce 2D ordered mesoporous carbons in between MXene layers, and metal removal affords all-carbon porous 2D–2D heterostructures in which restacking is prevented.
- Jie Wang
- , Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum tunnelling and charge accumulation in organic ferroelectric memory diodes
Quantum tunnelling and charge accumulation in organic ferroelectric memory diodes
Organic non-volatile memories based on ferroelectric and semiconductor polymers are one of promising candidates for flexible electronics, yet the relevant device physics remains elusive. Ghittorelliet al. show that quantum tunnelling and charge accumulation govern the ferroelectric memory operation.
- Matteo Ghittorelli
- , Thomas Lenz
- & Fabrizio Torricelli
-
Article
| Open Access Well-defined porous membranes for robust omniphobic surfaces via microfluidic emulsion templating
Well-defined porous membranes for robust omniphobic surfaces via microfluidic emulsion templating
Designing mechanically and chemically robust liquid-repellent surfaces remains a longstanding challenge. Here, Wang and colleagues report a microfluidic emulsion templating strategy to fabricate bioinspired omniphobic porous membranes with remarkable durability.
- Pingan Zhu
- , Tiantian Kong
- & Liqiu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion engineering of ions and charge carriers for stable efficient perovskite solar cells
Diffusion engineering of ions and charge carriers for stable efficient perovskite solar cells
Ion migration in perovskite solar cells are known to cause hysteresis and instability. Biet al., report a charge extraction layer based on graphene, fullerenes and carbon quantum dots which suppresses ion diffusion and enhances charge carrier diffusion leading to efficient devices with improved stability.
- Enbing Bi
- , Han Chen
- & Liyuan Han
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic strength improvement by utilizing room-temperature deformation twinning in a partially recrystallized VCrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
Cryogenic strength improvement by utilizing room-temperature deformation twinning in a partially recrystallized VCrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys have high fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures due to deformation twinning but twinning is not active in this alloy at room temperature. Here authors optimize composition and thermomechanical treatments to introduce non-recrystallized grains, producing high yield strength while maintaining good ductility.
- Y. H. Jo
- , S. Jung
- & S. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical resistance of individual defects at a topological insulator surface
Electrical resistance of individual defects at a topological insulator surface
Exploiting topological insulator surface states in electronic devices requires an understanding of the factors that affect transport. Here, the authors use scanning tunnelling potentiometry to determine the contributions of different kinds of surface defects to the electrical resistance.
- Felix Lüpke
- , Markus Eschbach
- & Bert Voigtländer
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic basis of differentiated inhibitors of the acute pancreatitis target kynurenine-3-monooxygenase
Structural and mechanistic basis of differentiated inhibitors of the acute pancreatitis target kynurenine-3-monooxygenase
Kynurenine-3-monooxygenase (KMO) is an emerging clinical target for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and acute pancreatitis. Here, the authors report potent inhibitors that bind KMO in an unexpected conformation, offering structural and mechanistic insights for future drug discovery ventures.
- Jonathan P. Hutchinson
- , Paul Rowland
- & Chun-wa Chung
-
Article
| Open Access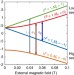 In-beam measurement of the hydrogen hyperfine splitting and prospects for antihydrogen spectroscopy
In-beam measurement of the hydrogen hyperfine splitting and prospects for antihydrogen spectroscopy
Comparing the ground-state hyperfine structure of antihydrogen to that of hydrogen will provide insights into CPT symmetry in nature. Here the authors report the most precise in-beam measurement of this quantity for hydrogen to demonstrate the viability of ASACUSA’s setup to measure it in antihydrogen.
- M. Diermaier
- , C. B. Jepsen
- & E. Widmann
-
Article
| Open Access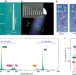 A solid state source of photon triplets based on quantum dot molecules
A solid state source of photon triplets based on quantum dot molecules
Multipartite photon states are desirable in quantum information technology but their generation in optical systems is less efficient with poor scaling. Here the authors demonstrate time-ordered photon triplets from a quantum dot molecule in a direct generation process with increased efficiency.
- Milad Khoshnegar
- , Tobias Huber
- & Hamed Majedi
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstruction of stochastic temporal networks through diffusive arrival times
Reconstruction of stochastic temporal networks through diffusive arrival times
Reconstruction of time-resolved interactions in networks is more challenging than for the time-independent case, as causal relations limit accessibility to empirical data. Here the authors propose a method based on first-arrival observations of a diffusion process to infer stochastic temporal networks.
- Xun Li
- & Xiang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoscopic chaos mediated by Drude electron-hole plasma in silicon optomechanical oscillators
Mesoscopic chaos mediated by Drude electron-hole plasma in silicon optomechanical oscillators
Chaotic behaviour of optomechanical systems has only recently been investigated and observed. Here, Wuet al. study the chaos dynamics in a silicon platform where coupled electron-hole plasma dynamics is possible, providing a route towards chip-scale mesoscopic nonlinear dynamics.
- Jiagui Wu
- , Shu-Wei Huang
- & Chee Wei Wong
-
Review Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional nanomagnetism
Three-dimensional nanomagnetism
Nanoscale magnetic devices play a key role in modern technologies but current applications involve only 2D structures like magnetic discs. Here the authors review recent progress in the fabrication and understanding of 3D magnetic nanostructures, enabling more diverse functionalities.
- Amalio Fernández-Pacheco
- , Robert Streubel
- & Russell P. Cowburn
-
Article
| Open Access An autonomous organic reaction search engine for chemical reactivity
An autonomous organic reaction search engine for chemical reactivity
While automated reaction systems typically work for the synthesis of pre-defined molecules, automated systems to discover reactivity are more challenging. Here the authors report an autonomous organic reaction search engine that allows discovery of the most reactive pathways in a multi-reagent, multistep reaction system.
- Vincenza Dragone
- , Victor Sans
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Taming interfacial electronic properties of platinum nanoparticles on vacancy-abundant boron nitride nanosheets for enhanced catalysis
Taming interfacial electronic properties of platinum nanoparticles on vacancy-abundant boron nitride nanosheets for enhanced catalysis
Tuning electronic properties of metallic catalysts is a useful way to improve their activity, however control over metal-support interactions is still challenging. Here the authors report a vacancy-induced interfacial electronic effect for Pt assembled on vacancy-abundanth-BN nanosheets leading to superior CO oxidation catalysis.
- Wenshuai Zhu
- , Zili Wu
- & Huiyuan Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Regulating guest access and release in porous materials remains an important goal. Here, May and colleagues elucidate the mechanism by which guest admission can be temperature-regulated in typical microporous materials, and experimentally exploit this process to achieve appreciable and reversible hydrogen storage.
- Gang (Kevin) Li
- , Jin Shang
- & Eric F. May
-
Article
| Open Access 11% efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with copper(II/I) hole transport materials
11% efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with copper(II/I) hole transport materials
Inadequate pore infiltration and low conductivity of hole transporter materials limit the performance of solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. Using fast charge-exchange Cu(II/I) complexes as part of the hole transporting material, Caoet al. overcome these issues to achieve a record photoconversion efficiency of 11%.
- Yiming Cao
- , Yasemin Saygili
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article
| Open Access A two-dimensional Dirac fermion microscope
A two-dimensional Dirac fermion microscope
Conventional 3D electron microscopes rely on emission, focusing, deflection, and detection of a focused beam of ballistic electrons to analyse the structure and composition of materials. Here, the authors examine the analogous concept of a 2D electron microscope based on graphene ballistic Dirac electrons.
- Peter Bøggild
- , José M. Caridad
- & Mads Brandbyge
-
Article
| Open Access Local probe of single phonon dynamics in warm ion crystals
Local probe of single phonon dynamics in warm ion crystals
An exhausting characterization of the coherence properties of quantum system becomes challenging with increasing system size. Here the authors demonstrate that phonon autocorrelation functions and quantum discord can be measured with local control, and validate it in a string of 42 trapped ions.
- A. Abdelrahman
- , O. Khosravani
- & H. Häffner
-
Article
| Open Access Ruthenium(II)-catalysed remote C–H alkylations as a versatile platform to meta-decorated arenes
Ruthenium(II)-catalysed remote C–H alkylations as a versatile platform to meta-decorated arenes
Whileortho-selective C-H activation is well explored, general meta-selective methods are rare and often require directing groups that are retained in the final products. Here the authors show that transient imine groups can be used to direct the meta-functionalization of a range of arenes.
- Jie Li
- , Korkit Korvorapun
- & Lutz Ackermann
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time observation of cation exchange kinetics and dynamics at the muscovite-water interface
Real-time observation of cation exchange kinetics and dynamics at the muscovite-water interface
Ion exchange at charged mineral-water interfaces is an important geochemical process, but a molecular-level understanding is still required. Here, the authors probe real-time variations of the interfacial ion exchange dynamics at the muscovite-water interface, providing a general picture of adsorbed ion coverage and speciation.
- Sang Soo Lee
- , Paul Fenter
- & Neil C. Sturchio
-
Article
| Open Access Pumping approximately integrable systems
Pumping approximately integrable systems
Integrable models have an infinite number of conserved quantities but most realizations suffer from integrability breaking perturbations. Here the authors show that weakly driving such a system by periodic perturbations leads to large nonlinear responses governed by the approximate conservation laws.
- Florian Lange
- , Zala Lenarčič
- & Achim Rosch
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling hybrid nonlinearities in transparent conducting oxides via two-colour excitation
Controlling hybrid nonlinearities in transparent conducting oxides via two-colour excitation
Metamaterials have enabled the tailored engineering of optical properties. Here, Clericiet al. show that independent interband and intraband nonlinearities in transparent conducting oxides allow dynamic optical control of the real and imaginary parts of the refractive index.
- M. Clerici
- , N. Kinsey
- & M. Ferrera
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon nanotube-based three-dimensional monolithic optoelectronic integrated system
Carbon nanotube-based three-dimensional monolithic optoelectronic integrated system
Single-material monolithic optoelectronic integrated circuits via CMOS compatible low-temperature approaches are crucial to the continued development of post-Moore electronics. Liuet al., report carbon nanotube based electrically driven 3D monolithic optoelectronic integrated circuits.
- Yang Liu
- , Sheng Wang
- & Lian-Mao Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Parity-time-symmetric quantum critical phenomena
Parity-time-symmetric quantum critical phenomena
Parity-time (PT) symmetry has been mainly studied in optical and weakly interacting open quantum systems without many-body correlations. Here the authors show that in a strongly correlated many-body system the interplay between correlations and PT symmetry leads to the emergence of new critical phenomena.
- Yuto Ashida
- , Shunsuke Furukawa
- & Masahito Ueda
-
Article
| Open Access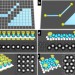 Vector assembly of colloids on monolayer substrates
Vector assembly of colloids on monolayer substrates
Precise assembly of undecorated colloids demands a clever approach. Here, the authors draw unlikely inspiration from vector graphics to direct colloids into 2D structures, pinning the ends and corners of assembled patterns with optical tweezers and manipulating the segments like vectors.
- Lingxiang Jiang
- , Shenyu Yang
- & Steve Granick
-
Article
| Open Access Current-induced skyrmion generation and dynamics in symmetric bilayers
Current-induced skyrmion generation and dynamics in symmetric bilayers
The creation of practical devices based on magnetic skyrmions depends on the development of methods to create and control stable individual skyrmions. Here, the authors present a bilayer device that uses dipolar interactions to stabilize skyrmions that can be manipulated using electric currents.
- A. Hrabec
- , J. Sampaio
- & S. Rohart
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Lorlatinib—a ROS1/ALK inhibitor—is currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancers. Here the authors develop synthetic routes to11C- and 18F-labelled lorlatinib, with subsequent PET imaging showing good blood brain barrier permeability in non-human primates.
- Thomas Lee Collier
- , Marc D. Normandin
- & Neil Vasdev
-
Article
| Open Access Conditional internalization of PEGylated nanomedicines by PEG engagers for triple negative breast cancer therapy
Conditional internalization of PEGylated nanomedicines by PEG engagers for triple negative breast cancer therapy
The majority of treatment options for cancers are ineffective due to limited therapeutic targeting. Here, the authors develop bispecific antibodies that effectively target nanomaterials to triple-negative breast cancer cell receptors and deliver therapeutics leading to inhibition of tumour growth.
- Yu-Cheng Su
- , Pierre-Alain Burnouf
- & Steve R. Roffler
-
Article
| Open Access Preventing tissue fibrosis by local biomaterials interfacing of specific cryptic extracellular matrix information
Preventing tissue fibrosis by local biomaterials interfacing of specific cryptic extracellular matrix information
Matrix metalloproteinase enzymes are widely known to contribute to the breakdown of tissues. Here, the authors utilise a biomaterial substrate functionalised with a laminin fragment to modulate the expression of these enzymes, subsequently controlling the integrity of tissue.
- Christine-Maria Horejs
- , Jean-Philippe St-Pierre
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging using photothermal stimuli-responsive composite nanomodulators
Dynamic contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging using photothermal stimuli-responsive composite nanomodulators
Photoacoustic imaging becomes an enabling technology that is designed for clinic diagnosis of disease. Here, Chenet al. report an imaging contrast agent—plasmonic nanoparticles caged in hydrogel subject to reversible volume change depending on temperature, which exhibits tunable photoacoustic signal.
- Yun-Sheng Chen
- , Soon Joon Yoon
- & Stanislav Emelianov
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of the crossover from polarons to Fermi liquids in transition metal oxides
Origin of the crossover from polarons to Fermi liquids in transition metal oxides
Photoemission spectroscopy studies of anatase titanium oxide have demonstrated a doping-driven crossover in the polaronic character of charge carriers. Here, the authors obtain a first principles understanding of these observations in terms of plasma screening and electron–phonon coupling.
- Carla Verdi
- , Fabio Caruso
- & Feliciano Giustino
-
Article
| Open Access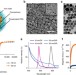 Magnetic forces enable controlled drug delivery by disrupting endothelial cell-cell junctions
Magnetic forces enable controlled drug delivery by disrupting endothelial cell-cell junctions
The transportation of large molecules through the vascular endothelium presents a major challenge forin vivodrug delivery. Here, the authors demonstrate the potential of using external magnetic fields and magnetic nanoparticles to enhance the local extravasation of circulating large molecules.
- Yongzhi Qiu
- , Sheng Tong
- & Gang Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Spaser as a biological probe
Spaser as a biological probe
Advanced diagnostic probes are required for monitoring disease progression. Here Galanzhaet al. demonstrate a 22 nm plasmonic nanolaser to serve as a super-bright, biocompatible probe capable of generating stimulated emission directly inside living cells and animal tissue, while targeting cancer cells.
- Ekaterina I. Galanzha
- , Robert Weingold
- & Vladimir P. Zharov
-
Article
| Open Access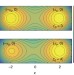 Quantum annealing with all-to-all connected nonlinear oscillators
Quantum annealing with all-to-all connected nonlinear oscillators
Quantum annealing aims at solving optimization problems mapped to Ising interactions between neighbouring spins, but it is crucial to implement it in a noise-resilient way. Here the authors propose a network of all-to-all connected driven Kerr-nonlinear resonators, which exhibits high success probabilities.
- Shruti Puri
- , Christian Kraglund Andersen
- & Alexandre Blais
-
Article
| Open Access Time-programmable drug dosing allows the manipulation, suppression and reversal of antibiotic drug resistance in vitro
Time-programmable drug dosing allows the manipulation, suppression and reversal of antibiotic drug resistance in vitro
It is unclear whether strategies involving antibiotic cycling can efficiently control the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Here, Yoshidaet al. show that the evolution of multi-drug-resistant bacteria in vitrocan be manipulated by administering pairs of antibiotics and switching between them.
- Mari Yoshida
- , Sabrina Galiñanes Reyes
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Ising and chiral ferroelectric domain walls revealed by nonlinear optical microscopy
Non-Ising and chiral ferroelectric domain walls revealed by nonlinear optical microscopy
Understanding the structure of domain walls is an important step in developing nanoscale ferroelectric devices. Here, the authors use second harmonic imaging to verify predictions of Bloch and Néel, rather than simple Ising, domain wall structures in lead zirconium titanate and lithium tantalate.
- Salia Cherifi-Hertel
- , Hervé Bulou
- & Patrycja Paruch
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoimaging of resonating hyperbolic polaritons in linear boron nitride antennas
Nanoimaging of resonating hyperbolic polaritons in linear boron nitride antennas
Here, the authors report a near-field study of hyperbolic phonon polaritons in linear antennas made of hexagonal boron nitride. Infrared nanospectroscopy and nanoimaging experiments reveal sharp Fabry-Perot resonances with large quality factors, exhibiting atypical modal behaviour.
- F. J. Alfaro-Mozaz
- , P. Alonso-González
- & R. Hillenbrand
-
Article
| Open Access Towards colloidal spintronics through Rashba spin-orbit interaction in lead sulphide nanosheets
Towards colloidal spintronics through Rashba spin-orbit interaction in lead sulphide nanosheets
Exploring the Rashba spin splitting in colloidal materials enables spintronic device with low cost and high flexibility. Here, the authors report Rashba spin splitting in colloidal PbS nanosheets and demonstrate a mechanism for selectively exciting the carriers with different spin states.
- Mohammad Mehdi Ramin Moayed
- , Thomas Bielewicz
- & Christian Klinke
-
Article
| Open Access Universal emulsion stabilization from the arrested adsorption of rough particles at liquid-liquid interfaces
Universal emulsion stabilization from the arrested adsorption of rough particles at liquid-liquid interfaces
Emulsions are dispersions of two liquids which have industrial applications and can be stabilized by solid particles. Here Zaniniet al. investigate the effect of particle roughness and demonstrate that particles with a particular surface roughness can effectively stabilize different types of emulsions.
- Michele Zanini
- , Claudia Marschelke
- & Lucio Isa
-
Article
| Open Access Inhomogeneous spatial distribution of the magnetic transition in an iron-rhodium thin film
Inhomogeneous spatial distribution of the magnetic transition in an iron-rhodium thin film
Films of iron-rhodium alloy undergo a magnetic transition at 100°C, and so are attractive for applications, but a detailed understanding of the transition mechanism has not been achieved. Here, the authors use electron holography to quantitatively map the transition’s progress through the film depth.
- C. Gatel
- , B. Warot-Fonrose
- & M.J. Casanove
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-bright and highly efficient inorganic based perovskite light-emitting diodes
Ultra-bright and highly efficient inorganic based perovskite light-emitting diodes
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites are garnering attention for light emitting diode (LED) applications. Employing a thin hydrophilic insulating polymer, Zhanget al. report LEDs exhibiting a brightness of 91,000 cd m−2and external quantum efficiency of 10.4% using a mixed-cation perovskite.
- Liuqi Zhang
- , Xiaolei Yang
- & Jingbi You
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix
Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix
Energy and chirality transfer play a crucial role in living systems. Here, the authors show that achiral acceptors and chiral donor gelators can assemble in a chirally-controlled manner into a supramolecular nanohelix that can additionally harvest circularly polarized energy.
- Dong Yang
- , Pengfei Duan
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Multimode entanglement in reconfigurable graph states using optical frequency combs
Multimode entanglement in reconfigurable graph states using optical frequency combs
Multimode entanglement is an important resource for quantum information processing, but setups are often able to generate specific configurations only. Here the authors present an on-demand reconfigurable multimode entangled state source, realizing thirteen cluster states of various sizes and connectivities.
- Y. Cai
- , J. Roslund
- & N. Treps
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring protein nanomechanics with chemical reactivity
Tailoring protein nanomechanics with chemical reactivity
Post-translational modifications modulate nanomechanics of proteins. Here the authors use single-molecule force-clamp spectroscopy supported by density functional theory calculations to show how reactive low-weight molecular thiol compounds directly affect mechanical protein folding.
- Amy E. M. Beedle
- , Marc Mora
- & Sergi Garcia-Manyes

 Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 °C
Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 °C