Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of bound state self-interaction in a nano-eV atom collider
Observation of bound state self-interaction in a nano-eV atom collider
Self-interaction of a bound state through its coupling to the continuum is a phenomenon that is very difficult to observe. Here, the authors optically collide atomic clouds of rubidium and potassium to observe the self-interaction energy through precise measurements of magnetically tunable Feshbach resonances.
- Ryan Thomas
- , Matthew Chilcott
- & Niels Kjærgaard
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid perovskite light emitting diodes under intense electrical excitation
Hybrid perovskite light emitting diodes under intense electrical excitation
Hybrid perovskite semiconductors are promising for wavelength-tunable laser diodes but their behavior under intense electrical excitation remains unexplored. Kim et al. investigate perovskite light emitting diodes at current densities nearing 1 kA cm−2 and suggest that a laser diode is within reach.
- Hoyeon Kim
- , Lianfeng Zhao
- & Noel C. Giebink
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring atomic layer growth at the liquid-metal interface
Tailoring atomic layer growth at the liquid-metal interface
Ultrathin metallic films are most often fabricated by atomic or molecular beam epitaxy under ultrahigh vacuum conditions, where it is difficult to control deposition and growth. Here, the authors describe a wet deposition method, using solution-borne gold nanocluster precursors, to regulate growth of atomically flat gold nanoislands on a surface.
- Hai Cao
- , Deepali Waghray
- & Steven De Feyter
-
Article
| Open Access Customizing supercontinuum generation via on-chip adaptive temporal pulse-splitting
Customizing supercontinuum generation via on-chip adaptive temporal pulse-splitting
Controlling complex properties of optical systems, like the output of nonlinear light sources, is increasingly important for applications. Here, Wetzel et al. use an actively-controlled photonic chip to prepare patterns of femtosecond laser pulses used for tailoring supercontinuum generation.
- Benjamin Wetzel
- , Michael Kues
- & Roberto Morandotti
-
Article
| Open Access A third generation of radical fluorinating agents based on N-fluoro-N-arylsulfonamides
A third generation of radical fluorinating agents based on N-fluoro-N-arylsulfonamides
Common radical fluorination reagents, such as Selectofluor®, are penalized by the need for metal catalysts and possible oxidation side reactions. Here, the authors reported the synthesis and application of N-fluoro-N-arylsulfonamides (NFASs) as third generation of radical fluorinating reagents to overcome those limitations.
- Daniel Meyer
- , Harish Jangra
- & Philippe Renaud
-
Article
| Open Access Design of an inherently-stable water oxidation catalyst
Design of an inherently-stable water oxidation catalyst
A current challenge in the development of molecular water oxidation catalysts is to overcome their inherent susceptibilities to oxidative or hydrolytic degradation under turnover conditions in water. Here, the authors design an inherently-stable water oxidation catalyst using oxidatively-inert ligands to harness a reactive metal oxide.
- Biswarup Chakraborty
- , Gal Gan-Or
- & Ira A. Weinstock
-
Article
| Open Access Crossover from positive to negative optical torque in mesoscale optical matter
Crossover from positive to negative optical torque in mesoscale optical matter
Negative optical torque has been predicted theoretically, but experimental demonstrations have been scarce. Here, the authors show that the optical torque in a mesoscopic optical matter array can be reversed depending on number, separation and configuration of nanoparticles in a circularly polarized optical trap.
- Fei Han
- , John A. Parker
- & Zijie Yan
-
Article
| Open Access The spread of low-credibility content by social bots
The spread of low-credibility content by social bots
Online misinformation is a threat to a well-informed electorate and undermines democracy. Here, the authors analyse the spread of articles on Twitter, find that bots play a major role in the spread of low-credibility content and suggest control measures for limiting the spread of misinformation.
- Chengcheng Shao
- , Giovanni Luca Ciampaglia
- & Filippo Menczer
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous negative-to-positive tuning of thermal expansion achieved by controlled gas sorption in porous coordination frameworks
Continuous negative-to-positive tuning of thermal expansion achieved by controlled gas sorption in porous coordination frameworks
Achieving control over the thermomechanical properties of functional materials is desirable, yet remains highly challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous negative-to-positive tuning of thermal expansion in two Prussian blue analogues, by varying the concentration of adsorbed CO2.
- Josie E. Auckett
- , Arnold A. Barkhordarian
- & Cameron J. Kepert
-
Article
| Open Access A continuous-time MaxSAT solver with high analog performance
A continuous-time MaxSAT solver with high analog performance
Continuous-time computation paradigm could represent a viable alternative to the standard digital one when dealing with certain classes of problems. Here, the authors propose a generalised version of a continuous-time solver and simulate its performances in solving MaxSAT and two-colour Ramsey problems.
- Botond Molnár
- , Ferenc Molnár
- & Mária Ercsey-Ravasz
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional tessellation by molecular tiles constructed from halogen–halogen and halogen–metal networks
Two-dimensional tessellation by molecular tiles constructed from halogen–halogen and halogen–metal networks
Molecular tessellations of complex tilings are difficult to design and construct. Here, the authors show that molecular tessellations can be formed from a single building block that gives rise to two distinct supramolecular phases, whose self-similar subdomains serve as tiles in the periodic tessellations.
- Fang Cheng
- , Xue-Jun Wu
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Effective removal of mercury from aqueous streams via electrochemical alloy formation on platinum
Effective removal of mercury from aqueous streams via electrochemical alloy formation on platinum
Removal of anthropogenic mercury from water streams is of great importance given its high toxicity and ability to spread rapidly. Here, the authors demonstrate the direct alloying of mercury with a fully recyclable platinum electrode, providing effective removal at different concentrations and pH, and in the presence of other contaminants.
- Cristian Tunsu
- & Björn Wickman
-
Article
| Open Access Control of spin-wave transmission by a programmable domain wall
Control of spin-wave transmission by a programmable domain wall
Magnon-based spintronic devices crucially rely on the capability of spin wave manipulation. Here the authors achieve active control of spin wave transmission by programming a pinned 90 degree Néel domain wall in a continuous CoFeB/BaTiO3 film with abrupt rotations of uniaxial magnetic anisotropy.
- Sampo J. Hämäläinen
- , Marco Madami
- & Sebastiaan van Dijken
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulation of the dephasing time by strong coupling between localized and propagating surface plasmon modes
Manipulation of the dephasing time by strong coupling between localized and propagating surface plasmon modes
Strong coupling between two resonant modes is a prerequisite for many scientifically and technologically interesting effects. Here, Yang et al. demonstrate strong coupling between localized and propagating plasmon modes with a splitting energy of 144 meV and controllable dephasing times.
- Jinghuan Yang
- , Quan Sun
- & Qihuang Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Flow of cerebrospinal fluid is driven by arterial pulsations and is reduced in hypertension
Flow of cerebrospinal fluid is driven by arterial pulsations and is reduced in hypertension
Arterial pulsations are thought to drive CSF flow through perivascular spaces (PVSs), but this has never been quantitatively shown. Using particle tracking to quantify CSF flow velocities in PVSs of live mice, the authors show that flow speeds match the instantaneous speeds of the pulsing artery walls that form the inner boundaries of the PVSs.
- Humberto Mestre
- , Jeffrey Tithof
- & Douglas H. Kelley
-
Article
| Open Access Shockwave generates < 100 > dislocation loops in bcc iron
Shockwave generates < 100 > dislocation loops in bcc iron
Irradiating iron introduces defects such as interstitial dislocation loops, whose exact formation mechanism remains unclear. Here, the authors use large scale molecular dynamics simulations to reveal a punch out mechanism that can directly create < 100 > interstitial dislocation loops.
- Qing Peng
- , Fanjiang Meng
- & Fei Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Barren plateaus in quantum neural network training landscapes
Barren plateaus in quantum neural network training landscapes
Gradient-based hybrid quantum-classical algorithms are often initialised with random, unstructured guesses. Here, the authors show that this approach will fail in the long run, due to the exponentially-small probability of finding a large enough gradient along any direction.
- Jarrod R. McClean
- , Sergio Boixo
- & Hartmut Neven
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene mechanical pixels for Interferometric Modulator Displays
Graphene mechanical pixels for Interferometric Modulator Displays
The electro-optical response of suspended graphene membranes measured by change in wavelength-dependent reflectance can enable interferometric modulation display (IMOD) technology. Here, the authors report suspended double layer graphene based IMOD drums with 2500 pixels per inch.
- Santiago J. Cartamil-Bueno
- , Dejan Davidovikj
- & Samer Houri
-
Article
| Open Access In situ synthesis of supported metal nanocatalysts through heterogeneous doping
In situ synthesis of supported metal nanocatalysts through heterogeneous doping
Supported metal nanoparticles hold great promise for many fields, including catalysis and renewable energy. Here the authors report a novel methodology for the in-situ growth of architecturally tailored, regenerative metal nanocatalysts that is applicable to a wide range of materials.
- No Woo Kwak
- , Seung Jin Jeong
- & WooChul Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy of dilute gas-phase nanosystems
Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy of dilute gas-phase nanosystems
Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy has greatly advanced our understanding of molecular dynamics but was so far broadly limited to complex condensed phase probes. Bruder et al. extend the method to isolated nanosystems in the gas phase and study cold molecules in a superfluid helium environment.
- Lukas Bruder
- , Ulrich Bangert
- & Frank Stienkemeier
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of copper-free Sonogashira reaction operates through palladium-palladium transmetallation
Mechanism of copper-free Sonogashira reaction operates through palladium-palladium transmetallation
Although the Sonogashira coupling of acetylenes and vinyl/aryl halides has been applied for decades, many mechanistic questions have remained unanswered. Here, the authors provide experimental and theoretical support for two interlinked palladium cycles operating in the debated Sonogashira coupling mechanism.
- Martin Gazvoda
- , Miha Virant
- & Janez Košmrlj
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-color live-cell super-resolution volume imaging with multi-angle interference microscopy
Multi-color live-cell super-resolution volume imaging with multi-angle interference microscopy
3D super-resolution imaging of dynamic processes in live cells is still challenging, especially in a large field of view. Here the authors combine SIM with multi-angle evanescent light illumination and achieve improved lateral and axial resolution, with stack acquisition time in the range of 1–2 s.
- Youhua Chen
- , Wenjie Liu
- & Xu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Water assisted biomimetic synergistic process and its application in water-jet rewritable paper
Water assisted biomimetic synergistic process and its application in water-jet rewritable paper
Water based inks used for water-jet rewritable paper (WJRP) are an environmental friendly alternative to conventional printing, but black colour in WJRP could not be realized so far. Here the authors demonstrate black as well as other colour WJRP based on binary systems containing less-sensitive acidochromic dyes and mild proton donors.
- Guan Xi
- , Lan Sheng
- & Sean Xiao-An Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Non-obstructive intracellular nanolasers
Non-obstructive intracellular nanolasers
While the sharp emission lines of microlasers are advantageous for cell tagging, their relatively large size can impede cell migration and behavior. Here, Fikouras et al. develop nano-sized lasers that can readily tag and track various types of cells, including through narrow constrictions.
- Alasdair H. Fikouras
- , Marcel Schubert
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access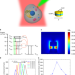 Over 1000-fold enhancement of upconversion luminescence using water-dispersible metal-insulator-metal nanostructures
Over 1000-fold enhancement of upconversion luminescence using water-dispersible metal-insulator-metal nanostructures
Upconversion nanoparticles are already used in bio-imaging but still suffer from low luminescence. Here, metal-insulator-metal nanostructures with 1-2 orders magnitude enhancement in upconversion are introduced enabling bioimaging at reduced particle or excitation power densities, respectively.
- Ananda Das
- , Chenchen Mao
- & Wounjhang Park
-
Article
| Open Access A majority of HIV persistence during antiretroviral therapy is due to infected cell proliferation
A majority of HIV persistence during antiretroviral therapy is due to infected cell proliferation
HIV infected cells persist for decades in patients under ART, but the mechanisms responsible remain unclear. Here, Reeves et al. use modeling approaches adapted from ecology to show that cellular proliferation, rather than viral replication, generates a majority of infected cells during ART.
- Daniel B. Reeves
- , Elizabeth R. Duke
- & Joshua T. Schiffer
-
Article
| Open Access Parity transitions in the superconducting ground state of hybrid InSb–Al Coulomb islands
Parity transitions in the superconducting ground state of hybrid InSb–Al Coulomb islands
Understanding the ground state (GS) phase transitions in the quantum tunneling regime of a superconducting system is important for future qubit devices. Here, Shen, Heedt and Borsoi et al. report distinct types of fermion parity GS transitions as a function of magnetic field and gate voltages in a Coulomb-blockaded InSb–Al island.
- Jie Shen
- , Sebastian Heedt
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Samarium(II) folding cascades involving hydrogen atom transfer for the synthesis of complex polycycles
Samarium(II) folding cascades involving hydrogen atom transfer for the synthesis of complex polycycles
Diversity-oriented synthesis is a valuable strategy to construct complex molecules of medicinal interest. Here, the authors show a folding cascade strategy to convert linear substrates into polycyclic compounds with multiple stereocentres by combining the reductive chemistry of SmI2 with 1,5-hydrogen atom transfer.
- Mateusz P. Plesniak
- , Monserrat H. Garduño-Castro
- & David J. Procter
-
Article
| Open Access Organic field-effect optical waveguides
Organic field-effect optical waveguides
Despite recent advances in organic optoelectronics development, integration of electronics and photonics in a chip remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate organic field-effect optical waveguides that control propagating photons by the electric field produced in an organic transistor.
- Guangyao Zhao
- , Huanli Dong
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
The short exciton life time in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides poses limitations to efficient control of the valley pseudospin and coherence. Here, the authors manipulate the exciton coherence in a WSe2 monolayer embedded in an optical microcavity in the strong light-matter coupling regime.
- S. Dufferwiel
- , T. P. Lyons
- & A. I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Lattice-contraction triggered synchronous electrochromic actuator
Lattice-contraction triggered synchronous electrochromic actuator
Materials that exhibit synchronous color change and actuation may benefit biomimetic camouflage, but stimuli can be difficult to control. Here the authors report a composite with electricity-driven electrochromic and actuating capabilities for use in a solid-state ionic polymer-metal composite actuator.
- Kerui Li
- , Yuanlong Shao
- & Hongzhi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Winding around non-Hermitian singularities
Winding around non-Hermitian singularities
A general description of observable effects induced by non-Hermitian singularities is complex. Here, Zhong et al. develop such a formalism, showing that loops around the same exceptional point starting from the same point in the same direction do not need to have the same outcome.
- Qi Zhong
- , Mercedeh Khajavikhan
- & Ramy El-Ganainy
-
Article
| Open Access Metastable silica high pressure polymorphs as structural proxies of deep Earth silicate melts
Metastable silica high pressure polymorphs as structural proxies of deep Earth silicate melts
As silica melts are believed to be important components of the Earth’s mantle, their structure should determine many of its properties. Here, the authors identify two crystalline modifications of SiO2, whose local structures closely resemble those of known melts, providing a structural model for their atomic ordering at the nanoscale.
- E. Bykova
- , M. Bykov
- & L. Dubrovinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale insights into structure instability and decomposition pathway of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Atomic scale insights into structure instability and decomposition pathway of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Hybrid perovskites are highly promising for photovoltaic applications, but they are prone to decomposition. Here, the authors probe the stability of CH3NH3PbI3 films in a transmission electron microscope, defining the threshold conditions to avoid damage under the electron beam, and describing a decomposition pathway.
- Shulin Chen
- , Xiaowei Zhang
- & Peng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access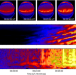 A diagnosis of the plasma waves responsible for the explosive energy release of substorm onset
A diagnosis of the plasma waves responsible for the explosive energy release of substorm onset
The origin of geomagnetic substorms is still uncertain due to lack of comprehensive quantitative analyses. Here, the authors construct an observational dispersion relation of auroral forms that correspond to the explosive energy release from substorm onset.
- N. M. E. Kalmoni
- , I. J. Rae
- & C. Forsyth
-
Article
| Open Access Martian magmatism from plume metasomatized mantle
Martian magmatism from plume metasomatized mantle
A unified model for the formation of martian rock types is required to understand Mars’s formation and evolution. Here the authors show that nakhlite and chassignite meteorites originate from melting of metasomatized depleted mantle lithosphere, whereas shergottite melts originate from deep plume sources.
- James M. D. Day
- , Kimberly T. Tait
- & Clive R. Neal
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable high performance radio frequency electronics based on large domain bilayer MoS2
Scalable high performance radio frequency electronics based on large domain bilayer MoS2
Large area two-dimensional materials show promise for applications in DC and RF flexible electronics. Here, the authors report RF transistors based on chemical vapor deposited bilayer MoS2 with 23 GHz extrinsic maximum oscillation frequency, and gigahertz mixers on flexible polyimide substrates.
- Qingguo Gao
- , Zhenfeng Zhang
- & Yanqing Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Myths and reality of HPbI3 in halide perovskite solar cells
Myths and reality of HPbI3 in halide perovskite solar cells
Hydriodic acid or hydrogen lead iodide is widely used to stabilize all-inorganic perovskite cesium lead iodide to make high performing solar cells. Here Ke et al. reveal the real composition of the perovskites, where dimethylammonium partially take place of cesium cation at the A-site.
- Weijun Ke
- , Ioannis Spanopoulos
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
Article
| Open Access Dehydrative π-extension to nanographenes with zig-zag edges
Dehydrative π-extension to nanographenes with zig-zag edges
Nanographenes with zig-zag peripheries are expected to have unique electronic properties, but their application in organic electronics has been curbed by their difficult synthesis. Here, the authors develop a facile route to zig-zag nanographenes based on a key dehydrative π-extension reaction.
- Dominik Lungerich
- , Olena Papaianina
- & Konstantin Amsharov
-
Article
| Open Access Light-controlled switching of the spin state of iron(III)
Light-controlled switching of the spin state of iron(III)
Controlled switching of the spin state of transition metal ions is key in many enzymatic reactions, but difficult to replicate in synthetic systems. Here the authors report on an iron(III) porphyrin with a photochromic axial ligand that, in solution, reversibly switches between low-spin and high-spin upon irradiation with two different wavelengths.
- Sreejith Shankar
- , Morten Peters
- & Rainer Herges
-
Article
| Open Access Large-area and adaptable electrospun silicon-based thermoelectric nanomaterials with high energy conversion efficiencies
Large-area and adaptable electrospun silicon-based thermoelectric nanomaterials with high energy conversion efficiencies
To realize waste heat recovery solutions based on thermoelectricity, high-performance materials with device and manufacturing compatibility are required. Here, the authors demonstrate large-area paper-like nanostructured fabrics consisting of aligned nanotubes with high thermoelectric performance.
- Alex Morata
- , Mercè Pacios
- & Albert Tarancón
-
Article
| Open Access Designer liquid-liquid interfaces made from transient double emulsions
Designer liquid-liquid interfaces made from transient double emulsions
Surfaces with adsorbed and arrested colloids are of interest for the engineering of advanced mesostructured materials. Here the authors demonstrate a method for producing particle-stabilised droplets with controlled surface coverage and composition.
- Greet Dockx
- , Steffen Geisel
- & Jan Vermant
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure shock fronts formed by ultra-fast shear cracks in viscoelastic materials
Pressure shock fronts formed by ultra-fast shear cracks in viscoelastic materials
Propagating shear cracks in solids emit both shear and pressure waves, but it is usually thought that only shear waves coalesce to form shock fronts when the crack exceeds the shear wave speed. Here, the authors show that local material stiffening can further increase rupture speed and produce pressure shock fronts that hint at supersonic propagation.
- M. Gori
- , V. Rubino
- & N. Lapusta
-
Article
| Open Access Calcium stabilizes the strongest protein fold
Calcium stabilizes the strongest protein fold
Staphylococcal pathogens adhere to their human targets using adhesins, which can withstand extremely high forces. Here, authors use single-molecule force spectroscopy to determine the similarly high unfolding forces of B domains that link the adhesin to the bacterium.
- Lukas F. Milles
- , Eduard M. Unterauer
- & Hermann E. Gaub
-
Article
| Open Access 5D operando tomographic diffraction imaging of a catalyst bed
5D operando tomographic diffraction imaging of a catalyst bed
Multi-scale chemical imaging holds the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the relationships between structure and functionality in complex catalytic materials. Here the authors report the results from the first 5D tomographic diffraction imaging experiment of a complex Ni – Pd/ CeO2 – ZrO2/ Al2O3 catalyst used for methane reforming.
- A. Vamvakeros
- , S. D. M. Jacques
- & A. M. Beale
-
Article
| Open Access Deformation twinning and grain partitioning in a hexagonal close-packed magnesium alloy
Deformation twinning and grain partitioning in a hexagonal close-packed magnesium alloy
Magnesium deforms via twins that form in a grain then expand both forward and laterally, causing local stresses that have yet to be measured. Here, the authors measure the full strain and stress tensors around a twin in a bulk polycrystal and show that the twinning grain deforms heterogeneously.
- M. Arul Kumar
- , B. Clausen
- & C. N. Tomé
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput three-dimensional chemotactic assays reveal steepness-dependent complexity in neuronal sensation to molecular gradients
High-throughput three-dimensional chemotactic assays reveal steepness-dependent complexity in neuronal sensation to molecular gradients
In vitro chemotactic assays are often 2D, low-throughput and lack fine gradient control. Here the authors present a hydrogel-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput 3D chemotactic assays, and use it to study neuronal sensitivity to guidance molecule gradient steepness.
- Zhen Xu
- , Peilin Fang
- & Peng Shi
-
Article
| Open Access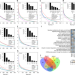 Pathway-based subnetworks enable cross-disease biomarker discovery
Pathway-based subnetworks enable cross-disease biomarker discovery
Accurate and actionable biomarkers that integrate diverse molecular, functional and clinical information hold great promise in precision medicine. Here, the authors develop SIMMS, a method for pathway-based cross-disease biomarker discovery.
- Syed Haider
- , Cindy Q. Yao
- & Paul C. Boutros
-
Correspondence
| Open Access The diamine cation is not a chemical example where density functional theory fails
The diamine cation is not a chemical example where density functional theory fails
- Zulfikhar A. Ali
- , Fredy W. Aquino
- & Bryan M. Wong

 Integrated mapping of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in a patient-derived xenograft model of glioblastoma
Integrated mapping of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in a patient-derived xenograft model of glioblastoma