Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mercury’s anomalous magnetic field caused by a symmetry-breaking self-regulating dynamo
Mercury’s anomalous magnetic field caused by a symmetry-breaking self-regulating dynamo
A new regime of planetary magnetic fields was revealed through the MESSENGER spacecraft mission to Mercury. Here, the authors present a numerical dynamo model that can re-produce both the axisymmetric and anomalously axially offset dipolar magnetic field of Mercury.
- Futoshi Takahashi
- , Hisayoshi Shimizu
- & Hideo Tsunakawa
-
Article
| Open Access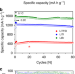 Achieving three-dimensional lithium sulfide growth in lithium-sulfur batteries using high-donor-number anions
Achieving three-dimensional lithium sulfide growth in lithium-sulfur batteries using high-donor-number anions
The development of new electrolyte systems is needed to optimize performance in lithium-sulfur batteries. Here the authors employ anions with high donor numbers in electrolytes to prevent passivation of the cathode surface, thereby improving sulfur utilization and energy density in a lithium-sulfur cell.
- Hyunwon Chu
- , Hyungjun Noh
- & Hee-Tak Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A micro-dispenser for long-term storage and controlled release of liquids
A micro-dispenser for long-term storage and controlled release of liquids
The integration and release of reagents in portable diagnostic devices is critical for the good functioning of such devices. Here the authors propose a device with a reservoir for long-term storage of reagents with integrated, pressure operated, normally closed, passive check-valve for dispensing.
- Amin Kazemzadeh
- , Anders Eriksson
- & Aman Russom
-
Article
| Open Access Far-field acoustic subwavelength imaging and edge detection based on spatial filtering and wave vector conversion
Far-field acoustic subwavelength imaging and edge detection based on spatial filtering and wave vector conversion
Plasmonic effects and subwavelength scattering arrays are used in the optical domain to access subwavelength resolution imaging in the far field. Here, the authors develop an analogous strategy for far-field, subwavelength imaging at acoustic wavelengths and demonstrate edge detection of acoustic scattering objects.
- Chu Ma
- , Seok Kim
- & Nicholas X. Fang
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance Raman quantum memory with optimal control in room temperature atoms
High-performance Raman quantum memory with optimal control in room temperature atoms
Storage and retrieval of memory is important for applications in quantum information processing. Here the authors demonstrate an efficient quantum Raman memory protocol by preparing hot rubidium atoms in specific states using control pulse scheme.
- Jinxian Guo
- , Xiaotian Feng
- & Weiping Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access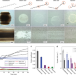 Mechano-chemical decomposition of organic friction modifiers with multiple reactive centres induces superlubricity of ta-C
Mechano-chemical decomposition of organic friction modifiers with multiple reactive centres induces superlubricity of ta-C
The mechanism underlying the superlubricity of tetrahedral amorphous carbon coatings lubricated with organic friction modifiers is still under debate. Here the authors combine experiments and simulations to reveal that superlubricious layers form due the mechano-chemical decomposition of friction modifiers.
- Takuya Kuwahara
- , Pedro A. Romero
- & Michael Moseler
-
Article
| Open Access Flat acoustics with soft gradient-index metasurfaces
Flat acoustics with soft gradient-index metasurfaces
Here, the authors report an approach for creating various acoustic wavefronts in free space by using soft gradient-index porous metasurfaces. These flat lenses generate steered planar, focused spherical and helical ultrasonic beams in water by manipulating the spatial distribution of the material porosity.
- Yabin Jin
- , Raj Kumar
- & Thomas Brunet
-
Article
| Open Access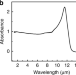 Phonon-enhanced photothermoelectric effect in SrTiO3 ultra-broadband photodetector
Phonon-enhanced photothermoelectric effect in SrTiO3 ultra-broadband photodetector
Broadband photodetectors for various applications are in high demand, however, often suffering from non-linearities at high power densities. Here, a reduced strontium titanate based photodetector exhibiting linear response up to 1235 W/cm2 is presented not achieved by other broadband photodetectors.
- Xiaowei Lu
- , Peng Jiang
- & Xinhe Bao
-
Article
| Open Access In situ atomistic observation of disconnection-mediated grain boundary migration
In situ atomistic observation of disconnection-mediated grain boundary migration
Shear-induced grain boundary migration at the atomic level is still not well understood. Here the authors combine in situ shear testing experiments and molecular dynamic simulations to reveal the atomistic mechanism of disconnection-mediated GB migration in different gold nanostructures.
- Qi Zhu
- , Guang Cao
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Long-lasting field-free alignment of large molecules inside helium nanodroplets
Long-lasting field-free alignment of large molecules inside helium nanodroplets
Strong molecular alignment without a laser field present is important for fundamental experiments in molecular science, but so far this has not been obtained for complex molecules. Here the authors use a shaped laser pulse to demonstrate field-free alignment of complex molecules in helium droplets.
- Adam S. Chatterley
- , Constant Schouder
- & Henrik Stapelfeldt
-
Article
| Open Access Promoted cobalt metal catalysts suitable for the production of lower olefins from natural gas
Promoted cobalt metal catalysts suitable for the production of lower olefins from natural gas
The conversion of natural gas to chemicals and fuels via the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis process, depends on the ability of catalyst materials to suppress the formation of methane and carbon dioxide. Here, the authors develop a Co1Mn3-Na2S catalyst, which has a hydrocarbon product spectrum deviating from the Anderson–Schulz–Flory distribution.
- Jingxiu Xie
- , Pasi P. Paalanen
- & Krijn P. de Jong
-
Article
| Open Access Chromium-ruthenium oxide solid solution electrocatalyst for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction in acidic media
Chromium-ruthenium oxide solid solution electrocatalyst for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction in acidic media
H2 generated from water electrolysis is a promising, carbon-neutral fuel, but sluggish oxidation kinetics and poor catalyst stability in acid limits the chemistry. Here, authors prepare solid-solution catalysts based on ruthenium-chromium oxides that are stable and active for acidic water oxidation.
- Yichao Lin
- , Ziqi Tian
- & Liang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Reducing aggregation caused quenching effect through co-assembly of PAH chromophores and molecular barriers
Reducing aggregation caused quenching effect through co-assembly of PAH chromophores and molecular barriers
Organic luminescent materials are often used in modern technologies, but aggregation induced quenching caused by planar aromatic structures hampers their applicability. Here, the authors demonstrate a facile co-assembly method for luminescent cocrystals and protection with hydrophilic PEO chains which allow good dispersibility in water.
- Yinjuan Huang
- , Jie Xing
- & Qichun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual synergistic effect in layered Ruddlesden−Popper oxide enables ultrafast hydrogen evolution
Unusual synergistic effect in layered Ruddlesden−Popper oxide enables ultrafast hydrogen evolution
Water may serve as a renewable hydrogen fuel source to replace fossil fuels, although such electrolysis requires highly active catalysts. Here, authors explore Ruddlesden−Popper oxides as hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts that feature an unusual synergistic effect to promote high activity.
- Yinlong Zhu
- , Hassan A. Tahini
- & Zongping Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Altered chemistry of oxygen and iron under deep Earth conditions
Altered chemistry of oxygen and iron under deep Earth conditions
Iron oxides prevail in the deep Earth, at extreme pressures and temperatures, with different stoichiometries than in ambient conditions. Here, high-pressure synchrotron X-ray spectroscopic measurements reveal the oxidation states of Fe and O in iron superoxide, shedding light on the puzzling chemistry of iron and oxygen in the deep Earth
- Jin Liu
- , Qingyang Hu
- & Wendy L. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Dinitroimidazoles as bifunctional bioconjugation reagents for protein functionalization and peptide macrocyclization
Dinitroimidazoles as bifunctional bioconjugation reagents for protein functionalization and peptide macrocyclization
The selective formation of protein bioconjugates under physiological conditions is a challenging task. Here, the authors report that 1,4-dinitroimidazoles are reagents of choice for protein bioconjugation at either cysteine or lysine sites within short times and provide facile access to peptide macrocycles.
- Qunfeng Luo
- , Youqi Tao
- & Huan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Functional imaging of visual cortical layers and subplate in awake mice with optimized three-photon microscopy
Functional imaging of visual cortical layers and subplate in awake mice with optimized three-photon microscopy
Two-photon microscopy is a powerful tool for studying neuronal activity but cannot easily image deeper cortical layers. Here, the authors design a custom microscope for three-photon microscopy and use it to reveal response properties of layer 5, 6, and subplate visual cortical neurons.
- Murat Yildirim
- , Hiroki Sugihara
- & Mriganka Sur
-
Article
| Open Access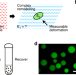 Dispersible hydrogel force sensors reveal patterns of solid mechanical stress in multicellular spheroid cultures
Dispersible hydrogel force sensors reveal patterns of solid mechanical stress in multicellular spheroid cultures
Understanding how forces orchestrate tissue formation requires technologies to map internal tissue stress at cellular length scales. Here, authors develop ultrasoft sensors that visibly deform under cell-generated stress to capture patterns of internal stress development during multicellular spheroid formation.
- Wontae Lee
- , Nikita Kalashnikov
- & Christopher Moraes
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating all-optical switching with spintronics
Integrating all-optical switching with spintronics
The high speed switching and energy efficiency nature grant all-optical switching (AOS) great potential for future photonic integrated spintronic devices. Here the authors demonstrate the combination of AOS and domain wall propagation in Pt/Co/Gd synthetic ferrimagnetic racetrack for applications in photonic memory technologies.
- M. L. M. Lalieu
- , R. Lavrijsen
- & B. Koopmans
-
Article
| Open Access A metamaterial-enabled design enhancing decades-old short backfire antenna technology for space applications
A metamaterial-enabled design enhancing decades-old short backfire antenna technology for space applications
There is significant interest in providing real-world applications for metamaterials. Here, the authors design an Advanced Short Backfire Antenna, augmented with anisotropic metamaterial surfaces to achieve high aperture efficiency across two frequency bands, making the antenna ideal for spaceborne applications.
- J. Daniel Binion
- , Erik Lier
- & Douglas H. Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Iron-catalyzed carboazidation of alkenes and alkynes
Iron-catalyzed carboazidation of alkenes and alkynes
Carboazidation of alkenes and alkynes holds the promise to construct valuable, functionalized molecules. Here, the authors report a general and efficient iron-catalyzed carboazidation of both alkenes and alkynes enabled by t-butyl perbenzoate.
- Haigen Xiong
- , Nagarajan Ramkumar
- & Hongli Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-optoelectronic devices based on hybrid organic-inorganic trihalide perovskites
Spin-optoelectronic devices based on hybrid organic-inorganic trihalide perovskites
Hybrid organic-inorganic trihalide perovskites can make remarkable optoelectronic devices but their spin characteristics are less investigated. Here Wang et al. show spin-polarized carriers injection into methylammonium lead bromide films with long lifetime and realize spin LEDs and spin valves.
- Jingying Wang
- , Chuang Zhang
- & Z. Valy Vardeny
-
Article
| Open Access Bifurcation-based embodied logic and autonomous actuation
Bifurcation-based embodied logic and autonomous actuation
The demonstration of nature-inspired embodied control logic in simple autonomous material systems is of significant interest in applications such as soft robots and drug delivery. Here, the authors demonstrate 3D printed self-actuating structures with control logic in response to suitable stimuli.
- Yijie Jiang
- , Lucia M. Korpas
- & Jordan R. Raney
-
Article
| Open Access Solution-processed intermediate-band solar cells with lead sulfide quantum dots and lead halide perovskites
Solution-processed intermediate-band solar cells with lead sulfide quantum dots and lead halide perovskites
Intermediate-band solar cell presents a possible route to break the Shockley-Queisser limit but the fabrication has been difficult. Here Hosokawa et al. exhibit working cells at room temperature in solution processed quantum dot-perovskite system with carefully designed miscibility and energy levels.
- Hiroji Hosokawa
- , Ryo Tamaki
- & Toshihiro Yano
-
Article
| Open Access Precision ultrasound sensing on a chip
Precision ultrasound sensing on a chip
With the wide adoption of ultrasound methods in biomedical and technological diagnostics, sensitive probes are in demand. Here, the authors employ cavity optomechanics where optical and mechanical resonances are coupled, both enhancing the sensitivity of the device and allowing its chip-integration.
- Sahar Basiri-Esfahani
- , Ardalan Armin
- & Warwick P. Bowen
-
Article
| Open Access Olefin-accelerated solid-state C–N cross-coupling reactions using mechanochemistry
Olefin-accelerated solid-state C–N cross-coupling reactions using mechanochemistry
Cross-coupling reactions have been achieved in solution, yet tend to be inefficient in a solid state. Here, the authors report a solid-state palladium-catalyzed Buchwald-Hartwig cross-coupling using olefins as molecular dispersants, enabling reduction of solvent waste.
- Koji Kubota
- , Tamae Seo
- & Hajime Ito
-
Article
| Open Access The synthesis and characterization of giant Calixarenes
The synthesis and characterization of giant Calixarenes
Calixarenes are cyclic oligomers obtained by condensation reactions between phenols and formaldehyde and usually include up to eight phenolic subunits. Here the authors demonstrate the synthesis of calixarenes with up to 90 phenolic subunits with up to 65% yield via a scalable process.
- Vincent Guérineau
- , Marion Rollet
- & Vincent Huc
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal radiation control from hot graphene electrons coupled to a photonic crystal nanocavity
Thermal radiation control from hot graphene electrons coupled to a photonic crystal nanocavity
Efficient control of thermal radiation is at the core of device design for a variety of applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a high-temperature thermal emitter with selective emission from a graphene-silicon photonic crystal nanocavity.
- Ren-Jye Shiue
- , Yuanda Gao
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access 9.2%-efficient core-shell structured antimony selenide nanorod array solar cells
9.2%-efficient core-shell structured antimony selenide nanorod array solar cells
Antimony selenide is a promising thin film solar cell absorber material in which grain orientation is crucial for high device performance. Here Li et al. grow the material in nanorod arrays along the [001] direction and obtain record high efficiency of 9.2%.
- Zhiqiang Li
- , Xiaoyang Liang
- & Yaohua Mai
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-Orbit induced phase-shift in Bi2Se3 Josephson junctions
Spin-Orbit induced phase-shift in Bi2Se3 Josephson junctions
An anomalous phase shift in a topological insulator based Josephson junction is expected but never been observed. Here, Assouline et al. observe an anomalous phase shift in a Bi2Se3 based Josephson junction in presence of an in-plane magnetic field, opening opportunities for phase-controlled Josephson devices.
- Alexandre Assouline
- , Cheryl Feuillet-Palma
- & Hervé Aubin
-
Article
| Open Access Room temperature multi-phonon upconversion photoluminescence in monolayer semiconductor WS2
Room temperature multi-phonon upconversion photoluminescence in monolayer semiconductor WS2
Two-dimensional materials show promise for photon upconversion processes due to their strong photon-exciton and phonon-exciton interactions. Here, the authors report room temperature upconversion photoluminescence in monolayer WS2 with high energy gain up to 150 meV based on variable temperature.
- J. Jadczak
- , L. Bryja
- & P. Hawrylak
-
Article
| Open Access Shifts in the selectivity filter dynamics cause modal gating in K+ channels
Shifts in the selectivity filter dynamics cause modal gating in K+ channels
Spontaneous activity shifts at constant experimental conditions are widespread among ion channels but the molecular origins are poorly understood. Here, using solid-state NMR and MD simulations, the authors reveal that modal gating shifts in K + channels are caused by large shifts in the channel dynamics which perturb the selectivity filter.
- Shehrazade Jekhmane
- , João Medeiros-Silva
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article
| Open Access Size-dependent kinetics during non-equilibrium lithiation of nano-sized zinc ferrite
Size-dependent kinetics during non-equilibrium lithiation of nano-sized zinc ferrite
Reducing particle size of electrode materials to nanoscale dimensions is believed responsible for their enhanced reaction kinetics and electrochemical performance. Here, the authors use in situ transmission electron microscopy to study the dynamic process of the spinel zinc ferrite nanoparticles as a function of size, finding that the intercalation reaction pathway changes below a critical particle size.
- Jing Li
- , Qingping Meng
- & Eric A. Stach
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of dissociative quasi-free electron attachment to nucleoside via excited anion radical in solution
Observation of dissociative quasi-free electron attachment to nucleoside via excited anion radical in solution
Radiation-induced low-energy electrons in solution are implicated in DNA damage, but their relaxation dynamics are not well understood. Here the authors observe how quasi-free electrons dissociate glycosidic bonds via an excited nucleoside anion radical, whereas solvated electrons reside on the nucleoside as a relatively stable anion radical.
- Jun Ma
- , Anil Kumar
- & Mehran Mostafavi
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-enabled phase control for arc welding of unweldable aluminum alloy 7075
Nanoparticle-enabled phase control for arc welding of unweldable aluminum alloy 7075
In contrast to steels, fusion welding high strength aluminum alloys such as AA7075 is notoriously difficult. Here, the authors add nanoparticles to a weld filler rod to successfully weld AA7075 without hot cracks or loss of strength at the weld.
- Maximilian Sokoluk
- , Chezheng Cao
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasonic sculpting of virtual optical waveguides in tissue
Ultrasonic sculpting of virtual optical waveguides in tissue
Optical imaging of tissue is a powerful technique but delivering light deep into scattering tissue is not possible without using invasive methods. Here, the authors demonstrate that patterned ultrasound can define and control the trajectory of light in tissue using pressure-induced index contrasts.
- Maysamreza Chamanzar
- , Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti
- & Michel M. Maharbiz
-
Article
| Open Access A miniature multi-contrast microscope for functional imaging in freely behaving animals
A miniature multi-contrast microscope for functional imaging in freely behaving animals
Measuring multiple neurophysiologic variables usually requires bulky benchtop optical systems and working with anesthetized animals. Here the authors present a miniature portable microscope for neurovascular imaging in awake rodents, combining fluorescence, intrinsic optical signals and laser speckle contrast.
- Janaka Senarathna
- , Hang Yu
- & Arvind P. Pathak
-
Article
| Open Access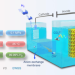 Room-temperature electrochemical water–gas shift reaction for high purity hydrogen production
Room-temperature electrochemical water–gas shift reaction for high purity hydrogen production
Traditional water–gas shift reaction process is hindered by harsh reaction conditions and extra steps for hydrogen separation and purification. Here, the authors report a room temperature electrochemical water–gas shift process for direct production of high purity hydrogen with a faradaic efficiency of approximately 100%.
- Xiaoju Cui
- , Hai-Yan Su
- & Xinhe Bao
-
Article
| Open Access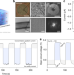 Artificial light-driven ion pump for photoelectric energy conversion
Artificial light-driven ion pump for photoelectric energy conversion
Biological light-driven ion pumps move ions against a concentration gradient to create a membrane potential, converting sunlight into an osmotic potential. Here, the authors make an artificial ion pump which drives ions thermodynamically uphill against a large concentration gradient upon illumination, which can be used for harvesting solar energy.
- Kai Xiao
- , Lu Chen
- & Markus Antonietti
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of colossal Seebeck effect in metallic Cu2Se
Discovery of colossal Seebeck effect in metallic Cu2Se
Recent research efforts have aimed at discovering thermoelectric materials with high efficiency in the middle-low temperature range, where a majority of waste heat is lost to the ambient. Here, the authors discover colossal Seebeck coefficient values in metallic copper selenide from 340 K to 400 K.
- Dogyun Byeon
- , Robert Sobota
- & Tsunehiro Takeuchi
-
Article
| Open Access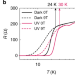 Light induced non-volatile switching of superconductivity in single layer FeSe on SrTiO3 substrate
Light induced non-volatile switching of superconductivity in single layer FeSe on SrTiO3 substrate
How photoexcitations influence superconductivity at the FeSe/SrTiO3 interface remains elusive. Here, the authors report fast optical generation of a metastable superconducting state and its reversal by voltage pulses at the FeSe monolayer/SrTiO3 interface.
- Ming Yang
- , Chenhui Yan
- & Cheng Cen
-
Article
| Open Access The transcription factor STAT5 catalyzes Mannich ligation reactions yielding inhibitors of leukemic cell proliferation
The transcription factor STAT5 catalyzes Mannich ligation reactions yielding inhibitors of leukemic cell proliferation
The oncogene STAT5 is involved in cancer cell proliferation. Here, the authors use STAT5 protein to assemble its own small molecule inhibitors via Mannich ligation (three-component-reactions) and show that the resultant ligands can inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells in a mouse model.
- Ee Lin Wong
- , Eric Nawrotzky
- & Jörg Rademann
-
Article
| Open Access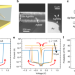 Surface diffusion-limited lifetime of silver and copper nanofilaments in resistive switching devices
Surface diffusion-limited lifetime of silver and copper nanofilaments in resistive switching devices
Resistive random-access memory is operated based on the formation and disruption of nanoscale conductive filaments, but a mechanistic understanding of this process remains unclear. Here, Wang et al. develop a surface-diffusion model to describe lifetime of filaments ranging from microseconds to years.
- Wei Wang
- , Ming Wang
- & Daniele Ielmini
-
Article
| Open Access Identity crisis in alchemical space drives the entropic colloidal glass transition
Identity crisis in alchemical space drives the entropic colloidal glass transition
Fluids may avoid crystallization via an underlying mechanism that remains hotly debated. Teich et al. show that hard polyhedral particles form glass because of the competition of local structural motifs, each of which is prevalent in crystals self-assembled from particles of closely related shapes.
- Erin G. Teich
- , Greg van Anders
- & Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Article
| Open Access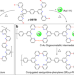 Selective on-surface covalent coupling based on metal-organic coordination template
Selective on-surface covalent coupling based on metal-organic coordination template
Synthesizing precise conjugated nanostructures on a surface requires fine control over the covalent reaction pathways. Here, the authors show that reversible coordinative bonds can be used to template on-surface C-C coupling reactions, guiding the formation of porous organic nanoribbons.
- Shuaipeng Xing
- , Zhe Zhang
- & Ziliang Shi
-
Article
| Open Access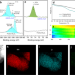 Electrochemically activated spinel manganese oxide for rechargeable aqueous aluminum battery
Electrochemically activated spinel manganese oxide for rechargeable aqueous aluminum battery
The instability of the host structure of cathode materials and sluggish aluminium ion diffusion are the major challenges facing the Al-ion battery. Here the authors show AlxMnO2·nH2O as a cathode that allows for reversible Al3+ (de)intercalation in an aqueous electrolyte and impressive electrochemical performance for a battery device.
- Chuan Wu
- , Sichen Gu
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access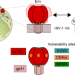 Molecular recognition of the native HIV-1 MPER revealed by STED microscopy of single virions
Molecular recognition of the native HIV-1 MPER revealed by STED microscopy of single virions
The Membrane-Proximal External Region (MPER) of the HIV Env gp41 subunit is a target for broadly neutralizing antibodies. Here, the authors apply super-resolution stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy on single virions and provide insights into how the MPER epitope is recognized.
- Pablo Carravilla
- , Jakub Chojnacki
- & José L. Nieva
-
Article
| Open Access On chaotic dynamics in transcription factors and the associated effects in differential gene regulation
On chaotic dynamics in transcription factors and the associated effects in differential gene regulation
It is becoming clear that the dynamics of transcription factors may be important for gene regulation. Here, the authors study the implications of oscillatory and chaotic dynamics of NF-κB and demonstrate that it allows a degree of control of gene expression and can generate phenotypic heterogeneity.
- Mathias L. Heltberg
- , Sandeep Krishna
- & Mogens H. Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access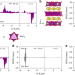 Manganese based layered oxides with modulated electronic and thermodynamic properties for sodium ion batteries
Manganese based layered oxides with modulated electronic and thermodynamic properties for sodium ion batteries
Mn-based layered oxides are promising cathode materials for next generation sodium ion batteries. To address two existing issues facing the system, here the authors show that a simple zinc doping can suppress both Jahn–Teller distortion and phase separation, enabling enhanced cycling performance.
- Kai Zhang
- , Duho Kim
- & Yong-Mook Kang

 Reconfigurable shape-morphing dielectric elastomers using spatially varying electric fields
Reconfigurable shape-morphing dielectric elastomers using spatially varying electric fields