Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Modular Design of Programmable Mechanofluorescent DNA Hydrogels
Modular Design of Programmable Mechanofluorescent DNA Hydrogels
Mechanosensitive materials typically lack complex response patterns due to difficult synthetic methods. Here, the authors introduce FRET-based DNA tension probes into macroscopic 3D DNA hydrogels to prepare mechanofluorescent materials with programmable sacrificial bonds and stress relaxation behaviour.
- Remi Merindol
- , Giovanne Delechiave
- & Andreas Walther
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced, reversible phase transitions in all-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals
Photoinduced, reversible phase transitions in all-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals
Lead trihalide perovskites are notable for their excellent optoelectronic properties and uncommon phase behavior. Here, Kirschner et al. show that cesium lead bromide nanocrystals experience a reversible orthorhombic-to-cubic phase transition at moderate excitation fluences and become amorphous at higher fluences.
- Matthew S. Kirschner
- , Benjamin T. Diroll
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced strength–ductility synergy in ultrafine-grained eutectic high-entropy alloys by inheriting microstructural lamellae
Enhanced strength–ductility synergy in ultrafine-grained eutectic high-entropy alloys by inheriting microstructural lamellae
Producing in situ composite materials with superior strength and ductility has long been a challenge. Here, the authors use lamellar microstructure inherited from casting, rolling, and annealing to produce an ultrafine duplex eutectic high entropy alloy with outstanding properties.
- Peijian Shi
- , Weili Ren
- & Peter K. Liaw
-
Article
| Open Access Gauge ambiguities imply Jaynes-Cummings physics remains valid in ultrastrong coupling QED
Gauge ambiguities imply Jaynes-Cummings physics remains valid in ultrastrong coupling QED
Modelling of light-matter interaction in the ultrastrong coupling regime is still debated. Here, the authors study the consequences of gauge freedom for a two-level system in a single-mode cavity, showing that the Jaynes-Cummings model can outperform the quantum Rabi model even for ultrastrong coupling.
- Adam Stokes
- & Ahsan Nazir
-
Article
| Open Access Ingestible hydrogel device
Ingestible hydrogel device
High swelling ratio, speed and long term robustness tend not coexist in hydrogels which limits their use in devices. Here, the authors introduce a pufferfish-inspired hydrogel device ingested as a standard-sized pill, swells rapidly and maintains robustness under repeated mechanical loads in the stomach.
- Xinyue Liu
- , Christoph Steiger
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-directed rotation of homogeneous micromotors via catalytic self-electrophoresis
Shape-directed rotation of homogeneous micromotors via catalytic self-electrophoresis
Self-propelled motors operating at the micro- or nanoscale can be powered by catalytic reactions and show appealing potential in robotic applications. Brooks et al. describe how the motions of platinum spinners in hydrogen peroxide solutions can be rationally designed by controlling particle shape.
- Allan M. Brooks
- , Mykola Tasinkevych
- & Kyle J. M. Bishop
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible decapyrrylcorannulene hosts
Flexible decapyrrylcorannulene hosts
The structures of fullerenes, or buckyballs, are often very difficult to resolve. Here, the authors describe a decapyrrylcorannulene host with ten flexible pyrryl groups that can efficiently co-crystallize with diverse fullerene derivatives in a ‘hand-ball-hand’ fashion, allowing crystallographic identification of commonly known types of fullerenes.
- Yun-Yan Xu
- , Han-Rui Tian
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum mechanics and the covariance of physical laws in quantum reference frames
Quantum mechanics and the covariance of physical laws in quantum reference frames
Reference frames are ultimately physical systems, and thus it should be possible to quantise them in a consistent way. Here, the authors use a relational formalism to quantise a reference frame and show the covariance of physical laws under transformations between such quantum reference frames.
- Flaminia Giacomini
- , Esteban Castro-Ruiz
- & Časlav Brukner
-
Article
| Open Access Porous supraparticle assembly through self-lubricating evaporating colloidal ouzo drops
Porous supraparticle assembly through self-lubricating evaporating colloidal ouzo drops
Mass fabrication of supraparticles is essential for their applications, but it is not easy. Tan et al. produce porous supraparticles with tunable shapes by drying colloidal particles in water-ethanol-oil ternary drops, where the pining effect at drop edges is alleviated by the formation of oil rings.
- Huanshu Tan
- , Sanghyuk Wooh
- & Detlef Lohse
-
Article
| Open Access Indirect tail states formation by thermal-induced polar fluctuations in halide perovskites
Indirect tail states formation by thermal-induced polar fluctuations in halide perovskites
The weak effects induced by lattice disorder on the optoelectronic properties of halide perovskites still remain elusive. Here Wu et al. confirm the indirect transition tail states in perovskite crystals which explain their low photoluminescence quantum yield, dual emission peaks and difficulties in realizing lasing.
- Bo Wu
- , Haifeng Yuan
- & Tze Chien Sum
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared-pump electronic-probe of methylammonium lead iodide reveals electronically decoupled organic and inorganic sublattices
Infrared-pump electronic-probe of methylammonium lead iodide reveals electronically decoupled organic and inorganic sublattices
It has been challenging to probe whether dynamically disordered organic cations affect optical properties of CH3NH3PbI3. Here, Guo et al. employ infrared-pump electronic-probe spectroscopy and show that pump-induced atomic motions of the organic cations do not substantially alter optoelectronic properties.
- Peijun Guo
- , Arun Mannodi-Kanakkithodi
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article
| Open Access Frustrated supercritical collapse in tunable charge arrays on graphene
Frustrated supercritical collapse in tunable charge arrays on graphene
Placement of charge centres with atomic precision on graphene allows exploration of new types of confinement of charge carriers. Here, the authors fabricate atomically precise arrays of point charges on graphene and observe the onset of a frustrated supercritical regime.
- Jiong Lu
- , Hsin-Zon Tsai
- & Michael F. Crommie
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular weight fractionation by confinement of polymer in one-dimensional pillar[5]arene channels
Molecular weight fractionation by confinement of polymer in one-dimensional pillar[5]arene channels
Confinement of polymers in nano-spaces can induce unique molecular dynamics and properties. Here the authors show high mass fractionation by the confinement of single polymer chains of poly(ethylene oxide) in the one-dimensional channels of crystalline pillar[5]arene.
- Tomoki Ogoshi
- , Ryuta Sueto
- & Motohiro Mizuno
-
Article
| Open Access Towards maximized volumetric capacity via pore-coordinated design for large-volume-change lithium-ion battery anodes
Towards maximized volumetric capacity via pore-coordinated design for large-volume-change lithium-ion battery anodes
Here the authors show a pore-coordinated rational design to enable a Si hybrid anode that exhibits minimized electrode swelling comparable to conventional graphite and therefore high volumetric capacity and energy density.
- Jiyoung Ma
- , Jaekyung Sung
- & Jaephil Cho
-
Article
| Open Access China’s coal mine methane regulations have not curbed growing emissions
China’s coal mine methane regulations have not curbed growing emissions
Chinese government has implemented regulations to reduce mining-related methane emission since 2010. Here the authors estimated methane emissions in China using GOSAT satellite observation and results reveal a business-as-usual increase in methane emissions since 2010 despite those ambitious targets.
- Scot M. Miller
- , Anna M. Michalak
- & Stefan Schwietzke
-
Article
| Open Access Bisnorgammacerane traces predatory pressure and the persistent rise of algal ecosystems after Snowball Earth
Bisnorgammacerane traces predatory pressure and the persistent rise of algal ecosystems after Snowball Earth
It remains unclear when and why the world’s oceans, once largely occupied by bacteria, became dominated by photosynthetic algae. Here, using fossil lipids in million year old rocks, the authors show that predation after the Snowball Earth glaciations created the opportunity for a global shift to algal ecosystems.
- Lennart M. van Maldegem
- , Pierre Sansjofre
- & Christian Hallmann
-
Article
| Open Access Visible light-induced direct α C–H functionalization of alcohols
Visible light-induced direct α C–H functionalization of alcohols
Alcohols are very useful building blocks in organic synthesis, however C–H functionaliztion in presence of free –OH groups is highly challenging. Here, the authors report a selective visible light-promoted α-functionalization of free alcohols with heteroarenes mediated by Selectofluor.
- Linbin Niu
- , Jiamei Liu
- & Aiwen Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental time-reversed adaptive Bell measurement towards all-photonic quantum repeaters
Experimental time-reversed adaptive Bell measurement towards all-photonic quantum repeaters
Storage-free quantum repeaters represent a viable alternative to quantum-memory-based ones. Here, the authors propose a modified scheme for Bell state measurements which reduces the necessary resources for realising such an all-photonic repeater, and show a proof-of-principle implementation.
- Yasushi Hasegawa
- , Rikizo Ikuta
- & Nobuyuki Imoto
-
Article
| Open Access Amide nitrogen pyramidalization changes lactam amide spinning
Amide nitrogen pyramidalization changes lactam amide spinning
Cis-trans lactam amide rotation is a fundamental process and its understanding might aid molecular design. Here, the authors report the synthesis and study of bicyclic lactams which undergo spin through 360 degrees as in open-chain amides, due to the occurrence of nitrogen pyramidalization.
- Yuko Otani
- , Xin Liu
- & Tomohiko Ohwada
-
Article
| Open Access High-flux ultrafast extreme-ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy at 18.4 MHz pulse repetition rate
High-flux ultrafast extreme-ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy at 18.4 MHz pulse repetition rate
Space charge effects can distort the results of photoelectron spectroscopic measurements, and usually limit the allowable photon flux in an experiment. Here, the authors present an 18.4 MHz repetition rate high harmonic source in the 25–60 eV range, with a large count rate improvement over state-of-the-art attosecond setups under identical space charge conditions.
- T. Saule
- , S. Heinrich
- & I. Pupeza
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a two-dimensional \({\cal P}{\cal T}\)-symmetric crystal
Demonstration of a two-dimensional \({\cal P}{\cal T}\)-symmetric crystal
To date, experimental demonstrations of PT-symmetric systems have been restricted to one dimension. Here, the authors experimentally realize and characterize a two-dimensional PT-symmetric system using photonic lattice waveguides with judiciously designed refractive index landscape and an alternating loss distribution.
- Mark Kremer
- , Tobias Biesenthal
- & Alexander Szameit
-
Article
| Open Access A highly active Ni(II)-triadamantylphosphine catalyst for ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene synthesis
A highly active Ni(II)-triadamantylphosphine catalyst for ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene synthesis
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene is a desirable commodity. Here the authors show that a tri-1-adamantylphosphine-nickel complex, when exposed to alkyl aluminium activators, polymerizes ethylene to ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene with initial activities reaching 3.8 million turnovers/h at 10 °C.
- Andrew L. Kocen
- , Maurice Brookhart
- & Olafs Daugulis
-
Article
| Open Access Robust and synthesizable photocatalysts for CO2 reduction: a data-driven materials discovery
Robust and synthesizable photocatalysts for CO2 reduction: a data-driven materials discovery
While the conversion of greenhouse CO2 to chemical fuels offers a promising renewable energy technology, there is a dire need for new materials. Here, authors report the largest CO2 photocathode search using a first-principles approach to identify both known and unreported candidate photocatalysts.
- Arunima K. Singh
- , Joseph H. Montoya
- & Kristin A. Persson
-
Article
| Open Access A meta-analysis of catalytic literature data reveals property-performance correlations for the OCM reaction
A meta-analysis of catalytic literature data reveals property-performance correlations for the OCM reaction
The incomplete nature and undefined structure of the existing catalysis research data has prevented comprehensive knowledge extraction. Here, the authors report a novel meta-analysis method that identifies correlations between a catalyst’s physico-chemical properties and its performance in a particular reaction.
- Roman Schmack
- , Alexandra Friedrich
- & Ralph Kraehnert
-
Article
| Open Access Light- and bias-induced structural variations in metal halide perovskites
Light- and bias-induced structural variations in metal halide perovskites
Organic–inorganic metal halide perovskite solar cells have been under the spotlight but what happens in the working solar cell device at the nanoscale remains elusive. Here Kim et al. show that light and voltage bias can induce strain and structural variation which may cause J–V scan hysteresis.
- Dohyung Kim
- , Jae Sung Yun
- & Jan Seidel
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-high on-chip optical gain in erbium-based hybrid slot waveguides
Ultra-high on-chip optical gain in erbium-based hybrid slot waveguides
Realizing efficient on-chip amplification in silicon is challenging due to either non-compatible integration or small gain per unit length of the amplifier material. Here, the authors report ultra-high on-chip optical gain in erbium-based hybrid silicon nitride slot waveguides with a monolithic, CMOS-compatible and scalable atomic-layer deposition process.
- John Rönn
- , Weiwei Zhang
- & Zhipei Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental demonstration of angular momentum-dependent topological transport using a transmission line network
Experimental demonstration of angular momentum-dependent topological transport using a transmission line network
Here, the authors show that a system can exhibit angular momentum-dependent topological properties through angular-momentum-orbital coupling and provide a proof-of-principle experimental demonstration using a transmission line network.
- Tianshu Jiang
- , Meng Xiao
- & C. T. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical fuel-driven living and transient supramolecular polymerization
Chemical fuel-driven living and transient supramolecular polymerization
Temporal control over self-assembly processes is a desirable trait for discovering adaptable and controllable materials. Here the authors show that a chemical fuel driven system can not only self-assemble in a controlled manner, but can also result in precise control over the assembly and disassembly kinetics.
- Ankit Jain
- , Shikha Dhiman
- & Subi J. George
-
Article
| Open Access Highly twisted supercoils for superelastic multi-functional fibres
Highly twisted supercoils for superelastic multi-functional fibres
The development of electrically conductive fibres is attractive for wearable electronics, but performance should be maintained upon deformation and tensile strain. Here the authors fabricate flexible, stretchable, carbon nanotube-coated spandex fibres for supercapacitors and artificial muscles.
- Wonkyeong Son
- , Sungwoo Chun
- & Changsoon Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Platinum-trimer decorated cobalt-palladium core-shell nanocatalyst with promising performance for oxygen reduction reaction
Platinum-trimer decorated cobalt-palladium core-shell nanocatalyst with promising performance for oxygen reduction reaction
Fuel cells are promising for converting fuel into electricity, but rely on development of high-performance catalysts for oxygen reduction. Here the authors report a highly durable platinum-trimer decorated cobalt-palladium catalyst with low platinum loading for electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction.
- Sheng Dai
- , Jyh-Pin Chou
- & Tsan-Yao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access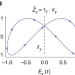 Floquet group theory and its application to selection rules in harmonic generation
Floquet group theory and its application to selection rules in harmonic generation
It is commonly assumed that a complete theory for selection rules in optical nonlinear harmonic generation was developed previously. Here, the authors present more general group theory based formalism for harmonic generation from dilute and dense media, yielding new symmetries and selection rules.
- Ofer Neufeld
- , Daniel Podolsky
- & Oren Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Clear and transparent nanocrystals for infrared-responsive carrier transfer
Clear and transparent nanocrystals for infrared-responsive carrier transfer
Infrared-light-induced carrier transfer is a key technology for ‘invisible’ optical devices, but making materials with the right properties remains a challenge. Here, the authors fabricate a clear and colourless material which converts infrared light to an electrical signal or energy based on a localized surface plasmon resonance, with implications for the development of invisible optical devices.
- Masanori Sakamoto
- , Tokuhisa Kawawaki
- & Toshiharu Teranishi
-
Article
| Open Access Binder-free graphene oxide doughs
Binder-free graphene oxide doughs
Graphene oxide (GO) dispersions may be used as starting materials for graphene-based architectures. Here, a malleable and versatile dough state of GO is discovered, completing the GO–water continuum, which can be diluted or converted to glassy GO or graphene solids without long-range stacking order with enhanced mechanical and electrochemical properties
- Che-Ning Yeh
- , Haiyue Huang
- & Jiaxing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Bond percolation in coloured and multiplex networks
Bond percolation in coloured and multiplex networks
Percolation is a tool used to investigate a network’s response as random links are removed. Here the author presents a generic analytic theory to describe how percolation properties are affected in coloured networks, where the colour can represent a network feature such as multiplexity or the belonging to a community.
- Ivan Kryven
-
Article
| Open Access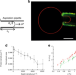 Membrane reshaping by micrometric curvature sensitive septin filaments
Membrane reshaping by micrometric curvature sensitive septin filaments
Septins are cytoskeletal filaments that localize at constriction sites and impact membrane remodeling. Here authors examine the curvature sensitivity of septins using bilayers on wavy patterns and derive a theoretical model that quantitatively describe the results.
- Alexandre Beber
- , Cyntia Taveneau
- & Aurélie Bertin
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced semiconductor-metal transition in ultrathin troilite FeS nanosheets to trigger efficient hydrogen evolution
Photoinduced semiconductor-metal transition in ultrathin troilite FeS nanosheets to trigger efficient hydrogen evolution
While earth-abundant materials are promising catalysts for renewable energy conversion, such materials tend to display poor activities. Here, authors show FeS troilite nanosheets to undergo a near-infrared light-triggered transition to a phase that displays improved H2 evolution performances.
- Gang Zhou
- , Yun Shan
- & Xinglong Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling coherently driven hyperpolarization dynamics in signal amplification by reversible exchange
Unveiling coherently driven hyperpolarization dynamics in signal amplification by reversible exchange
There is increasing effort to improve the signal sensitivity and explore the hyperpolarization dynamics. Here the authors demonstrate the parahydrogen spin transfer dynamics in compounds containing 15N using SABRE hyperpolarization technique with different strengths of the magnetic field.
- Jacob R. Lindale
- , Shannon L. Eriksson
- & Warren S. Warren
-
Article
| Open Access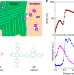 Ultrafast hole transfer mediated by polaron pairs in all-polymer photovoltaic blends
Ultrafast hole transfer mediated by polaron pairs in all-polymer photovoltaic blends
All-polymer solar cells have shown high efficiencies but the ultrafast charge transfer processes are less known. Here Wang et al. show that polaron pairs play vital role facilitating the hole transfer, which is quite different from the exciton dominated pathway in polymer-fullerene blends.
- Rui Wang
- , Yao Yao
- & Min Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Active control of anapole states by structuring the phase-change alloy Ge2Sb2Te5
Active control of anapole states by structuring the phase-change alloy Ge2Sb2Te5
High-index dielectric nanoparticles support a great wealth of multipolar responses but active tunability is still elusive. Here, the authors report how structured Ge2Sb2Te5 can support multipolar Mie resonances and demonstrate the spectral shifting between electric dipole and anapole modes.
- Jingyi Tian
- , Hao Luo
- & Sergey I. Bozhevolnyi
-
Article
| Open Access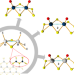 Tuning and mechanistic insights of metal chalcogenide molecular catalysts for the hydrogen-evolution reaction
Tuning and mechanistic insights of metal chalcogenide molecular catalysts for the hydrogen-evolution reaction
While hydrogen offers a potential carbon neutral fuel, its production from water using earth-abundant, heterogeneous materials has proven challenging to understand. Here, authors present a series of molecular electrocatalysts based on molybdenum, sulphur, and oxygen for aqueous hydrogen evolution.
- James McAllister
- , Nuno A. G. Bandeira
- & Haralampos N. Miras
-
Article
| Open Access Spin current generation and relaxation in a quenched spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate
Spin current generation and relaxation in a quenched spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensate
Spin-orbit coupling is interesting for fundamental understanding of spin transport and quench dynamics. Here the authors demonstrate spin-current generation and its relaxation in spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates of Rb atoms in different spin states.
- Chuan-Hsun Li
- , Chunlei Qu
- & Yong P. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning coarse grained models for water
Machine learning coarse grained models for water
A computationally efficient description of ice-water systems at the mesoscopic scale is challenging due to system size and timescale limitations. Here the authors develop a machine-learned coarse-grained water model to elucidate the ice nucleation process much more efficiently than previous models.
- Henry Chan
- , Mathew J. Cherukara
- & Subramanian K. R. S. Sankaranarayanan
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent population trapping by dark state formation in a carbon nanotube quantum dot
Coherent population trapping by dark state formation in a carbon nanotube quantum dot
Transport in quantum systems is complex and can be suppressed by coherent superposition of the involved states. Here, the authors find all-electronic suppression of transport in a carbon nanotube originating from coherent population trapping and give criteria for the presence of such a dark state.
- Andrea Donarini
- , Michael Niklas
- & Milena Grifoni
-
Article
| Open Access A broadband achromatic polarization-insensitive metalens consisting of anisotropic nanostructures
A broadband achromatic polarization-insensitive metalens consisting of anisotropic nanostructures
Polarization-insensitive metasurfaces implies limiting the choice of constituent elements to isotropic nanostructures. Here, the authors demonstrate a polarization-insensitive metalens using anisotropic nanofins, allowing achromatic and polarization-insensitive behaviour across the entire visible.
- Wei Ting Chen
- , Alexander Y. Zhu
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Strong-correlation induced high-mobility electrons in Dirac semimetal of perovskite oxide
Strong-correlation induced high-mobility electrons in Dirac semimetal of perovskite oxide
Electron correlation normally makes electrons less mobile, but it is still not clear when correlation becomes very strong in Dirac semimetals. Here, Fujioka et al. report a very high electron mobility exceeding 60,000 cm2V−1s−1 in correlated Dirac semimetal of perovskite CaIrO3, due to the enhanced electron correlation nearby the Mott transition.
- J. Fujioka
- , R. Yamada
- & Y. Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Control of structural flexibility of layered-pillared metal-organic frameworks anchored at surfaces
Control of structural flexibility of layered-pillared metal-organic frameworks anchored at surfaces
Understanding the structural dynamics of flexible metal-organic frameworks at a thin-film level is key if they are to be implemented in devices. Here, Fischer and colleagues anchor flexible MOF crystallites onto substrates and identify a structural responsiveness that is distinct to that of the bulk.
- Suttipong Wannapaiboon
- , Andreas Schneemann
- & Roland A. Fischer
-
Article
| Open Access Over 56.55% Faradaic efficiency of ambient ammonia synthesis enabled by positively shifting the reaction potential
Over 56.55% Faradaic efficiency of ambient ammonia synthesis enabled by positively shifting the reaction potential
While direct N2 reduction using electrochemistry offers an appealing method to obtain usable nitrogen, materials typically show poor activities and efficiencies. Here, authors demonstrate a single-atom catalyst, iron on N-doped carbon, to have dramatically enhanced N2 reduction efficiencies.
- Mengfan Wang
- , Sisi Liu
- & Chenglin Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Quantized angular momentum in topological optical systems
Quantized angular momentum in topological optical systems
While the Chern number is used to characterize topological states in both electronic and photonic systems, its direct physical meaning in photonics has not yet been established. Here, Silveirinha shows that the photonic Chern number can be understood as a quantum of the optical angular momentum.
- Mário G. Silveirinha
-
Article
| Open Access A variable-stiffness tendril-like soft robot based on reversible osmotic actuation
A variable-stiffness tendril-like soft robot based on reversible osmotic actuation
Plant-inspired osmotic actuation has been proposed as a competitive actuation strategy yet reversibility is still an open issue hampering its implementation in soft robotics. Here the authors show a low input voltage reversible osmotic actuation strategy based on the electrosorption of ions on flexible electrodes.
- Indrek Must
- , Edoardo Sinibaldi
- & Barbara Mazzolai

 Volume expansion and TRPV4 activation regulate stem cell fate in three-dimensional microenvironments
Volume expansion and TRPV4 activation regulate stem cell fate in three-dimensional microenvironments