News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News |
 Scientists supersize quantum mechanics
Scientists supersize quantum mechanics
Largest ever object put into quantum state.
- Geoff Brumfiel
-
Spotlight |
Spotlight on Chemistry
-
News |
 Hunt for the sterile neutrino heats up
Hunt for the sterile neutrino heats up
The elusive particles, if they exist, could help solve some of the most pressing problems in astrophysics.
- Eric Hand
-
News |
 South African astronomer reinstated amid recriminations
South African astronomer reinstated amid recriminations
Royal Society of South Africa calls for inquiry into Phil Charles's suspension.
- Michael Cherry
-
Article |
 Quantum ground state and single-phonon control of a mechanical resonator
Quantum ground state and single-phonon control of a mechanical resonator
Quantum mechanics provides an accurate description of a wide variety of physical systems but it is very challenging to prove that it also applies to macroscopic (classical) mechanical systems. This is because it has been impossible to cool a mechanical mode to its quantum ground state, in which all classical noise is eliminated. Recently, various mechanical devices have been cooled to a near-ground state, but this paper demonstrates the milestone result of a piezoelectric resonator with a mechanical mode cooled to its quantum ground state.
- A. D. O’Connell
- , M. Hofheinz
- & A. N. Cleland
-
News |
 Are the Universe's secrets hiding on a chip?
Are the Universe's secrets hiding on a chip?
Topological insulator could help to test quantum field theory.
- Geoff Brumfiel
-
News |
 Italian molecular cookery 'ban' condemned
Italian molecular cookery 'ban' condemned
Decree to rein in additives could put more processed foods on restaurant tables.
- Emiliano Feresin
-
News |
 Japan prepares for Venus countdown
Japan prepares for Venus countdown
Akatsuki probe could help to explain why Venus is so different from Earth.
- David Cyranoski
-
News |
 Nano-antennas could help keep quantum secrets
Nano-antennas could help keep quantum secrets
Nanorod arrays can guide light along the path toward quantum communication.
- Zeeya Merali
-
Letter |
 Transmission of electrical signals by spin-wave interconversion in a magnetic insulator
Transmission of electrical signals by spin-wave interconversion in a magnetic insulator
An insulator does not conduct electricity, and so cannot in general be used to transmit an electrical signal. But an insulator's electrons possess spin in addition to charge, and so can transmit a signal in the form of a spin wave. Here a hybrid metal–insulator–metal structure is reported, in which an electrical signal in one metal layer is directly converted to a spin wave in the insulating layer; this wave is then transmitted to the second metal layer, where the signal can be directly recovered as an electrical voltage.
- Y. Kajiwara
- , K. Harii
- & E. Saitoh
-
Letter |
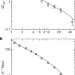 Confirmation of general relativity on large scales from weak lensing and galaxy velocities
Confirmation of general relativity on large scales from weak lensing and galaxy velocities
Although general relativity underlies modern cosmology, its applicability on cosmological length scales has yet to be stringently tested. Now, at a length scale of tens of megaparsecs, the quantity EG, which combines measures of large-scale gravitational lensing, galaxy clustering, and the growth rate of structure, has been measured to be 0.39±0.06, in agreement with the general relativistic prediction of about 0.4.
- Reinabelle Reyes
- , Rachel Mandelbaum
- & Robert E. Smith
-
Letter |
 Tunable polymer multi-shape memory effect
Tunable polymer multi-shape memory effect
When a shape memory polymer is deformed at a temperature defined by a specific phase transition, the deformed shape is fixed upon cooling, but the original shape can be recovered on reheating. Here the perfluorosulphonic acid ionomer Nafion is shown to exhibit at least four different shapes as a result of its broad reversible phase transition.
- Tao Xie
-
Letter |
 A large atomic chlorine source inferred from mid-continental reactive nitrogen chemistry
A large atomic chlorine source inferred from mid-continental reactive nitrogen chemistry
The presence of gaseous chlorine atom precursors within the troposphere was thought only to occur in marine areas but now nitryl chloride has been found at a distance of 1,400 km from the nearest coastline. A model study shows that the amount of nitryl chloride production in the continental USA alone is similar to previous global estimates for marine regions. A significant fraction of tropospheric chlorine atoms may arise directly from anthropogenic pollutants.
- Joel A. Thornton
- , James P. Kercher
- & Steven S. Brown
-
Letter |
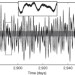 Deviations from a uniform period spacing of gravity modes in a massive star
Deviations from a uniform period spacing of gravity modes in a massive star
Measuring the oscillations of a star can allow the various mixing processes in its interior to be disentangled, through the signature they leave on period spacings in the gravity mode spectrum. Here numerous gravity modes in a young star of about seven solar masses are reported: the mean period spacing enables the extent of the convective core to be determined, and the clear periodic deviation from the mean constrains the location of the chemical transition zone — at about 10 per cent of the radius.
- Pieter Degroote
- , Conny Aerts
- & Eric Michel
-
Research Highlights |
Biomaterials: Squishy particles
-
Research Highlights |
Physics: Photon storage for telecoms
-
Research Highlights |
 Nanotechnology: Harvesting heat
Nanotechnology: Harvesting heat
-
-
-
Research Highlights |
Chemistry: Cellulose busters
-
News & Views |
 Gravity tested on cosmic scales
Gravity tested on cosmic scales
Einstein's theory of general relativity has been tested — and confirmed — on scales far beyond those of our Solar System. But the results don't exclude all alternative theories of gravity.
- J. Anthony Tyson
-
Books & Arts |
 Evolution of the motor car
Evolution of the motor car
A proposed reinvention for urban motoring based on ultra-small electric vehicles does not address the bigger environmental or social challenges, finds Daniel Sperling.
- Daniel Sperling
-
-
News & Views |
 Sticking to sugars
Sticking to sugars
If evolution has had trouble making effective carbohydrate receptors, what hope do humans have of creating synthetic versions? A method for preparing libraries of such receptors boosts the chances of success.
- Anthony P. Davis
-
Highlights |
Highlight:Physics
-
News & Views |
 Wider role for airborne chlorine
Wider role for airborne chlorine
Unexpected chlorine chemistry in the lowest part of the atmosphere can affect the cycling of nitrogen oxides and the production of ozone, and reduce the lifetime of the greenhouse gas methane.
- Roland von Glasow
-
News Feature |
 Nuclear weapons physics: Welcome to the Atomic Weapons Establishment
Nuclear weapons physics: Welcome to the Atomic Weapons Establishment
With the launch of a powerful laser facility, Britain's most secretive lab is opening up to academics. Geoff Brumfiel secures a preview.
- Geoff Brumfiel
-
News Feature |
 Bioengineering: What to make with DNA origami
Bioengineering: What to make with DNA origami
Chemists looking to create complex self-assembling nanostructures are turning to DNA. Katharine Sanderson looks at the science beneath the fold.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
News |
 Einstein passes cosmic test
Einstein passes cosmic test
General relativity fits survey observations but there's still room for its rivals.
- Zeeya Merali
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Electron liquids and solids in one dimension
Electron liquids and solids in one dimension
- Vikram V. Deshpande
- , Marc Bockrath
- & Amir Yacoby
-
-
-
News |
 Old rocks drown dry Moon theory
Old rocks drown dry Moon theory
Samples collected during Apollo missions suggest a wet interior, raising questions about lunar origins.
- Eric Hand
-
News |
 Galileo backed Copernicus despite data
Galileo backed Copernicus despite data
Stars viewed through early telescopes suggested that Earth stood still.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
News |
 Heavy antimatter created in gold collisions
Heavy antimatter created in gold collisions
Most massive antimatter nucleus yet identified in particle experiments.
- Geoff Brumfiel
-
-
Letter |
 Linking dwarf galaxies to halo building blocks with the most metal-poor star in Sculptor
Linking dwarf galaxies to halo building blocks with the most metal-poor star in Sculptor
Current models indicate that the Milky Way's stellar halo was assembled from many smaller systems, and recent studies claimed that the true Galactic building blocks must have been vastly different from the surviving dwarfs. But the overall abundance pattern of elements in S1020549, the most iron-poor star in the Sculptor dwarf galaxies, is now found to follow that seen in low-metallicity halo stars, indicating that the systems destroyed to form the halo billions of years ago were not fundamentally different from the progenitors of present-day dwarfs.
- Anna Frebel
- , Evan N. Kirby
- & Joshua D. Simon
-
Letter |
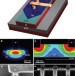 Reinventing germanium avalanche photodetector for nanophotonic on-chip optical interconnects
Reinventing germanium avalanche photodetector for nanophotonic on-chip optical interconnects
To integrate microchips with optical communications a photodetector is required to mediate the optical and electronic signals. Although germanium photodetectors are compatible with silicon their performance is impaired by poor intrinsic noise. Here the noise is reduced by nanometre engineering of optical and electrical fields to produce a compact and efficient photodetector.
- Solomon Assefa
- , Fengnian Xia
- & Yurii A. Vlasov
-
Letter |
 Superconductivity in alkali-metal-doped picene
Superconductivity in alkali-metal-doped picene
The phenomenon of superconductivity continues to intrigue, and several new superconducting materials have been discovered in recent years — but in the case of organic superconductors, no new material system with a high superconducting transition temperature has been identified in the past decade. Now it has been shown that the introduction of potassium into crystals of organic molecule picene can yield superconductivity at temperatures as high as 18 K.
- Ryoji Mitsuhashi
- , Yuta Suzuki
- & Yoshihiro Kubozono
-
Letter |
 Helical crack-front instability in mixed-mode fracture
Helical crack-front instability in mixed-mode fracture
The addition of shear orthogonal to the tension-loading plane of crack propagation generates an instability that results in three-dimensional helical crack propagation, atomically rough surfaces and a fracture pattern resembling a series of lance shapes. Here numerical simulations reveal a new law that governs crack propagation in space for materials subject to general stress conditions.
- Antonio J. Pons
- & Alain Karma
-
-
Research Highlights |
Applied physics: Sound lasers hum along
-
Correspondence |
Esaki diode is still a radio star, half a century on
- Leo Esaki
- , Yasuhiko Arakawa
- & Masatoshi Kitamura
-
-
-
Research Highlights |
 Electronics: Caught on film
Electronics: Caught on film

 Expanding versatility
Expanding versatility Genius who shuns the limelight
Genius who shuns the limelight Space to contemplate
Space to contemplate Non-Abelian states of matter
Non-Abelian states of matter Superconductivity gets an iron boost
Superconductivity gets an iron boost The birth of topological insulators
The birth of topological insulators The enigma of supersolidity
The enigma of supersolidity Spin liquids in frustrated magnets
Spin liquids in frustrated magnets Quantum computers
Quantum computers Spring awakening planned for Mars rover Spirit
Spring awakening planned for Mars rover Spirit