Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusive-like redistribution in state-changing collisions between Rydberg atoms and ground state atoms
Diffusive-like redistribution in state-changing collisions between Rydberg atoms and ground state atoms
Here, the authors discuss state-changing inelastic collisions between rubidium Rydberg and ground state atoms. They employ high-resolution magneto-optical trap recoil-ion momentum spectroscopy to measure the distribution of the final states.
- Philipp Geppert
- , Max Althön
- & Herwig Ott
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous formation of trihydrogen cations from water on nanoparticles
Anomalous formation of trihydrogen cations from water on nanoparticles
The H3+ ion plays a key role in interstellar chemistry and can be formed from organic compounds upon interaction with charged particles or radiation. Here the authors demonstrate that H3+ can also be formed from water adsorbed on silica nanoparticles exposed to intense laser pulses, conditions that mimic the impact of charged particles on dust in astrophysical settings.
- M. Said Alghabra
- , Rami Ali
- & Ali S. Alnaser
-
Article
| Open Access Active coacervate droplets are protocells that grow and resist Ostwald ripening
Active coacervate droplets are protocells that grow and resist Ostwald ripening
Active coacervate droplets are droplets coupled to a chemical reaction that maintains them out of equilibrium, which can be used to drive active processes, but coacervates are still subject to passive processes that compete with or mask growth. Here, the authors present a nucleotide-based model for active coacervate droplets that form and grow by fuel-driven synthesis of ATP, and, importantly, do not undergo Ostwald ripening.
- Karina K. Nakashima
- , Merlijn H. I. van Haren
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access Tailored cobalt-salen complexes enable electrocatalytic intramolecular allylic C–H functionalizations
Tailored cobalt-salen complexes enable electrocatalytic intramolecular allylic C–H functionalizations
Oxidative allylic C–H functionalizations minimise the need for functional group activation and generate alkenyl-substituted products amenable to further chemical modifications. Here the authors report an oxidant-free, electrocatalytic approach to achieve intramolecular oxidative allylic C–H amination and alkylation by employing tailored cobalt-salen complexes as catalysts.
- Chen-Yan Cai
- , Zheng-Jian Wu
- & Hai-Chao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Improved prediction of solvation free energies by machine-learning polarizable continuum solvation model
Improved prediction of solvation free energies by machine-learning polarizable continuum solvation model
Accurate theoretical evaluation of solvation free energy is challenging. Here the authors introduce a machine-learning based polarizable continuum solvation approach to improve the accuracy of widely accepted continuum solvation models by almost one order of magnitude without additional computational costs.
- Amin Alibakhshi
- & Bernd Hartke
-
Article
| Open Access Photon upconversion through triplet exciton-mediated energy relay
Photon upconversion through triplet exciton-mediated energy relay
Photon upconversion in lanthanide-doped nanoparticles enables important technological developments. Here the authors demonstrate a mechanism leading to enhanced upconversion emission in core-shell nanoparticles, and long-distance energy transfer between nanoparticles, through triplet state population of an organic surface ligand.
- Sanyang Han
- , Zhigao Yi
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering (fs-TRXSS) measurements provide information on the structural dynamics of proteins in solution. Here, the authors present a structure refinement method for the analysis of fs-TRXSS data and use it to characterise the ultrafast structural changes of homodimeric haemoglobin.
- Yunbeom Lee
- , Jong Goo Kim
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access Large Stokes shift fluorescence activation in an RNA aptamer by intermolecular proton transfer to guanine
Large Stokes shift fluorescence activation in an RNA aptamer by intermolecular proton transfer to guanine
Fluorogenic RNA aptamers such as Chili display strong fluorescence enhancement upon aptamer–ligand complex formation. Here, the authors provide insights into the mechanism of fluorescence activation of Chili by solving the crystal structures of Chili with its bound positively charged ligands DMHBO+ and DMHBI+, and they reveal that Chili uses an excited state proton transfer mechanism based on time-resolved optical spectroscopy measurements.
- Mateusz Mieczkowski
- , Christian Steinmetzger
- & Claudia Höbartner
-
Article
| Open Access Manifestations of metastable criticality in the long-range structure of model water glasses
Manifestations of metastable criticality in the long-range structure of model water glasses
The subtle connections between water’s supercooled liquid and glassy states are difficult to characterize. Gartner et al. suggest with MD simulations that the long-range structure of glassy water may reflect signatures of water’s debated second critical point in the supercooled liquid.
- Thomas E. Gartner III
- , Salvatore Torquato
- & Pablo G. Debenedetti
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the water oxidative limit for ultra-high-workfunction hole-doped polymers
Overcoming the water oxidative limit for ultra-high-workfunction hole-doped polymers
Realizing ultra-high work functions (UHWFs) in hole-doped polymer semiconductors remains a challenge due to water-oxidation reactions. Here, the authors determine the role of water-anion complexes in limiting the work function and develop a design strategy for realizing UHWF polymers.
- Qi-Mian Koh
- , Cindy Guanyu Tang
- & Peter K. H. Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Through bonds or contacts? Mapping protein vibrational energy transfer using non-canonical amino acids
Through bonds or contacts? Mapping protein vibrational energy transfer using non-canonical amino acids
Vibrational energy transfer (VET) is essential for protein function as it is responsible for efficient energy dissipation in reaction sites and is linked to pathways of allosteric communication. Here authors equipped a tryptophan zipper with a VET injector and a VET sensor for femtosecond pump probe experiments to map the VET.
- Erhan Deniz
- , Luis Valiño-Borau
- & Jens Bredenbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Room temperature exciton–polariton Bose–Einstein condensation in organic single-crystal microribbon cavities
Room temperature exciton–polariton Bose–Einstein condensation in organic single-crystal microribbon cavities
The use of room temperature exciton–polariton Bose–Einstein condensation is limited by the need for external high-finesse microcavities. The authors generate room temperature EPs with single-crystal microribbons as waveguide Fabry–Pérot microcavities, and demonstrate controllable output of coherent light.
- Ji Tang
- , Jian Zhang
- & Yong Sheng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Barrier-free reverse-intersystem crossing in organic molecules by strong light-matter coupling
Barrier-free reverse-intersystem crossing in organic molecules by strong light-matter coupling
Strong coupling of organic materials with optical cavities allows to manipulate the rate of energy transfer between their internal states. Here, the authors show a hybrid state of singlet character with energy lower than the triplet state, and a flow of energy from the triplet to the hybrid state.
- Yi Yu
- , Suman Mallick
- & Karl Börjesson
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and nature of ice XIX
Structure and nature of ice XIX
Water’s phase diagram exhibits several hydrogen-disordered phases which become ordered upon cooling, but the behavior of ice VI is still debated. The authors, using high-pressure neutron diffraction, identify structural distortions that transform ice VI into ice XIX, here identified as a hydrogen disordered phase.
- Christoph G. Salzmann
- , John S. Loveday
- & Craig L. Bull
-
Article
| Open Access Motion of water monomers reveals a kinetic barrier to ice nucleation on graphene
Motion of water monomers reveals a kinetic barrier to ice nucleation on graphene
The dynamics of water molecules at interfaces controls natural and artificial processes, but experimental investigations have been challenging. Here the authors investigate water molecules on a graphene surface using helium spin-echo spectroscopy, and reveal a regime where freely mobile molecules undergo strong repulsive mutual interactions which inhibit ice nucleation.
- Anton Tamtögl
- , Emanuel Bahn
- & William Allison
-
Article
| Open Access A graph-based network for predicting chemical reaction pathways in solid-state materials synthesis
A graph-based network for predicting chemical reaction pathways in solid-state materials synthesis
Predictive computational approaches are fundamental to accelerating solid-state inorganic synthesis. This work demonstrates a computational tractable approach constructed from available thermochemistry data and based on a graph-based network model for predicting solid-state inorganic reaction pathways.
- Matthew J. McDermott
- , Shyam S. Dwaraknath
- & Kristin A. Persson
-
Article
| Open Access All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
Raman optical activity (ROA) is useful for studying conformational structure and behavior of chiral molecules, but is limited by the weak signals. Here, the authors demonstrate 100x signal enhancement via an all-dielectric approach, using a silicon nanodisk array and exploiting its dark mode.
- Ting-Hui Xiao
- , Zhenzhou Cheng
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access 2,6-diaminopurine promotes repair of DNA lesions under prebiotic conditions
2,6-diaminopurine promotes repair of DNA lesions under prebiotic conditions
UV-induced photodamage that likely occurred during the prebiotic synthesis of DNA and RNA is still an untackled issue for their origin on early Earth. Here, the authors show that substitution of 2,6-diaminopurine for adenine enables repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers with high yields, and demonstrate that both 2,6-diaminopurine and adenine nucleosides can be formed under the same prebiotic conditions.
- Rafał Szabla
- , Magdalena Zdrowowicz
- & Janusz Rak
-
Article
| Open Access Autocatalytic and oscillatory reaction networks that form guanidines and products of their cyclization
Autocatalytic and oscillatory reaction networks that form guanidines and products of their cyclization
So far, only a few chemical oscillators based on organic reactions have been developed. Here, the authors report both autocatalytic and oscillatory reaction networks that form substituted guanidines from thiouronium salts; when coupled to cascade cyclization, this reaction network produces oscillations in the production of pyrimidine-based heterocycles.
- Alexander I. Novichkov
- , Anton I. Hanopolskyi
- & Sergey N. Semenov
-
Article
| Open Access Excitonic structure and charge separation in the heliobacterial reaction center probed by multispectral multidimensional spectroscopy
Excitonic structure and charge separation in the heliobacterial reaction center probed by multispectral multidimensional spectroscopy
The primary energy conversion step in photosynthesis, charge separation, takes place in the reaction center. Here the authors investigate the heliobacterial reaction center using multispectral two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy, identifying the primary electron acceptor and revealing the charge separation mechanism.
- Yin Song
- , Riley Sechrist
- & Jennifer P. Ogilvie
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing pseudorotation and ring-opening reactions in colloidal organic molecules
Revealing pseudorotation and ring-opening reactions in colloidal organic molecules
Anisotropically functionalized colloids can serve as meso-atoms for self-assembly of new materials. Swinkels et al. extend the analogy with atomic scale counterparts and show how familiar ring opening and puckering emerges in alkane-like assemblies of tetraedric patchy particles.
- P. J. M. Swinkels
- , S. G. Stuij
- & P. Schall
-
Article
| Open Access Equilibrium and non-equilibrium furanose selection in the ribose isomerisation network
Equilibrium and non-equilibrium furanose selection in the ribose isomerisation network
Furanose species have a key role in the chemistry of life despite their instability over pyranose ones. The authors, through NMR characterization of the anomeric ratios at equilibrium and a non-equilibrium theoretical treatment, show that a steady temperature gradient, at temperatures relevant to the early Earth, favors furanose over pyranose isomers.
- Avinash Vicholous Dass
- , Thomas Georgelin
- & Francesco Piazza
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of ammoniated phyllosilicates on dwarf planet Ceres and asteroids
Origin of ammoniated phyllosilicates on dwarf planet Ceres and asteroids
The authors here propose a chemical reaction that forms ammoniated phyllosilicates on Ceres. This process could trigger at a very low temperature, suggesting Ceres evolution in a region different from its current location.
- Santosh K. Singh
- , Alexandre Bergantini
- & Ralf I. Kaiser
-
Article
| Open Access Confinement effects and acid strength in zeolites
Confinement effects and acid strength in zeolites
The structure of water around Brønsted acid sites in zeolites is shown to influence their catalytic activity. Here the authors shed light on confinement effects in different pores zeolites/water interfaces acidic strength by means of ab-initio molecular dynamics and enhanced sampling metadynamics techniques.
- Emanuele Grifoni
- , GiovanniMaria Piccini
- & Michele Parrinello
-
Article
| Open Access A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
In situ vibrational spectroscopy affords a powerful tool for probing elementary chemical processes on catalytic surfaces. Using surface enhanced Raman scattering, authors identify an array of multicarbon species formed on a Ag nanoparticle catalyst in plasmon-driven reduction of CO2 in water.
- Dinumol Devasia
- , Andrew J. Wilson
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access Three body photodissociation of the water molecule and its implications for prebiotic oxygen production
Three body photodissociation of the water molecule and its implications for prebiotic oxygen production
Three-body dissociation of water, producing one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, has been difficult to investigate due to the lack of intense vacuum ultraviolet sources. Here, using a tunable free-electron laser, the authors obtain quantum yields for this channel showing that it is a possible route to prebiotic oxygen formation in interstellar environments.
- Yao Chang
- , Yong Yu
- & Xueming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Precisely spun super rotors
Precisely spun super rotors
Optical pulses can be useful to create and control molecules in higher quantum states. Here the authors use optical pumping to create rotationally excited states of SiO+ molecular ion into super rotor ensemble.
- Ivan O. Antonov
- , Patrick R. Stollenwerk
- & Brian C. Odom
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ plasmonic tracking oxygen evolution reveals multistage oxygen diffusion and accumulating inhibition
In-situ plasmonic tracking oxygen evolution reveals multistage oxygen diffusion and accumulating inhibition
Understanding mass transfer processes concomitant with gas evolution reactions is important in energy research. Here, the authors show diffusion tracking of dissolved oxygen on copper nanostructured interface with plasmonic signal, and provide a direct observation of the interfacial mass transfer processes.
- Jun-Gang Wang
- , Lifang Shi
- & Di Li
-
Article
| Open Access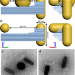 Long- and short-ranged chiral interactions in DNA-assembled plasmonic chains
Long- and short-ranged chiral interactions in DNA-assembled plasmonic chains
Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate chiral transfer over large distances up to 100 nm. They realise the coupling with an achiral nanosphere situated between a pair of distant gold nanorods arranged in a chiral fashion using DNA origami, and observe enhanced circular dichroism signals.
- Kevin Martens
- , Felix Binkowski
- & Tim Liedl
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion in dense supercritical methane from quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
Diffusion in dense supercritical methane from quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
Methane is abundant in the Universe, is an important energy carrier and a model system for fundamental studies. Here, the authors measure the self-diffusion coefficient of supercritical methane at ambient temperature up to the freezing pressure, and find a different behavior than expected based on previous models.
- Umbertoluca Ranieri
- , Stefan Klotz
- & Livia E. Bove
-
Article
| Open Access Polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions
Polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions
Exploiting delocalized organic polaritons for enhanced exciton harvesting has been advantageous for organic optoelectronic with planar heterojunctions. Here, the authors report polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions coupled to the same cavity mode.
- Mao Wang
- , Manuel Hertzog
- & Karl Börjesson
-
Article
| Open Access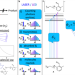 Predicting wavelength-dependent photochemical reactivity and selectivity
Predicting wavelength-dependent photochemical reactivity and selectivity
Predicting the conversion and selectivity of a photochemical reactions is challenging. Here, the authors introduce a framework for the quantitative prediction of the time-dependent progress of a photoligation reaction and predict LED-light induced conversion through a wavelength-resolved numerical simulation.
- Jan P. Menzel
- , Benjamin B. Noble
- & Christopher Barner-Kowollik
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution and universality of two-stage Kondo effect in single manganese phthalocyanine molecule transistors
Evolution and universality of two-stage Kondo effect in single manganese phthalocyanine molecule transistors
The Kondo effect can serve as a powerful paradigm to understand strongly correlated many-body processes in physics. Here, Guo et al. utilize single molecule transistor devices as a testbed to study multi-level Kondo correlation and show electrical gate evolution and the universality of the two-stage Kondo effect.
- Xiao Guo
- , Qiuhao Zhu
- & Wenjie Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow distance-dependent triplet energy migration mediated by endothermic charge-transfer
Shallow distance-dependent triplet energy migration mediated by endothermic charge-transfer
Spin-triplet energy transfer in molecular systems underlies important applications for chemistry and devices. Here, the authors investigate the triplet energy transfer in CdSe quantum dots with varying ZnS shell thicknesses to surface-anchored anthracene molecules and identify a stepwise mechanism mediated by endothermic charge-transfer states.
- Runchen Lai
- , Yangyi Liu
- & Kaifeng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Momentarily trapped exciton polaron in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites
Momentarily trapped exciton polaron in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites
Two-dimensional perovskite shows potential for optoelectronic applications due to its large exciton binding energy, yet the exciton-phonon interaction with the polar soft lattice is not well-understood. Here, the authors reveal the intermediate coupling regime where exciton polarons are momentarily trapped by lattice vibrations.
- Weijian Tao
- , Chi Zhang
- & Haiming Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Thermochromic aggregation-induced dual phosphorescence via temperature-dependent sp3-linked donor-acceptor electronic coupling
Thermochromic aggregation-induced dual phosphorescence via temperature-dependent sp3-linked donor-acceptor electronic coupling
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) has proven to be a viable strategy to achieve highly efficient room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) in bulk by restricting molecular motions. Here, the authors present an RTP design strategy by combining the concept of AIE and donor-acceptor motif and demonstrate unusual thermochromic dual phosphorescence.
- Tao Wang
- , Zhubin Hu
- & Guoqing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The atomistic details of the ice recrystallisation inhibition activity of PVA
The atomistic details of the ice recrystallisation inhibition activity of PVA
Understanding ice re-crystallization is key to improve the current cryopreservation technologies. Here, the authors bring together experiments and simulations to unravel the atomistic details of the ice re-crystallization inhibition (IRI) activity of poly(vinyl)alcohol—the most potent biomimetic IRI agent.
- Fabienne Bachtiger
- , Thomas R. Congdon
- & Gabriele C. Sosso
-
Article
| Open Access Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Vibronic coupling is a key feature of molecular electronic transitions, but its visualization in real space is an experimental challenge. Here the authors, using scanning tunneling microscopy induced luminescence, resolve the effect of vibronic coupling with different modes on the electron distributions in real space in a single pentacene molecule.
- Fan-Fang Kong
- , Xiao-Jun Tian
- & J. G. Hou
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to “A Thermodynamic assessment of the reported room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2”
Reply to “A Thermodynamic assessment of the reported room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2”
- Kazunori Miyamoto
- , Shodai Narita
- & Masanobu Uchiyama
-
Article
| Open Access Ice-nucleating proteins are activated by low temperatures to control the structure of interfacial water
Ice-nucleating proteins are activated by low temperatures to control the structure of interfacial water
Ice-nucleating proteins promote ice formation at high sub-zero temperatures, but the mechanism is still unclear. The authors investigate a model ice-nucleating protein at the air-water interface using vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy and simulations, revealing its reorientation at low temperatures, which increases contact with water molecules and promotes their ordering.
- Steven J. Roeters
- , Thaddeus W. Golbek
- & Tobias Weidner
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence for the existence of a second partially-ordered phase of ice VI
Experimental evidence for the existence of a second partially-ordered phase of ice VI
Water ice exhibits several hydrogen-ordered and disordered phases and it’s unclear if a disordered phase can transform into only one ordered phase. Here, the authors identify a partially hydrogen-ordered phase at high pressure, ice XIX, as the second hydrogen-ordered phase of ice VI beside ice XV.
- Ryo Yamane
- , Kazuki Komatsu
- & Hiroyuki Kagi
-
Article
| Open Access Structural characterization of ice XIX as the second polymorph related to ice VI
Structural characterization of ice XIX as the second polymorph related to ice VI
Water ice exhibits several hydrogen-disordered phases that become ordered upon lowering the temperature, but ordering of ice VI, one of the main ice phases, is not well understood. Here the authors identify and structurally refine a partially hydrogen-ordered phase, ice XIX, obtained from ice VI, and observe its transition to its partially hydrogen-ordered sibling ice XV.
- Tobias M. Gasser
- , Alexander V. Thoeny
- & Thomas Loerting
-
Article
| Open Access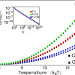 Thermodynamics of structure-forming systems
Thermodynamics of structure-forming systems
Structure-forming systems, such as chemical reaction networks, are usually described with the grand-canonical ensemble, but this may be inaccurate for small-sized systems. Here, the authors propose a canonical ensemble approach for closed structure-forming systems, showing its application to physical problems including the self-assembly of soft matter.
- Jan Korbel
- , Simon David Lindner
- & Stefan Thurner
-
Article
| Open Access Short-lived metal-centered excited state initiates iron-methionine photodissociation in ferrous cytochrome c
Short-lived metal-centered excited state initiates iron-methionine photodissociation in ferrous cytochrome c
The dissociation mechanism of the heme axial ligand in heme proteins is not yet fully understood. The authors investigate the photodissociation dynamics of the bond between heme Fe and methionine S in ferrous cytochrome c using femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering and X-ray emission spectroscopy, simultaneously tracking electronic and nuclear structure changes.
- Marco E. Reinhard
- , Michael W. Mara
- & Kelly J. Gaffney
-
Article
| Open Access Reentrant liquid condensate phase of proteins is stabilized by hydrophobic and non-ionic interactions
Reentrant liquid condensate phase of proteins is stabilized by hydrophobic and non-ionic interactions
Elucidating the molecular driving forces underlying liquid–liquid phase separation is a key objective for understanding biological function and malfunction. Here the authors show that a wide range of cellular proteins, including FUS, TDP-43, Brd4, Sox2, and Annexin A11, which form condensates at low salt concentrations, can reenter a phase-separated regime at high salt concentrations.
- Georg Krainer
- , Timothy J. Welsh
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Bridging scales in disordered porous media by mapping molecular dynamics onto intermittent Brownian motion
Bridging scales in disordered porous media by mapping molecular dynamics onto intermittent Brownian motion
The diffusion of fluids in complex nanoporous geometries represents a challenge for modelling approaches. Here, the authors describe the macroscopic diffusivity of a simple fluid in disordered nanoporous materials by bridging microscopic and mesoscopic dynamics with parameters obtained from simple physical laws.
- Colin Bousige
- , Pierre Levitz
- & Benoit Coasne
-
Article
| Open Access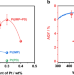 Sequential cocatalyst decoration on BaTaO2N towards highly-active Z-scheme water splitting
Sequential cocatalyst decoration on BaTaO2N towards highly-active Z-scheme water splitting
Activation of narrow-bandgap photocatalysts holds key to applicable solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion. Here, the authors demonstrate effective sequential cocatalyst decoration for such narrow-bandgap photocatalysts to realise highly-efficient hydrogen evolution and Z-scheme water splitting.
- Zheng Wang
- , Ying Luo
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism for rapid autoxidation in α-pinene ozonolysis
Molecular mechanism for rapid autoxidation in α-pinene ozonolysis
Oxidation of volatile organic compounds leads to aerosol formation in the atmosphere, but the mechanism of some fast reactions is still unclear. The authors, using quantum chemical modelling and experiments, reveal that in key monoterpenes the cyclobutyl ring that would hinder the reactivity is broken in the early exothermic steps of the reaction.
- Siddharth Iyer
- , Matti P. Rissanen
- & Theo Kurtén
-
Article
| Open Access Colloidal CdSe nanocrystals are inherently defective
Colloidal CdSe nanocrystals are inherently defective
Colloidal CdSe nanocrystals hold great promise in applications due to their tunable optical spectrum. Using hybrid time-dependent density functional theory, the authors show that colloidal CdSe nanocrystals are inherently defective with a low energy spectrum dominated by dark, surface-associated excitations.
- Tamar Goldzak
- , Alexandra R. McIsaac
- & Troy Van Voorhis

 Interactions between large molecules pose a puzzle for reference quantum mechanical methods
Interactions between large molecules pose a puzzle for reference quantum mechanical methods