Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence and implications of direct charge excitation as the dominant mechanism in plasmon-mediated photocatalysis
Evidence and implications of direct charge excitation as the dominant mechanism in plasmon-mediated photocatalysis
The excitation of metal nanoparticles with light can lead to localized surface plasmon resonances, capable of driving chemical reactions in bound species. Here, the authors elucidate this mechanism and suggest that future plasmonic catalysts may be able to selectively activate specific chemical bonds.
- Calvin Boerigter
- , Robert Campana
- & Suljo Linic
-
Article
| Open Access High-contrast and fast electrochromic switching enabled by plasmonics
High-contrast and fast electrochromic switching enabled by plasmonics
Slow switching speeds in device configurations have severely limited the applications of electrochromic materials. Here, Xu et al. use plasmonic nanoslit arrays and demonstrate fast, high-contrast, monochromatic and full-colour electrochromic switching using two different electrochromic polymers.
- Ting Xu
- , Erich C. Walter
- & A. Alec Talin
-
Article
| Open Access Electropolymerization on wireless electrodes towards conducting polymer microfibre networks
Electropolymerization on wireless electrodes towards conducting polymer microfibre networks
Electropolymerization of aromatic monomers on bipolar electrodes is emerging as promising route to the surface modification of conductive objects. Here, the authors discover that some conducting polymers propagate as fibres, opening up the possibility of growing conductive polymer networks via a wireless process.
- Yuki Koizumi
- , Naoki Shida
- & Shinsuke Inagi
-
Article
| Open Access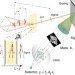 Mapping multidimensional electronic structure and ultrafast dynamics with single-element detection and compressive sensing
Mapping multidimensional electronic structure and ultrafast dynamics with single-element detection and compressive sensing
Many spectral regions lack the sensitive pixel array detectors needed for multidimensional spectroscopy. Here, the authors report a method for rapidly collecting multidimensional optical spectra without an array detector, instead utilizing spatial encoding and a single-element detector.
- Austin P. Spencer
- , Boris Spokoyny
- & Elad Harel
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband single-molecule excitation spectroscopy
Broadband single-molecule excitation spectroscopy
In single-molecule spectroscopy typically only emission spectra are recorded. Here, the authors develop a technique to record single-molecule excitation spectra under ambient conditions, which is robust against blinking and bleaching, and reveals a large distribution of spectra across the molecule ensemble.
- Lukasz Piatkowski
- , Esther Gellings
- & Niek F. van Hulst
-
Article
| Open Access Pulse-density modulation control of chemical oscillation far from equilibrium in a droplet open-reactor system
Pulse-density modulation control of chemical oscillation far from equilibrium in a droplet open-reactor system
Biological systems typically operate at conditions far from chemical equilibrium. Here, the authors model and develop a microfluidic reactor allowing control over time-variable supply and dissipation of chemicals by droplet fusion and fission, allowing non-equilibrium chemical reactions to be regulated.
- Haruka Sugiura
- , Manami Ito
- & Masahiro Takinoue
-
Article
| Open Access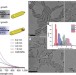 Optimal metal domain size for photocatalysis with hybrid semiconductor-metal nanorods
Optimal metal domain size for photocatalysis with hybrid semiconductor-metal nanorods
The efficiency of photocatalysis on semiconductor-metal hybrid nanostructures can be influenced by myriad factors. Here, through both experimental and theoretical efforts, the authors elucidate the influence of metal domain size upon performance of such structures, allowing future rational design.
- Yuval Ben-Shahar
- , Francesco Scotognella
- & Uri Banin
-
Article
| Open Access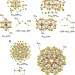 Hierarchy of bond stiffnesses within icosahedral-based gold clusters protected by thiolates
Hierarchy of bond stiffnesses within icosahedral-based gold clusters protected by thiolates
The hierarchy of bond stiffness may contribute to the thermal properties of metal clusters. Here, the authors use X-ray absorption spectroscopy to study the stiffness of the gold–gold and gold–sulfur bonds in a series of thiolate-protected, icosahedral-based gold clusters.
- Seiji Yamazoe
- , Shinjiro Takano
- & Tatsuya Tsukuda
-
Article
| Open Access Insertion compounds and composites made by ball milling for advanced sodium-ion batteries
Insertion compounds and composites made by ball milling for advanced sodium-ion batteries
New sodium-ion battery technology requires better control over solid electrolyte interface formation. Here, the authors report a series of ball-milled sodium alloys and enriched insertion electrodes, which act as sodium reservoirs compensating for sodium loss during solid electrolyte interface formation.
- Biao Zhang
- , Romain Dugas
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article
| Open Access A simple and versatile design concept for fluorophore derivatives with intramolecular photostabilization
A simple and versatile design concept for fluorophore derivatives with intramolecular photostabilization
Synthetic organic fluorophores are powerful tools for bioimaging, but frequently display shortened observation times and signal fluctuations. Here, the authors report a general method to covalently label a biomolecule with a fluorophore and photostabilizer, reducing unwanted photophysical effects by intramolecular quenching of reactive fluorophore states.
- Jasper H. M. van der Velde
- , Jens Oelerich
- & Thorben Cordes
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional controlled growth of monodisperse sub-50 nm heterogeneous nanocrystals
Three-dimensional controlled growth of monodisperse sub-50 nm heterogeneous nanocrystals
Atomic-level control over size, shape and surface composition of nanoparticles is vital for developing materials with integrated multiple functionalities. Here, the authors probe the different roles of oleate ions and oleic acid molecules and their effects on growth mechanisms for sub-50 nm nanoparticles.
- Deming Liu
- , Xiaoxue Xu
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemically driven mechanical energy harvesting
Electrochemically driven mechanical energy harvesting
There is intensive research underway into the development of various mechanical energy harvesters. Here, the authors report an electrochemically driven mechanical energy harvester that uses the stress-induced potential difference of lithiated silicon electrodes to generate continuous electricity.
- Sangtae Kim
- , Soon Ju Choi
- & Ju Li
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of mineral–organic composite formation reveals occlusion mechanism
Direct observation of mineral–organic composite formation reveals occlusion mechanism
The occlusion of biomacromolecules can endow biominerals with enhanced mechanical properties. Here, the authors usein situatomic force microscopy and micromechanical simulations to trace micelle incorporation in calcite to shed light on the mechanism of occlusion and cavity formation.
- Kang Rae Cho
- , Yi-Yeoun Kim
- & James J. De Yoreo
-
Article
| Open Access Transition state theory demonstrated at the micron scale with out-of-equilibrium transport in a confined environment
Transition state theory demonstrated at the micron scale with out-of-equilibrium transport in a confined environment
Transition state theory has proven to be a powerful tool for the analysis of a number of processes, perhaps most commonly chemical reactions. Here, the authors use transition state theory to model a directly observable, micron scale process—the transport of DNA molecules in a confined environment.
- Christian L. Vestergaard
- , Morten Bo Mikkelsen
- & Henrik Flyvbjerg
-
Article
| Open Access The hydrogen-bond network of water supports propagating optical phonon-like modes
The hydrogen-bond network of water supports propagating optical phonon-like modes
How the local structure of water varies as a function of temperature is a long-studied topic, which is still under debate. Here, the authors show that dielectric susceptibility measurements might be used to probe and identify propagating optical phonon-like modes in the hydrogen-bond network of water.
- Daniel C. Elton
- & Marivi Fernández-Serra
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale simulation of carbon nanotube nucleation from hydrocarbon precursors
Atomic scale simulation of carbon nanotube nucleation from hydrocarbon precursors
Atomic scale simulation of the nucleation and growth of carbon nanotubes is essential for understanding their growth mechanism. Here, the authors look at cap nucleation of nanotubes from hydrocarbon precursors, specifically probing the role of hydrogen in the early stages of growth.
- Umedjon Khalilov
- , Annemie Bogaerts
- & Erik C. Neyts
-
Article
| Open Access Tracking molecular resonance forms of donor–acceptor push–pull molecules by single-molecule conductance experiments
Tracking molecular resonance forms of donor–acceptor push–pull molecules by single-molecule conductance experiments
Donor-acceptor molecules are important components for molecular electronics applications. Here, the authors show that donor-acceptor molecular wires exhibit changes in conductivity under the influence of small changes in the environment.
- Henriette Lissau
- , Riccardo Frisenda
- & Kurt V. Mikkelsen
-
Article
| Open Access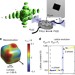 Avalanching strain dynamics during the hydriding phase transformation in individual palladium nanoparticles
Avalanching strain dynamics during the hydriding phase transformation in individual palladium nanoparticles
Phase transformations in nanoparticles can have a large effect on the performance of electrochemical devices and are strongly determined by parameters such as surface energy and faceting. Here, the authors study the hydriding phase transformation in individual palladium nanocubes and uncover individual structure-function relationships.
- A. Ulvestad
- , M. J. Welland
- & O. G. Shpyrko
-
Article
| Open Access A small-gap electrostatic micro-actuator for large deflections
A small-gap electrostatic micro-actuator for large deflections
Most electrostatic actuators suffer from an operational instability, the so-called pull-in effect. Here, the authors report an electrostatic actuator concept which makes the huge electrostatic forces within nanometre small electrode separation accessible for large deflections.
- Holger Conrad
- , Harald Schenk
- & Miriam Lenz
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational gating of DNA conductance
Conformational gating of DNA conductance
DNA could find a role in molecular electronics. Here, the authors show that the conductance of DNA can be reversibly changed by an order of magnitude when its conformation is changed from one form to another by controlling its chemical environment.
- Juan Manuel Artés
- , Yuanhui Li
- & Joshua Hihath
-
Review Article
| Open Access The structural origin of anomalous properties of liquid water
The structural origin of anomalous properties of liquid water
Water is the most common liquid in nature, with unusual properties that could be linked to the peculiar hydrogen-bonding network holding the molecules together. Here, Nilsson and Pettersson review recent progress in searching the connections between local configurations and thermodynamic responses of water.
- Anders Nilsson
- & Lars G. M. Pettersson
-
Article
| Open Access Boundaries can steer active Janus spheres
Boundaries can steer active Janus spheres
Self-propelled colloidal particles can be potentially used to transport cargoes at the microscale, but it is challenging to prevent randomization of their motion by Brownian rotations. Here, Das et al.quench these rotations by solid walls, which guide in-plane swimming without the need for external fields.
- Sambeeta Das
- , Astha Garg
- & Stephen J. Ebbens
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency polymer solar cells with small photon energy loss
High-efficiency polymer solar cells with small photon energy loss
Maximising short-circuit current density and open circuit voltage in polymer-fullerene solar cells is a critical issue. Here, the authors use an aphthobisoxadiazole-based polymer and observe a low photon energy loss of 0.5 eV, with an open-circuit voltage of 1 V and power conversion efficiency of 9%.
- Kazuaki Kawashima
- , Yasunari Tamai
- & Kazuo Takimiya
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation and patterning of supermicelles using dynamic holographic assembly
Transformation and patterning of supermicelles using dynamic holographic assembly
Block copolymers can form micelles and assemblies of micelles (supermicelles) when placed in suitable solvents. Here, the authors use optical tweezers to control the arrangement and deposition of supermicelles into higher-order patterned nanostructures.
- Oliver E.C. Gould
- , Huibin Qiu
- & Ian Manners
-
Article
| Open Access Suppressing molecular motions for enhanced room-temperature phosphorescence of metal-free organic materials
Suppressing molecular motions for enhanced room-temperature phosphorescence of metal-free organic materials
Phosphorescent materials made of purely organic components are typically less efficient than their organometallic counterparts. Here, the authors report a strategy to improve the phosphorescence efficiency of metal-free materials by reducing radiationless transitions by covalently linking into a polymer matrix.
- Min Sang Kwon
- , Youngchang Yu
- & Jinsang Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A tyrosine–tryptophan dyad and radical-based charge transfer in a ribonucleotide reductase-inspired maquette
A tyrosine–tryptophan dyad and radical-based charge transfer in a ribonucleotide reductase-inspired maquette
Tyrosine-tryptophan dyads are known to mediate electron transfer reactions in a range of different proteins. Here, the authors study a beta hairpin peptide, probing the tyrosine-tryptophan interaction and showing no hydrogen bonding but rather charge transfer between the tyrosyl radical and tryptophan'.
- Cynthia V. Pagba
- , Tyler G. McCaslin
- & Bridgette A. Barry
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced optoelectronic quality of perovskite thin films with hypophosphorous acid for planar heterojunction solar cells
Enhanced optoelectronic quality of perovskite thin films with hypophosphorous acid for planar heterojunction solar cells
An imbalance in I/Pb stoichiometry is thought to lead to defects in metal halide films. Here, Zhang et al. show that the addition of hypophosphorous acid in the precursor solution can significantly improve the film quality and enhance the photoluminescence intensity, leading to improved photovoltaic devices.
- Wei Zhang
- , Sandeep Pathak
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging thermal conductivity with nanoscale resolution using a scanning spin probe
Imaging thermal conductivity with nanoscale resolution using a scanning spin probe
Many aspects of energy flow in nanostructures are not well understood due to difficulties associated with resolution. Here, Laraoui et al. use a diamond-nanocrystal-hosted nitrogen vacancy centre as a nanoscale probe with atomic force microscopy to image thermal conductivity.
- Abdelghani Laraoui
- , Halley Aycock-Rizzo
- & Carlos A. Meriles
-
Article
| Open Access Patterning two-dimensional free-standing surfaces with mesoporous conducting polymers
Patterning two-dimensional free-standing surfaces with mesoporous conducting polymers
Solution-state patterning of functional materials on surfaces is important for a number of emerging technologies. Here, the authors demonstrate a bottom-up method of endowing freestanding surfaces with mesoporous conducting polymer coatings for enhanced electrochemical capacitance properties.
- Shaohua Liu
- , Pavlo Gordiichuk
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient near-infrared up-conversion photoluminescence in carbon nanotubes
Efficient near-infrared up-conversion photoluminescence in carbon nanotubes
Photoluminescent objects absorb light and then relax by emitting photons, usually with a lower energy. Here, the authors show that carbon nanotubes also emit larger energy photons thanks to one-phonon-assisted up-conversion, suggesting that nanotubes could be used as near-infrared up-converters.
- Naoto Akizuki
- , Shun Aota
- & Yuhei Miyauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene liquid crystal retarded percolation for new high-k materials
Graphene liquid crystal retarded percolation for new high-k materials
It is commonly believed that graphene flakes form electrical percolation networks at low concentration, and thus can be used as conductive materials. Here, Yuan et al. show in graphene polymer composites that the transition to liquid crystals hinders the formation of percolated networks, resulting in high-kmaterials.
- Jinkai Yuan
- , Alan Luna
- & Philippe Poulin
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray photoemission analysis of clean and carbon monoxide-chemisorbed platinum(111) stepped surfaces using a curved crystal
X-ray photoemission analysis of clean and carbon monoxide-chemisorbed platinum(111) stepped surfaces using a curved crystal
Systematic variation of surface sites may allow for more efficient testing of surface chemical reactions. Here, the authors use a platinum curved crystal and, by carrying out photoemission scans, are able to systematically address the fundamental CO-chemisorption process on a ‘tunable’ vicinal surface.
- Andrew L. Walter
- , Frederik Schiller
- & J. Enrique Ortega
-
Article
| Open Access Atomistic electrodynamics simulations of bare and ligand-coated nanoparticles in the quantum size regime
Atomistic electrodynamics simulations of bare and ligand-coated nanoparticles in the quantum size regime
Investigating the properties of metallic nanoparticles in the 2–10 nm range is a computational challenge. Here, the authors introduce an atomistic electrodynamics model to describe bare and coated particles and dimers, and show that the ligand layer modifies the near-field properties of the particles.
- Xing Chen
- , Justin E. Moore
- & Lasse Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Sponge-like nanoporous single crystals of gold
Sponge-like nanoporous single crystals of gold
Naturally occurring single crystals can exhibit various intricate porous morphologies. Here, the authors are able to grow nanoporous single crystals of gold following solidification of a eutectic composition melt that forms as a result of the dewetting of nanometric thin films.
- Maria Koifman Khristosov
- , Leonid Bloch
- & Boaz Pokroy
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced spontaneous free-carrier generation in semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes
Photoinduced spontaneous free-carrier generation in semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes
Photoinduced carrier-generation in individual semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes is controversial. Here, the authors demonstrate that free carriers can be generated even in the absence of dissociating interfaces by performing time-resolved microwave conductivity on solutions of dispersed nanotubes.
- Jaehong Park
- , Obadiah G. Reid
- & Garry Rumbles
-
Article
| Open Access General synthesis of inorganic single-walled nanotubes
General synthesis of inorganic single-walled nanotubes
Single walled nanotubes are promising materials for both fundamental research and advanced applications. Here, the authors develop the synthesis of four types of inorganic single walled nanotube, and show that their formation is initiated by the self-coiling of their ultrathin building blocks.
- Bing Ni
- , Huiling Liu
- & Xun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of bimetallic clusters in superfluid helium nanodroplets analysed by atomic resolution electron tomography
Formation of bimetallic clusters in superfluid helium nanodroplets analysed by atomic resolution electron tomography
Advancing electron tomography to atomic resolution is a powerful and challenging process. Here, the authors demonstrate atomic resolution electron tomography on silver-gold core-shell nanoclusters grown in superfluid helium nanodroplets, revealing their three-dimensional morphology and composition.
- Georg Haberfehlner
- , Philipp Thaler
- & Gerald Kothleitner
-
Article
| Open Access Mussel adhesion is dictated by time-regulated secretion and molecular conformation of mussel adhesive proteins
Mussel adhesion is dictated by time-regulated secretion and molecular conformation of mussel adhesive proteins
Interfacial water constitutes a formidable barrier to strong surface bonding, hampering the development of water-resistant synthetic adhesives. Here, the authors elucidate the precise time-regulated secretion of mussel adhesive proteins in Perna viridis, probing their surface structures and subsequent roles.
- Luigi Petrone
- , Akshita Kumar
- & Ali Miserez
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous enhancements in photon absorption and charge transport of bismuth vanadate photoanodes for solar water splitting
Simultaneous enhancements in photon absorption and charge transport of bismuth vanadate photoanodes for solar water splitting
Bismuth vanadate is a promising photoanode for water-splitting, although its performance is limited by its wide bandgap. Here, the authors show that a gentle nitrogen treatment can result in nitrogen doping and oxygen vacancy generation, simultaneously reducing bandgap and increasing charge transport.
- Tae Woo Kim
- , Yuan Ping
- & Kyoung-Shin Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Designing bioinspired composite reinforcement architectures via 3D magnetic printing
Designing bioinspired composite reinforcement architectures via 3D magnetic printing
Superior mechanical properties in natural composites are frequently achieved by the inclusion of locally orientated reinforcing particles. Here, the authors implement this design strategy synthetically by employing a 3D magnetic printing protocol to create programmable composite architectures.
- Joshua J. Martin
- , Brad E. Fiore
- & Randall M. Erb
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of ultrafast coherent exciton dynamics in helical π-stacks of self-assembled perylene bisimides
Direct observation of ultrafast coherent exciton dynamics in helical π-stacks of self-assembled perylene bisimides
Molecular self-assemblies have potential as photon processing materials, yet observation of exciton delocalization dynamics can be challenging. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate Frenkel exciton dynamics of H-type aggregates, studying delocalisation of excitons directly after photoexcitation.
- Jooyoung Sung
- , Pyosang Kim
- & Dongho Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Multimaterial magnetically assisted 3D printing of composite materials
Multimaterial magnetically assisted 3D printing of composite materials
Endowing composite materials with spatially discrete mechanical behaviours is possible by varying the internal concentration and arrangement of particles. Here, the authors demonstrate a 3D magnetic printing technique which enables the fabrication of materials with intricate internal designs.
- Dimitri Kokkinis
- , Manuel Schaffner
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt/Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt/Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
There is economic impetus to achieve low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation. Here, the authors use time-resolved diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy and mass spectrometry to show that platinum carbonates formed reversibly from platinum/aluminium oxide can oxidize carbon monoxide at room temperature.
- Mark A. Newton
- , Davide Ferri
- & Maarten Nachtegaal
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh sensitivity and layer-dependent sensing performance of phosphorene-based gas sensors
Ultrahigh sensitivity and layer-dependent sensing performance of phosphorene-based gas sensors
Phosphorene is one of a growing number of 2D materials with high potential for device applications. Here, the authors report a sensor composed of phosphorene nanosheets, showing a high sensitivity to NO2in dry air and also demonstrate that the sensitivity depends on the nanosheet thickness.
- Shumao Cui
- , Haihui Pu
- & Junhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Turning bubbles on and off during boiling using charged surfactants
Turning bubbles on and off during boiling using charged surfactants
Bubble generation during boiling is essential to power generation and heating/cooling systems, but it remains uncontrollable even with state-of-the-art surface engineering. Cho et al. electrostatically attract surfactants to the surface, on which bubble nucleation is manipulated in an on-demand manner.
- H. Jeremy Cho
- , Jordan P. Mizerak
- & Evelyn N. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the density and utilization of active sites in non-precious metal oxygen electroreduction catalysts
Quantifying the density and utilization of active sites in non-precious metal oxygen electroreduction catalysts
Iron and nitrogen doped carbon materials are widely studied electrocatalysts, however measurement of features such as intrinsic turn-over frequency and active site utilization has proved difficult. Here, the authors use a combination of chemisorption and spectroscopy techniques to determine these properties.
- Nastaran Ranjbar Sahraie
- , Ulrike I. Kramm
- & Peter Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Observing in space and time the ephemeral nucleation of liquid-to-crystal phase transitions
Observing in space and time the ephemeral nucleation of liquid-to-crystal phase transitions
The phenomenon of crystallization is common in nature, but surprisingly the nucleation pathways from liquid to solid are poorly understood due to the lack of effective experimental probes. Yoo et al. observe the existence of a nucleation precursor in titanium dioxide using single-pulse electron microscopy.
- Byung-Kuk Yoo
- , Oh-Hoon Kwon
- & Ahmed H. Zewail
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity of black phosphorus nanoribbons at temperatures higher than 100 K
Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity of black phosphorus nanoribbons at temperatures higher than 100 K
Understanding the flow of heat in materials just one or a few atoms thick is vital for harnessing them in compact electronic devices. Here, the authors present the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity of black phosphorus ribbons and demonstrate an intrinsic orientation dependence.
- Sangwook Lee
- , Fan Yang
- & Junqiao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity observed in few-layer black phosphorus
Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity observed in few-layer black phosphorus
The two-dimensional material black phosphorus could find uses in energy applications. Here, the authors study the difference in in-plane thermal conductivity along the armchair and zigzag directions in suspended few-layer black phosphorus, and show the dependence of this anisotropy on sample thickness.
- Zhe Luo
- , Jesse Maassen
- & Xianfan Xu

 Structure sensitivity in the nonscalable regime explored via catalysed ethylene hydrogenation on supported platinum nanoclusters
Structure sensitivity in the nonscalable regime explored via catalysed ethylene hydrogenation on supported platinum nanoclusters