Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Energy cascades in donor-acceptor exciton-polaritons observed by ultrafast two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy
Energy cascades in donor-acceptor exciton-polaritons observed by ultrafast two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy
Exciton-polaritons are hybridized light-matter states that exhibit intriguing phenomena that are unobserved in purely excitonic states. Here, the authors elucidate the photophysical mechanism of polariton-assisted long-range energy transfer in carbon nanotubes using two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy and quantum calculations.
- Minjung Son
- , Zachary T. Armstrong
- & Martin T. Zanni
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of a transient intermediate in the ultrafast relaxation dynamics of the excess electron in strong-field-ionized liquid water
Observation of a transient intermediate in the ultrafast relaxation dynamics of the excess electron in strong-field-ionized liquid water
A unified picture of the electronic relaxation dynamics of ionized liquid water remains elusive despite decades of study. Here, the authors use few-cycle optical pump-probe spectroscopy and ab initio quantum dynamics to unambiguously identify a new transient intermediate in the relaxation pathway.
- Pei Jiang Low
- , Weibin Chu
- & Zhi-Heng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of Fermat’s spiral patterns by solutal Marangoni-driven coiling in an aqueous two-phase system
Generation of Fermat’s spiral patterns by solutal Marangoni-driven coiling in an aqueous two-phase system
In this work, the authors describe a three-dimensional Marangoni transport process in an aqueous two-phase system. Marangoni-driven spreading initiated with salt leads to the formation of Fermat’s spiral patterns, that are of relevance for materials fabrication and microfluidics.
- Yang Xiao
- , Neil M. Ribe
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of site-selective chemical bond changes via ultrafast chemical shifts
Observation of site-selective chemical bond changes via ultrafast chemical shifts
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy probes the chemical environment in a molecule at a specific atomic site. Here the authors extend this concept with a site selective trigger to follow chemical bond changes as they occur on the femtosecond time scale.
- Andre Al-Haddad
- , Solène Oberli
- & Christoph Bostedt
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of hydronium ions on the Pd-catalyzed furfural hydrogenation
Impact of hydronium ions on the Pd-catalyzed furfural hydrogenation
Hydrogen binding and furfural adsorption are critical steps in Pd-catalyzed furfural hydrogenation reactions in aqueous phases. Here, the authors explore how hydronium ion at different pH values modifies the rate constant for this reaction.
- Iris K. M. Yu
- , Fuli Deng
- & Johannes A. Lercher
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation disrupts long-distance electron transport in cytochrome c
Phosphorylation disrupts long-distance electron transport in cytochrome c
Electron transfer between mitochondrial cytochrome c and subunit of cytochrome bc1 can proceed at long distance. Here the authors investigate further the mechanism and show phosphorylation regulation of the interactions between the protein partners in the electron transport chain.
- Alexandre M. J. Gomila
- , Gonzalo Pérez-Mejías
- & Anna Lagunas
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning the Hohenberg-Kohn map for molecular excited states
Machine learning the Hohenberg-Kohn map for molecular excited states
Density functional theory provides a formal map from the electron density to all observables of interest of a many-body system; however, maps for electronic excited states are unknown. Here, the authors demonstrate a data-driven machine learning approach for constructing multistate functionals.
- Yuanming Bai
- , Leslie Vogt-Maranto
- & William J. Glover
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking through water-splitting bottlenecks over carbon nitride with fluorination
Breaking through water-splitting bottlenecks over carbon nitride with fluorination
Graphitic carbon nitride has long been considered a poor oxygen evolution catalyst. Here, the authors report a simple fluorination strategy to prevent the accumulation of inert C=O on carbon nitride to break through this bottleneck.
- Ji Wu
- , Zhonghuan Liu
- & Yongsheng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Retinal chromophore charge delocalization and confinement explain the extreme photophysics of Neorhodopsin
Retinal chromophore charge delocalization and confinement explain the extreme photophysics of Neorhodopsin
Fluorescent proteins that self-assemble and localize in the neuron membrane are vital in neurosciences, particularly in optogenetics applications. Here the authors present a quantum-mechanics/molecular mechanics model for the photoisomerization of the natural highly fluorescent Neorhodopsin, explaining the highly fluorescent quantum yield that could lead to effective visualization of neural signals.
- Riccardo Palombo
- , Leonardo Barneschi
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article
| Open Access Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor
Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor
Improving the efficiency of light-driven molecular rotary motors is a challenging task. Here, the authors combine theoretical modeling, synthesis and spectroscopy to prepare a prototype molecular motor capable of avoiding inefficient thermally activated motion; thus offering prospects to implement a 2-stroke photon-only molecular motor.
- Michael Filatov(Gulak)
- , Marco Paolino
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article
| Open Access Effective screening of Coulomb repulsions in water accelerates reactions of like-charged compounds by orders of magnitude
Effective screening of Coulomb repulsions in water accelerates reactions of like-charged compounds by orders of magnitude
The reaction speed of like-charged compounds in water is extremely slow due to Coulomb repulsions. Here, the authors boost kinetics up to 5 million times by screening these interactions and increasing the local concentration of reactants using positively charged micelles. They show the effect for two independent systems and present a theoretical explanation.
- Adam Kowalski
- , Krzysztof Bielec
- & Robert Holyst
-
Article
| Open Access On the fluorescence enhancement of arch neuronal optogenetic reporters
On the fluorescence enhancement of arch neuronal optogenetic reporters
Arch-3 rhodopsin variants are common fluorescent reporters of neuronal activity. Here, the authors show with quantum chemical modelling that a set of these proteins reveals a direct proportionality between their observed fluorescence intensity and the stability of an exotic excited-state diradical intermediate.
- Leonardo Barneschi
- , Emanuele Marsili
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article
| Open Access The coupling of the hydrated proton to its first solvation shell
The coupling of the hydrated proton to its first solvation shell
The Zundel [H(H2O)2]+ and Eigen [H(H2O)4]+ cations exhibit radicallly different infrared spectra and are the limiting dynamical structures involved in proton mobility in liquid water. Here, the authors find through quantum dynamics simulations that two polarized water molecules and a proton suffice to explain the key spectroscopic features connected to proton mobility for both species.
- Markus Schröder
- , Fabien Gatti
- & Oriol Vendrell
-
Article
| Open Access Selective activation of four quasi-equivalent C–H bonds yields N-doped graphene nanoribbons with partial corannulene motifs
Selective activation of four quasi-equivalent C–H bonds yields N-doped graphene nanoribbons with partial corannulene motifs
Selective activation of C–H bonds is a key challenge in organic reactions. Here, the authors achieve the selective activation of four quasi-equivalent C–H bonds, leading to the formation of N-doped graphene nanoribbons with partial corannulene motifs.
- Yixuan Gao
- , Li Huang
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Facet effect of hematite on the hydrolysis of phthalate esters under ambient humidity conditions
Facet effect of hematite on the hydrolysis of phthalate esters under ambient humidity conditions
With a combined experimental and computational study, Jin et al. demonstrate that hematite nanoparticles can efficiently degrade phthalates under ambient humidity conditions, with a rate strongly dependent on the exposed facet via bidentate coordination involving neighbor Fe atoms, suggesting their possible use for indoor air purification
- Xin Jin
- , Dingding Wu
- & Cheng Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into memory effect mechanisms of layered double hydroxides with solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Insights into memory effect mechanisms of layered double hydroxides with solid-state NMR spectroscopy
The “memory effect” of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) plays a critical role in their applications, yet the details of the mechanism are still under debate. Here authors reveal the nature of the “memory effect” with ex situ and in situ solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
- Li Jin
- , Xiaoyuan Zhou
- & Luming Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Towards fully ab initio simulation of atmospheric aerosol nucleation
Towards fully ab initio simulation of atmospheric aerosol nucleation
Atmosphere aerosol nucleation contributes to climate change, air pollution, and human health, however the mechanisms are complex and elusive. Here the authors propose a general workflow based on deep neural network-based force field, paving the way towards fully ab initio simulation of atmospheric aerosol nucleation.
- Shuai Jiang
- , Yi-Rong Liu
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural diversity in three-dimensional self-assembly of nanoplatelets by spherical confinement
Structural diversity in three-dimensional self-assembly of nanoplatelets by spherical confinement
Nanoplatelets can be used as anisotropic building blocks for constructing novel optoelectronic materials. Here, Wang et al. show a route of assembling nanoplatelets with controllable positional and orientational order in three dimensions facilitated by the surface tension of drying emulsion droplets.
- Da Wang
- , Michiel Hermes
- & Alfons van Blaaderen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of ultrafast singlet exciton fission in three dimensions
Direct observation of ultrafast singlet exciton fission in three dimensions
Here, the authors use quantitative ultrafast interferometric pump-probe microscopy to track photoexcitations with sub-10 nm spatial precision in three dimensions and 15 fs temporal resolution to study the spatiotemporal dynamics of singlet exciton fission in polycrystalline pentacene films.
- Arjun Ashoka
- , Nicolas Gauriot
- & Akshay Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Direct production of olefins from syngas with ultrahigh carbon efficiency
Direct production of olefins from syngas with ultrahigh carbon efficiency
Zhong et al report sodium-promoted metallic Ru nanoparticles for the direct production of olefins from syngas with ultrahigh carbon efficiency where the total selectivity of undesired CH4 and CO2 is suppressed to only 5% for over 500 hours on stream.
- Hailing Yu
- , Caiqi Wang
- & Liangshu Zhong
-
Comment
| Open AccessCritical aspects to enable viable solar-driven evaporative technologies for water treatment
While passive solar-driven evaporative systems promise higher economic and environmental sustainability in water treatment, many challenges remain for their effective adoption. Here, the author identifies three main pillars and corresponding issues which future research should focus on to bring these technologies to the next maturity level.
- Eliodoro Chiavazzo
-
Article
| Open Access Insight into the transient inactivation effect on Au/TiO2 catalyst by in-situ DRIFT and UV–vis spectroscopy
Insight into the transient inactivation effect on Au/TiO2 catalyst by in-situ DRIFT and UV–vis spectroscopy
A molecular-level understanding of the Au-catalyzed CO oxidation on a fast time-resolved scale is still lacking. Here the authors monitor the rapid dynamic changes during CO oxidation over Au/TiO2 using in situ DRIFTS and UV-Vis spectroscopy, and reveal that the catalyst undergoes a surprising structural change at the beginning of the reaction.
- Xianwei Wang
- , Arnulf Rosspeintner
- & Thomas Bürgi
-
Article
| Open Access Water regulates the residence time of Benzamidine in Trypsin
Water regulates the residence time of Benzamidine in Trypsin
Water is an essential part of any biological system, yet many aspects of its role remain elusive. Here the authors show, in a paradigmatic ligand-protein system, that water modulates the ligand residence time in a complex and non-local way, with possible implications in drug design.
- Narjes Ansari
- , Valerio Rizzi
- & Michele Parrinello
-
Article
| Open Access Role of chemisorbing species in growth at liquid metal-electrolyte interfaces revealed by in situ X-ray scattering
Role of chemisorbing species in growth at liquid metal-electrolyte interfaces revealed by in situ X-ray scattering
Growth at liquid-liquid interfaces differ inherently from that on solids, making it attractive for nanomaterial formation. Here, the authors use X-ray scattering to derive a detailed microscopic picture of lead-halide growth on liquid mercury that reveals the key importance of anion adsorption.
- Andrea Sartori
- , Rajendra P. Giri
- & Olaf M. Magnussen
-
Article
| Open Access AC amplification gain in organic electrochemical transistors for impedance-based single cell sensors
AC amplification gain in organic electrochemical transistors for impedance-based single cell sensors
The authors develop a quantitative description of alternating current amplification gain in organic electrochemical transistors. The findings are applied to achieve detection of single glioblastoma cell adhesion with 20 dB gain compared to microelectrodes.
- Filippo Bonafè
- , Francesco Decataldo
- & Beatrice Fraboni
-
Article
| Open Access Triple ionization and fragmentation of benzene trimers following ultrafast intermolecular Coulombic decay
Triple ionization and fragmentation of benzene trimers following ultrafast intermolecular Coulombic decay
Higher-order aromatic clusters are prevalent in biochemical systems, but a full understanding of their structural and dynamical properties is lacking. Here, the authors demonstrate that inner-valence ionization can induce ultrafast relaxation and further fragmentation mechanisms in benzene trimers.
- Jiaqi Zhou
- , Xitao Yu
- & Xueguang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access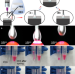 Liquid-liquid triboelectric nanogenerator based on the immiscible interface of an aqueous two-phase system
Liquid-liquid triboelectric nanogenerator based on the immiscible interface of an aqueous two-phase system
While liquid-liquid interface offers better contact and charge transfer potential than solid-based counterparts, fluidity still poses challenges for their application. Here, authors show that charge transfer exists in aqueous two-phase systems and propose a nanogenerator design based on the immiscible aqueous-aqueous interface.
- Ye Lu
- , Longlong Jiang
- & Xiaoxiong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access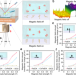 Spin-selected electron transfer in liquid–solid contact electrification
Spin-selected electron transfer in liquid–solid contact electrification
Electron transfer has been shown to contribute to contact electrification at liquid–solid interface. Here, authors investigate the magnetic field effect on the liquid–solid electron transfer and propose a spin conversion model for the liquid–solid contact electrification.
- Shiquan Lin
- , Laipan Zhu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Momentum-selective orbital hybridisation
Momentum-selective orbital hybridisation
When a molecule interacts chemically with a metal, its orbitals hybridise with metal states to form the new eigenstates of the coupled system. Here, the authors show that in addition to overlap in real space and energy, hybridizing states must fulfil a momentum-matching condition.
- Xiaosheng Yang
- , Matteo Jugovac
- & F. Stefan Tautz
-
Article
| Open Access Step-by-step state-selective tracking of fragmentation dynamics of water dications by momentum imaging
Step-by-step state-selective tracking of fragmentation dynamics of water dications by momentum imaging
Determining the time evolution of reactions at the quantum mechanical level improves our understanding of molecular dynamics. Here, authors separate the breakup of water, one bond at a time, from other processes leading to the same final products and experimentally identify, separate, and follow step by step two breakup paths of the transient OD+ fragment.
- Travis Severt
- , Zachary L. Streeter
- & Itzik Ben-Itzhak
-
Article
| Open Access Electron-phonon coupling and vibrational properties of size-selected linear carbon chains by resonance Raman scattering
Electron-phonon coupling and vibrational properties of size-selected linear carbon chains by resonance Raman scattering
H-capped polyynes are the simplest system to observe finite-length effects in carbyne. Here, the authors exploit synchrotron-based UV resonance Raman spectroscopy to explain a peculiar intensity behavior of multiple phonons scattering and show a size-dependent electron-phonon coupling.
- P. Marabotti
- , M. Tommasini
- & C. S. Casari
-
Article
| Open Access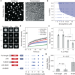 Multivalent interactions between molecular components involved in fast endophilin mediated endocytosis drive protein phase separation
Multivalent interactions between molecular components involved in fast endophilin mediated endocytosis drive protein phase separation
Here the authors show that protein phase separation is a key mechanism in cellular receptor internalization via fast endophilin mediated endocytosis (FEME). Phase separation facilitates multivalent FEME-protein assembly in this clathrin-independent pathway.
- Samsuzzoha Mondal
- , Karthik Narayan
- & Tobias Baumgart
-
Article
| Open Access Electron-mediated control of nanoporosity for targeted molecular separation in carbon membranes
Electron-mediated control of nanoporosity for targeted molecular separation in carbon membranes
Controlled molecular separation by membranes requires 2D materials with precise structures to achieve the desired selectivity. Here authors demonstrate precise selectivity tuning in carbon membranes using electron irradiation.
- Banseok Oh
- , Hyeokjun Seo
- & Dong-Yeun Koh
-
Article
| Open Access A Ziegler-type spherical cap model reveals early stage ethylene polymerization growth versus catalyst fragmentation relationships
A Ziegler-type spherical cap model reveals early stage ethylene polymerization growth versus catalyst fragmentation relationships
Ziegler-type polyolefin catalysts have proven to be hard to characterize. Here the authors present a model system consisting of patterned LaOCl spherical caps, simulating bulk particles while facilitating the use of micro(-spectro)scopic characterization techniques specifically aimed at surfaces.
- Koen W. Bossers
- , Laurens D. B. Mandemaker
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-10-fs observation of bound exciton formation in organic optoelectronic devices
Sub-10-fs observation of bound exciton formation in organic optoelectronic devices
Ultrafast action spectroscopies of organic optoelectronic devices reveal that the formation of bound exciton state occurs as fast as 10 fs. Excitons having excess energy can dissociate spontaneously within 50-fs before acquiring bound character.
- Marios Maimaris
- , Allan J. Pettipher
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Article
| Open Access Precise electrical gating of the single-molecule Mizoroki-Heck reaction
Precise electrical gating of the single-molecule Mizoroki-Heck reaction
Guiding chemical reactions in a predictable and controllable manner is an ultimate goal of chemistry. Here, the authors show tuning of the single-molecule Mizoroki-Heck catalytic cycle through electrical gating and direct in-situ detection.
- Lei Zhang
- , Chen Yang
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Steering the multiexciton generation in slip-stacked perylene dye array via exciton coupling
Steering the multiexciton generation in slip-stacked perylene dye array via exciton coupling
Understanding structure-property relationship of dye arrays is of great importance for designing organic photonic and photovoltaic materials. Here, authors present a slip-stacked perylene bisimide array as a model system to investigate singlet fission mechanisms by depending upon interchromophoric interaction.
- Yongseok Hong
- , Maximilian Rudolf
- & Frank Würthner
-
Article
| Open Access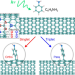 Photochemical spin-state control of binding configuration for tailoring organic color center emission in carbon nanotubes
Photochemical spin-state control of binding configuration for tailoring organic color center emission in carbon nanotubes
Chemical functionalization of the sidewalls of single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) is an emerging route to introduce fluorescent quantum defects and tailor the emission properties. Here, authors demonstrate that spin-selective photochemistry diversifies SWCNT emission tunability by controlling the morphology of the emitting sites.
- Yu Zheng
- , Yulun Han
- & Sergei Tretiak
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected steric hindrance failure in the gas phase F− + (CH3)3CI SN2 reaction
Unexpected steric hindrance failure in the gas phase F− + (CH3)3CI SN2 reaction
Base-induced elimination (E2) and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2) are of significant importance in physical organic chemistry. Here, the authors show that the competing factor of E2 as opposed to steric hindrance determines the low reactivity of SN2 in the F− + (CH3)3CI reaction.
- Xiaoxiao Lu
- , Chenyao Shang
- & Dong H. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by PELDOR/DEER and single-molecule FRET
Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by PELDOR/DEER and single-molecule FRET
Pulsed electron-electron double resonance spectroscopy (PELDOR/DEER) and single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer spectroscopy (smFRET) are used to determine conformational changes and probe distances in biological macromolecules. Here the authors compare the methods on a large set of samples.
- Martin F. Peter
- , Christian Gebhardt
- & Gregor Hagelueken
-
Article
| Open Access A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation
A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation
Despite a promising water harvesting approach solar steam generation low efficiency remains a challenging obstacle. Here, authors present a macro- and microscopically reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly towards a dynamic evaporation system with improved performance and salt resistance.
- Yajie Hu
- , Hongyun Ma
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Bipolar charge collecting structure enables overall water splitting on ferroelectric photocatalysts
Bipolar charge collecting structure enables overall water splitting on ferroelectric photocatalysts
While ferroelectric materials are promising candidates for solar water splitting, most examples show poor activities. Here, authors prepare charge-collecting nanostructures on the positive and negative domains of BaTiO3 and demonstrate photocatalytic overall water splitting.
- Yong Liu
- , Mingjian Zhang
- & Fengtao Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral signatures of excess-proton waiting and transfer-path dynamics in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions
Spectral signatures of excess-proton waiting and transfer-path dynamics in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions
The spectroscopic signatures of excess protons in HCl solutions are studied by ab initio simulations and THz experiments. Two contributions beyond the normal-mode scenario are identified that reflect proton-waiting and proton-transfer processes.
- Florian N. Brünig
- , Manuel Rammler
- & Roland R. Netz
-
Article
| Open Access Energy-efficient pathway for selectively exciting solute molecules to high vibrational states via solvent vibration-polariton pumping
Energy-efficient pathway for selectively exciting solute molecules to high vibrational states via solvent vibration-polariton pumping
Hybrid light-matter states formed in the strong light-matter coupling regime can alter the molecular ground-state reactivity. Here, Li et al. computationally demonstrate that pumping a collection of solvent molecules forming hybrid vibrational light-matter states in an optical cavity can excite solute molecules to very high excited states.
- Tao E. Li
- , Abraham Nitzan
- & Joseph E. Subotnik
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational heterogeneity of molecules physisorbed on a gold surface at room temperature
Conformational heterogeneity of molecules physisorbed on a gold surface at room temperature
Tip-enhanced vibrational spectroscopy at room temperature is complicated by molecular conformational dynamics, photobleaching, contaminations, and chemical reactions in air. This study demonstrates that a sub-nm protective layer of Al2O3 provides robust conditions for probing single-molecule conformations.
- Mingu Kang
- , Hyunwoo Kim
- & Kyoung-Duck Park
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic control over the fundamental structure of atomic wires
Magnetic control over the fundamental structure of atomic wires
Magnetic effects can emerge due to structural variations when the size of materials is reduced towards the nanoscale. Here, Chakrabarti et al demonstrates the opposite effect, showing that the interatomic distance in atomic wires changes by up to 20% depending on the orientation of an applied magnetic field.
- Sudipto Chakrabarti
- , Ayelet Vilan
- & Oren Tal
-
Article
| Open Access Preparation of photonic molecular trains via soft-crystal polymerization of lanthanide complexes
Preparation of photonic molecular trains via soft-crystal polymerization of lanthanide complexes
Soft-crystals are molecular solids with highly ordered structures. Here, authors report the soft-crystal copolymerization of green-luminescent Tb(III) and yellow-luminescent Dy(III) complexes, and study the long-range energy transfer from one crystal to the other.
- Pedro Paulo Ferreira da Rosa
- , Yuichi Kitagawa
- & Yasuchika Hasegawa
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the molecular mechanism of MIL-53(Al) crystallization
Unraveling the molecular mechanism of MIL-53(Al) crystallization
The discovery and control of the synthesis of metal–organic frameworks remains challenging due to the lack of understanding of their nucleation and growth. Here, the authors report a detailed molecular-level mechanism of the formation of MIL-53(Al).
- Daniil Salionov
- , Olesya O. Semivrazhskaya
- & Vitaly L. Sushkevich
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a quasi-liquid phase at solid–liquid interface
Identification of a quasi-liquid phase at solid–liquid interface
Solid–liquid interfaces are ubiquitous in natural and technological processes, but their imaging at the atomic scale has been challenging. The authors, using liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy, identify a quasi-liquid phase and the mass transport between the surface of In and Sn nanocrystals and an aqueous solution.
- Xinxing Peng
- , Fu-Chun Zhu
- & Haimei Zheng

 A dish-like molecular architecture for dynamic ultralong room-temperature phosphorescence through reversible guest accommodation
A dish-like molecular architecture for dynamic ultralong room-temperature phosphorescence through reversible guest accommodation