Featured
-
-
Article |
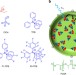 Collective fluorescence switching of counterion-assembled dyes in polymer nanoparticles
Collective fluorescence switching of counterion-assembled dyes in polymer nanoparticles
Fluorescent organic nanoparticles are attractive alternatives to quantum dots for imaging applications. Here, the authors assemble dyes with bulky counterions inside polymer nanoparticles to achieve high fluorescence brightness, as well as a photoinducible and reversible on/off switching.
- Andreas Reisch
- , Pascal Didier
- & Andrey S. Klymchenko
-
Article |
 Roaming dynamics in radical addition–elimination reactions
Roaming dynamics in radical addition–elimination reactions
Roaming dynamics have been shown to be important in unimolecular decompositions, but the relevance to bimolecular reactions has been less clear. Here, the authors study radical addition/elimination reactions and implicate a roaming transition state in a bimolecular reaction.
- Baptiste Joalland
- , Yuanyuan Shi
- & Alexander M. Mebel
-
Article |
 Extreme surface propensity of halide ions in water
Extreme surface propensity of halide ions in water
The surface chemistry of aqueous solutions plays a ubiquitous role in many chemical and biological processes. Here, the authors probe the surfaces of sodium halide solutions with surface-specific femtosecond vibrational spectroscopy, and observe surface concentrations of halide ions several times greater than in the bulk.
- Lukasz Piatkowski
- , Zhen Zhang
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article |
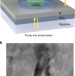 Electrochemically tunable thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide
Electrochemically tunable thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide
Materials with variable and reversible thermal conductivities are important in technologies, and yet such materials are rare. Here, Cho et al. report in situmeasurements of thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide, and show how to reversibly modulate thermal conductivities over a considerable range.
- Jiung Cho
- , Mark D. Losego
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article |
 Nanotechnology makes biomass electrolysis more energy efficient than water electrolysis
Nanotechnology makes biomass electrolysis more energy efficient than water electrolysis
Electrolytic water splitting requires high electrical energy consumption. Here, the authors report a new type of electrolyser that thanks to palladium-doped titania nanotubes oxidizes bio-alcohols, resulting in energy-convenient hydrogen generation as well as valuable chemical production.
- Y. X. Chen
- , A. Lavacchi
- & F. Vizza
-
Article |
 Oxidation-assisted ductility of aluminium nanowires
Oxidation-assisted ductility of aluminium nanowires
The mechanical properties of small volumes are often studied but rarely are the effects of surface oxidation considered. Here, the authors perform a simulation of an aluminium nanowire with an oxide shell deforming in oxygen, finding that the oxide demonstrates superplastic deformation under load.
- Fatih G. Sen
- , Ahmet T. Alpas
- & Yue Qi
-
Article |
 An unconventional bilayer ice structure on a NaCl(001) film
An unconventional bilayer ice structure on a NaCl(001) film
The complication of water adsorption on surfaces goes well beyond a simple hexagonal bilayer model predicted by the ice rule. Chen et al.observe an extended cyclical pattern of water tetramers on an insulator surface, which is attributable to the formation of periodic Bjerrum defects at high density.
- Ji Chen
- , Jing Guo
- & En-Ge Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the force field of a hydrogen-bonded assembly
Mapping the force field of a hydrogen-bonded assembly
Hydrogen bonding is an important force in nature, directing and controlling the assembly of numerous natural and synthetic structures. Here the authors show that the interpretation of intermolecular contrast in atomic force microscope images of hydrogen-bonded assemblies necessitates detailed consideration of the coupled tip-molecule system.
- A. M. Sweetman
- , S. P. Jarvis
- & P. Moriarty
-
Article |
 An electrochemical system for efficiently harvesting low-grade heat energy
An electrochemical system for efficiently harvesting low-grade heat energy
Thermoelectric devices can convert low-grade heat sources into electricity, but suffer from low efficiency. Here, Lee et al.present a thermally regenerative electrochemical device with copper hexacyanoferrate electrode material, which enables efficient heat-to-electricity energy conversion.
- Seok Woo Lee
- , Yuan Yang
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
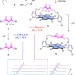 Enolate chemistry with anion–π interactions
Enolate chemistry with anion–π interactions
Interactions between anions and π-systems are possible with electron-poor aromatic surfaces. Here the authors show that anion-π interactions can stabilize enolates—lowering the pKa of the carbonyl compound by almost two units—and likewise accelerate the addition of enolates to electrophiles.
- Yingjie Zhao
- , Naomi Sakai
- & Stefan Matile
-
Article |
 Cold ablation driven by localized forces in alkali halides
Cold ablation driven by localized forces in alkali halides
Cold laser material processing has relied on the use of high-peak-power lasers in order to reach the universal threshold for plasma formation of ~1 J cm−2in most solids. Here, the authors show a cold ablation process that takes off below both the threshold for plasma formation and that of the melting point of alkali halides.
- Masaki Hada
- , Dongfang Zhang
- & R.J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article |
 Desorption kinetics from a surface derived from direct imaging of the adsorbate layer
Desorption kinetics from a surface derived from direct imaging of the adsorbate layer
Desorption kinetics cannot be simply described by the standard method, the temperature-programmed desorption. Here, Günther et al.use low-energy electron microscopy to image an adsorbate layer during desorption, and propose a model that quantitatively explains the complex desorption process.
- S. Günther
- , T. O. Menteş
- & J. Wintterlin
-
Article |
 Solvent-induced immiscibility of polymer brushes eliminates dissipation channels
Solvent-induced immiscibility of polymer brushes eliminates dissipation channels
Interdigitation between polymer brushes decorated on two sliding surfaces induces low friction, which needs to be minimized for bio-lubricant applications. Here the authors show that this friction can be substantially reduced in the systems where immiscible polymer brushes are in contact.
- Sissi de Beer
- , Edit Kutnyanszky
- & Martin H. Müser
-
Article
| Open Access Site-selective photoemission from delocalized valence shells induced by molecular rotation
Site-selective photoemission from delocalized valence shells induced by molecular rotation
Due to the delocalization of molecular orbitals, valence-shell spectroscopy does not allow distinction between individual atoms. Here, the authors show that for photoionization, the difference in mass—and hence recoil momentum—between atoms in a diatomic molecule allows site-selective emission to be observed.
- Catalin Miron
- , Quan Miao
- & Faris Gel'mukhanov
-
Article |
 Subfemtosecond steering of hydrocarbon deprotonation through superposition of vibrational modes
Subfemtosecond steering of hydrocarbon deprotonation through superposition of vibrational modes
Subfemtosecond selective breaking of chemical bonds—such as carbon-hydrogen bonds in organic molecules—can open up new routes for laser-driven synthesis. Here, the authors show directional control of proton ejection in a symmetric acetylene molecule.
- A.S. Alnaser
- , M. Kübel
- & M.F. Kling
-
Article |
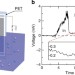 Waving potential in graphene
Waving potential in graphene
Attempts have been made in flowing liquids over carbon nanomaterials to generate electric voltages, but a convincing or significant voltage is yet to be obtained. Here, Yin et al.show an electrokinetic process in which an electric potential of 0.1 V is generated in graphene by a moving liquid–gas boundary.
- Jun Yin
- , Zhuhua Zhang
- & Wanlin Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled multistep synthesis in a three-phase droplet reactor
Controlled multistep synthesis in a three-phase droplet reactor
Droplet chemistry is less susceptible to channel-fouling than single-phase flow chemistry, but is largely limited to simple reactions where all reagents are preloaded into droplets. Here, the authors report a method for multistep chemistry in droplets, using two immiscible liquids and a gas to achieve controlled, sequential reagent addition.
- Adrian M. Nightingale
- , Thomas W. Phillips
- & John C. de Mello
-
Article
| Open Access A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
Chiral determination of vapours is possible in biological systems as an important part of the olfactory system. Here, the authors describe a system that is capable of visually detecting and distinguishing the chirality of vapour-phase molecules by structural changes in a liquid crystal confined in open microchannels.
- Takuya Ohzono
- , Takahiro Yamamoto
- & Jun-ichi Fukuda
-
Article |
 Orbital resolution of molecules covalently attached to a clean semiconductor surface
Orbital resolution of molecules covalently attached to a clean semiconductor surface
It is difficult to spatially resolve molecular orbitals of molecules on highly reactive semiconductor surfaces. Here, Xu et al.use scanning tunnelling microscopy to study pyridazine molecules on a clean germanium surface, and hybridized molecular orbitals are directly imaged.
- Jing Hui He
- , Wei Mao
- & Eng Soon Tok
-
Article |
 Unexpected interplay of bonding height and energy level alignment at heteromolecular hybrid interfaces
Unexpected interplay of bonding height and energy level alignment at heteromolecular hybrid interfaces
Typically for surface adsorption there is a direct relationship between interaction strength and geometric distance—a stronger interaction leads to a shorter distance between interacting objects. Here the authors show a case where a stronger interaction leads to a larger distance, and explain this apparent paradox.
- Benjamin Stadtmüller
- , Daniel Lüftner
- & Christian Kumpf
-
Article |
 Vibrational nano-spectroscopic imaging correlating structure with intermolecular coupling and dynamics
Vibrational nano-spectroscopic imaging correlating structure with intermolecular coupling and dynamics
Quantifying intermolecular coupling and local morphology is important to understand soft matter systems. Pollard et al. show how multispectral vibrational near-field optical microscopy can be used to image molecular-scale morphology and intermolecular interactions with nanometre spatial resolution.
- Benjamin Pollard
- , Eric A. Muller
- & Markus B. Raschke
-
Article |
 Large-scale self-assembled zirconium phosphate smectic layers via a simple spray-coating process
Large-scale self-assembled zirconium phosphate smectic layers via a simple spray-coating process
The large-scale assembly of asymmetric colloidal particles is used in creating high-performance fibres and two-dimensional materials. Here, the authors present a spray-coating process for the fabrication of thin, flexible nanoplatelet/epoxy films and study their gas barrier properties.
- Minhao Wong
- , Ryohei Ishige
- & Hung-Jue Sue
-
Article
| Open Access Hydride ions in oxide hosts hidden by hydroxide ions
Hydride ions in oxide hosts hidden by hydroxide ions
The oxidation state of hydride ions in oxide hosts is a matter of debate. Here, the authors address this question with a range of techniques and suggest that the electron density near an incorporated hydride ion is less than that at the hydrogen in a hydroxide ion, contrary to formal valence arguments.
- Katsuro Hayashi
- , Peter V. Sushko
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Article |
 Ammonia as a case study for the spontaneous ionization of a simple hydrogen-bonded compound
Ammonia as a case study for the spontaneous ionization of a simple hydrogen-bonded compound
Ionization of highly compressed ammonia has previously been predicted by computation. Here, the authors provide experimental evidence for this autoionization process at high pressures, showing the transformation of molecular ammonia into ammonium amide.
- Taras Palasyuk
- , Ivan Troyan
- & Pavel Naumov
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpectedly high pressure for molecular dissociation in liquid hydrogen by electronic simulation
Unexpectedly high pressure for molecular dissociation in liquid hydrogen by electronic simulation
Studying the high pressure phase diagram of hydrogen experimentally or by simulations presents significant challenges. Here, the authors apply a combined molecular dynamics and many-body quantum Monte Carlo approach, finding that the molecular liquid phase is stable at higher pressures than previously believed.
- Guglielmo Mazzola
- , Seiji Yunoki
- & Sandro Sorella
-
Article |
 8.4% efficient fullerene-free organic solar cells exploiting long-range exciton energy transfer
8.4% efficient fullerene-free organic solar cells exploiting long-range exciton energy transfer
Organic solar cells usually require the incorporation of costly fullerene acceptor layers. Cnops et al.report a multilayer organic solar cell that extracts photogenerated excitons by a two-step mechanism and achieves unprecedented conversion efficiencies of up to 8.4% without the use of fullerenes.
- Kjell Cnops
- , Barry P. Rand
- & Paul Heremans
-
Article |
 Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
The structure of hydrogels is normally isotropic, but anisotropic hydrogels with a periodic lamellar structure can also be synthesized. Here the confined water layers in a lamellar hydrogel are used to guide the growth of large area, single-crystalline gold membranes with two-dimensional properties.
- Jian Niu
- , Dong Wang
- & Jian Jin
-
Article |
 Casimir-like forces at the percolation transition
Casimir-like forces at the percolation transition
Colloidal particles may experience a long-range force because of the confinement of solvent fluctuations. Gnan et al.show numerically that such Casimir-like effect also occurs when colloids are immersed in a chemical sol close to percolation, which provides an alternative way to tune colloidal interactions.
- Nicoletta Gnan
- , Emanuela Zaccarelli
- & Francesco Sciortino
-
Article |
 Polystyrene sulphonic acid resins with enhanced acid strength via macromolecular self-assembly within confined nanospace
Polystyrene sulphonic acid resins with enhanced acid strength via macromolecular self-assembly within confined nanospace
Solid acid catalysts allow easy separation and reduction in waste not easily achievable with mineral acids. Here the authors report polystyrene sulphonic acid resins whose acid strength and catalytic performance can be tuned by changing their morphology within a confined nanospace.
- Xiaomin Zhang
- , Yaopeng Zhao
- & Qihua Yang
-
Article |
 The isotopic effects of deuteration on optoelectronic properties of conducting polymers
The isotopic effects of deuteration on optoelectronic properties of conducting polymers
Isotopic substitution alters the optoelectronic properties of conducting polymers, but a microscopic understanding is still missing. Shao et al.address this effect using a series of polymer isotopes that are synthesized with deuterium atoms substituted either on their backbone or side chains.
- Ming Shao
- , Jong Keum
- & Kai Xiao
-
Article |
 A very stable complex of a modified marine cyclopeptide with chloroform
A very stable complex of a modified marine cyclopeptide with chloroform
Typically dispersion forces are weak interactions, and host–guest chemistry is dominated by more powerful events such as hydrogen bonding. Here, the authors show extremely high binding between a modified marine peptide and chloroform, driven by dispersion interactions with the chlorine atoms.
- Gebhard Haberhauer
- , Áron Pintér
- & Sascha Woitschetzki
-
Article |
 Adaptive strong-field control of chemical dynamics guided by three-dimensional momentum imaging
Adaptive strong-field control of chemical dynamics guided by three-dimensional momentum imaging
Shaped femtosecond laser pulses can control the dynamics of chemical reactions but understanding the underlying control process is difficult. Towards this end, Wells et al.show that feedback from rapid inversion of velocity map images of photofragment ions can target specific adaptive control outcomes.
- E. Wells
- , C.E. Rallis
- & I. Ben-Itzhak
-
Article |
 Surface tension and contact with soft elastic solids
Surface tension and contact with soft elastic solids
Solid contacts on a microscopic level are widely described by a classical contact mechanics theory. Here Styleet al.show that this theory breaks down when a small particle adheres to a soft surface where a fluid-like behaviour is observed because of the predominant role played by surface tension.
- Robert W. Style
- , Callen Hyland
- & Eric R. Dufresne
-
Article |
 A solid–solid phase transition in carbon dioxide at high pressures and intermediate temperatures
A solid–solid phase transition in carbon dioxide at high pressures and intermediate temperatures
It is desirable for scientists to be able to predict the structures, spectra and phase diagrams of molecular crystals using ab initio computation. Li et al. demonstrate such an approach, which is able to determine the phase behaviour of solid carbon dioxide at a range of pressures and temperatures.
- Jinjin Li
- , Olaseni Sode
- & So Hirata
-
Article |
 Harvesting singlet fission for solar energy conversion via triplet energy transfer
Harvesting singlet fission for solar energy conversion via triplet energy transfer
The efficiency of organic solar cells may be increased by the incorporation of materials capable of singlet fission. Here, Tritsch and colleagues identify strategies to enhance the extraction of multiple excitons from the desirable singlet fission process.
- John R. Tritsch
- , Wai-Lun Chan
- & X-Y. Zhu
-
Article |
 An electrostatic model for the determination of magnetic anisotropy in dysprosium complexes
An electrostatic model for the determination of magnetic anisotropy in dysprosium complexes
Understanding the anisotropic electronic structure of lanthanide complexes is useful for a range of advanced applications. Here, the authors present a simple electrostatic method, capable of predicting the magnetic anisotropy of low-symmetry mononuclear and polynuclear dysprosium(III) complexes.
- Nicholas F. Chilton
- , David Collison
- & Alessandro Soncini
-
Article |
 Model studies of force-dependent kinetics of multi-barrier reactions
Model studies of force-dependent kinetics of multi-barrier reactions
In chemical reactions, inner barriers, which precede the rate-determining transition state, are kinetically invisible but mechanistically significant. On an example of reduction of macrocyclic disulphides, the authors quantify these inner barriers by studying the reaction rate as a function of applied force.
- Yancong Tian
- , Timothy J. Kucharski
- & Roman Boulatov
-
Article |
 Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Liquid water shows anomalous behaviour, which is expected to be related with critical phenomena below its melting temperature. Taschinet al.experimentally identify two intermolecular vibrational modes that provide evidence for the coexistence of high-density and low-density water forms.
- A. Taschin
- , P. Bartolini
- & R. Torre
-
Article |
 Carbon precipitation from heavy hydrocarbon fluid in deep planetary interiors
Carbon precipitation from heavy hydrocarbon fluid in deep planetary interiors
Methane is a major constituent of planetary interiors, yet phase relations in the C–H system are poorly understood. This work documents the chemical reactivity of the C–H system over a wide range of temperatures and pressures, and sheds light on the chemical composition of Earth and icy giants.
- Sergey S. Lobanov
- , Pei-Nan Chen
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article |
 A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries
A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries
Anode materials in sodium-ion batteries can undergo significant volume change upon sodium insertion and extraction, leading to deteriorated cycling performance. Wang et al. report a layered metal oxide anode with zero-strain characteristics, which may lead to extended battery cycle life.
- Yuesheng Wang
- , Xiqian Yu
- & Xuejie Huang
-
Article |
 Membrane-less hydrogen bromine flow battery
Membrane-less hydrogen bromine flow battery
Membrane-less electrochemical systems eliminate the need for costly ion-exchange membranes, but typically suffer from low-power densities. Braff et al.propose a hydrogen bromine laminar flow battery, which rivals the performance of the best membrane-based systems.
- William A. Braff
- , Martin Z. Bazant
- & Cullen R. Buie
-
Article
| Open Access Role of point defects on the reactivity of reconstructed anatase titanium dioxide (001) surface
Role of point defects on the reactivity of reconstructed anatase titanium dioxide (001) surface
Theory suggests that the anatase (001) surface is the most catalytically reactive of all the crystal facets of titanium dioxide. Wang et al.show that the active sites are four-coordinated titanium states and in their absence this surface is even inert for water adsorption at room temperature.
- Yang Wang
- , Huijuan Sun
- & J. G. Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Hypervalent surface interactions for colloidal stability and doping of silicon nanocrystals
Hypervalent surface interactions for colloidal stability and doping of silicon nanocrystals
Electrically insulating ligands and doping of colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals continue to be significant challenges for practical nanocrystal-based optoelectronics. Wheeler et al.demonstrate a new surface chemistry technique that confronts both of these challenges simultaneously.
- Lance M. Wheeler
- , Nathan R. Neale
- & Uwe R. Kortshagen
-
Article |
 Understanding the role of phase in chemical bond breaking with coincidence angular streaking
Understanding the role of phase in chemical bond breaking with coincidence angular streaking
Ultrafast laser pulses are useful to study electron dynamics in chemical bonds, but their influence on bond breaking is not fully understood. Wu et al. study H2 bond breaking with coincidence techniques, and find a phase-dependent anisotropy of the H+fragmentation even for isotropic multicycle laser pulses.
- J. Wu
- , M. Magrakvelidze
- & R. Dörner
-
Article
| Open Access Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Many interesting chemical problems like photosynthesis and photovoltaics involve non-adiabatic dynamical phenomena, which are difficult to predict theoretically. Here, the authors develop a new numerical method capable of recovering quantum interferences that are neglected by conventional methods.
- Vyacheslav N. Gorshkov
- , Sergei Tretiak
- & Dmitry Mozyrsky
-
Article |
 Multistep kinetic self-assembly of DNA-coated colloids
Multistep kinetic self-assembly of DNA-coated colloids
The final state of self-assembled systems is determined by both their thermodynamic and kinetic pathways. Di Michele et al.develop a strategy to realize predesigned amorphous structures of complex DNA colloidal mixtures by selectively activating local inter- or intra-species interactions upon freezing.
- Lorenzo Di Michele
- , Francesco Varrato
- & Erika Eiser
-
Article
| Open Access Nonvolatile liquid anthracenes for facile full-colour luminescence tuning at single blue-light excitation
Nonvolatile liquid anthracenes for facile full-colour luminescence tuning at single blue-light excitation
Nonvolatile luminescent liquids are solvent-free fluids with a range of flexible electronic applications. Here, the authors show that anthracenes enveloped in branched aliphatic compounds are stable emissive liquids, with emissive and thermoresponsive properties that may be tuned by addition of dopants.
- Sukumaran Santhosh Babu
- , Martin J. Hollamby
- & Takashi Nakanishi
-
Article |
 Catalytically active single-atom niobium in graphitic layers
Catalytically active single-atom niobium in graphitic layers
Noble metallic subnanometre clusters exhibit superior catalytic activities, but their stability remains a problem. Zhang et al. report that single niobium atoms can be stabilized in graphitic layers and the resulting carbide complex exhibits higher activity compared with commercial platinum nanoclusters.
- Xuefeng Zhang
- , Junjie Guo
- & Matthew F. Chisholm
-
Article |
 Using 20-million-year-old amber to test the super-Arrhenius behaviour of glass-forming systems
Using 20-million-year-old amber to test the super-Arrhenius behaviour of glass-forming systems
Classical theory predicts that glass dynamics exhibit a singularity at some finite temperature. Zhao et al. test this theory in fossil amber by determining upper bounds of the equilibrium relaxation times, and find no such behaviour even far below the glass transition challenging conventional assumptions.
- Jing Zhao
- , Sindee L. Simon
- & Gregory B. McKenna

 Isolation and reversible dimerization of a selenium–selenium three-electron σ-bond
Isolation and reversible dimerization of a selenium–selenium three-electron σ-bond