Article |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Multi-body coalescence in Pickering emulsions
Multi-body coalescence in Pickering emulsions
Pickering emulsions are particle-stabilized droplets suspended in an immiscible liquid, and the study of individual droplet coalescence has yielded many interesting findings. Here, Wu et al. move towards larger droplet numbers to investigate the influence of population on coalescence.
- Tong Wu
- , Haitao Wang
- & Chongzheng Na
-
Article |
 Exciton dynamics reveal aggregates with intermolecular order at hidden interfaces in solution-cast organic semiconducting films
Exciton dynamics reveal aggregates with intermolecular order at hidden interfaces in solution-cast organic semiconducting films
Grain boundaries between crystalline domains in solution-processed organic semiconductor thin films are believed to inhibit charge transport, but their structure is invisible to conventional characterization techniques. Wong et al. show the existence of nano-crystalline aggregates at domain interfaces.
- Cathy Y. Wong
- , Benjamin L. Cotts
- & Naomi S. Ginsberg
-
Article |
 Single-crystal field-effect transistors of new Cl2-NDI polymorph processed by sublimation in air
Single-crystal field-effect transistors of new Cl2-NDI polymorph processed by sublimation in air
Charge transport in organic semiconductors is highly sensitive to crystalline polymorphs. Here, He et al. manufacture the first n-channel single-crystal transistor via sublimation at ambient conditions and identify a new polymorphous phase that does not exist in its solution-processed counterpart.
- Tao He
- , Matthias Stolte
- & Frank Würthner
-
Article |
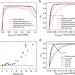 Correlating hydrogen oxidation and evolution activity on platinum at different pH with measured hydrogen binding energy
Correlating hydrogen oxidation and evolution activity on platinum at different pH with measured hydrogen binding energy
Hydrogen oxidation and evolution are two of the key reactions in renewable energy conversion and storage devices. Here, the authors report the correlation between reaction rate and measured hydrogen binding energy for polycrystalline platinum in buffer solutions ranging from pH 0 to 13.
- Wenchao Sheng
- , Zhongbin Zhuang
- & Yushan Yan
-
Article |
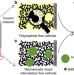 Sulphur-impregnated flow cathode to enable high-energy-density lithium flow batteries
Sulphur-impregnated flow cathode to enable high-energy-density lithium flow batteries
Redox flow batteries are a promising technique for large-scale electricity storage, but suffer from low energy density and volumetric capacity. Here, the authors present a lithium redox flow battery with a sulphur-impregnated carbon composite as the catholyte, which leads to substantial performance improvement.
- Hongning Chen
- , Qingli Zou
- & Yi-Chun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access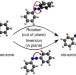 Fast photodynamics of azobenzene probed by scanning excited-state potential energy surfaces using slow spectroscopy
Fast photodynamics of azobenzene probed by scanning excited-state potential energy surfaces using slow spectroscopy
Azobenzene is perhaps the archetypal light-activated molecule, widely used for photoswitching applications, but the mechanism of isomerisation remains in doubt. Here, the authors provide high-resolution excitation spectra of trans-azobenzene, identifying the structural changes accompanying photoisomerisation.
- Eric M. M. Tan
- , Saeed Amirjalayer
- & Wybren Jan Buma
-
Article |
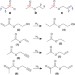 ParaHydrogen Induced Polarization of 13C carboxylate resonance in acetate and pyruvate
ParaHydrogen Induced Polarization of 13C carboxylate resonance in acetate and pyruvate
Compounds such as acetate and pyruvate are useful probes for MRI, but their hyperpolarization relies on difficult and expensive dynamic nuclear polarization techniques. Here, the authors show how parahydrogen-induced polarization can be used to quickly and inexpensively hyperpolarize these compounds.
- Francesca Reineri
- , Tommaso Boi
- & Silvio Aime
-
Article |
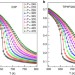 Widom line and dynamical crossovers as routes to understand supercritical water
Widom line and dynamical crossovers as routes to understand supercritical water
Liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable at supercritical conditions. Here, Gallo et al.show that this convention is not precisely true for supercritical water on approaching its critical point due to the existence of the Widom line, which separates a liquid-like and a gas-like regime on its two sides.
- P. Gallo
- , D. Corradini
- & M. Rovere
-
Article |
 Imaging the structure of the trimer systems 4He3 and 3He4He2
Imaging the structure of the trimer systems 4He3 and 3He4He2
Helium is an atom of great scientific interest, yet much debate exists surrounding the shape its molecules form. Here Voigtsberger et al. present experimental results imaging the wavefuction of 4He3 and 3He4He2 trimer systems, which suggest that 4He3 is a random cloud while 3He4He2is a quantum halo state.
- J. Voigtsberger
- , S. Zeller
- & R. Dörner
-
Article |
 Pressure-induced chemistry in a nitrogen-hydrogen host–guest structure
Pressure-induced chemistry in a nitrogen-hydrogen host–guest structure
There is extensive research in the topochemistry of molecular systems at high pressure, although studies of binary gas mixtures are rarer. Here, the authors study a nitrogen/hydrogen mixture under pressure, identifying new van der Waals compounds and probing the room-temperature, high-pressure chemistry.
- Dylan K. Spaulding
- , Gunnar Weck
- & Michael Hanfland
-
Article
| Open Access Observing classical nucleation theory at work by monitoring phase transitions with molecular precision
Observing classical nucleation theory at work by monitoring phase transitions with molecular precision
Many nanoscale systems can form ordered microphases through non-classical multistep nucleation. Here, the authors report that glucose isomerase, which is known to exhibit the characteristics of multi-step nucleation in 3D, nucleates along the pathway predicted by classical nucleation theory in 2D.
- Mike Sleutel
- , Jim Lutsko
- & Dominique Maes
-
Article
| Open Access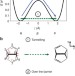 X-ray imaging of chemically active valence electrons during a pericyclic reaction
X-ray imaging of chemically active valence electrons during a pericyclic reaction
X-ray scattering experiments give details of the electrons in a system, although typically this is dominated by core and inert valence electrons. Here, the authors report a method to follow changes in the chemically active valence electrons, and use it to study the reaction mechanism of a pericyclic reaction.
- Timm Bredtmann
- , Misha Ivanov
- & Gopal Dixit
-
Article
| Open Access Non-additivity of molecule-surface van der Waals potentials from force measurements
Non-additivity of molecule-surface van der Waals potentials from force measurements
Van der Waals interactions are difficult to calculate at an atomistic level for moderate sized structures due to the many distinct atoms involved. Here, the authors measure the van der Waals force between an organic molecule and a metal surface, examining the non-additive part of these interactions.
- Christian Wagner
- , Norman Fournier
- & F. Stefan Tautz
-
Article |
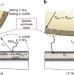 Deciphering the scaling of single-molecule interactions using Jarzynski’s equality
Deciphering the scaling of single-molecule interactions using Jarzynski’s equality
Adhesion forces depend on the strength and density of the individual molecular interactions of which they are composed. Here, the authors use surface force apparatus and atomic force microscopy to experimentally probe the scaling of single-molecule interactions into macroscopic properties.
- Sangeetha Raman
- , Thomas Utzig
- & Markus Valtiner
-
Article |
 Ostwald’s rule of stages governs structural transitions and morphology of dipeptide supramolecular polymers
Ostwald’s rule of stages governs structural transitions and morphology of dipeptide supramolecular polymers
Suparmolecular polymers are built by monomers via non-covalent bonds, whilst the pathway of their nucleation processes is not yet clear. Here, Levin et al.show that the self-assembly of monomers proceeds through a series of metastable states, which are energetically governed by Ostwald’s rule of stages.
- Aviad Levin
- , Thomas O. Mason
- & Ehud Gazit
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the multilayer growth of the fullerene C60 in real time
Unravelling the multilayer growth of the fullerene C60 in real time
Despite the technological relevance of molecular thin films, there is limited understanding of their growth on a molecular level. Here, the authors characterize the relevant processes in real time and determine energy parameters using a combination of X-ray techniques and kinetic Monte Carlo simulations.
- S. Bommel
- , N. Kleppmann
- & S. Kowarik
-
Article |
 Fingering versus stability in the limit of zero interfacial tension
Fingering versus stability in the limit of zero interfacial tension
Complex patterns arise in the non-linear growth regime upon the injection of a less viscous fluid into a more viscous one. Here, the authors show that the viscosity ratio between the two fluids controls a transition from branched fingers to blunt structures, and then eventually to a stable displacement.
- Irmgard Bischofberger
- , Radha Ramachandran
- & Sidney R. Nagel
-
Article |
 The unlikely Carnot efficiency
The unlikely Carnot efficiency
Carnot efficiency is the highest theoretically possible efficiency that a heat engine can have. Verley et al.use the fluctuation theorem to show that the Carnot value is the least likely efficiency in the long time limit.
- Gatien Verley
- , Massimiliano Esposito
- & Christian Van den Broeck
-
Article |
 Low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation catalysed by regenerable atomically dispersed palladium on alumina
Low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation catalysed by regenerable atomically dispersed palladium on alumina
There has been a great deal of interest in single-atom heterogeneous catalysis recently. Here, the authors show that industrially relevant lanthanum oxide-doped alumina supports are capable of stabilizing atomically dispersed palladium species, which are evaluated for low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation.
- Eric J. Peterson
- , Andrew T. DeLaRiva
- & Abhaya K. Datye
-
Article |
 Vibrational coherence probes the mechanism of ultrafast electron transfer in polymer–fullerene blends
Vibrational coherence probes the mechanism of ultrafast electron transfer in polymer–fullerene blends
Dissociation of excitons at the donor/acceptor interface in organic solar cells occurs on fast timescales. Here, the authors apply two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy to study the electron transfer process in a polymer blend, reporting dynamic maps for the charge-transfer pathways.
- Yin Song
- , Scott N. Clafton
- & Gregory D. Scholes
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer collapse in miscible good solvents is a generic phenomenon driven by preferential adsorption
Polymer collapse in miscible good solvents is a generic phenomenon driven by preferential adsorption
Smart polymers exhibit a swelling–collapse–swelling transition in mixed (co)solvents and the underlined mechanism remains a matter of debate. Mukherji et al. explain this transition using a generic model based purely on a thermodynamic treatment of preferential polymer–cosolvent interaction.
- Debashish Mukherji
- , Carlos M. Marques
- & Kurt Kremer
-
Article |
 Chemo-mechanics of salt damage in stone
Chemo-mechanics of salt damage in stone
Growth of salt crystals in pores is one of the most damaging weathering mechanisms for stone in ornamental structures and historical buildings. Here, the authors present a simple yet powerful treatment for predicting when salt damage will occur, quantifying this susceptibility to salt crystallization.
- Robert J. Flatt
- , Francesco Caruso
- & George W. Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access Energy-filtered cold electron transport at room temperature
Energy-filtered cold electron transport at room temperature
Electrons can behave as if they are at a temperature different from that of the solid in which they are embedded. Here, the authors demonstrate a room temperature device that can generate electrons with an effective temperature of 45 K by using quantum wells to filter out energetic particles.
- Pradeep Bhadrachalam
- , Ramkumar Subramanian
- & Seong Jin Koh
-
Article |
 Pressure-stabilized lithium caesides with caesium anions beyond the −1 state
Pressure-stabilized lithium caesides with caesium anions beyond the −1 state
In chemical compounds, alkali metal ions typically assume a positive oxidation state where they lose an electron, and only rarely are in a charge state where they receive an electron. Here, the authors predict lithium cesides with oxidation states where caesium receives more than one electron.
- Jorge Botana
- & Mao-Sheng Miao
-
Article |
 Evidence of Stranski–Krastanov growth at the initial stage of atmospheric water condensation
Evidence of Stranski–Krastanov growth at the initial stage of atmospheric water condensation
Water condensation on surfaces occurs in nature everywhere, but the study of its initial stage at ambient conditions is very challenging. Here, Song et al.address this issue using thermal controlled atomic force microscopy and identify a mixture of layer-by-layer and island-like modes.
- Jie Song
- , Qiang Li
- & Mingdong Dong
-
Article |
 Diffraction using laser-driven broadband electron wave packets
Diffraction using laser-driven broadband electron wave packets
Developments in ultrafast optical science bring the promise of being able to directly monitor atomic motions during various physical processes. Towards this end, Xu et al.present fixed-angle broadband laser-induced electron scattering as a method to image molecular structures from photoelectron spectra.
- Junliang Xu
- , Cosmin I. Blaga
- & Louis F. DiMauro
-
Article |
 A structural signature of liquid fragility
A structural signature of liquid fragility
Glass fragility characterises the rate of change in viscosity as a liquid is cooled towards the glass transition temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate via neutron diffraction that the rate at which structural ordering occurs within the melt correlates with kinetic fragility in a range of metallic glass samples.
- N. A. Mauro
- , M. Blodgett
- & K. F. Kelton
-
Article
| Open Access From molecular spectra to a density shift in dense Rydberg gases
From molecular spectra to a density shift in dense Rydberg gases
Ultracold Rydberg atoms — atoms with highly excited electrons — can form molecules with ground state atoms. By tuning the principal quantum number of the Rydberg state, Gaj et al.study the transition from resolvable molecular lines to the mean shift regime, where indistinguishable lines form a band.
- A. Gaj
- , A. T. Krupp
- & T. Pfau
-
Article |
 Anisotropic thermal conductivity in uranium dioxide
Anisotropic thermal conductivity in uranium dioxide
Uranium dioxide fuels the world’s nuclear-power reactors, and so a full understanding of its thermal properties is essential. Gofryk et al. now demonstrate that, despite its cubic atomic structure, the thermal conductivity of uranium dioxide is anisotropic owing to phonon-spin scattering.
- K. Gofryk
- , S. Du
- & D. A. Andersson
-
Article |
 Stabilizing colloidal crystals by leveraging void distributions
Stabilizing colloidal crystals by leveraging void distributions
It is challenging to prepare colloidal crystals with long-range order for their applications. Mahynski et al. propose a method to achieve this goal through tailoring energy loss of absorbed polymers in crystal voids to selectively stabilize one crystal structure among its competing polymorphs.
- Nathan A. Mahynski
- , Athanassios Z. Panagiotopoulos
- & Sanat K. Kumar
-
Article |
 Tabletop imaging of structural evolutions in chemical reactions demonstrated for the acetylene cation
Tabletop imaging of structural evolutions in chemical reactions demonstrated for the acetylene cation
Femto-chemistry allows researchers to probe the individual transitions in a molecule during a chemical reaction. Here, the authors show that a relatively simple tabletop experiment is capable of capturing the dynamics of isomerization and fragmentation of the acetylene cation to record a molecular movie.
- Heide Ibrahim
- , Benji Wales
- & François Légaré
-
Article |
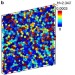 Multiple reentrant glass transitions in confined hard-sphere glasses
Multiple reentrant glass transitions in confined hard-sphere glasses
Wall–fluid interactions are known to have a large influence on the physics of confined glasses. Here, the authors observe a multiple re-entrant glass transition for a polydisperse hard-sphere system confined between two surfaces, when the wall separation distance is of the order of a few particle diameters.
- Suvendu Mandal
- , Simon Lang
- & Fathollah Varnik
-
Article
| Open Access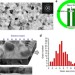 Grain rotation mediated by grain boundary dislocations in nanocrystalline platinum
Grain rotation mediated by grain boundary dislocations in nanocrystalline platinum
Grain rotation is proposed as an active deformation mechanism in nanocrystalline metals at room temperature. Here, during in-situatomic scale experimentation, the authors observe that grains with a size <6 nm deform by coordinated rotation of multiple grains, associated with dislocation climb at grain boundaries.
- Lihua Wang
- , Jiao Teng
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article |
 Water-induced correlation between single ions imaged at the solid–liquid interface
Water-induced correlation between single ions imaged at the solid–liquid interface
The organization of ions at solid–liquid interfaces is of interest in many fields, but little information at the nanoscale is available. Here, the authors report atomic-level observations of ordering of ions at surfaces in solutions, which is driven by water instead of the conventional electrostatic correlations.
- Maria Ricci
- , Peter Spijker
- & Kislon Voïtchovsky
-
Article |
 Momentum-resolved hidden-order gap reveals symmetry breaking and origin of entropy loss in URu2Si2
Momentum-resolved hidden-order gap reveals symmetry breaking and origin of entropy loss in URu2Si2
URu2Si2 undergoes a prominent phase transition to an ordered state of unknown nature. Using high-resolution 3D ARPES, Bareille et al. image an abrupt symmetry reconstruction of its heavy-fermion electronic structure that could explain the origin of the ordered state and its missing entropy.
- C. Bareille
- , F. L. Boariu
- & A. F. Santander-Syro
-
Article |
 The key role of vibrational entropy in the phase transitions of dithiazolyl-based bistable magnetic materials
The key role of vibrational entropy in the phase transitions of dithiazolyl-based bistable magnetic materials
Some organic radicals are diamagnetic at low temperatures but switch to a paramagnetic state at higher temperatures. Vela at al. now present computer simulations that indicate this phase change is a result of vibrational entropy, which causes the radicals to organize into neat stacks.
- Sergi Vela
- , Fernando Mota
- & Jordi Ribas-Arino
-
Article |
 Casimir–Polder interactions in the presence of thermally excited surface modes
Casimir–Polder interactions in the presence of thermally excited surface modes
It is a huge challenge to measure long-range atom–surface interactions, the Casimir–Polder effects, at elevated temperatures. Here, Laliotis et al.report a spectroscopic measurement on caesium atoms approximately 100 nm away from a hot sapphire surface, influenced by the thermal excitation of surface modes.
- Athanasios Laliotis
- , Thierry Passerat de Silans
- & Daniel Bloch
-
Article |
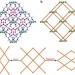 Giant negative linear compression positively coupled to massive thermal expansion in a metal–organic framework
Giant negative linear compression positively coupled to massive thermal expansion in a metal–organic framework
Negative linear compressibility in materials is usually accompanied by a thermal contraction upon heating. Here, the authors report a metal organic framework that breaks this rule, exhibiting large intrinsic negative linear compressibility coinciding with strong positive thermal expansion.
- Weizhao Cai
- & Andrzej Katrusiak
-
Article |
 Water clustering on nanostructured iron oxide films
Water clustering on nanostructured iron oxide films
It is not well-understood how nanoscale variations in surface structures impact the ordering of the first few wetting layers on oxide surfaces. Here, the authors employ a model surface, a hydroxylated iron oxide film, which allows direct probing of the impact of hydroxyl groups on the adsorbed water molecules.
- Lindsay R. Merte
- , Ralf Bechstein
- & Flemming Besenbacher
-
Article |
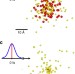 Femtosecond X-ray-induced explosion of C60 at extreme intensity
Femtosecond X-ray-induced explosion of C60 at extreme intensity
Understanding the dynamics of molecules exposed to intense X-ray beams is crucial to ongoing efforts in biomolecular imaging with free-electron lasers. Here, the authors study C60molecules interacting with femtosecond X-ray free-electron laser pulses and present a model based on classical and quantum physics.
- B. F. Murphy
- , T. Osipov
- & N. Berrah
-
Article |
 Single-molecule chemical reaction reveals molecular reaction kinetics and dynamics
Single-molecule chemical reaction reveals molecular reaction kinetics and dynamics
Chemical reactions are typically composed of a number of elementary steps, but elucidating these steps is a challenge, particularly in the condensed phase. Here, the authors use quantum chemical calculations and single-molecule spectroscopy to unravel the details of a reversible redox process.
- Yuwei Zhang
- , Ping Song
- & Weilin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Encapsulation kinetics and dynamics of carbon monoxide in clathrate hydrate
Encapsulation kinetics and dynamics of carbon monoxide in clathrate hydrate
Carbon monoxide clathrate hydrate has been widely studied and although the structure-II gas hydrate is predicted to be thermodynamically favourable, it is the structure-I hydrate that has been observed. Here, the authors synthesize the structure-II carbon monoxide hydrate and probe its structure and formation.
- Jinlong Zhu
- , Shiyu Du
- & Yusheng Zhao
-
Article |
 Interfacial mobility scale determines the scale of collective motion and relaxation rate in polymer films
Interfacial mobility scale determines the scale of collective motion and relaxation rate in polymer films
Interfacial mobility in thin polymer films is crucial for their technological applications. Here, Hanakata et al.provide computational evidence for a general relationship between the scale of interfacial mobility and collective motion within the films, which explains their glass transition behaviour.
- Paul Z. Hanakata
- , Jack F. Douglas
- & Francis W. Starr
-
Article |
 Direct observation of spin-forbidden transitions through the use of suitably polarized light
Direct observation of spin-forbidden transitions through the use of suitably polarized light
The study of excited triplet states in molecular systems is in some cases hindered by the difficulty in accessing them and the intense signals of singlet states. Here, the authors show that the combination of polarized light and molecular alignment can enhance the triplet absorption for sulphur dioxide.
- Camille Lévêque
- , Daniel Peláez
- & Richard Taïeb
-
Article |
 Isolation and reversible dimerization of a selenium–selenium three-electron σ-bond
Isolation and reversible dimerization of a selenium–selenium three-electron σ-bond
Three-electron σ-bonds are known as intermediates in chemical reactions, but they typically are unstable and transient. Here, the authors observe, isolate and characterize a room-temperature-stable organic compound with a three-electron selenium–selenium σ-bond.
- Senwang Zhang
- , Xingyong Wang
- & Xinping Wang
-
Article |
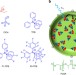 Collective fluorescence switching of counterion-assembled dyes in polymer nanoparticles
Collective fluorescence switching of counterion-assembled dyes in polymer nanoparticles
Fluorescent organic nanoparticles are attractive alternatives to quantum dots for imaging applications. Here, the authors assemble dyes with bulky counterions inside polymer nanoparticles to achieve high fluorescence brightness, as well as a photoinducible and reversible on/off switching.
- Andreas Reisch
- , Pascal Didier
- & Andrey S. Klymchenko
-
Article |
 Roaming dynamics in radical addition–elimination reactions
Roaming dynamics in radical addition–elimination reactions
Roaming dynamics have been shown to be important in unimolecular decompositions, but the relevance to bimolecular reactions has been less clear. Here, the authors study radical addition/elimination reactions and implicate a roaming transition state in a bimolecular reaction.
- Baptiste Joalland
- , Yuanyuan Shi
- & Alexander M. Mebel
-
Article |
 Extreme surface propensity of halide ions in water
Extreme surface propensity of halide ions in water
The surface chemistry of aqueous solutions plays a ubiquitous role in many chemical and biological processes. Here, the authors probe the surfaces of sodium halide solutions with surface-specific femtosecond vibrational spectroscopy, and observe surface concentrations of halide ions several times greater than in the bulk.
- Lukasz Piatkowski
- , Zhen Zhang
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article |
 Electrochemically tunable thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide
Electrochemically tunable thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide
Materials with variable and reversible thermal conductivities are important in technologies, and yet such materials are rare. Here, Cho et al. report in situmeasurements of thermal conductivity of lithium cobalt oxide, and show how to reversibly modulate thermal conductivities over a considerable range.
- Jiung Cho
- , Mark D. Losego
- & Paul V. Braun

 A borane laser
A borane laser