Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access In-operando high-speed tomography of lithium-ion batteries during thermal runaway
In-operando high-speed tomography of lithium-ion batteries during thermal runaway
It is important to understand the mechanisms of thermally induced battery degradation and any safety hazards. Here, the authors use high-speed synchrotron radiation X-ray computed tomography to shed light on the structural and thermal dynamics associated with thermal runaway and failure of commercial Li-ion batteries.
- Donal P. Finegan
- , Mario Scheel
- & Paul R. Shearing
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional nanoscale molecular imaging by extreme ultraviolet laser ablation mass spectrometry
Three-dimensional nanoscale molecular imaging by extreme ultraviolet laser ablation mass spectrometry
Mass spectral analysis is used to map the composition of materials and surfaces in numerous fields. Here, the authors report a mass spectral technique based on extreme ultraviolet laser ablation that allows three-dimensional imaging of chemical composition in addition to giving highly sensitive nanoscale resolution.
- Ilya Kuznetsov
- , Jorge Filevich
- & Carmen S. Menoni
-
Article |
 Radially aligned hierarchical columnar structure as a cathode material for high energy density sodium-ion batteries
Radially aligned hierarchical columnar structure as a cathode material for high energy density sodium-ion batteries
There are intensive efforts in developing cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Here, the authors present a spherical particle with a radially aligned hierarchical columnar structure as a cathode material which leads to good performance of capacity, retention, rate capability and thermal stability.
- Jang-Yeon Hwang
- , Seung-Min Oh
- & Yang-Kook Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Separation and conversion dynamics of nuclear-spin isomers of gaseous methanol
Separation and conversion dynamics of nuclear-spin isomers of gaseous methanol
The conversion dynamics of nuclear-spin isomers has only been observed for a small number of molecules, generally with rotational symmetry. Here, the authors observe the separation of nuclear-spin isomers of gaseous methanol and show a decreased interconversion at higher pressures.
- Zhen-Dong Sun
- , Meihua Ge
- & Yujun Zheng
-
Article |
 Energy transfer pathways in semiconducting carbon nanotubes revealed using two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy
Energy transfer pathways in semiconducting carbon nanotubes revealed using two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy
Thin films of carbon nanotubes are been considered for energy harvesting and optoelectronic devices but their energy transfer pathways are largely unknown. Here, Mehlenbacher et al. use two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy to investigate the ultrafast energy redistribution in carbon nanotube films.
- Randy D. Mehlenbacher
- , Thomas J. McDonough
- & Martin T. Zanni
-
Article |
 Transition from near-field thermal radiation to phonon heat conduction at sub-nanometre gaps
Transition from near-field thermal radiation to phonon heat conduction at sub-nanometre gaps
Heat transfer typically occurs by conduction via phonons and radiation via photons, but the distinction between them blurs as surfaces come into contact. Chiloyan et al.study heat transfer between surfaces at sub-nanometre separation and explore the behaviour of phonons as the surfaces approach each other.
- Vazrik Chiloyan
- , Jivtesh Garg
- & Gang Chen
-
Article |
 Ultrasonic hammer produces hot spots in solids
Ultrasonic hammer produces hot spots in solids
The initiation of explosions is thought to result from ‘hot spot’ generation at localized microstructures in energetic material, although experimental evidence has been limited. Here, the authors show controllable hot spot formation in solid composites using an ultrasonic hammer, introducing a new method of study.
- Sizhu You
- , Ming-Wei Chen
- & Kenneth S. Suslick
-
Article |
 Harvesting dissipated energy with a mesoscopic ratchet
Harvesting dissipated energy with a mesoscopic ratchet
Thermoelectric devices convert waste heat to electrical power but suffer from low efficiency. Roche et al.create a mesoscopic heat engine comprising capacitively coupled hot and cold electrical circuits in which thermal fluctuations in the former are converted to potential fluctuations in the latter
- B. Roche
- , P. Roulleau
- & D.C. Glattli
-
Article
| Open Access Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis
Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis
Transition metal fluorides have high theoretical specific capacities as cathodes for lithium ion batteries, but low working potentials and poor energy efficiency limit their practical applications. Here, the authors report a group of ternary metal fluorides, which may overcome these problems.
- Feng Wang
- , Sung-Wook Kim
- & Jason Graetz
-
Article |
 Ti-substituted tunnel-type Na0.44MnO2 oxide as a negative electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries
Ti-substituted tunnel-type Na0.44MnO2 oxide as a negative electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries
Aqueous sodium-ion batteries could be a potential solution for large-scale energy storage, but the conventional negative electrodes are not efficient. Here, the authors report a titanium-substituted tunnel-type Na0.44MnO2material as a promising negative electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries.
- Yuesheng Wang
- , Jue Liu
- & Xuejie Huang
-
Article |
 Quantum dynamics of CO–H2 in full dimensionality
Quantum dynamics of CO–H2 in full dimensionality
Interpreting astronomical observations relies on accurate rate coefficients for molecular vibrational transitions caused by collisions with H2. Yang et al. exploit state-of-the-art inelastic quantum dynamic simulations to provide a full-dimensional computation for rovibrational quenching of CO by H2.
- Benhui Yang
- , P. Zhang
- & R.C. Forrey
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical synthesis of mesoporous gold films toward mesospace-stimulated optical properties
Electrochemical synthesis of mesoporous gold films toward mesospace-stimulated optical properties
The selective growth of mesoporous gold thin films with control over the porosity is a challenging task. Here, the authors report a soft-templating method allowing the growth of tunable, mesoporous gold films and examine their optical properties
- Cuiling Li
- , Ömer Dag
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Aqueous proton transfer across single-layer graphene
Aqueous proton transfer across single-layer graphene
Proton transfer across graphene is associated with large computed energy barriers and is thought to be generally unfavourable. Here, the authors observe aqueous proton transfer through graphene subjected to pH cycling, suggesting that it is due to transfer through rare, naturally occurring atomic defects.
- Jennifer L. Achtyl
- , Raymond R. Unocic
- & Franz M. Geiger
-
Article
| Open Access Electrodeposition of hierarchically structured three-dimensional nickel–iron electrodes for efficient oxygen evolution at high current densities
Electrodeposition of hierarchically structured three-dimensional nickel–iron electrodes for efficient oxygen evolution at high current densities
Development of efficient and affordable oxygen evolution catalysts is essential for large-scale electrolytic water splitting. Here, the authors report mesoporous nickel–iron composite nanosheets loaded on macroporous nickel foam substrates, and evaluate their electrocatalytic oxygen evolution in basic media.
- Xunyu Lu
- & Chuan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access High performing and stable supported nano-alloys for the catalytic hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone
High performing and stable supported nano-alloys for the catalytic hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone
The hydrogenation of leuvinic acid to γ-valerolactone is an important step in the conversion of lignocellulose to high value chemicals. Here, the authors report that bimetallic alloys are active and stable catalysts for this reaction, and attribute this to geometric and electronic effects.
- Wenhao Luo
- , Meenakshisundaram Sankar
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access Highly porous non-precious bimetallic electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution
Highly porous non-precious bimetallic electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution
Investigations into non-precious metal catalysts for hydrogen evolution are ongoing. Here, the authors report a hierarchical, nanoporous copper-titanium electrocatalyst, and demonstrate that it catalyses hydrogen production at twice the over-all rate of commercial platinum-based catalysts.
- Qi Lu
- , Gregory S. Hutchings
- & Jingguang G. Chen
-
Article |
 Complete information acquisition in dynamic force microscopy
Complete information acquisition in dynamic force microscopy
An often overlooked component of scanning probe microscopy involves information transfer from the tip–surface junction to a macroscopic measurement system. Here, the authors present an information–theory-based approach that relies on capturing the response at a wide-frequency band, allowing a complete and unbiased look at probing interaction.
- Alexei Belianinov
- , Sergei V. Kalinin
- & Stephen Jesse
-
Article |
 Surface transfer doping induced effective modulation on ambipolar characteristics of few-layer black phosphorus
Surface transfer doping induced effective modulation on ambipolar characteristics of few-layer black phosphorus
Black phosphorus is a graphene-like material that can be harnessed for two-dimensional electronic devices. Here, Xiang et al. demonstrate that adding caesium carbonate or molybdenum trioxide can significantly enhance the electron or hole conduction, respectively, of this promising material.
- Du Xiang
- , Cheng Han
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular catalyst for water oxidation that binds to metal oxide surfaces
A molecular catalyst for water oxidation that binds to metal oxide surfaces
Molecular catalysts can exhibit high activity, but their practical application may be limited by solubility and stability issues. Here, the authors report stable, direct binding of an iridium molecular catalyst to conductive oxide surfaces and demonstrate its activity for electrochemical water oxidation.
- Stafford W. Sheehan
- , Julianne M. Thomsen
- & Charles A. Schmuttenmaer
-
Article
| Open Access Description of quantum coherence in thermodynamic processes requires constraints beyond free energy
Description of quantum coherence in thermodynamic processes requires constraints beyond free energy
The statistical nature of standard thermodynamics provides an incomplete picture for individual processes at the nanoscale, and new relations have been developed to extend it. Here, the authors show that by quantifying time-asymmetry it is also possible to characterize how quantum coherence is modified in such processes.
- Matteo Lostaglio
- , David Jennings
- & Terry Rudolph
-
Article |
 How intermolecular geometrical disorder affects the molecular doping of donor–acceptor copolymers
How intermolecular geometrical disorder affects the molecular doping of donor–acceptor copolymers
Doping of conjugated polymers is an important strategy for the development of organic electronics. Here, the authors study the spatial organization of dopants in donor–acceptor polymers, indicating that charge transfer is improved when the dopant and donor moiety are in close proximity.
- Daniele Di Nuzzo
- , Claudio Fontanesi
- & Enrico Da Como
-
Article |
 Origin of pressure-induced crystallization of Ce75Al25 metallic glass
Origin of pressure-induced crystallization of Ce75Al25 metallic glass
It is commonly believed that pressure-induced crystallization in Ce-Al amorphous alloy is caused by Ce 4f orbital delocalization. Here, Wu et al. propose an alternative mechanism, whereby the crystallization is driven by a steric effect of dominant packing of cerium atoms at high pressure.
- Min Wu
- , John S. Tse
- & J.Z. Jiang
-
Article |
 Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Degrees of freedom can be frozen in glassy material, which results in a hysteresis in heat capacity under cooling or heating. Here, the authors show that the hysteresis can be minimized at selected thermodynamic conditions, leading to thermally reversible glasses that are isostatically rigid.
- M. Bauchy
- & M. Micoulaut
-
Article |
 Direct mechanochemical cleavage of functional groups from graphene
Direct mechanochemical cleavage of functional groups from graphene
Breaking chemical bonds with mechanical force can be a useful route to modify chemical species, but studying the process in detail can be challenging. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to apply pressure and monitor bond cleavage on chemically modified graphene.
- Jonathan R. Felts
- , Andrew J. Oyer
- & Paul E. Sheehan
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic formation of single-atom catalytic active sites on ceria-supported gold nanoparticles
Dynamic formation of single-atom catalytic active sites on ceria-supported gold nanoparticles
Computational investigation of heterogeneous catalytic systems is fundamentally important. Here, the authors show that, under reaction conditions, reactant-induced structural changes in ceria-supported gold nanoparticle catalysts lead to the dynamic formation of single-atom catalytic sites at the interface.
- Yang-Gang Wang
- , Donghai Mei
- & Roger Rousseau
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular magnetic switch for a metallofullerene
Molecular magnetic switch for a metallofullerene
Endohedral fullerenes are known to stabilize reactive radicals; however, the external magnetic manipulation of these species’ remains challenging. Here, the authors link a nitroxide radical to a paramagnetic fullerene system and are able to alter the spin behaviour of the fullerene via spin–spin interactions.
- Bo Wu
- , Taishan Wang
- & Chunru Wang
-
Article |
 Ultrathin platinum nanowires grown on single-layered nickel hydroxide with high hydrogen evolution activity
Ultrathin platinum nanowires grown on single-layered nickel hydroxide with high hydrogen evolution activity
There is extensive interest in the design of efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Here, the authors show that exfoliated single-layer nickel hydroxide can be used for the controllable surface growth of platinum nanowires, and evaluate the electrocatalytic performance of the composite material.
- Huajie Yin
- , Shenlong Zhao
- & Zhiyong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing the non-equilibrium dynamics of photoinduced intramolecular electron transfer with femtosecond X-ray pulses
Visualizing the non-equilibrium dynamics of photoinduced intramolecular electron transfer with femtosecond X-ray pulses
Photoinduced electron transfer in solvated molecular assemblies occurs on the ultrafast timescale before full electronic and geometric relaxation take place. Here Canton et al.monitor this out-of-equilibrium process in a donor–acceptor bimetallic assembly using an X-ray free-electron laser.
- Sophie E. Canton
- , Kasper S. Kjær
- & Martin M. Nielsen
-
Article |
 Edge dislocation slows down oxide ion diffusion in doped CeO2 by segregation of charged defects
Edge dislocation slows down oxide ion diffusion in doped CeO2 by segregation of charged defects
Electrochemical devices based on oxide materials, such as batteries or fuel cells, rely on the transport of ions through the crystal lattice. Here, the authors model ion diffusion through CeO2and observe that edge dislocations slow down ion diffusion, contrary to similar processes in metals.
- Lixin Sun
- , Dario Marrocchelli
- & Bilge Yildiz
-
Article
| Open Access Ambipolar zinc-polyiodide electrolyte for a high-energy density aqueous redox flow battery
Ambipolar zinc-polyiodide electrolyte for a high-energy density aqueous redox flow battery
Conventional redox flow batteries have low energy densities. Here the authors present an aqueous redox flow battery with an ambipolar and bifunctional zinc-polyiodide electrolyte, which exhibits an energy density approaching to that of lithium ion batteries.
- Bin Li
- , Zimin Nie
- & Wei Wang
-
Article |
 Visualization and thermodynamic encoding of single-molecule partition function projections
Visualization and thermodynamic encoding of single-molecule partition function projections
It is challenging to determine thermodynamic quantities for single molecules. Here, the authors access single-molecule thermodynamic information via a microscopic and computational study of a confined molecule, for which the resulting patterns represent a real-space equilibrium probability distribution.
- Carlos-Andres Palma
- , Jonas Björk
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article |
 Towards graphyne molecular electronics
Towards graphyne molecular electronics
α-Graphyne, a carbon-expanded version of graphene, is predicted to exhibit high conductivity due to its Dirac cone electronic structure. Here, Li et al.design and synthesize a series of molecular fragments of α-graphyne, on the basis of which single molecular junctions are realized.
- Zhihai Li
- , Manuel Smeu
- & Eric Borguet
-
Article |
 Electroneutrality breakdown and specific ion effects in nanoconfined aqueous electrolytes observed by NMR
Electroneutrality breakdown and specific ion effects in nanoconfined aqueous electrolytes observed by NMR
It is generally believed that charge neutrality is maintained in electrolytes nanoconfined by uncharged surfaces. Here, the authors show that electroneutrality breakdown is substantial in nanoconfined aqueous electrolytes, and it depends on ion-specific interfacial interactions and ion–ion correlations.
- Zhi-Xiang Luo
- , Yun-Zhao Xing
- & Yue Wu
-
Article
| Open Access High rate and stable cycling of lithium metal anode
High rate and stable cycling of lithium metal anode
Lithium metal is an ideal anode material for rechargeable batteries, but lithium dendritic growth and limited Columbic efficiency prevent its applications. Here, the authors report the use of highly concentrated electrolytes composed of ether solvents and the salt lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide to enable high-rate cycling of lithium anode.
- Jiangfeng Qian
- , Wesley A. Henderson
- & Ji-Guang Zhang
-
Article |
 Unfolding a molecular trefoil derived from a zwitterionic metallopeptide to form self-assembled nanostructures
Unfolding a molecular trefoil derived from a zwitterionic metallopeptide to form self-assembled nanostructures
Molecular self-assembly can be influenced by a number of external factors, though solvent effects are less commonly explored. Here, the authors present a three-armed metallopeptide complex that has a folded monomeric conformation in organic solvent, but can self-assemble in water into a supramolecular gel.
- Ye Zhang
- , Ning Zhou
- & Bing Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Origin and consequences of silicate glass passivation by surface layers
Origin and consequences of silicate glass passivation by surface layers
The long term durability of silicate glasses is of significant importance, not least due to applications in nuclear waste repositories. Here, the authors study glass corrosion and show that its rate drops as a passivating layer forms via a self-healing mechanism.
- Stéphane Gin
- , Patrick Jollivet
- & Thibault Charpentier
-
Article |
 Hydrodynamic phonon transport in suspended graphene
Hydrodynamic phonon transport in suspended graphene
Hydrodynamic phonon transport occurs when phonons are able to drift over macroscopic distances, leading to the breakdown of Fourier’s law of heat conduction. Here, the authors predict that this regime occurs in suspended graphene at higher temperatures than bulk materials.
- Sangyeop Lee
- , David Broido
- & Gang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical work makes important contributions to surface chemistry at steps
Mechanical work makes important contributions to surface chemistry at steps
Surface strain affects the performance of catalysts. Here, the authors present computational evidence that mechanical strain of late transition metals can modify binding energies at stepped surfaces through a mechanical energy contribution yielding chemical trends unique from the established d-band model.
- M. F. Francis
- & W. A. Curtin
-
Article |
 Undesired usage and the robust self-assembly of heterogeneous structures
Undesired usage and the robust self-assembly of heterogeneous structures
Biological and synthetic systems seek to assemble complex structures, such as protein or DNA assemblies, out of many distinct building blocks. Here, the authors show that the optimal supply of building blocks must account for the composition of undesired structures and not just the desired structure.
- Arvind Murugan
- , James Zou
- & Michael P. Brenner
-
Article |
 Design concept for α-hydrogen-substituted nitroxides
Design concept for α-hydrogen-substituted nitroxides
Nitroxyl radicals have many important applications but are generally stabilized through steric bulk on the adjacent carbon centres. Here, the authors design a simple, modular preparation of nitroxyl radicals with α-hydrogens that are stable for extended periods and are catalytically active.
- Michal Amar
- , Sukanta Bar
- & Alex M. Szpilman
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of weak interactions in the atom-by-atom condensation of xenon within quantum boxes
Interplay of weak interactions in the atom-by-atom condensation of xenon within quantum boxes
Condensation in the regime of weakly interactions is of fundamental importance. Here, the authors study the condensation process one atom at a time, showing the forces driving the behaviour of xenon atoms as they condense into aggregate structures in nanoscale pores.
- Sylwia Nowakowska
- , Aneliia Wäckerlin
- & Thomas A. Jung
-
Article |
 Selecting core-hole localization or delocalization in CS2 by photofragmentation dynamics
Selecting core-hole localization or delocalization in CS2 by photofragmentation dynamics
Molecular core levels are localized around a single atomic site, but for indistinguishable atoms, photoionised core-holes can either be seen as localized or delocalized. Using a prototypical symmetric system, CS2, Guillemin et al. show that these states can be disentangled by fragmentation dynamics.
- R. Guillemin
- , P. Decleva
- & M. Simon
-
Article |
 Discovery of optimal zeolites for challenging separations and chemical transformations using predictive materials modeling
Discovery of optimal zeolites for challenging separations and chemical transformations using predictive materials modeling
Zeolites are industrially important materials, functioning as separation media and catalyst supports. Here, the authors use a large-scale, multi-step computational screening process to identify promising zeolites for challenging separations, namely ethanol purification and alkane adsorption.
- Peng Bai
- , Mi Young Jeon
- & J. Ilja Siepmann
-
Article |
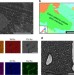 Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy
Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy
Alloys containing multiple elements of equal distributions are known to show enhanced properties as they tend to form single phases. Here, the authors demonstrate that even in cases of elemental segregation and chemical ordering, these alloys can still maintain enhanced properties.
- Louis J. Santodonato
- , Yang Zhang
- & Peter K Liaw
-
Article |
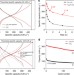 Graphene-modified nanostructured vanadium pentoxide hybrids with extraordinary electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries
Graphene-modified nanostructured vanadium pentoxide hybrids with extraordinary electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries
Vanadium pentoxide is considered a promising lithium battery electrode, but suffers from poor rate capability and cyclability. Here, the authors synthesize graphene-modified nanostructured vanadium pentoxide and show significant improvement in rate performance and cycle life.
- Qi Liu
- , Zhe-Fei Li
- & Jian Xie
-
Article |
 Revealing a double-inversion mechanism for the F−+CH3Cl SN2 reaction
Revealing a double-inversion mechanism for the F−+CH3Cl SN2 reaction
The SN2 reaction is a stereospecific process, normally occurring via back-side inversion or front-side retention. Here, the authors report a global potential energy surface for the reaction between fluoride and CH3Cl and identify an additional double inversion mechanism.
- István Szabó
- & Gábor Czakó
-
Article |
 Photoswitchable semiconductor nanocrystals with self-regulating photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer acceptors
Photoswitchable semiconductor nanocrystals with self-regulating photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer acceptors
Photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer endows nanosensors with photoswitchable fluorescence properties. Diaz et al. present a system with two photostationary end states, one of which exhibits constant quenching of the quantum dot donor independent of its mean distance to the photochromic acceptors.
- Sebastián A. Díaz
- , Florencia Gillanders
- & Thomas M. Jovin
-
Article
| Open Access Size dependence of phase transitions in aerosol nanoparticles
Size dependence of phase transitions in aerosol nanoparticles
Although phase transitions are fundamental for understanding aerosol particles, current models are insufficient to explain observations at the nanoscale. Here, the authors present a method for investigating droplets, suggesting particle size is a key determinant in the phase diagram of nanoparticles.
- Yafang Cheng
- , Hang Su
- & Ulrich Pöschl
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality-selected phase behaviour in ionic polypeptide complexes
Chirality-selected phase behaviour in ionic polypeptide complexes
Complexes that form between oppositely charged polyelectrolytes may be solid or liquid. Here, Perry et al.show that chirality in polypeptides can determine the state of those complexes based on a propensity for hydrogen-bond formation.
- Sarah L. Perry
- , Lorraine Leon
- & Matthew Tirrell

 Competition between recombination and extraction of free charges determines the fill factor of organic solar cells
Competition between recombination and extraction of free charges determines the fill factor of organic solar cells