Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Suppressed electronic contribution in thermal conductivity of Ge2Sb2Se4Te
Suppressed electronic contribution in thermal conductivity of Ge2Sb2Se4Te
Integrated nanophotonics is an emerging research direction that has attracted great interests. Here, the authors show upon substituting Te with Se, the thermal conductivity of ordered Ge2Sb2Te5 transitions from an electron to a phonon dominated regime.
- Kiumars Aryana
- , Yifei Zhang
- & Patrick E. Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access Self assembling cluster crystals from DNA based dendritic nanostructures
Self assembling cluster crystals from DNA based dendritic nanostructures
Experimental realization of cluster crystals- periodic structures with lattice sites occupied by several, overlapping building blocks, has been elusive. Here, the authors show the existence of well-controlled soft matter cluster crystals composed of a thermosensitive water-soluble polymer and nanometer-scale all-DNA dendrons.
- Emmanuel Stiakakis
- , Niklas Jung
- & Christos N. Likos
-
Article
| Open Access Second sound in the crossover from the Bose-Einstein condensate to the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer superfluid
Second sound in the crossover from the Bose-Einstein condensate to the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer superfluid
The second sound is an entropy oscillation propagating with constant pressure. Here the authors demonstrate the variation of the second sound wave in the crossover from the Bose-Einstein condensate to the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer superfluid using 6Li.
- Daniel K. Hoffmann
- , Vijay Pal Singh
- & Johannes Hecker Denschlag
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant tunneling driven metal-insulator transition in double quantum-well structures of strongly correlated oxide
Resonant tunneling driven metal-insulator transition in double quantum-well structures of strongly correlated oxide
The metal-insulator transition is typically controlled by carrier accumulation or chemical doping. Here, the authors realize an alternative method based on resonant tunnelling in a double quantum well structure of strongly correlated oxides, which offers practical advantages over conventional methods.
- R. Yukawa
- , M. Kobayashi
- & H. Kumigashira
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental realization of a 3D random hopping model
Experimental realization of a 3D random hopping model
Three-dimensional spin models with random hopping disorder are relevant to a large variety of physical systems. Here, the authors present an experimental realization of such a model in a Rydberg system with dipole-dipole coupling and show signatures of a localization-delocalization transition.
- Carsten Lippe
- , Tanita Klas
- & Herwig Ott
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling strong electronic interlayer and intralayer correlations in a transition metal dichalcogenide
Unravelling strong electronic interlayer and intralayer correlations in a transition metal dichalcogenide
Electronic and interlayer correlations are expected to affect the electronic and optical properties of transition metal dichalcogenides. Here, by using spectroscopic ellipsometry in the broad energy range, the authors uncover new electronic transitions and correlated plasmons in bulk MoS2.
- T. J. Whitcher
- , Angga Dito Fauzi
- & A. Rusydi
-
Article
| Open Access Overactivated transport in the localized phase of the superconductor-insulator transition
Overactivated transport in the localized phase of the superconductor-insulator transition
Despite extensive work on the superconductor-insulator transition in two-dimensional materials, the nature of the insulator is still debated. The authors report measurements and simulations of NbxSi1–x films, showing that conduction in the insulating state occurs by single charges hopping between superconducting grains.
- V. Humbert
- , M. Ortuño
- & C. A. Marrache-Kikuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Bosonic spinons in anisotropic triangular antiferromagnets
Bosonic spinons in anisotropic triangular antiferromagnets
Spinons are quasisparticles that can appear in anisotropic triangular lattices, however, probing the statistics and dynamics of such excitations is experimentally challenging. Here, Choi et al present Raman spectroscopy measurements of anisotropic triangular lattices, showing a bosonic evolution of the spinon scattering.
- Youngsu Choi
- , Suheon Lee
- & Kwang-Yong Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Slow oxidation of magnetite nanoparticles elucidates the limits of the Verwey transition
Slow oxidation of magnetite nanoparticles elucidates the limits of the Verwey transition
The Verwey transition in magnetite has been studied for nearly eight decades since its discovery in the 1940s. Here, Kim et al. elucidate the influence of chemical doping by extremely slow oxidization process with magnetite nanoparticles, revealing why first- and second-order regimes of the Verwey transition are observed.
- Taehun Kim
- , Sangwoo Sim
- & Je-Geun Park
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental quantum simulation of superradiant phase transition beyond no-go theorem via antisqueezing
Experimental quantum simulation of superradiant phase transition beyond no-go theorem via antisqueezing
Quantum simulation allows to investigate otherwise inaccessible physical scenarios. Here, the authors simulate a quantum Rabi model using nuclear spins, including the A2 term and an anti-squeezing term, which allows them to see signatures of a superradiant phase transition in the simulated system.
- Xi Chen
- , Ze Wu
- & Jiangfeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Band-selective Holstein polaron in Luttinger liquid material A0.3MoO3 (A = K, Rb)
Band-selective Holstein polaron in Luttinger liquid material A0.3MoO3 (A = K, Rb)
The mechanism of the charge density wave transition in quasi one-dimensional blue bronzes is still debated. Here, the authors report evidence of a Luttinger liquid in the normal state of blue bronzes and Holstein polarons below the transition temperature, revealing the important role of electron-phonon coupling in the transition.
- L. Kang
- , X. Du
- & L. X. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Multiband charge density wave exposed in a transition metal dichalcogenide
Multiband charge density wave exposed in a transition metal dichalcogenide
While multiband superconductivity is the subject of extensive studies, the possibility of multiband charge density waves (CDW) remains elusive. Here, the authors report evidence of gap opening on both inner and outer bands by a CDW state in 2H-NbSe2, suggesting a possible multiband CDW.
- Árpád Pásztor
- , Alessandro Scarfato
- & Christoph Renner
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of a single quasicrystal upon collision of multiple grains
Formation of a single quasicrystal upon collision of multiple grains
Quasicrystals exhibit long-range order without periodicity. The authors report an approach for quasicrystal fabrication and show through in situ imaging and corresponding simulations the formation of a single decagonal quasicrystal arising from coalescence of multiple quasicrystals in a liquid.
- Insung Han
- , Kelly L. Wang
- & Ashwin J. Shahani
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling unconventional magnetism at the surface of Sr2RuO4
Unveiling unconventional magnetism at the surface of Sr2RuO4
Strontium Ruthenate, Sr2RuO4, displays a remarkable number of intriguing physical phenomena, from superconductivity, to strain-induced ferromagnetism. Here, using low-energy muon spectroscopy, Fittipaldi et al. demonstrate the existence of unconventional magnetism at the surface of Sr2RuO4 in its normal state and without any applied strain.
- R. Fittipaldi
- , R. Hartmann
- & A. Di Bernardo
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic-field-controlled spin fluctuations and quantum criticality in Sr3Ru2O7
Magnetic-field-controlled spin fluctuations and quantum criticality in Sr3Ru2O7
Sr3Ru2O7 exhibits a quantum critical point tunable by magnetic field and has been widely used in the study of criticality. Here, by using inelastic neutron scattering, the authors measure collective magnetic excitations near the quantum critical point and relate them to thermodynamic properties and spin density wave order.
- C. Lester
- , S. Ramos
- & S. M. Hayden
-
Article
| Open Access Boson-peak-like anomaly caused by transverse phonon softening in strain glass
Boson-peak-like anomaly caused by transverse phonon softening in strain glass
Strain glass is a new glassy state characterized by frozen ferroelastic nanodomains. Here, the authors discover a low-temperature feature in the specific heat of a strain glass, which is similar to the well-known boson peak anomaly of structural glasses, but cannot be explained by existing mechanisms.
- Shuai Ren
- , Hong-Xiang Zong
- & Wei-Hua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Field-induced quantum spin disordered state in spin-1/2 honeycomb magnet Na2Co2TeO6
Field-induced quantum spin disordered state in spin-1/2 honeycomb magnet Na2Co2TeO6
The honeycomb lattice with a spin-orbit interaction can give rise to exotic quantum states. With the measurements of bulk properties and inelastic neutron scattering, Lin et al demonstrate the existence of a field induced spin-disordered state in Na2Co2TeO6 and extend the Kitaev model to 3d system.
- Gaoting Lin
- , Jaehong Jeong
- & Jie Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Decay and renormalization of a longitudinal mode in a quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnet
Decay and renormalization of a longitudinal mode in a quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnet
Anisotropic spin S >1/2 quantum magnets can have multiple low energy modes. In this manuscript, the authors study the interaction of such low energy modes in the S = 1 antiferromagnet Ba2FeSi2O7 by combining neutron scattering measurements with an SU(3) generalization of the 1/S expansion.
- Seung-Hwan Do
- , Hao Zhang
- & Andrew D. Christianson
-
Article
| Open Access Fractionalized conductivity and emergent self-duality near topological phase transitions
Fractionalized conductivity and emergent self-duality near topological phase transitions
Conventional quantum particles can break up into fractionalized excitations under the right conditions; however, their direct experimental observation is challenging. Here, the authors predict strong optical conductivity signatures of such excitations in the vicinity of a topological phase transition.
- Yan-Cheng Wang
- , Meng Cheng
- & Zi Yang Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric phase-transition frustration near a tricritical composition point
Ferroelectric phase-transition frustration near a tricritical composition point
Phase transition brings a plethora of exotic phenomena and intriguing effects such as spin and charge frustration. However, the phase transition order is not always explicit. Here, the authors discover phase transition frustration near a tricritical composition point in ferroelectric Pb(Zr,Ti)O3.
- Xian-Kui Wei
- , Sergei Prokhorenko
- & Zuo-Guang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Multistep nucleation of anisotropic molecules
Multistep nucleation of anisotropic molecules
Multistep nucleation phenomena are of considerable fundamental interest. Here the authors combine molecular dynamics, machine learning and molecular cluster analysis to investigate the multistep nucleation of smectic clusters from a nematic fluid that cannot be accounted for by the classical nucleation theory.
- Kazuaki Z. Takahashi
- , Takeshi Aoyagi
- & Jun-ichi Fukuda
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic Floquet gyro-liquid crystal
Electronic Floquet gyro-liquid crystal
The nonequilibrium regime provides an exciting frontier in the search for novel quantum phases of matter. Here, the authors show that optically driving a lightly-doped semiconductor can lead to the spontaneous formation of a dynamical quantum liquid crystalline phase with a rotating magnetization.
- Iliya Esin
- , Gaurav Kumar Gupta
- & Netanel H. Lindner
-
Article
| Open Access Exceptional dynamical quantum phase transitions in periodically driven systems
Exceptional dynamical quantum phase transitions in periodically driven systems
Understanding phase transitions in systems out of equilibrium is a topic of high interest. Here the author discusses the spontaneous antiunitary symmetry breaking leading to exceptional dynamical quantum phase transitions in driven many-body systems.
- Ryusuke Hamazaki
-
Article
| Open Access Subpicosecond metamagnetic phase transition in FeRh driven by non-equilibrium electron dynamics
Subpicosecond metamagnetic phase transition in FeRh driven by non-equilibrium electron dynamics
In FeRh, it is possible to optically drive a phase transition between ferromagnetic (FM) and anti-ferromagnetic (AFM) ordering. Here, using a combination of photoelectron spectroscopy and ab-initio calculations, the authors demonstrate the existence of a transient intermediate phase, explaining the delayed appearance of the FM phase.
- Federico Pressacco
- , Davide Sangalli
- & Fausto Sirotti
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-dependent kinetic pathways of heterogeneous ice nucleation competing between classical and non-classical nucleation
Temperature-dependent kinetic pathways of heterogeneous ice nucleation competing between classical and non-classical nucleation
Classically, ice nucleation on foreign surfaces is considered a one-step process. Here, Li et al. uncover a two-barrier pathway which becomes competitive at lower temperatures, facilitated by synergistic, entropic effects of rhombic and hexagonal ice structures.
- Chu Li
- , Zhuo Liu
- & Xuhui Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging symmetric strain response and weakening nematic fluctuations in strongly hole-doped iron-based superconductors
Emerging symmetric strain response and weakening nematic fluctuations in strongly hole-doped iron-based superconductors
Whether the electronic nematicity is related to electronic pairing in strongly hole-doped iron-based superconductors remains controversial. Here, the authors perform transport measurements on AFe2As2 (A = K, Rb, Cs) superconductors under elastic strain, and find no indication of a nematic ordered state.
- P. Wiecki
- , M. Frachet
- & A. E. Böhmer
-
Article
| Open Access Quasi-equilibrium phase coexistence in single component supercritical fluids
Quasi-equilibrium phase coexistence in single component supercritical fluids
In their supercritical state simple fluids are generally thought to assume a homogeneous phase throughout. Lee et al. find that liquid droplets temporarily formed in a supercritical background after sub-critical injection can survive for a surprisingly long time.
- Seungtaek Lee
- , Juho Lee
- & Gunsu Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Unfolding the multiscale structure of networks with dynamical Ollivier-Ricci curvature
Unfolding the multiscale structure of networks with dynamical Ollivier-Ricci curvature
The analysis of networks and network processes can require low-dimensional representations, possible for specific structures only. The authors propose a geometric formalism which allows to unfold the mechanisms of dynamical processes propagation in various networks, relevant for control and community detection.
- Adam Gosztolai
- & Alexis Arnaudon
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity in an extreme strange metal
Superconductivity in an extreme strange metal
Understanding the strange metal behavior, characterized by linear-in-temperature resistivity, could shed light on the mechanism of unconventional superconductivity. Here, by using electrical resistivity measurements into the micro-Kelvin regime, the authors report evidence of unconventional superconductivity in the strange metal YbRh2Si2 and propose a possible pairing mechanism.
- D. H. Nguyen
- , A. Sidorenko
- & S. Paschen
-
Article
| Open Access Dimensional reduction by geometrical frustration in a cubic antiferromagnet composed of tetrahedral clusters
Dimensional reduction by geometrical frustration in a cubic antiferromagnet composed of tetrahedral clusters
Dimensionality reduction can occur in magnetically frustrated systems; however, it typically involves lattice distortions. Here, the authors report two- and one-dimensional character of spin correlations in a three-dimensional tetrahedral cluster antiferromagnet, driven purely by geometrical frustration.
- Ryutaro Okuma
- , Maiko Kofu
- & Zenji Hiroi
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput design of high-performance lightweight high-entropy alloys
High-throughput design of high-performance lightweight high-entropy alloys
Advanced screening strategies for the design of high-entropy alloys are highly desirable. Here the authors use the project-oriented design strategy and CALPHAD-based high-throughput calculation tool to rapidly screen promising Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ti structural HEAs for high-temperature applications.
- Rui Feng
- , Chuan Zhang
- & Peter K. Liaw
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous control of classical-quantum crossover by external high pressure in the coupled chain compound CsCuCl3
Continuous control of classical-quantum crossover by external high pressure in the coupled chain compound CsCuCl3
In real materials, a spin quantum number assumes a fixed value, which makes it challenging to realize a crossover between quantum and classical spin regimes. Here the authors demonstrate such a crossover in a weakly coupled chain compound by controlling the amount of quantum correlations, in the form of the inverse spin quantum number, with external pressure.
- Daisuke Yamamoto
- , Takahiro Sakurai
- & Yoshiya Uwatoko
-
Article
| Open Access Phase management in single-crystalline vanadium dioxide beams
Phase management in single-crystalline vanadium dioxide beams
Control of the phases associated with the metal-insulator transition in VO2 underpins its applications as a phase change material. Here, the authors report phase management by means of oxide inhibitor-assisted growth and present high-performance VO2 actuators based on asymmetric phase transition routes.
- Run Shi
- , Yong Chen
- & Chun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing thermally-activated nucleation pathways of diffusionless solid-to-solid transition
Revealing thermally-activated nucleation pathways of diffusionless solid-to-solid transition
Normally the diffusionless solid-to-solid transition between phases are driven by athermal processes, due to strain being overwhelmingly dominant. Here, the authors present a unique series of in-situ particle level observations of the solid-to-solid transition in colloidal particles suspended in a solvent, revealing new transition pathways.
- Minhuan Li
- , Zhengyuan Yue
- & Peng Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Avalanches and edge-of-chaos learning in neuromorphic nanowire networks
Avalanches and edge-of-chaos learning in neuromorphic nanowire networks
Neuromorphic nanowire networks are found to exhibit neural-like dynamics, including phase transitions and avalanche criticality. Hochstetter and Kuncic et al. show that the dynamical state at the edge-of-chaos is optimal for learning and favours computationally complex information processing tasks.
- Joel Hochstetter
- , Ruomin Zhu
- & Zdenka Kuncic
-
Article
| Open Access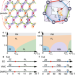 Identification of magnetic interactions and high-field quantum spin liquid in α-RuCl3
Identification of magnetic interactions and high-field quantum spin liquid in α-RuCl3
The nature of spin interactions and the field-induced quantum spin liquid phase in the Kitaev material α-RuCl3 have been debated. Here, using a combination of many-body techniques, the authors derive an effective spin model that explains the majority of experimental findings and predicts a new quantum spin liquid phase in strong out-of-plane magnetic field.
- Han Li
- , Hao-Kai Zhang
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Order-by-disorder from bond-dependent exchange and intensity signature of nodal quasiparticles in a honeycomb cobaltate
Order-by-disorder from bond-dependent exchange and intensity signature of nodal quasiparticles in a honeycomb cobaltate
It was suggested that some 3d materials display bond-dependent exchange interactions, leading to exotic many-body effects. Here, using inelastic neutron scattering, the authors reveal such interactions in the stacked honeycomb magnet CoTiO3 and show how they induce a spectral gap and affect the Dirac magnon band structure.
- M. Elliot
- , P. A. McClarty
- & R. Coldea
-
Article
| Open Access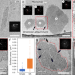 Nucleation of protein mesocrystals via oriented attachment
Nucleation of protein mesocrystals via oriented attachment
Past studies on protein nucleation have focused on the routes that molecules follow towards a crystalline cluster, while possible interactions that may occur between nuclei have not been investigated. Here, the authors show that in the high supersaturation limit such interactions dominate the nucleation process in the form of inter-nucleus docking driving by oriented attachment.
- Alexander E. S. Van Driessche
- , Nani Van Gerven
- & Mike Sleutel
-
Article
| Open Access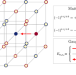 Lattice quantum electrodynamics in (3+1)-dimensions at finite density with tensor networks
Lattice quantum electrodynamics in (3+1)-dimensions at finite density with tensor networks
Tensor network simulations of lattice gauge theories may overcome the limitations of the Monte Carlo approach, but results have been limited to 1+1 and 2+1 dimensions so far. Here, the authors report a tree-tensor-based numerical study of a 3+1d truncated U(1) lattice gauge theory with fermionic matter.
- Giuseppe Magnifico
- , Timo Felser
- & Simone Montangero
-
Article
| Open Access Manifestations of metastable criticality in the long-range structure of model water glasses
Manifestations of metastable criticality in the long-range structure of model water glasses
The subtle connections between water’s supercooled liquid and glassy states are difficult to characterize. Gartner et al. suggest with MD simulations that the long-range structure of glassy water may reflect signatures of water’s debated second critical point in the supercooled liquid.
- Thomas E. Gartner III
- , Salvatore Torquato
- & Pablo G. Debenedetti
-
Article
| Open Access Non-universal current flow near the metal-insulator transition in an oxide interface
Non-universal current flow near the metal-insulator transition in an oxide interface
Macroscopic properties usually follow algebraic scaling laws near phase transitions. Here, the authors investigate the scaling properties of the metal‐insulator transition at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface, finding that coupling between structural and electronic properties prevents the universal behavior.
- Eylon Persky
- , Naor Vardi
- & Beena Kalisky
-
Article
| Open Access Incentive-driven transition to high ride-sharing adoption
Incentive-driven transition to high ride-sharing adoption
Ride-sharing, combining similar concurrent trips into one, may support sustainable urban mobility yet lacks broad adoption. Storch et al. reveal how collective interactions in shared rides explain essential characteristics of ride-sharing adoption patterns e.g. observed in New York City and Chicago.
- David-Maximilian Storch
- , Marc Timme
- & Malte Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of the quasi-quantized Hall effect in ZrTe5
Origin of the quasi-quantized Hall effect in ZrTe5
A 3D quantum Hall effect has been reported in Dirac semimetal ZrTe5 due to a magnetic-field-driven Fermi surface instability. Here, the authors show evidence of quasi-quantized Hall response without Fermi surface instability, but they argue that it is due to the interplay of the intrinsic properties of ZrTe5 electronic structure and Dirac semi-metallic character.
- S. Galeski
- , T. Ehmcke
- & J. Gooth
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Abelian three-loop braiding statistics for 3D fermionic topological phases
Non-Abelian three-loop braiding statistics for 3D fermionic topological phases
Non-Abelian statistics plays a crucial role towards realizing topological quantum computation. Here, the authors discover new types of non-Abelian three-loop braiding statistics that can only be realized in 3D interacting fermionic systems.
- Jing-Ren Zhou
- , Qing-Rui Wang
- & Zheng-Cheng Gu
-
Article
| Open Access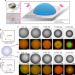 Non-associative phase separation in an evaporating droplet as a model for prebiotic compartmentalization
Non-associative phase separation in an evaporating droplet as a model for prebiotic compartmentalization
Prebiotic compartmentalization could prove essential for the evolution of life. Guo et al. show that liquid-liquid separation in an aqueous two-phase system driven by evaporation may already suffice to facilitate chemical processes required for the RNA world hypothesis.
- Wei Guo
- , Andrew B. Kinghorn
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic fingerprint of fractionalized excitations in single-crystalline Cu3Zn(OH)6FBr
Dynamic fingerprint of fractionalized excitations in single-crystalline Cu3Zn(OH)6FBr
Spinon excitations of a Kagome quantum spin liquid are expected to give rise to a magnetic continuum in Raman spectroscopy. Here, the authors report a magnetic Raman continuum in the Kagome spin liquid candidate Cu3Zn(OH)6FBr, in contrast to a sharp magnon Raman peak in the Kagome antiferromagnet EuCu3(OH)6Cl3.
- Ying Fu
- , Miao-Ling Lin
- & Jia-Wei Mei
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductor-insulator transition in space charge doped one unit cell Bi2.1Sr1.9CaCu2O8+x
Superconductor-insulator transition in space charge doped one unit cell Bi2.1Sr1.9CaCu2O8+x
Previous work on critical scaling at the superconductor-to-insulator transition has shown variations across different materials. Here, the authors use a space charge doping technique to tune the transition in a single layer cuprate sample and present evidence of the universal scaling behaviour.
- Fang Wang
- , Johan Biscaras
- & Abhay Shukla
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond control of phonon dynamics near a magnetic order critical point
Femtosecond control of phonon dynamics near a magnetic order critical point
Precise control of vibrational states coupled to electronic degrees of freedom could enable control over charge or magnetic order in a material. Here, the authors use a double-pulse photoexcitation combined with an X-ray probe to control vibrational states near the critical point of spin density wave in Cr films.
- O. Yu. Gorobtsov
- , L. Ponet
- & A. Singer
-
Article
| Open Access In situ correlation between metastable phase-transformation mechanism and kinetics in a metallic glass
In situ correlation between metastable phase-transformation mechanism and kinetics in a metallic glass
The competition between the formation of different phases and their kinetics need to be clearly understood to make materials with on-demand and multifaceted properties. Here, the authors reveal, by a combination of complementary in situ techniques, the mechanism of a Cu-Zr-Al metallic glass’s high propensity for metastable phase formation, which is partially through a kinetic mechanism of Al partitioning.
- Jiri Orava
- , Shanoob Balachandran
- & Ivan Kaban

 Folded network and structural transition in molten tin
Folded network and structural transition in molten tin