Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access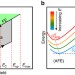 Designing lead-free antiferroelectrics for energy storage
Designing lead-free antiferroelectrics for energy storage
Antiferroelectric capacitors hold great promise for high-power energy storage. Here, through a first-principles-based computational approach, authors find high theoretical energy densities in rare earth substituted bismuth ferrite, and propose a simple model to assess the storage properties of a general antiferroelectric material.
- Bin Xu
- , Jorge Íñiguez
- & L. Bellaiche
-
Article
| Open Access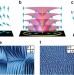 Morphogenesis of liquid crystal topological defects during the nematic-smectic A phase transition
Morphogenesis of liquid crystal topological defects during the nematic-smectic A phase transition
Defects in liquid crystals play a central role in determining their structural and dynamic properties, whilst it is challenging to characterize the defects at a molecule level. Here, Gimet al. trace the evolution pathway of defects during a phase transition from a nematic to a smectic state.
- Min-Jun Gim
- , Daniel A. Beller
- & Dong Ki Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access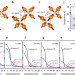 Magnetic-field induced multiple topological phases in pyrochlore iridates with Mott criticality
Magnetic-field induced multiple topological phases in pyrochlore iridates with Mott criticality
The interplay between multiple electronic interactions in solid promotes the emergence of exotic phases. Here, Uedaet al. report magnetotransport study on pyrochlore iridates R2Ir2O7near quantum metal-insulator transition reflecting the emergence of multiple Weyl semimetal states.
- Kentaro Ueda
- , Taekoo Oh
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access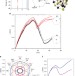 Emptying Dirac valleys in bismuth using high magnetic fields
Emptying Dirac valleys in bismuth using high magnetic fields
Materials in large magnetic fields can be driven into the quantum limit, where electrons occupy only the lowest Landau level and the response is determined by interactions. Here the authors go beyond this limit by emptying one or two of bismuth’s electronic valleys, depending on the field direction.
- Zengwei Zhu
- , Jinhua Wang
- & Kamran Behnia
-
Article
| Open Access Probing nanofriction and Aubry-type signatures in a finite self-organized system
Probing nanofriction and Aubry-type signatures in a finite self-organized system
Superlubricity has been predicted and observed at an atomistic level, yet its dynamics is not well understood due to the lack ofin situ characterization of contact surfaces. Kiethe et al. use a trapped two-dimensional ion crystal as a model for the study of nanofriction in self-organized structures.
- J. Kiethe
- , R. Nigmatullin
- & T. E. Mehlstäubler
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusive and martensitic nucleation kinetics in solid-solid transitions of colloidal crystals
Diffusive and martensitic nucleation kinetics in solid-solid transitions of colloidal crystals
Solid-solid transitions between different crystalline structures have broad implications in earth science, steel and ceramic materials. Penget al. show a transformation pathway that starts off as being martensitic then switches to diffusive at the single particle level in a colloidal system under pressure.
- Yi Peng
- , Wei Li
- & Yilong Han
-
Article
| Open Access Underwater Leidenfrost nanochemistry for creation of size-tailored zinc peroxide cancer nanotherapeutics
Underwater Leidenfrost nanochemistry for creation of size-tailored zinc peroxide cancer nanotherapeutics
Water can function as a sustainable reactor for the synthesis of size-controlled, functional nanoparticles. Here, the authors introduce an underwater Leidenfrost synthesis that reproduces the dynamic chemistry of the deep ocean, in which anticancer therapeutic ZnO2nanoclusters form in an overheated zone and migrate to colder water to continue growth.
- Mady Elbahri
- , Ramzy Abdelaziz
- & Moheb Abdelaziz
-
Article
| Open Access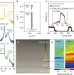 Large polarization gradients and temperature-stable responses in compositionally-graded ferroelectrics
Large polarization gradients and temperature-stable responses in compositionally-graded ferroelectrics
Future technologies based on ferroelectric materials will require new routes to control the nature of polar order. Through a combined experimental and theoretical study of compositionally and strain-graded Ba1-xSrxTiO3 heterostructures, Damodaranet al. demonstrate the ability to engineer large polarization gradients and temperature-stable susceptibilities.
- Anoop R. Damodaran
- , Shishir Pandya
- & Lane W. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Field induced spontaneous quasiparticle decay and renormalization of quasiparticle dispersion in a quantum antiferromagnet
Field induced spontaneous quasiparticle decay and renormalization of quasiparticle dispersion in a quantum antiferromagnet
Spontaneous magnon decay in canted antiferromagnets has been theoretically investigated extensively, but experimental evidence is limited. Here the authors study the spin ½ antiferromagnet DLCB via neutron scattering, revealing field-induced spontaneous magnon decay associated with three-magnon interactions.
- Tao Hong
- , Y. Qiu
- & A. L. Chernyshev
-
Article
| Open Access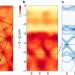 Hallmarks of Hunds coupling in the Mott insulator Ca2RuO4
Hallmarks of Hunds coupling in the Mott insulator Ca2RuO4
Detailed knowledge of the low-energy electronic structure is required to understand the Mott insulating phase of Ca2RuO4. Here, Sutter et al. provide directly the experimental band structure of the paramagnetic insulating phase of Ca2RuO4and unveil the electronic origin of its Mott phase.
- D. Sutter
- , C. G. Fatuzzo
- & J. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access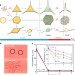 Efficient self-emulsification via cooling-heating cycles
Efficient self-emulsification via cooling-heating cycles
Emulsions are mixtures of liquids which have applications to pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food components. Here Tcholakovaet al. have developed a low-energy emulsification method which requires a low amount of surfactant, works for temperature-sensitive compounds and has potential for scale-up.
- Slavka Tcholakova
- , Zhulieta Valkova
- & Stoyan K. Smoukov
-
Article
| Open Access Fine structure of the topological defect cores studied for disclinations in lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals
Fine structure of the topological defect cores studied for disclinations in lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals
Topological defects play important roles in determining material properties, whilst their core regions remain unexplored due to strongly distorted structures. Zhouet al. take advantage of extended core regions in a chromonic liquid crystal and show both a radial and azimuthal dependent director and scalar order parameter.
- Shuang Zhou
- , Sergij V. Shiyanovskii
- & Oleg D. Lavrentovich
-
Article
| Open Access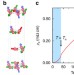 Simultaneous loss of interlayer coherence and long-range magnetism in quasi-two-dimensional PdCrO2
Simultaneous loss of interlayer coherence and long-range magnetism in quasi-two-dimensional PdCrO2
Incoherent transport is an important feature of many anisotropic quantum materials but often its origin is not well understood. Here, the authors show that in a layered quantum magnet, incoherence is driven by the interaction of electrons with spin fluctuations after the melting of magnetic order.
- S. Ghannadzadeh
- , S. Licciardello
- & N. E. Hussey
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the complex free-energy landscape of the simplest glass by rheology
Exploring the complex free-energy landscape of the simplest glass by rheology
The ground states of amorphous solids are predicted to exhibit a complex energy landscape, which cannot be explained by the theories developed for crystals. Jin and Yoshino propose a simple rheological protocol to probe these states, with a demonstration by extensive molecular dynamics simulations.
- Yuliang Jin
- & Hajime Yoshino
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing rare fluctuations in soft particulate flows
Characterizing rare fluctuations in soft particulate flows
Soft particulate flows such as granular media are prone to fluctuations like jamming and avalanches. Here Rahbari et al. consider the statistics of rare fluctuations to identify an effective temperature which, unlike previous ones, is valid for packing fractions both near and far from the jamming point.
- S.H.E. Rahbari
- , A.A. Saberi
- & J. Vollmer
-
Article
| Open Access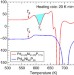 Hidden amorphous phase and reentrant supercooled liquid in Pd-Ni-P metallic glasses
Hidden amorphous phase and reentrant supercooled liquid in Pd-Ni-P metallic glasses
An anomalous exothermal calorimetric peak far below crystallization temperatures in prototypical Pd-Ni-P glasses has been recognized for four decades. Here authors use neutron and high-energy X-ray diffraction to find evidence for a polyamorphous phase transition where medium-range order undergoes large changes while short-range order changes little.
- S. Lan
- , Y. Ren
- & X. -L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access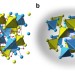 Ground state selection under pressure in the quantum pyrochlore magnet Yb2Ti2O7
Ground state selection under pressure in the quantum pyrochlore magnet Yb2Ti2O7
An understanding of how quantum spin liquids arise in frustrated magnets at low temperatures remains elusive. Here the authors demonstrate a pressure-driven ferromagnetic transition out of a quantum spin liquid phase in the pyrochlore Yb2Ti2O7, highlighting its proximity to a phase boundary.
- E. Kermarrec
- , J. Gaudet
- & B. D. Gaulin
-
Article
| Open Access Hidden phase in a two-dimensional Sn layer stabilized by modulation hole doping
Hidden phase in a two-dimensional Sn layer stabilized by modulation hole doping
Broken symmetry phases may occur in 2D materials upon doping, yet introducing doping without inducing chemical disorder remains a challenge. Here, the authors use a modulation doping approach that unveils a hidden equilibrium phase involving spontaneous symmetry breaking in a hole-doped Sn bilayer.
- Fangfei Ming
- , Daniel Mulugeta
- & Hanno H. Weitering
-
Article
| Open Access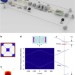 Observation of optomechanical buckling transitions
Observation of optomechanical buckling transitions
Optomechanical systems could form logic gates, but key requirements are two stable static states and the ability to switch between them. Here, the authors observe radiation-pressure induced buckling transitions in an optomechanical system, and control this transition by varying laser power and detuning.
- H. Xu
- , U. Kemiktarak
- & J. M. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access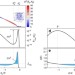 Canonical free-energy barrier of particle and polymer cluster formation
Canonical free-energy barrier of particle and polymer cluster formation
Droplet formation processes are ubiquitous in nature and accompanied by a free-energy barrier. Here, the authors present a numerical approach for a shape-free determination of free-energy barriers and demonstrate on this level an analogy between particle condensation and polymer aggregation.
- Johannes Zierenberg
- , Philipp Schierz
- & Wolfhard Janke
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum criticality at the superconductor-insulator transition revealed by specific heat measurements
Quantum criticality at the superconductor-insulator transition revealed by specific heat measurements
To detect thermodynamic signatures of quantum fluctuations for quantum phase transitions is challenging. Here, Poranet al. report a significant increase in the specific heat when the thickness of granular Pb films approaches a superconductor-insulator transition.
- S. Poran
- , T. Nguyen-Duc
- & Olivier Bourgeois
-
Article
| Open Access Strong electronic interaction and multiple quantum Hall ferromagnetic phases in trilayer graphene
Strong electronic interaction and multiple quantum Hall ferromagnetic phases in trilayer graphene
Few-layered graphene offers a powerful platform to investigate electronic interactions beyond the non-interacting electron picture approximation. Here, the authors report the signature of strong electronic interactions and quantum Hall ferromagnetism in trilayer graphene with ABA stacking.
- Biswajit Datta
- , Santanu Dey
- & Mandar M. Deshmukh
-
Article
| Open Access Zero-gap semiconductor to excitonic insulator transition in Ta2NiSe5
Zero-gap semiconductor to excitonic insulator transition in Ta2NiSe5
The nature of an insulating phase in Ta2NiSe5 is an open question. Here, Lu et al. report transport, thermodynamic and optical evidences being fully consistent with an excitonic insulator phase in this material.
- Y. F. Lu
- , H. Kono
- & H. Takagi
-
Article
| Open Access In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
In situ study on atomic mechanism of melting and freezing of single bismuth nanoparticles
The atomic mechanisms of reversible phase transitions are challenging to probe experimentally. Here, the authors induce melting and freezing processes in bismuth nanoparticles inside a high-resolution electron microscope, observing the atom-level stages of this phase transition pathway in real time.
- Yingxuan Li
- , Ling Zang
- & Chuanyi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Control of finite critical behaviour in a small-scale social system
Control of finite critical behaviour in a small-scale social system
Proximity to criticality can be advantageous under changing conditions, but it also entails reduced robustness. Here, the authors analyse fight sizes in a macaque society and find not only that it sits near criticality, but also that the distance from the critical point is tunable through adjustment of individual behaviour and social conflict management.
- Bryan C. Daniels
- , David C. Krakauer
- & Jessica C. Flack
-
Article
| Open Access Articulation points in complex networks
Articulation points in complex networks
An articulation point in a network is a node whose removal disconnects the network. Here the authors develop analytical tools to study key issues pertinent to articulation points, such as the expected number of them and the network vulnerability against their removal, in arbitrary complex networks.
- Liang Tian
- , Amir Bashan
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A metastable liquid melted from a crystalline solid under decompression
A metastable liquid melted from a crystalline solid under decompression
It is experimentally challenging to observe an intermediate liquid in solid–solid phase transitions due to short lifetimes of the resulting metastable states. Here, Linet al. show that a metastable bismuth liquid can be formed from a crystalline solid through decompression and maintained for hours.
- Chuanlong Lin
- , Jesse S. Smith
- & Guoyin Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast evolution and transient phases of a prototype out-of-equilibrium Mott–Hubbard material
Ultrafast evolution and transient phases of a prototype out-of-equilibrium Mott–Hubbard material
Ultrafast photoexcitation stabilizes new states of matter with rich out-of-equilibrium behaviours. Here, Lantzet al. report a transient non-thermal phase developing immediately after photoexcitation in V2O3, shedding a light on optical manipulation of strongly correlated systems.
- G. Lantz
- , B. Mansart
- & M. Marsi
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of network structural dissimilarities
Quantification of network structural dissimilarities
Identifying and quantifying dissimilarities among graphs is a problem of practical importance, but current approaches are either limited or computationally demanding. Here, the authors propose an efficiently computable measure for network comparison that can identify structural topological differences.
- Tiago A. Schieber
- , Laura Carpi
- & Martín G. Ravetti
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent order in the kagome Ising magnet Dy3Mg2Sb3O14
Emergent order in the kagome Ising magnet Dy3Mg2Sb3O14
Frustration in lattices of interacting spins can lead to rich and exotic physics, such as fractionalized excitations and emergent order. Here, the authors demonstrate a low-temperature transition from a disordered spin-ice-like phase to an emergent charge ordered phase in the bulk kagome Ising magnet Dy3Mg2Sb3O14.
- Joseph A. M. Paddison
- , Harapan S. Ong
- & S. E. Dutton
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent Weyl excitations in systems of polar particles
Emergent Weyl excitations in systems of polar particles
Systems with Weyl excitations can display very interesting physical phenomena. Here the authors demonstrate that Weyl excitations exist generically in 3D systems of dipolar particles following angular momentum transfer, and discuss how to observe them in cold alkaline-earth-atom systems.
- Sergey V. Syzranov
- , Michael L. Wall
- & Ana Maria Rey
-
Article
| Open Access Critical exponents and scaling invariance in the absence of a critical point
Critical exponents and scaling invariance in the absence of a critical point
Thermodynamic observables develop power laws and singularities when approaching the Curie point of a ferromagnetic phase transition. Here, Saratz et al. demonstrate that topological excitations (that is, magnetic domains in Fe/Cu(100) films that even persist above the Curie point) remove those singularities compatibly with an avoided critical point.
- N. Saratz
- , D. A. Zanin
- & A. Vindigni
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically resolved phase transition of fullerene cations solvated in helium droplets
Atomically resolved phase transition of fullerene cations solvated in helium droplets
'Atkins snowballs', solid layers of helium around an ion core in bulk superfluid He, have been investigated for simple ions but many properties remain unknown. Here, the authors show via photofragmentation experiments that a phase transition occurs in C60-doped He droplets depending on the number of He atoms.
- M. Kuhn
- , M. Renzler
- & P. Scheier
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum criticality in an organic spin-liquid insulator κ-(BEDT-TTF)2Cu2(CN)3
Quantum criticality in an organic spin-liquid insulator κ-(BEDT-TTF)2Cu2(CN)3
Quantum spin liquids emerge when quantum fluctuations suppress a magnetically ordered state. Here the authors measure magnetic torque inκ-(BEDT-TTF)2Cu2(CN)3, showing universal critical scaling in the magnetic susceptibilities, with critical exponents incompatible with known models for quantum spin liquids.
- Takayuki Isono
- , Taichi Terashima
- & Shinya Uji
-
Article
| Open Access The reversibility and first-order nature of liquid–liquid transition in a molecular liquid
The reversibility and first-order nature of liquid–liquid transition in a molecular liquid
The nature of the phenomenon of so-called ‘liquid-liquid transitions’ in molecular liquids is a long-standing debate. Here, the authors demonstrate the reversibility and first-order nature of the liquid-liquid transition in triphenyl phosphite via flash differential scanning calorimetry.
- Mika Kobayashi
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access New porous water ice metastable at atmospheric pressure obtained by emptying a hydrogen-filled ice
New porous water ice metastable at atmospheric pressure obtained by emptying a hydrogen-filled ice
By trapping guest molecules, solid water shows peculiar structures in addition to the known fifteen forms of ice at different conditions. Here, the authors report a new porous ice phase, termed ice XVII, which is metastable at ambient pressure and is able to adsorb and release hydrogen reversibly.
- Leonardo del Rosso
- , Milva Celli
- & Lorenzo Ulivi
-
Article
| Open Access Striped nanoscale phase separation at the metal–insulator transition of heteroepitaxial nickelates
Striped nanoscale phase separation at the metal–insulator transition of heteroepitaxial nickelates
Probing the evolution of mixed-phase states in materials offers unique insights into the microscopic mechanism of phase transitions. Here, Mattoni et al. report imaging of nanoscale formation and growth of insulating domains across the metal-insulator transition in NdNiO3thin films, uncovering a rich interplay between structural and electronic degrees of freedom.
- G. Mattoni
- , P. Zubko
- & A. D. Caviglia
-
Article
| Open Access The role of fivefold symmetry in suppressing crystallization
The role of fivefold symmetry in suppressing crystallization
The suppression of crystallization due to the appearance of structures with fivefold symmetry is widely adopted, but its kinetic and thermodynamic origin remains elusive. Taffs et al.show that fivefold symmetry substantially slows down the nucleation rate but not the crystal growth rate as expected.
- Jade Taffs
- & C. Patrick Royall
-
Article
| Open Access Field-induced spin-density wave beyond hidden order in URu2Si2
Field-induced spin-density wave beyond hidden order in URu2Si2
The strongly-correlated electron system URu2Si2 possesses a hidden-order phase whose order parameter remains unidentified. Here, the authors demonstrate the development of spin-density-wave phases in URu2Si2under high magnetic fields, providing a potential in-road to understanding this system.
- W. Knafo
- , F. Duc
- & L.-P. Regnault
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-polarized surface resonances accompanying topological surface state formation
Spin-polarized surface resonances accompanying topological surface state formation
The spin-orbit interaction is central to the defining characteristics of topological insulators. Here, Jozwiaket al. report a spin-polarized unoccupied surface resonance coevolving with topological surface states from a pair of Rashba-like states through spin-orbit induced band inversion.
- Chris Jozwiak
- , Jonathan A. Sobota
- & Alessandra Lanzara
-
Article
| Open Access Colossal magnetic phase transition asymmetry in mesoscale FeRh stripes
Colossal magnetic phase transition asymmetry in mesoscale FeRh stripes
FeRh possesses a unique hysteretic metamagnetic phase transition between antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic order close to room temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate a strong enhancement of the asymmetry of this transition in mesoscale stripes of FeRh.
- V. Uhlíř
- , J. A. Arregi
- & E. E. Fullerton
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of metastable phases by spinodal decomposition
Formation of metastable phases by spinodal decomposition
Metastable phases are usually formed through nucleation, upon overcoming an energy barrier. Here, Alert et al. theoretically predict and experimentally verify the unexpected formation of a metastable phase by spinodal decomposition through direct phase separation from an unstable phase.
- Ricard Alert
- , Pietro Tierno
- & Jaume Casademunt
-
Article
| Open Access The backtracking survey propagation algorithm for solving random K-SAT problems
The backtracking survey propagation algorithm for solving random K-SAT problems
The K-satisfability problem is a combinatorial discrete optimization problem, which for K=3 is NP-complete, and whose random formulation is of interest for understanding computational complexity. Here, the authors introduce the backtracking survey propagation algorithm for studying it for K=3 and K=4.
- Raffaele Marino
- , Giorgio Parisi
- & Federico Ricci-Tersenghi
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially inhomogeneous electron state deep in the extreme quantum limit of strontium titanate
Spatially inhomogeneous electron state deep in the extreme quantum limit of strontium titanate
At sufficiently strong magnetic fields and low temperatures, electrons assume a quasi-one-dimensional quantum state that is challenging to observe. Here, Bhattacharya et al. report on electron transport in lightly-doped single crystals of SrTiO3deep in this extreme quantum limit.
- Anand Bhattacharya
- , Brian Skinner
- & Alexey V. Suslov
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of a new superfluid phase for 3He embedded in nematically ordered aerogel
Observation of a new superfluid phase for 3He embedded in nematically ordered aerogel
Anisotropic disorder is predicted to change the stability of the superfluid state in3He and leads to new phases. Here, Zhelev et al. report signatures of the phase transitions in 3He confined in an extremely anisotropic ordered aerogel including a new polar phase.
- N. Zhelev
- , M. Reichl
- & J. M. Parpia
-
Article
| Open Access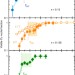 Unconventional charge order in a co-doped high-Tc superconductor
Unconventional charge order in a co-doped high-Tc superconductor
Understanding of how charge stripe order emerges in cuprates remains elusive. Here, Pelc et al. report the discovery of a charge nematic phase between charge-stripe order and pseudogap state in La1.8-xEu0.2SrxCuO4, resolving the process of charge stripe development in cuprates.
- D. Pelc
- , M. Vučković
- & M. Požek
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-current probe for phase transition in an insulator
Spin-current probe for phase transition in an insulator
Whilst neutron scattering is a powerful tool for studying spin fluctuations in materials, its availability is limited to large-scale user facilities. Here, the authors demonstrate how the pumping of pure spin currents can be used as a desktop probe to detect an antiferromagnetic transition.
- Zhiyong Qiu
- , Jia Li
- & Eiji Saitoh
-
Article
| Open Access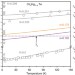 Temperature-driven massless Kane fermions in HgCdTe crystals
Temperature-driven massless Kane fermions in HgCdTe crystals
Kane fermions are predicted to be tunable with external parameters such as temperature. Here, Teppe et al. show a band structure evolution of bulk HgCdTe as temperature is tuned across topological phase transition, demonstrating that Kane fermions change sign in rest-mass and remain constant in velocity.
- F. Teppe
- , M. Marcinkiewicz
- & S. A. Dvoretskii
-
Article
| Open Access A possible four-phase coexistence in a single-component system
A possible four-phase coexistence in a single-component system
Gibbs' phase rule states that the maximum number of coexisting phases in a one-component system, and in absence of external fields, is three. Here, the authors show that directly controlling the Hamiltonian allows the extension of this rule to four phases.
- Kenji Akahane
- , John Russo
- & Hajime Tanaka

 Polymorphism in a high-entropy alloy
Polymorphism in a high-entropy alloy