Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access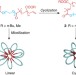 Tuneable enhancement of the salt and thermal stability of polymeric micelles by cyclized amphiphiles
Tuneable enhancement of the salt and thermal stability of polymeric micelles by cyclized amphiphiles
The cyclic structure of cell membrane lipids is known to allow thermophilic archaea to survive in extreme environments. Here, Honda et al.report an improvement in thermal and salt stability of self-assembled micelles by cyclized polymeric amphiphiles.
- Satoshi Honda
- , Takuya Yamamoto
- & Yasuyuki Tezuka
-
Article
| Open Access Excitation-dependent visible fluorescence in decameric nanoparticles with monoacylglycerol cluster chromophores
Excitation-dependent visible fluorescence in decameric nanoparticles with monoacylglycerol cluster chromophores
Organic fluorescent nanoparticles have potential biomaterials applications due to their low-toxicity and ‘green’ synthesis. Here, a series of self-assembled nanoparticles and polymers are synthesized with intense visible fluorescence stemming from chromophores of hydrogen-bonded monoacylglycerol clusters.
- Kwang-Ming Lee
- , Wan-Yin Cheng
- & Bi-Yun Lin
-
Article |
 A six-carbon 10π-electron aromatic system supported by group 3 metals
A six-carbon 10π-electron aromatic system supported by group 3 metals
Aromaticity predicts the existence of the benzene tetra-anion, although it has not been unambiguously observed. Here, the authors have synthesized a tetra-anionic substituted benzene as a ligand and characterize the six-carbon, 10 π-electron system by structural, spectroscopic and theoretical techniques.
- Wenliang Huang
- , Florian Dulong
- & Paula L. Diaconescu
-
Article
| Open Access Globally homochiral assembly of two-dimensional molecular networks triggered by co-absorbers
Globally homochiral assembly of two-dimensional molecular networks triggered by co-absorbers
The construction of homochiral surfaces may play a significant role in applications including heterogeneous catalysis and bio-sensors. Here, globally homochiral two-dimensional assemblies of achiral molecules are formed via co-assembly with chiral co-adsorbers, demonstrating a ‘majority rules’ effect.
- Ting Chen
- , Wen-Hong Yang
- & Li-Jun Wan
-
Article |
 Unprecedented high-temperature CO2 selectivity in N2-phobic nanoporous covalent organic polymers
Unprecedented high-temperature CO2 selectivity in N2-phobic nanoporous covalent organic polymers
Porous materials are well studied for gas capture and separation technologies. Here, the authors report nitrogen-rich, nanoporous polymers, which display very high CO2/N2 selectivity with increasing temperature, which may be attributable to an entropically driven N2-phobicity effect.
- Hasmukh A. Patel
- , Sang Hyun Je
- & Ali Coskun
-
Article |
 Hydrogen bond-promoted metallic state in a purely organic single-component conductor under pressure
Hydrogen bond-promoted metallic state in a purely organic single-component conductor under pressure
Purely organic materials are generally insulating and while charge-carrier generation can provide electrical conductivity, it is rare for single-component systems. Here, symmetric hydrogen bonding between tetrathiafulvalene-based molecules gives rise to room-temperature conductivity and low pressure metallic state transitions.
- Takayuki Isono
- , Hiromichi Kamo
- & Hatsumi Mori
-
Article
| Open Access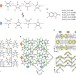 Above-room-temperature ferroelectricity and antiferroelectricity in benzimidazoles
Above-room-temperature ferroelectricity and antiferroelectricity in benzimidazoles
There are only a few known organic ferroelectrics, particularly ones that operate at high temperatures. Here the discovery of ferroelectricity above room temperature in members of an ubiquitous family of organic molecules reveals the possibility of novel low-cost electronic applications.
- Sachio Horiuchi
- , Fumitaka Kagawa
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article |
 Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
Acetylenes can be covalently linked by oxidative coupling reactions. Zhanget al. report terminal alkyne Csp-H bond activation and concomitant homo-coupling on a silver surface, yielding polymeric networks with a conjugated backbone.
- Yi-Qi Zhang
- , Nenad Kepčija
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article |
 Scalable organocatalytic asymmetric Strecker reactions catalysed by a chiral cyanide generator
Scalable organocatalytic asymmetric Strecker reactions catalysed by a chiral cyanide generator
The Strecker synthesis is an established method for the production of α-amino acids. Here, a scalable catalytic asymmetric Strecker reaction is reported that allows one-pot synthesis of enantiomerically pure α-amino acids.
- Hailong Yan
- , Joong Suk Oh
- & Choong Eui Song
-
Article
| Open Access Sn-Beta zeolites with borate salts catalyse the epimerization of carbohydrates via an intramolecular carbon shift
Sn-Beta zeolites with borate salts catalyse the epimerization of carbohydrates via an intramolecular carbon shift
Epimerization of carbohydrates to rare sugars yields products that have potential applications as anti-viral drugs or chiral building blocks. Here, Sn-Beta zeolite in the presence of sodium tetraborate is shown to catalyze the selective epimerization of aldoses in aqueous media.
- William R. Gunther
- , Yuran Wang
- & Yuriy Román-Leshkov
-
Article |
 Naphthol radical couplings determine structural features and enantiomeric excess of dalesconols in Daldinia eschscholzii
Naphthol radical couplings determine structural features and enantiomeric excess of dalesconols in Daldinia eschscholzii
The dalesconol natural products are biosynthesised in an enantiomeric excess of 67%, rather than as a single enantiomer or a racemate. Tanet al. report that this unusual enantioselectivity is a result of the dominance of particular conformers of naphthol dimer intermediates.
- Wei Fang
- , Shen Ji
- & Ren Xiang Tan
-
Article |
 Self-assembling subnanometer pores with unusual mass-transport properties
Self-assembling subnanometer pores with unusual mass-transport properties
Molecular systems with rigid macrocyclic backbones self-assemble into synthetic nanopores that mimic the mass-transport characteristics of biological channels. Zhouet al. produce self-assembling hydrophobic nanopores that mediate highly selective transmembrane ion transport and highly efficient transmembrane water permeability.
- Xibin Zhou
- , Guande Liu
- & Bing Gong
-
Article |
 Enantioselective synthesis of a chiral nitrogen-doped buckybowl
Enantioselective synthesis of a chiral nitrogen-doped buckybowl
Nitrogen-doped fullerenes and carbon nanotubes have been produced, but the synthesis of nitrogen-doped buckybowls, is an unsolved challenge. Tanet al. report an enantioselective synthesis of triazasumanene, and show that nitrogen doping leads to deeper bowl structures than in all-carbon buckybowls.
- Qitao Tan
- , Shuhei Higashibayashi
- & Hidehiro Sakurai
-
Article |
 Closed network growth of fullerenes
Closed network growth of fullerenes
The formation mechanisms of fullerenes remain unclear. This study shows that fullerenes self-assemble through a closed network growth mechanism in which atomic carbon and C2are incorporated into the growing closed cages.
- Paul W. Dunk
- , Nathan K. Kaiser
- & Harold W. Kroto
-
Article |
 First enantioseparation and circular dichroism spectra of Au38 clusters protected by achiral ligands
First enantioseparation and circular dichroism spectra of Au38 clusters protected by achiral ligands
Clusters of gold atoms protected with achiral thiolates can display chirality, and such chiral nanoparticles could open new possibilities in catalysis and sensing. Here, the first separation of the enantiomers of a gold cluster, protected by achiral thiolates, Au38(SCH2CH2Ph)24, is achieved.
- Igor Dolamic
- , Stefan Knoppe
- & Thomas Bürgi
-
Article |
 Room temperature ferromagnetism in Teflon due to carbon dangling bonds
Room temperature ferromagnetism in Teflon due to carbon dangling bonds
Teflon is a carbon based polymer that cannot be intrinsically ferromagnetic. This study shows that room temperature ferromagnetism can be induced in Teflon tape by applying mechanical stress such as stretching or cutting, which gives rise to dangling carbon bonds.
- Y.W. Ma
- , Y.H. Lu
- & J. Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Pore surface engineering in covalent organic frameworks
Pore surface engineering in covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks form a porous skeleton with a precise pore size and geometry, but control of the pore surface is challenging. Here, a protocol is introduced for pore surface engineering of covalent organic frameworks, allowing the control of composition and density of organic groups in the pores.
- Atsushi Nagai
- , Zhaoqi Guo
- & Donglin Jiang
-
Article |
 Direct stereoselective α-arylation of unmodified enals using an organocatalytic cross-coupling-like reaction
Direct stereoselective α-arylation of unmodified enals using an organocatalytic cross-coupling-like reaction
Cross-coupling reactions are widely used for creating new carbon–carbon bonds in chemical syntheses. Using the cross-coupling concept, Wang and colleagues present an organocatalytic strategy for the direct and stereoselective α-arylation of enals that occurs under mild conditions.
- Xixi Song
- , Aiguo Song
- & Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical models of nonlinear effects in two-component cooperative supramolecular copolymerizations
Theoretical models of nonlinear effects in two-component cooperative supramolecular copolymerizations
In multi-component mixtures of self-assembling molecules, small differences in association energy between components can be amplified by nonlinear effects. This theoretical investigation of self-assembling systems rationalizes chiral amplification in cooperative supramolecular copolymerizations.
- Albert J. Markvoort
- , Huub M.M. ten Eikelder
- & E.W. Meijer
-
Article |
 Bottom-up synthesis of finite models of helical (n,m)-single-wall carbon nanotubes
Bottom-up synthesis of finite models of helical (n,m)-single-wall carbon nanotubes
Hoop-shaped aromatic hydrocarbons can be considered as finite models of single-wall carbon nanotubes. Hitosugiet al. describe the bottom-up synthesis of a macrocyclic tetramer of chrysene, and show that its persistent rotational isomers are finite models of chiral nanotubes.
- Shunpei Hitosugi
- , Waka Nakanishi
- & Hiroyuki Isobe
-
Article |
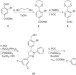 Selective fluorescent probes for live-cell monitoring of sulphide
Selective fluorescent probes for live-cell monitoring of sulphide
Molecular probes that can detect aqueous sulphides could help to elucidate their roles in biological signalling. Qianet al. develop two sulphide-selective fluorescent probes and demonstrate their ability to image free sulphide in living cells.
- Yong Qian
- , Jason Karpus
- & Chuan He
-
Article |
 Responsive nematic gels from the self-assembly of aqueous nanofibres
Responsive nematic gels from the self-assembly of aqueous nanofibres
Hydrogels have a variety of applications including tissue engineering and controlled drug delivery. Here, liquid-crystal hydrogels are developed which transform into a fluid solution upon cooling; cells can be encapsulated in the gel at room temperature, then released at physiological temperatures.
- Zhegang Huang
- , Hyojin Lee
- & Myongsoo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access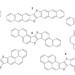 From computational discovery to experimental characterization of a high hole mobility organic crystal
From computational discovery to experimental characterization of a high hole mobility organic crystal
The development of new organic semiconductors with high mobility and air stability will facilitate their widespread application. In this Article,in silicoscreening of extended oligothiophenes leads to the synthesis of a high performance semiconductor.
- Anatoliy N. Sokolov
- , Sule Atahan-Evrenk
- & Alán Aspuru-Guzik
-
Article |
 Confined propagation of covalent chemical reactions on single-walled carbon nanotubes
Confined propagation of covalent chemical reactions on single-walled carbon nanotubes
Covalent reactions on carbon nanotube surfaces typically occur at random positions on the hexagonal lattice. Denget al. show that Billups–Birch reductive alkylation takes place at, and propagates from, sp3defect sites, leading to confinement of the reaction fronts in the tubular direction.
- Shunliu Deng
- , Yin Zhang
- & YuHuang Wang
-
Article |
 Burning vegetation produces cyanohydrins that liberate cyanide and stimulate seed germination
Burning vegetation produces cyanohydrins that liberate cyanide and stimulate seed germination
Cyanide, a known plant defence compound, can also stimulate seed germination. Flemattiet al. show that glyceronitrile is produced in wildfire smoke, which can release cyanide and stimulate seed germination of fire-responsive plant species, thus serving as an ecological store of cyanide.
- Gavin R. Flematti
- , David J. Merritt
- & Emilio L. Ghisalberti
-
Article |
 Mutual adaptation of a membrane protein and its lipid bilayer during conformational changes
Mutual adaptation of a membrane protein and its lipid bilayer during conformational changes
The detailed interactions of membrane proteins with their lipid environment are poorly understood. Sonntaget al. use low-resolution X-ray crystallographic data and molecular dynamics simulations to study the manner in which the sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+–ATPase adapts to different membrane environments.
- Yonathan Sonntag
- , Maria Musgaard
- & Lea Thøgersen
-
Article |
 Organocatalytic enantioselective β-functionalization of aldehydes by oxidation of enamines and their application in cascade reactions
Organocatalytic enantioselective β-functionalization of aldehydes by oxidation of enamines and their application in cascade reactions
The transformation of iminium ions to enamines has been used extensively in organocatalysis, but conversion of enamines to iminium species has not been exploited. In this study, oxidative enamine catalysis allows the conversion of enamines to iminium ions and the direct asymmetric β-functionalization of simple aldehydes.
- Shi-Lei Zhang
- , He-Xin Xie
- & Wei Wang
-
Article |
 Porous organic molecular solids by dynamic covalent scrambling
Porous organic molecular solids by dynamic covalent scrambling
The construction of porous solids from discrete organic molecules usually involves the formation of regular porous crystals. In this study, a covalent scrambling reaction gives molecules with a range of shapes that do not pack effectively — manipulation of the reagent ratio allows fine control of porosity.
- Shan Jiang
- , James T. A. Jones
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallographic observation of 'induced fit' in a cryptophane host–guest model system
Crystallographic observation of 'induced fit' in a cryptophane host–guest model system
Cryptophane-A is a prototypical organic host molecule that binds reversibly to neutral guest molecules. Taratulaet al.report X-ray structures of cryptophane-A complexed with a range of host molecules to show that the cryptophane host–guest system exhibits ‘induced fit’.
- Olena Taratula
- , P. Aru Hill
- & Ivan J. Dmochowski
-
Article |
 Effects of electronegative substitution on the optical and electronic properties of acenes and diazaacenes
Effects of electronegative substitution on the optical and electronic properties of acenes and diazaacenes
Large acene molecules are common components of organic electronics. Appletonet al.show that embedding pyrazine units in acenes results in unexpected red-shifted optical transitions upon electronegative substitution, which may aid the design of acene-type materials for organic electronics applications.
- Anthony Lucas Appleton
- , Scott M. Brombosz
- & Uwe H.F. Bunz
-
Review Article |
 Diversity-oriented synthesis as a tool for the discovery of novel biologically active small molecules
Diversity-oriented synthesis as a tool for the discovery of novel biologically active small molecules
Biologically active molecules can be identified through the screening of small-molecule libraries, but compound collections typically consist of large numbers of structurally similar compounds. Gallowayet al. review how diversity-oriented synthesis can efficiently generate structurally diverse compound libraries.
- Warren R.J.D. Galloway
- , Albert Isidro-Llobet
- & David R. Spring

 Solvent-free aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons and alcohols with Pd@N-doped carbon from glucose
Solvent-free aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons and alcohols with Pd@N-doped carbon from glucose