Featured
-
-
Article |
 Resonance shifts and spill-out effects in self-consistent hydrodynamic nanoplasmonics
Resonance shifts and spill-out effects in self-consistent hydrodynamic nanoplasmonics
Recent experiments with plasmonic nanostructures have found phenomena that cannot be explained classically, necessitating new theoretical models. Toscano et al. present a self-consistent hydrodynamic theory that describes both the nonlocal response and the electronic spill-out for noble and simple metals.
- Giuseppe Toscano
- , Jakob Straubel
- & Martijn Wubs
-
Article
| Open Access STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy enables sub-diffraction imaging with a wide range of fluorescent probes. Here, the authors show that a bright and very photostable class of fluorescent quantum dots can be super-resolved with STED as biolabels in cellular contexts.
- Janina Hanne
- , Henning J. Falk
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article |
 Theory of Floquet band formation and local pseudospin textures in pump-probe photoemission of graphene
Theory of Floquet band formation and local pseudospin textures in pump-probe photoemission of graphene
Condensed matter research has seen prominent recent advances in ultrafast optical manipulation and topological materials. Here, Sentef et al. simulate the development of the photoemission-measured band structure of Floquet states in graphene excited by low-frequency circularly-polarized laser pulses.
- M.A. Sentef
- , M. Claassen
- & T.P. Devereaux
-
Article |
 High-density waveguide superlattices with low crosstalk
High-density waveguide superlattices with low crosstalk
High-density integration will be vital for silicon photonics, but as we approach sub-wavelength distances between components, the crosstalk becomes intolerable. Here, Song et al. demonstrate waveguide integration at a half-wavelength pitch with low crosstalk using advanced superlattice design concepts.
- Weiwei Song
- , Robert Gatdula
- & Wei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Active graphene–silicon hybrid diode for terahertz waves
Active graphene–silicon hybrid diode for terahertz waves
Graphene has demonstrated the ability to modulate terahertz (THz) waves by optical or electrical excitation, but modulation depths have been low. Here, Li et al. demonstrate enhanced modulation and polarity-dependent THz attenuation using external voltage bias and photoexcitation on a graphene–silicon film.
- Quan Li
- , Zhen Tian
- & Weili Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of thickness and wrinkling of exfoliated two-dimensional zeolite nanosheets
Quantification of thickness and wrinkling of exfoliated two-dimensional zeolite nanosheets
Two-dimensional sheets of zeolites can function as molecular sieves for applications such as membranes or as catalysts. Here, the authors demonstrate a method using electron diffraction patterns to accurately measure the thickness and wrinkles of thin zeolite nanosheets.
- Prashant Kumar
- , Kumar Varoon Agrawal
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
Article
| Open Access Perovskite–fullerene hybrid materials suppress hysteresis in planar diodes
Perovskite–fullerene hybrid materials suppress hysteresis in planar diodes
Metal halide perovskites are promising for solar energy harvesting, but currently prone to a large hysteresis and current instability. Here, Xu et al. show improvements in a hybrid material in which the fullerene is distributed at perovskite grain boundaries and thus passivates defects effectively.
- Jixian Xu
- , Andrei Buin
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
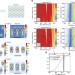 Subwavelength-thick lenses with high numerical apertures and large efficiency based on high-contrast transmitarrays
Subwavelength-thick lenses with high numerical apertures and large efficiency based on high-contrast transmitarrays
Replacing conventional components with flat optic devices such as flat lenses is desirable for imaging and on-chip integration, but performance has hindered their use. Here, Arbabi et al. report a wavelength-thin, high-contrast transmitarray micro-lens with a 0.57 λfocal spot and 82% focusing efficiency.
- Amir Arbabi
- , Yu Horie
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article |
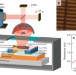 Electronic modulation of infrared radiation in graphene plasmonic resonators
Electronic modulation of infrared radiation in graphene plasmonic resonators
Graphene’s exotic properties make it suitable for many different optoelectronic devices. Brar et al. show that graphene plasmonic resonators can be exploited to produce narrow spectral emission in the mid-infrared, whose frequency and intensity can be modulated by electrostatic gating.
- Victor W. Brar
- , Michelle C. Sherrott
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and bright spontaneous emission of Er3+ ions in metallic nanocavity
Fast and bright spontaneous emission of Er3+ ions in metallic nanocavity
The Purcell effect predicts a spontaneous emission rate enhancement of several orders of magnitude, but experimental demonstrations have been much lower. Here, Song et al. show emission enhancement of Er3+ions in a metallic nanocavity with a 170 Purcell factor at room temperature and 55% extraction efficiency.
- Jung-Hwan Song
- , Jisu Kim
- & Yong-Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access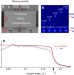 X-ray photonic microsystems for the manipulation of synchrotron light
X-ray photonic microsystems for the manipulation of synchrotron light
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) are essential in a wide range of photonics applications but have not been demonstrated for X-ray optics. Here, Mukhopadhyay et al.use single-crystal silicon to demonstrate a MEMS system that can preserve and manipulate the spatial, temporal and spectral correlations of the X-rays.
- D. Mukhopadhyay
- , D. A. Walko
- & G. K. Shenoy
-
Article
| Open Access High-power multi-megahertz source of waveform-stabilized few-cycle light
High-power multi-megahertz source of waveform-stabilized few-cycle light
Frequency combs have revolutionized the study of electronic structures and dynamics of matter but currently used lasers systems are limited in terms of achievable pulse energies. Here, Pronin et al.demonstrate few cycle pulse emission from a thin-disk laser with 150 nJ pulse energy and 7.7 fs pulse duration.
- O. Pronin
- , M. Seidel
- & F. Krausz
-
Article
| Open Access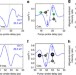 Observation of laser-induced electronic structure in oriented polyatomic molecules
Observation of laser-induced electronic structure in oriented polyatomic molecules
Although expected to have an influence, the effect of strong laser fields on molecules in high-harmonic generation in gases is rarely explored. Kraus et al.show that the laser modifies the electronic structure of large polyatomic molecules and present a new theoretical framework to model this.
- P. M. Kraus
- , O. I. Tolstikhin
- & H. J. Wörner
-
Article |
 Tuning the acoustic frequency of a gold nanodisk through its adhesion layer
Tuning the acoustic frequency of a gold nanodisk through its adhesion layer
The mechanical properties of metal nanostructures depend on nature of the adhesion layer attaching it to a substrate. Chang et al.find that the properties of phonons in gold nanodisks vary with adhesion layer thickness, and that this response can act as a probe of the metallic composition of the disk.
- Wei-Shun Chang
- , Fangfang Wen
- & Stephan Link
-
Article
| Open Access Witnessing magnetic twist with high-resolution observation from the 1.6-m New Solar Telescope
Witnessing magnetic twist with high-resolution observation from the 1.6-m New Solar Telescope
Understanding the behaviour of magnetic flux ropes in the Sun is crucial for explaining solar phenomena such as flares and space weather. Exploiting the high resolution available in the 1.6 m New Solar Telescope, Wang et al.capture the evolution of a flaring twisted flux rope in the low solar corona.
- Haimin Wang
- , Wenda Cao
- & Haisheng Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of charge transport on current–voltage characteristics and power-conversion efficiency of organic solar cells
Impact of charge transport on current–voltage characteristics and power-conversion efficiency of organic solar cells
Fitting current–voltage curves of organic solar cells with the Shockley equation often results in artificially high ideality factors. Here, the authors analyse inadequacy of the equation and propose an analytic model, which allows prediction of the efficiency potentials by explicit consideration of charge-carrier mobilities.
- Uli Würfel
- , Dieter Neher
- & Steve Albrecht
-
Article
| Open Access Optofluidic fabrication for 3D-shaped particles
Optofluidic fabrication for 3D-shaped particles
The current methods of fabricating three-dimensional particles include photolithography, layer-by-layer printing and several others. Here, Paulsen et al. demonstrate an optofluidic approach, whereby masked ultraviolet light is illuminated on photosensitive fluids whose cross-sections are shaped by fluid inertia.
- Kevin S. Paulsen
- , Dino Di Carlo
- & Aram J. Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Three-terminal heterojunction bipolar transistor solar cell for high-efficiency photovoltaic conversion
Three-terminal heterojunction bipolar transistor solar cell for high-efficiency photovoltaic conversion
Multiple junction solar cells offer the means to high-efficiency photovoltaics but suffer from complicated manufacturing and packing. Here Martí et al., propose a three-terminal heterojuntion bipolar transistor solar cell that simplifies the structure reducing the number of layers while maintaining the efficiency.
- A. Martí
- & A. Luque
-
Article
| Open Access Subdiffractional focusing and guiding of polaritonic rays in a natural hyperbolic material
Subdiffractional focusing and guiding of polaritonic rays in a natural hyperbolic material
Hexagonal boron nitride has many interesting properties, including a natural hyperbolic dispersion, making it attractive for nanophotonic applications. Here, Dai et al. show that metallic disks under the material launch phonon–polaritons, turning it into a hyper-focusing lens.
- S. Dai
- , Q. Ma
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article |
 The role of random nanostructures for the omnidirectional anti-reflection properties of the glasswing butterfly
The role of random nanostructures for the omnidirectional anti-reflection properties of the glasswing butterfly
The transparent wings of the glasswing butterfly have a low reflectance over the visible spectrum thanks to the nanopillars distributed across them. Siddique et al. show that this behaviour still works at high angles of incidence because of the random height distribution of the pillars.
- Radwanul Hasan Siddique
- , Guillaume Gomard
- & Hendrik Hölscher
-
Article
| Open Access Athermally photoreduced graphene oxides for three-dimensional holographic images
Athermally photoreduced graphene oxides for three-dimensional holographic images
Owing to its electronic and optical properties, graphene holds potential for flat display systems. Here, Li et al. write wide-angle, full-colour, three-dimensional holographic images using subwavelength, multilevel index modulation of athermally reduced graphene oxide by a single femtosecond pulse.
- Xiangping Li
- , Haoran Ren
- & Min Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Active control of all-fibre graphene devices with electrical gating
Active control of all-fibre graphene devices with electrical gating
Active control of light in optical fibres is of great interest, to this end, electric control of all-fibre graphene devices is desirable but highly challenging. Here, Lee et al. demonstrate electric control of the optical properties of a graphene sheet deposited on a side-polished fibre mediated by an ion liquid.
- Eun Jung Lee
- , Sun Young Choi
- & Dong-Il Yeom
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic evaluation of an atomic clock at 2 × 10−18 total uncertainty
Systematic evaluation of an atomic clock at 2 × 10−18 total uncertainty
Atomic clocks are increasingly important for many applications in scientific research and technology. Here, Nicholson et al. present a series of developments allowing them to achieve a new record in atomic clock performance, with a systematic uncertainty of just 2.1 × 10−18 for their 87Sr atomic clock.
- T.L. Nicholson
- , S.L. Campbell
- & J. Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Patterning two-dimensional chalcogenide crystals of Bi2Se3 and In2Se3 and efficient photodetectors
Patterning two-dimensional chalcogenide crystals of Bi2Se3 and In2Se3 and efficient photodetectors
Two-dimensional chalcogenides offer great potential in electronics, but accurate control of their growth is difficult. Here, the authors combine microintaglio printing and van der Waals epitaxy to pattern various large-area arrays of single-crystal chalcogenides with remarkable properties.
- Wenshan Zheng
- , Tian Xie
- & Hailin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Universal structure of transmission eigenchannels inside opaque media
Universal structure of transmission eigenchannels inside opaque media
The transmission of light through opaque media is a complex process, owing to the many scattering processes of light. Here, the authors develop a method to determine the transmission eigenchannels through an opaque medium as a solution of diffusion equations.
- Matthieu Davy
- , Zhou Shi
- & Azriel Z. Genack
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time tunable lasing from plasmonic nanocavity arrays
Real-time tunable lasing from plasmonic nanocavity arrays
Plasmonic lasers offer ultrasmall mode confinement via nanoscale structures, but their reliance on solid-state gain media makes tunability difficult. Yang et al, present a laser based on gold nanoparticle arrays in a microfluidic channel, whose liquid gain media enable dynamic tuning of the lasing wavelength.
- Ankun Yang
- , Thang B. Hoang
- & Teri W. Odom
-
Article
| Open Access Optical aperture synthesis with electronically connected telescopes
Optical aperture synthesis with electronically connected telescopes
In astronomy, interferometry between telescopes enables high-resolution imaging but optical links are limited by atmospheric turbulence. Here, the authors show how this can be circumvented, producing diffraction-limited images using an array of electronically connected optical telescopes.
- Dainis Dravins
- , Tiphaine Lagadec
- & Paul D. Nuñez
-
Article
| Open Access Cavity ring-up spectroscopy for ultrafast sensing with optical microresonators
Cavity ring-up spectroscopy for ultrafast sensing with optical microresonators
Whispering-gallery mode microresonators are powerful sensing tools, but spectrum acquisition has taken milliseconds or longer. Here, Rosenblum et al.introduce cavity ring-up spectroscopy, in which sharply rising detuned probe pulses capture spectra of microresonators on nanosecond timescales.
- Serge Rosenblum
- , Yulia Lovsky
- & Barak Dayan
-
Article
| Open Access All-photonic quantum repeaters
All-photonic quantum repeaters
Quantum repeaters are needed for long-distance quantum communication but it is thought that they require matter quantum memories. Azuma et al. introduce an all-photonic quantum repeater based on flying qubits that scales polynomially with the channel distance without the need for matter quantum memories.
- Koji Azuma
- , Kiyoshi Tamaki
- & Hoi-Kwong Lo
-
Article
| Open Access Probing long-range carrier-pair spin–spin interactions in a conjugated polymer by detuning of electrically detected spin beating
Probing long-range carrier-pair spin–spin interactions in a conjugated polymer by detuning of electrically detected spin beating
Interactions between weakly coupled pairs of electron spins are thought to play a role in biological magnetoreception and spin-dependent carrier dynamics in semiconductors. Here, the authors investigate such intrapair dipolar and exchange interactions in a polymer using electrically detected magnetic resonance experiments.
- Kipp J. van Schooten
- , Douglas L. Baird
- & Christoph Boehme
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-sensitive all-fibre photothermal spectroscopy with large dynamic range
Ultra-sensitive all-fibre photothermal spectroscopy with large dynamic range
Photothermal interferometry systems using free-space optics have limits in terms of light–matter interaction efficiency, size, optical alignment and integration. Here, Jin et al. use a gas-filled hollow-core photonic bandgap fibre to demonstrate an all-fibre gas sensor with ultrahigh sensitivity and dynamic range.
- Wei Jin
- , Yingchun Cao
- & Hoi Lut Ho
-
Article |
 Energy transfer pathways in semiconducting carbon nanotubes revealed using two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy
Energy transfer pathways in semiconducting carbon nanotubes revealed using two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy
Thin films of carbon nanotubes are been considered for energy harvesting and optoelectronic devices but their energy transfer pathways are largely unknown. Here, Mehlenbacher et al. use two-dimensional white-light spectroscopy to investigate the ultrafast energy redistribution in carbon nanotube films.
- Randy D. Mehlenbacher
- , Thomas J. McDonough
- & Martin T. Zanni
-
Article |
 Nanophotonic control of circular dipole emission
Nanophotonic control of circular dipole emission
Taking full advantage of photons as quantum information carriers requires faithful control of their lifetime, emission direction and orbital angular momentum. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate a technique for directionally coupling classical, circular dipoles to the modes of a photonic-crystal waveguide.
- B. le Feber
- , N. Rotenberg
- & L. Kuipers
-
Article
| Open Access Encoding and decoding spatio-temporal information for super-resolution microscopy
Encoding and decoding spatio-temporal information for super-resolution microscopy
Increasing the resolution of fluorescence microscopy is a fundamental need for modern cell biology. Lanzanò et al.demonstrate that arbitrary spatial resolution is, in principle, possible by encoding the fluorophore's spatial distribution information in the temporal dynamics of the fluorophore's transition.
- Luca Lanzanò
- , Iván Coto Hernández
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
Article
| Open Access Positioning and joining of organic single-crystalline wires
Positioning and joining of organic single-crystalline wires
Aligned, one-dimensional, single-crystal materials may allow on-demand photon/electron transfer. Here, the authors use a physical vapour transport technique to grow organic single-crystal wires with the guidance of pillar-structured substrates, and perform proof of concept waveguide experiments.
- Yuchen Wu
- , Jiangang Feng
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast helicity control of surface currents in topological insulators with near-unity fidelity
Ultrafast helicity control of surface currents in topological insulators with near-unity fidelity
Bulk contributions to transport measurements often inhibit the study of the surface states of topological insulators. Here, Kastl et al. demonstrate high-fidelity helicity-dependent photocurrents in the surface states of Bi2Se3, controlled via circularly polarized light with a picosecond time-resolution.
- Christoph Kastl
- , Christoph Karnetzky
- & Alexander W. Holleitner
-
Article |
 Experimental proof of nonlocal wavefunction collapse for a single particle using homodyne measurements
Experimental proof of nonlocal wavefunction collapse for a single particle using homodyne measurements
Quantum mechanics exhibit many unusual features, including Einstein’s so-called ‘spooky action at a distance’, wherein a wavefunction collapses at all points except where it is detected. Using homodyne measurements, Fuwa et al. verify this effect for a single photon split between two labs.
- Maria Fuwa
- , Shuntaro Takeda
- & Akira Furusawa
-
Article
| Open Access Ultimate thin vertical p–n junction composed of two-dimensional layered molybdenum disulfide
Ultimate thin vertical p–n junction composed of two-dimensional layered molybdenum disulfide
Molybdenum disulfide is a two-dimensional semiconducting material that has properties that make it useful for compact electronic devices. Here, the authors use molybdenum disulfide in an ultra-thin p–n junction that demonstrate ambipolar carrier transport and current rectification.
- Hua-Min Li
- , Daeyeong Lee
- & Won Jong Yoo
-
Article |
 Efficient hole-blocking layer-free planar halide perovskite thin-film solar cells
Efficient hole-blocking layer-free planar halide perovskite thin-film solar cells
Lead halide perovskite solar cells use hole-blocking layers to allow a separate collection of positive and negative charge carriers and to achieve high-operation voltages. Here, the authors demonstrate efficient lead halide perovskite solar cells that avoid using this extra layer.
- Weijun Ke
- , Guojia Fang
- & Yanfa Yan
-
Article |
 Graphene-enabled electrically switchable radar-absorbing surfaces
Graphene-enabled electrically switchable radar-absorbing surfaces
Controlling the electrical properties of radar absorbing materials is required for active camouflage systems in the microwave. Here, Balci et al.use large-area graphene electrodes to demonstrate electrical control of microwave reflection, transmission and absorption by electrostatic tuning of the charge density.
- Osman Balci
- , Emre O. Polat
- & Coskun Kocabas
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal isolation of attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window
Spatiotemporal isolation of attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window
Time-resolved probing of electronic dynamics such as exciton formation and annihilation requires attosecond pulses at photon energies covering the absorption edges of materials. Here, Silva et al. experimentally demonstrate spatio-temporal isolation of single-attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window.
- Francisco Silva
- , Stephan M. Teichmann
- & Jens Biegert
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale probing of image-dipole interactions in a metallic nanostructure
Nanoscale probing of image-dipole interactions in a metallic nanostructure
An emitter near a surface induces an image dipole that alters the emission pattern and creates errors in single-particle imaging applications. Here, Ropp et al.show that an image dipole can distort the polarization and measured position of an emitter, and that these distortions can be corrected.
- Chad Ropp
- , Zachary Cummins
- & Edo Waks
-
Article |
 Dynamically self-assembled silver nanoparticles as a thermally tunable metamaterial
Dynamically self-assembled silver nanoparticles as a thermally tunable metamaterial
Tunable metamaterials bring the promise of on-demand tailored optical properties, offering numerous device functionalities. Towards this aim, this study presents a tunable metamaterial based on dynamic self-assembly of nanoparticles coated with organic ligands, which also shows epsilon-near-zero behaviour.
- Wiktor Lewandowski
- , Martin Fruhnert
- & Ewa Górecka
-
Article |
 Spin-dependent charge transfer state design rules in organic photovoltaics
Spin-dependent charge transfer state design rules in organic photovoltaics
An important source of loss in solar cells is the recombination of the photogenerated charge carriers before they are extracted from the device. Chang et al. now show that such recombination can be reduced in organic solar cells by increasing the separation between donors and acceptors.
- Wendi Chang
- , Daniel N. Congreve
- & Marc A. Baldo
-
Article |
 Surface transfer doping induced effective modulation on ambipolar characteristics of few-layer black phosphorus
Surface transfer doping induced effective modulation on ambipolar characteristics of few-layer black phosphorus
Black phosphorus is a graphene-like material that can be harnessed for two-dimensional electronic devices. Here, Xiang et al. demonstrate that adding caesium carbonate or molybdenum trioxide can significantly enhance the electron or hole conduction, respectively, of this promising material.
- Du Xiang
- , Cheng Han
- & Wei Chen
-
Article |
 Red blood cell as an adaptive optofluidic microlens
Red blood cell as an adaptive optofluidic microlens
The shape of red blood cells is highly sensitive to surrounding liquid environment. Here, Miccio et al. make red blood cells into optofluidic lenses with fully controllable focal length at the microscale, which can be used for imaging and optical magnification in addition to blood diseases detection.
- L. Miccio
- , P. Memmolo
- & P. Ferraro
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic crystals cause active colour change in chameleons
Photonic crystals cause active colour change in chameleons
Colour change in many vertebrates originates from pigment dispersion or aggregation. Here, Teyssier et al. show that chameleons rapidly shift colour through a physical mechanism involving a lattice of nanocrystals in dermal iridophores, a second and deeper iridophore layer strongly reflects near-infrared light.
- Jérémie Teyssier
- , Suzanne V. Saenko
- & Michel C. Milinkovitch
-
Article
| Open Access Partially coherent ultrafast spectrography
Partially coherent ultrafast spectrography
Ultrafast metrology typically relies on pulse coherence, but full coherence is not always possible in emerging attosecond and ultrashort X-ray technologies. Here, Bourassin-Bouchet and Couprie adapt frequency-resolved optical gating (FROG) to measure partially coherent optical pulses in the attosecond scale.
- C. Bourassin-Bouchet
- & M.-E. Couprie
-
Article
| Open Access High-intensity double-pulse X-ray free-electron laser
High-intensity double-pulse X-ray free-electron laser
Two-colour X-ray pulses from free-electron lasers can be used to probe ultrafast dynamics, but the total power is a fraction of the saturation power. Here, Marinelli et al. use twin electron bunches to reach full saturation power and increase the two-colour intensity by an order of magnitude at hard-X-ray energies.
- A. Marinelli
- , D. Ratner
- & Z. Huang

 High-performance ternary blend polymer solar cells involving both energy transfer and hole relay processes
High-performance ternary blend polymer solar cells involving both energy transfer and hole relay processes