Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation of perovskite degradation with multiple-barrier for light-heat stable perovskite solar cells
Modulation of perovskite degradation with multiple-barrier for light-heat stable perovskite solar cells
The long-term stability of perovskite solar cells remains a critical challenge for the commercialization of the technology. Here, the authors adopt a non-noble metal/metal oxide/polymer multiple-barrier to suppress device degradation, achieving long-term stability in encapsulated p-i-n devices.
- Jing Zhou
- , Zonghao Liu
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Twisted moiré photonic crystal enabled optical vortex generation through bound states in the continuum
Twisted moiré photonic crystal enabled optical vortex generation through bound states in the continuum
The Authors in this work predict the radiation of twisted bilayer photonic crystals to host an optical vortex in the far field, which is enabled by connecting BIC modes in photonic crystals with the free space through a ‘moiré channel’.
- Tiancheng Zhang
- , Kaichen Dong
- & Jie Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Multimaterial fiber as a physical simulator of a capillary instability
Multimaterial fiber as a physical simulator of a capillary instability
Capillary breakup in multimaterial fibers is explored for the self-assembly of optoelectronic systems. However, its insights primarily stem from numerical simulations, qualitative at best. The authors formulate an analytical model of such breakup, obtaining a window in the governing parameters where the generally chaotic breakup becomes predictable and thus engineerable.
- Camila Faccini de Lima
- , Fan Wang
- & Alexander Gumennik
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
In this work, the authors demonstrate a ‘jointly modulated’ amplifying programmable metasurface (APM) for simultaneous wireless information and power transmission (SWIPT). Their technique outperforms existing methods, significantly improving power transmission and adaptability for conveying energy and data across various domains, including wireless implants, 6 G networks, and IoT systems.
- Xin Wang
- , Jia Qi Han
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access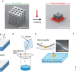 Pick and place process for uniform shrinking of 3D printed micro- and nano-architected materials
Pick and place process for uniform shrinking of 3D printed micro- and nano-architected materials
Three-dimensional structures with micro-/nanoscale features can be produced by two-photon polymerization lithography but suffering from a non-uniform shrinkage. Here, the authors report a poly(vinyl alcohol)-assisted pick-and-place process to uniformly heat shrink three-dimensional micro-/nano-architected materials printed by two-photon polymerization lithography.
- Tomohiro Mori
- , Hao Wang
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Proof of crystal-field-perturbation-enhanced luminescence of lanthanide-doped nanocrystals through interstitial H+ doping
Proof of crystal-field-perturbation-enhanced luminescence of lanthanide-doped nanocrystals through interstitial H+ doping
Lanthanide-doped inorganic nanocrystals are promising for optical imaging and biomedical applications. Here authors show that interstitial H+ doping-induced crystal-field perturbation enhances the photoluminescence intensity of lanthanide-doped inorganic nanocrystals.
- Guowei Li
- , Shihui Jiang
- & Maochun Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Efficiently accelerated free electrons by metallic laser accelerator
Efficiently accelerated free electrons by metallic laser accelerator
Accelerated electron beams are potentially useful for imaging and different type of light sources. Here the authors demonstrate electron acceleration using metallic laser acceleration with efficiency comparable to that of dielectric laser accelerators.
- Dingguo Zheng
- , Siyuan Huang
- & Jianqi Li
-
Article
| Open Access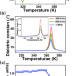 A molecular pyroelectric enabling broadband photo-pyroelectric effect towards self-driven wide spectral photodetection
A molecular pyroelectric enabling broadband photo-pyroelectric effect towards self-driven wide spectral photodetection
Broadband spectral photoresponse has potential for optoelectronic devices, but obtaining high photoactivity beyond the material bandgap is challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a molecular pyroelectric material with broadband photopyroelectric effects.
- Xi Zeng
- , Yi Liu
- & Zhihua Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Dissipative optomechanics in high-frequency nanomechanical resonators
Dissipative optomechanics in high-frequency nanomechanical resonators
Dissipative optomechanics, once limited to low frequencies, now operates in a sideband-resolved regime, reshaping optical and mechanical spectra and paving the way for the individual addressing of different mechanical modes in a single device.
- André G. Primo
- , Pedro V. Pinho
- & Thiago P. Mayer Alegre
-
Article
| Open Access Microcavity phonoritons – a coherent optical-to-microwave interface
Microcavity phonoritons – a coherent optical-to-microwave interface
Photonic, electronic and lattice resonances in patterned semiconductor microcavities are tailored to demonstrate coherent bidirectional microwave-to-optical conversion via phonon-exciton-photon quasi-particles in the strong-coupling regime.
- Alexander Sergeevich Kuznetsov
- , Klaus Biermann
- & Paulo Ventura Santos
-
Article
| Open Access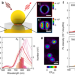 Photoluminescence upconversion in monolayer WSe2 activated by plasmonic cavities through resonant excitation of dark excitons
Photoluminescence upconversion in monolayer WSe2 activated by plasmonic cavities through resonant excitation of dark excitons
Here, the authors perform statistical measurements on hundreds of plasmonic nano-cavities embedding WSe2 monolayers, and show the activation of anti-Stokes photoluminescence in WSe2 through resonant excitation of a dark exciton at room temperature.
- Niclas S. Mueller
- , Rakesh Arul
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access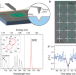 Photoluminescence imaging of single photon emitters within nanoscale strain profiles in monolayer WSe2
Photoluminescence imaging of single photon emitters within nanoscale strain profiles in monolayer WSe2
Here, the authors correlate the position and spectral emission properties of single photon emitters in monolayer WSe2 with the surrounding local strain potential by combining deep-subwavelength photoluminescence imaging and atomic force microscopy, providing insights on the microscopic mechanisms behind the formation of the quantum emitters.
- Artem N. Abramov
- , Igor Y. Chestnov
- & Vasily Kravtsov
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant perovskite solar cells with extended band edge
Resonant perovskite solar cells with extended band edge
Further extending the band edge of perovskite approaching the ideal bandgap of single-junction solar cell is essential to improve device efficiency. Here, the authors integrate optical resonances with perovskite solar cells to extend the band edge, achieving EQE-integrated current of 26.0 mA/cm2.
- Jiangang Feng
- , Xi Wang
- & Yi Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Linear-to-circular polarization conversion with full-silica meta-optics to reduce nonlinear effects in high-energy lasers
Linear-to-circular polarization conversion with full-silica meta-optics to reduce nonlinear effects in high-energy lasers
Nonlinear effects and damage of optical components are unavoidable when laser intensity is very high. Here the authors demonstrate metamaterial-based wave plate for linear to circular polarization conversion of a high-energy (high-power) laser to significantly weaken these effects.
- Nicolas Bonod
- , Pierre Brianceau
- & Jérôme Neauport
-
Article
| Open Access Charged biexciton polaritons sustaining strong nonlinearity in 2D semiconductor-based nanocavities
Charged biexciton polaritons sustaining strong nonlinearity in 2D semiconductor-based nanocavities
Here, the authors perform a spectroscopic study of monolayer WS2 coupled to a silver nanocavity and show the emergence of resonances in reflectance contrast measurements, which they attribute to exciton- (X), trion- (T) and charged biexciton- (XX-) polaritons, sustaining strong nonlinearity.
- Ke Wei
- , Qirui Liu
- & Tian Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing tight-binding Hamiltonians using site-controlled coupled cavity arrays
Realizing tight-binding Hamiltonians using site-controlled coupled cavity arrays
The authors demonstrate a programmable and mappable silicon photonic coupled cavity array capable of implementing a wide range of tight-binding Hamiltonians. This work is useful for realizing integrated photonic analog quantum simulators.
- Abhi Saxena
- , Arnab Manna
- & Arka Majumdar
-
Article
| Open Access A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves
A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves
The authors show a universal metasurface antenna capable of simultaneously and independently controlling all five fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves, including amplitude, phase, frequency, polarization, and momentum.
- Geng-Bo Wu
- , Jun Yan Dai
- & Chi Hou Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers
Hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers
Traditional optical tweezers require high laser powers risking photothermal damage of the trapped objects. Here, the authors present hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers (HOTTs), which use environmental cooling to simultaneously enhance thermophoretic trapping force at low laser powers and suppress the thermal damage to trapped objects.
- Pavana Siddhartha Kollipara
- , Xiuying Li
- & Yuebing Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered NIR-II fluorophores with ultralong-distance molecular packing for high-contrast deep lesion identification
Engineered NIR-II fluorophores with ultralong-distance molecular packing for high-contrast deep lesion identification
To achieve high-contrast in fluorescence imaging of deep tissues is challenging. Here, the authors develop NIR-II fluorescent small molecules with high brightness and emission extending to 1900 nm, enabling in vivo imaging of deep tissues with enhanced signal-to-background ratios.
- Zhe Feng
- , Yuanyuan Li
- & Jun Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Correlating metasurface spectra with a generation-elimination framework
Correlating metasurface spectra with a generation-elimination framework
The authors present a generation-elimination framework that correlates the spectra from different frequency bands, where the inaccessible spectra are precisely forecasted without consulting structural information. The spectral correlation will accelerate the unification of all metasurface designs and facilitate versatile applications involving cross-wavelength information correlation.
- Jieting Chen
- , Chao Qian
- & Hongsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable trapping of single nanosized extracellular vesicles using plasmonics
Scalable trapping of single nanosized extracellular vesicles using plasmonics
Manipulation of nano-sized extracellular vesicles are of significant interest for disease detection, monitoring, and therapeutics, yet it is still challenging to expedite the process. Here, the authors presented geometry-induced electrohydrodynamic tweezers, which enable fast parallel transport and trapping of single vesicle within seconds.
- Chuchuan Hong
- & Justus C. Ndukaife
-
Article
| Open Access Over-coupled resonator for broadband surface enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA)
Over-coupled resonator for broadband surface enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA)
Nanoresonator is proven to be an excellent platform for molecular detection, yet a set of them is necessary to identify a molecule fingerprint. Here, the authors utilise low quality resonators with large radiative losses, despite its lower quality factor, to identify molecular absorption spectrum between 5 and 10 μm.
- Laura Paggi
- , Alice Fabas
- & Patrick Bouchon
-
Article
| Open Access Superscattering emerging from the physics of bound states in the continuum
Superscattering emerging from the physics of bound states in the continuum
The scattering of light by small particles plays a central role in a myriad of fields. Here, the authors demonstrate a super dipole resonance that arises when two resonant modes of a small particle interfere, overcoming a widely accepted limitation to the cross section.
- Adrià Canós Valero
- , Hadi K. Shamkhi
- & Alexander S. Shalin
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh-efficient material informatics inverse design of thermal metamaterials for visible-infrared-compatible camouflage
Ultrahigh-efficient material informatics inverse design of thermal metamaterials for visible-infrared-compatible camouflage
The progress development of multispectral camouflage technologies has been limited to the choice of materials and structural design. Here, authors propose a material-informatics-based inverse design framework to efficiently design multilayer metamaterials with satisfying visible-infrared camouflage performance.
- Wang Xi
- , Yun-Jo Lee
- & Run Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Adiabatic topological photonic interfaces
Adiabatic topological photonic interfaces
Smooth topological photonic interfaces lead to less localized boundary modes which improves their guiding characteristics in both spin- and valley Hall metasurfaces. The modes become insensitive to the lattice details, showcasing improved bandgap crossing and longer propagation distances.
- Anton Vakulenko
- , Svetlana Kiriushechkina
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Article
| Open Access Incandescent temporal metamaterials
Incandescent temporal metamaterials
Here the authors employ quantum electrodynamics to formulate thermal emission effects in time-modulated media, resulting in innovative thermal emitters. They show that time modulation induces strong field fluctuations in epsilon-near-zero bodies, enabling narrowband emission across the entire range of wavevectors, from near to far-field regimes.
- J. Enrique Vázquez-Lozano
- & Iñigo Liberal
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-layer optical encryption fluorescent polymer waveguide chip based on optical pulse-code modulation technique
Dual-layer optical encryption fluorescent polymer waveguide chip based on optical pulse-code modulation technique
Data security of internet is increasingly more demanding in the current era, yet the traditional electronic approach is limited in speed and efficiency. Here, the authors proposed a dual-layer optical encryption fluorescent polymer waveguide chip based on optical pulse-code modulation to mitigate the limitations.
- Chunxue Wang
- , Daming Zhang
- & Teng Fei
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces
Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces
The authors present a high quality factor metasurface that enables sensitive and highly-parallelized detection of biomolecules. Amplification-free detection of gene fragments down to femtomolar levels is demonstrated within 5 minutes, for rapid nucleic acid analysis.
- Jack Hu
- , Fareeha Safir
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid topological photonic crystals
Hybrid topological photonic crystals
Owing to the nonequilibrium nature, photonic topological phenomena can involve multiple band gaps. Here the authors report on the discovery of a class of hybrid topological photonic crystals that host quantum anomalous Hall and valley Hall phases simultaneously.
- Yanan Wang
- , Hai-Xiao Wang
- & Guang-Yu Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Short-wave infrared cavity resonances in a single GeSn nanowire
Short-wave infrared cavity resonances in a single GeSn nanowire
Group-IV nanowires hold great promise for building ideal light sources for photonic integrated circuits. This study presents an observation of cavity resonances in a single GeSn nanowire, laying the foundation for realizing group-IV nanowire lasers.
- Youngmin Kim
- , Simone Assali
- & Oussama Moutanabbir
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic spin-orbit coupling in asynchronous optically driven micro-rotors
Hydrodynamic spin-orbit coupling in asynchronous optically driven micro-rotors
Hydrodynamically coupled rotors can be used to describe interactions ranging from molecular machines to atmospheric dynamics. Modin et al. show that optically-driven rotors in a non-tweezing beam can freely diffuse while spinning asynchronously and develop an analytical hydrodynamic model to explain.
- Alvin Modin
- , Matan Yah Ben Zion
- & Paul M. Chaikin
-
Article
| Open Access Fano resonant optical coatings platform for full gamut and high purity structural colors
Fano resonant optical coatings platform for full gamut and high purity structural colors
Fano resonant optical coatings (FROCs) present an ideal platform for structural coloring from thin-film metamaterials. This platform provides full-color gamut coverage at greater than 61% of the CIE gamut, with exceptionally high purity (up to 99%) and high brightness. FROCs exhibit tunable iridescence, cost-effective and scalable manufacturing, and significant advantages over existing structural coloring schemes.
- Mohamed ElKabbash
- , Nathaniel Hoffman
- & Chunlei Guo
-
Article
| Open Access An electroluminescent and tunable cavity-enhanced carbon-nanotube-emitter in the telecom band
An electroluminescent and tunable cavity-enhanced carbon-nanotube-emitter in the telecom band
Here, the authors report the scalable integration of electroluminescent semiconducting carbon nanotubes between nanographene electrical contacts in photonic crystal cavities, showing high coupling efficiency and dynamic electrical control of the enhanced electroluminescent light emission intensity in the telecom range.
- Anna P. Ovvyan
- , Min-Ken Li
- & Wolfram H. P. Pernice
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic control of hybrid grafted perfect vector vortex beams
Dynamic control of hybrid grafted perfect vector vortex beams
A metasurface is used to generate a hybrid grafted perfect vector vortex beam, which can be dynamically controlled with a half waveplate. The beam has spatially variant rates of polarization change due to the involvement of more topological charges.
- Hammad Ahmed
- , Muhammad Afnan Ansari
- & Xianzhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving near-perfect light absorption in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides through band nesting
Achieving near-perfect light absorption in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides through band nesting
The authors demonstrate near-perfect light absorption using only two atomic layers of transition metal dichalcogenides. This is achieved by reducing interlayer interaction which optimizes band nesting, and does not require the use of complex metasurfaces.
- Seungjun Lee
- , Dongjea Seo
- & Tony Low
-
Article
| Open Access Interspecies exciton interactions lead to enhanced nonlinearity of dipolar excitons and polaritons in MoS2 homobilayers
Interspecies exciton interactions lead to enhanced nonlinearity of dipolar excitons and polaritons in MoS2 homobilayers
In semiconductors, accessing nonlinear interactions between excitons strongly coupled to light will be key for quantum technologies. Here, in atomic bilayers of MoS2, new types of excitons are discovered showing strong inter-excitonic interactions.
- Charalambos Louca
- , Armando Genco
- & Alexander I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction-driven transport of dark excitons in 2D semiconductors with phonon-mediated optical readout
Interaction-driven transport of dark excitons in 2D semiconductors with phonon-mediated optical readout
Here, the authors demonstrate that dark excitons in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides can diffuse over several micrometers, and prove that this repulsion-driven propagation is robust across non-uniform samples.
- Saroj B. Chand
- , John M. Woods
- & Gabriele Grosso
-
Article
| Open Access All-organic polymeric materials with high refractive index and excellent transparency
All-organic polymeric materials with high refractive index and excellent transparency
The easy preparation of high efractive index transparent polymers is highly desirable owing to their interesting optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors apply an organobase catalyzed polymerization of bromoalkynes and dithiophenols to produce sulfur-containing all organic high refractive index polymers with excellent optical transparency.
- Jie Zhang
- , Tianwen Bai
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access A heterogeneously integrated lithium niobate-on-silicon nitride photonic platform
A heterogeneously integrated lithium niobate-on-silicon nitride photonic platform
Lithium niobate plays an important role in integrated photonics, but its widespread application requires a reliable solution. Here, the authors present a wafer-scale approach to LNOI integration via wafer bonding to silicon nitride PICs.
- Mikhail Churaev
- , Rui Ning Wang
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Collective excitations of a bound-in-the-continuum condensate
Collective excitations of a bound-in-the-continuum condensate
Bound-states-in-the-continuum (BICs) display unique features like symmetry protection from dissipation, long lifetimes and topological charges. Here the authors demonstrate anisotropic Bogoliubov excitation spectrum of polariton condensate from a BIC using a patterned semiconductor GaAs/AlGaAs waveguide.
- Anna Grudinina
- , Maria Efthymiou-Tsironi
- & Nina Voronova
-
Article
| Open Access Non-volatile electrically programmable integrated photonics with a 5-bit operation
Non-volatile electrically programmable integrated photonics with a 5-bit operation
Phase change materials (PCMs) are promising for low-power programmable photonic circuits. Here, authors show electrically controlled wide-bandgap PCM antimony sulfide achieving low loss, high cyclability and up to 32 levels, and post-fabrication trimming is also demonstrated.
- Rui Chen
- , Zhuoran Fang
- & Arka Majumdar
-
Article
| Open Access Long-wave infrared photothermoelectric detectors with ultrahigh polarization sensitivity
Long-wave infrared photothermoelectric detectors with ultrahigh polarization sensitivity
Infrared polarization-sensitive photodetectors are attractive owing to their widespread applications. Here, the authors report a long-wave infrared photodetector with an ultrahigh polarization sensitivity by leveraging the 1D geometry of Tellurium nanoribbon and the finite-size effect of a perfect plasmonic absorber.
- Mingjin Dai
- , Chongwu Wang
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access All-silicon quantum light source by embedding an atomic emissive center in a nanophotonic cavity
All-silicon quantum light source by embedding an atomic emissive center in a nanophotonic cavity
The use of silicon for integrated quantum photonic technologies is currently hindered by the lack of suitable on-demand quantum light sources. Here, the authors fill this gap by demonstrating the creation of single atomic emissive centers in silicon and their efficient coupling with nanophotonic cavities.
- W. Redjem
- , Y. Zhiyenbayev
- & B. Kanté
-
Article
| Open Access Eye accommodation-inspired neuro-metasurface focusing
Eye accommodation-inspired neuro-metasurface focusing
Here the authors propose for the first time the concept of supervised-evolving learning (SEL) and a corresponding SEL-driven adaptive focusing (SELAF) system. This metasurface can adaptively realize focusing at any specified position for waves incident from any direction. This work demonstrates unprecedented potential for tasks involving real-time, fast and complex electromagnetic wave manipulation.
- Huan Lu
- , Jiwei Zhao
- & Hongsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Giant optomechanical spring effect in plasmonic nano- and picocavities probed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Giant optomechanical spring effect in plasmonic nano- and picocavities probed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Extreme confinement of light in plasmonic nanocavities strongly enhances the optomechanical coupling of light with molecular vibrations. Here, the authors use a giant optical spring effect to reversibly weaken molecular bonds.
- Lukas A. Jakob
- , William M. Deacon
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access Point singularity array with metasurfaces
Point singularity array with metasurfaces
Optical singularities are typically 1D structures like vortices. This study used metasurfaces to position ten identical point singularities with tight confinement. This could miniaturize optical systems for super-resolution microscopy and dark traps.
- Soon Wei Daniel Lim
- , Joon-Suh Park
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Topological quadratic-node semimetal in a photonic microring lattice
Topological quadratic-node semimetal in a photonic microring lattice
Topological semimetals can host coexisting higher-order topological nodes that may enable unique physical properties. Here, based on these topological principles, authors design and experimentally realise simultaneous massive and massless chiral quasiparticles in a photonic microring lattice.
- Zihe Gao
- , Haoqi Zhao
- & Liang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid achromatic microlenses with high numerical apertures and focusing efficiencies across the visible
Hybrid achromatic microlenses with high numerical apertures and focusing efficiencies across the visible
Creating compact, lightweight and powerful optics that work well under visible light has been challenging. Here, the authors 3D print optically transparent polymers inside nanoporous glass in order to densely integrate refractive and diffractive elements, forming thin, high-performance hybrid achromatic imaging micro-optics.
- Corey A. Richards
- , Christian R. Ocier
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling chirality transfer mechanism by structural isomer-derived hydrogen bonding interaction in 2D chiral perovskite
Unraveling chirality transfer mechanism by structural isomer-derived hydrogen bonding interaction in 2D chiral perovskite
Chiral Ruddlesden-Popper perovskites are of interest as they exhibit circular dichroism in the visible light region. Here authors demonstrate the effect of asymmetric hydrogen bonding on the spin-polarization-based phenomena in chiral 2D perovskites by using structural isomer organic spacers.
- Jaehyun Son
- , Sunihl Ma
- & Jooho Moon

 Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling