Featured
-
-
Review Article
| Open Access Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential
Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential
Natural products are an important source of bioactive compounds and have versatile applications in different fields, but their discovery is challenging. Here, the authors review the recent developments in genome mining for discovery of natural products, focusing on compounds from unconventional microorganisms and microbiomes.
- Kirstin Scherlach
- & Christian Hertweck
-
Article
| Open Access Site selective C–H functionalization of Mitragyna alkaloids reveals a molecular switch for tuning opioid receptor signaling efficacy
Site selective C–H functionalization of Mitragyna alkaloids reveals a molecular switch for tuning opioid receptor signaling efficacy
Mitragynine (MG) is an indole alkaloid from kratom plant that binds opioid receptors and as such presents a scaffold for the development of atypical opioid receptor modulators. Here, the authors report a synthetic method for selective functionalization of the C11 position of MG, and show that this position is essential for fine-tuning opioid receptor signaling efficacy.
- Srijita Bhowmik
- , Juraj Galeta
- & Dalibor Sames
-
Article
| Open Access MolDiscovery: learning mass spectrometry fragmentation of small molecules
MolDiscovery: learning mass spectrometry fragmentation of small molecules
A large number of mass spectra from different samples have been collected, and to identify small molecules from these spectra, database searches are needed, which is challenging. Here, the authors report molDiscovery, a mass spectral database search method that uses an algorithm to generate mass spectrometry fragmentations and learns a probabilistic model to match small molecules with their mass spectra.
- Liu Cao
- , Mustafa Guler
- & Hosein Mohimani
-
Article
| Open Access Flavin-dependent halogenases catalyze enantioselective olefin halocyclization
Flavin-dependent halogenases catalyze enantioselective olefin halocyclization
Catalytic enantioselective halocyclization of alkenes is an important bond forming tool and a key step in natural product biosynthesis, but so far no examples of the enzymatic counterpart of this reaction on simple achiral olefins have been reported. Here, the authors describe examples of engineered flavin-dependent halogenases that catalyze halolactonization of olefins with high enantioselectivity and near-native catalytic activity.
- Dibyendu Mondal
- , Brian F. Fisher
- & Jared C. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery
Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery
Current genome mining methods predict many putative non-ribosomal peptides (NRPs) from their corresponding biosynthetic gene clusters, but it remains unclear which of those exist in nature and how to identify their post-assembly modifications. Here, the authors develop NRPminer, a modification-tolerant tool for the discovery of NRPs from large genomic and mass spectrometry datasets, and use it to find 180 NRPs from different environments.
- Bahar Behsaz
- , Edna Bode
- & Hosein Mohimani
-
Article
| Open Access Caerulomycin and collismycin antibiotics share a trans-acting flavoprotein-dependent assembly line for 2,2’-bipyridine formation
Caerulomycin and collismycin antibiotics share a trans-acting flavoprotein-dependent assembly line for 2,2’-bipyridine formation
Caerulomycins and collismycins are two types of 2,2’-bipyridine natural products that are biosynthesized via a hybrid NRPS-PKS pathway, but the details of their biosynthesis were unknown. Here, the authors elucidate their biosynthetic pathways, validate the generality of 2,2’-bipyridine formation, and clarify the process for 2,2’-bipyridine furcation.
- Bo Pang
- , Rijing Liao
- & Wen Liu
-
Article
| Open Access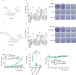 Naturally-occurring spinosyn A and its derivatives function as argininosuccinate synthase activator and tumor inhibitor
Naturally-occurring spinosyn A and its derivatives function as argininosuccinate synthase activator and tumor inhibitor
Arginine addiction induced by argininosuccinate synthase (ASSN1) deficiency has been exploited to treat ASS1-deficient cancers. Here, the authors show an alternative therapeutic approach where ASS1 activity is increased by the pesticide spinosyn A and is shown to inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation.
- Zizheng Zou
- , Xiyuan Hu
- & Zhiyong Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Computationally-guided exchange of substrate selectivity motifs in a modular polyketide synthase acyltransferase
Computationally-guided exchange of substrate selectivity motifs in a modular polyketide synthase acyltransferase
Engineering efforts have focused on acyltransferase (AT) domains of modular polyketide synthases (PKSs) to site-selectively modify the resulting polyketides, but critical AT residues involved in substrate selection have not been fully elucidated. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics to pinpoint mutations that impact AT domain selectivity and exchange structural motifs to obtain chimeric PKS modules with expanded substrate specificity.
- Edward Kalkreuter
- , Kyle S. Bingham
- & Gavin J. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access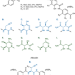 In vivo and in vitro reconstitution of unique key steps in cystobactamid antibiotic biosynthesis
In vivo and in vitro reconstitution of unique key steps in cystobactamid antibiotic biosynthesis
The biosynthetic pathway leading to the production of cystobactamids, a group of myxobacteria-derived topoisomerase inhibitors with potent anti-Gram-negative activity, remains unclear. Here, the authors report in vivo and in vitro evidence for unique steps in cystobactamid biosynthesis.
- Sebastian Groß
- , Bastien Schnell
- & Rolf Müller
-
Article
| Open Access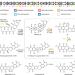 Enzymatic spiroketal formation via oxidative rearrangement of pentangular polyketides
Enzymatic spiroketal formation via oxidative rearrangement of pentangular polyketides
Rubromycin family of natural products belongs to aromatic polyketides with diverse bioactivities, but details of their biosynthesis are limited. Here, the authors report the complete in vitro reconstitution of enzymatic formation of the spiroketal moiety of rubromycin polyketides, driven by flavin-dependent enzymes, and characterize reaction intermediates.
- Britta Frensch
- , Thorsten Lechtenberg
- & Robin Teufel
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of combinatorial diversity in trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthase assembly lines across bacteria
Evolution of combinatorial diversity in trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthase assembly lines across bacteria
Trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases are multimodular enzymes that synthesise diverse polyketides. Here, the authors present an algorithm for the global study of their diversity, showing exchange of conserved consecutive modules as a driver of diversification, and guiding the discovery of polyketides.
- Eric J. N. Helfrich
- , Reiko Ueoka
- & Marnix H. Medema
-
Article
| Open Access Marine furanocembranoids-inspired macrocycles enabled by Pd-catalyzed unactivated C(sp3)-H olefination mediated by donor/donor carbenes
Marine furanocembranoids-inspired macrocycles enabled by Pd-catalyzed unactivated C(sp3)-H olefination mediated by donor/donor carbenes
Furanocembranoid-like natural products with the alkene-substituted furan scaffold display a range of biological activities, but are difficult to access. Here, the authors report a modular biomimetic strategy to synthesise diverse alkene-substituted furan-containing macrolactams via palladium-catalysed unactivated Csp3-H olefination.
- Jiping Hao
- , Xueying Guo
- & Weibo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the biosynthesis of lovastatin
Structural basis for the biosynthesis of lovastatin
Biosynthesis of the statin precursor lovastatin depends on the LovB–LovC megasynthase complex. Here, the authors present cryoEM structures of LovB–LovC and core LovB, providing structural insights into the catalytic cycle underlying lovastatin production.
- Jialiang Wang
- , Jingdan Liang
- & Zhijun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering and elucidation of the lipoinitiation process in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis
Engineering and elucidation of the lipoinitiation process in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis
Nonribosomal lipopeptides contain an acyl chain important for bioactivity, but its incorporation into the peptidyl backbone, mediated by the starter condensation (Cs) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthases, is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that acyl chains of different lengths can be obtained by engineering Cs domains and identify residues that determine the selectivity for acyl chains.
- Lin Zhong
- , Xiaotong Diao
- & Xiaoying Bian
-
Article
| Open Access Thioesterase-mediated side chain transesterification generates potent Gq signaling inhibitor FR900359
Thioesterase-mediated side chain transesterification generates potent Gq signaling inhibitor FR900359
FR900359 (FR) is a Gq protein inhibitor depsipeptide isolated from an uncultivable plant endosymbiont and synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases. Here, the authors discover a cultivable bacterial FR producer and show that FrsA thioesterase domain catalyses intermolecular transesterification of the FR side chain to the depsipeptide core during biosynthesis, improving Gq inhibition properties.
- Cornelia Hermes
- , René Richarz
- & Max Crüsemann
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of regio- and stereo-specificity in biosynthesis of bacterial heterodimeric diketopiperazines
Molecular basis of regio- and stereo-specificity in biosynthesis of bacterial heterodimeric diketopiperazines
Bacterial heterodimeric tryptophan-containing diketopiperazines (HTDKPs) are bioactive natural products that are difficult to access chemically. Here, the authors identify a family of three related HTDKP-forming cytochrome P450s and engineer key amino acid residues to produce distinct diketopiperazines frameworks.
- Chenghai Sun
- , Zhenyao Luo
- & Xudong Qu
-
Article
| Open Access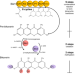 Pathway engineering in yeast for synthesizing the complex polyketide bikaverin
Pathway engineering in yeast for synthesizing the complex polyketide bikaverin
Bikaverin is a fungal-derived tetracyclic polyketide with antibiotic, antifungal and anticancer properties. Here, the authors employ various pathway engineering strategies to achieve high level production of bikaverin in baker’s yeast.
- Meng Zhao
- , Yu Zhao
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive prediction of secondary metabolite structure and biological activity from microbial genome sequences
Comprehensive prediction of secondary metabolite structure and biological activity from microbial genome sequences
Large-scale sequencing efforts have uncovered a large number of secondary metabolic pathways, but the chemicals they synthesise remain unknown. Here the authors present PRISM 4, which predicts the chemical structures encoded by microbial genome sequences, including all classes of bacterial antibiotics in clinical use.
- Michael A. Skinnider
- , Chad W. Johnston
- & Nathan A. Magarvey
-
Article
| Open Access GPAHex-A synthetic biology platform for Type IV–V glycopeptide antibiotic production and discovery
GPAHex-A synthetic biology platform for Type IV–V glycopeptide antibiotic production and discovery
Expansion of the chemical diversity of glycopeptide antibiotics (GPAs) to deal with the emergence and spread of GPA resistance is challenging. Here, the authors report a GPA synthetic biology platform in Streptomyces coelicolor for Type IV–V glycopeptide antibiotic production and discovery.
- Min Xu
- , Wenliang Wang
- & Gerard D. Wright
-
Article
| Open Access Oxepinamide F biosynthesis involves enzymatic d-aminoacyl epimerization, 3H-oxepin formation, and hydroxylation induced double bond migration
Oxepinamide F biosynthesis involves enzymatic d-aminoacyl epimerization, 3H-oxepin formation, and hydroxylation induced double bond migration
Oxepinamides are a class of fungal oxepins with biological activities. Here, the authors elucidate the biosynthetic pathway of oxepinamide F from Aspergillus ustus and show that it involves enyme-catalysed oxepin ring formation, hydroxylation-induced double bond migration, epimerization and methylation.
- Liujuan Zheng
- , Haowen Wang
- & Shu-Ming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the cytochrome P450-catalyzed methylenedioxy bridge formation in streptovaricins biosynthesis
Uncovering the cytochrome P450-catalyzed methylenedioxy bridge formation in streptovaricins biosynthesis
Streptovaricin C is an antibiotic containing a methylenedioxy bridge (MDB) moiety essential for its activity. Here, the authors show that a P450 monooxygenase StvP2 catalyses MDB formation, report its crystal structure in complex with the substrate, and elucidate mechanistic details of MDB formation.
- Guo Sun
- , Chaoqun Hu
- & Yuhui Sun
-
Article
| Open Access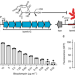 Continuous bioactivity-dependent evolution of an antibiotic biosynthetic pathway
Continuous bioactivity-dependent evolution of an antibiotic biosynthetic pathway
Biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) make small molecules with fitness-enhancing activities that drive BGC evolution. Here, the authors show that synthetic biology can leverage bioactivity to achieve continuous evolution of an antibiotic BGC in the lab and improve antibiotic production in a new host.
- Chad W. Johnston
- , Ahmed H. Badran
- & James J. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access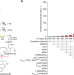 A yeast platform for high-level synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids
A yeast platform for high-level synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids
Plants synthesize more than 3000 tetrahydroisoquinoline (THIQ) alkaloids, but only a few of them have been produced by engineered microbes and titers are very low. Here, the authors increase (S)-reticuline titer to 4.6 g/L and repurpose the yeast Ehrlich pathway to synthesize a diverse array of THIQ scaffolds.
- Michael E. Pyne
- , Kaspar Kevvai
- & Vincent J. J. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Animal biosynthesis of complex polyketides in a photosynthetic partnership
Animal biosynthesis of complex polyketides in a photosynthetic partnership
Complex polyketides are usually produced by microbes, whereas the origin of polyketides found in animals remained unknown. This study shows that sacoglossan animals, such as sea slugs, employ fatty acid synthase-like proteins to produce microbe-like polyketides.
- Joshua P. Torres
- , Zhenjian Lin
- & Eric W. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Minimal lactazole scaffold for in vitro thiopeptide bioengineering
Minimal lactazole scaffold for in vitro thiopeptide bioengineering
Lactazole A is a thiopeptide from Streptomyces lactacystinaeus, encoded by a compact 9.8 kb biosynthetic gene cluster. Here, the authors show a platform for in vitro biosynthesis of lactazole A via a combination of a flexible in vitro translation system with recombinantly produced lactazole biosynthetic enzymes.
- Alexander A. Vinogradov
- , Morito Shimomura
- & Hiroyasu Onaka
-
Article
| Open Access BrtB is an O-alkylating enzyme that generates fatty acid-bartoloside esters
BrtB is an O-alkylating enzyme that generates fatty acid-bartoloside esters
O-alkylation of carboxylates by alkyl halides has only been observed transiently in enzymatic processes. Here, the authors show a carboxylate alkylating enzyme, BrtB, that catalyzes C-O bond formation between free fatty acids and secondary alkyl chlorides.
- João P. A. Reis
- , Sandra A. C. Figueiredo
- & Pedro N. Leão
-
Article
| Open Access Plant metabolism of nematode pheromones mediates plant-nematode interactions
Plant metabolism of nematode pheromones mediates plant-nematode interactions
Small molecules in the rhizosphere regulate interactions between plants and other organisms. Here the authors show that an ascaroside pheromone secreted by plant-parasitic nematodes is converted by host plant peroxisomal β-oxidation into shorter side-chained ascarosides that repel nematodes.
- Murli Manohar
- , Francisco Tenjo-Castano
- & Frank C. Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access Production of zosteric acid and other sulfated phenolic biochemicals in microbial cell factories
Production of zosteric acid and other sulfated phenolic biochemicals in microbial cell factories
Toxicity and limited solubility inhibits the biological production of many organic compounds. Here the authors metabolically engineer sulfate uptake and activation in order to produce sulfate esters of phenolic compounds, such as zosteric acid, thereby addressing these issues.
- Christian Bille Jendresen
- & Alex Toftgaard Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Emulating evolutionary processes to morph aureothin-type modular polyketide synthases and associated oxygenases
Emulating evolutionary processes to morph aureothin-type modular polyketide synthases and associated oxygenases
The wealth of complex polyketides is an essential source for drug discovery. Here, the authors report an evolution-guided rational morphing of modular polyketide synthases (PKSs) for aurothin and neoaurothin biosynthesis, and reveal engineering site suitable for diversifying PKS systems.
- Huiyun Peng
- , Keishi Ishida
- & Christian Hertweck
-
Article
| Open Access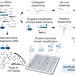 Uncovering the biosynthetic potential of rare metagenomic DNA using co-occurrence network analysis of targeted sequences
Uncovering the biosynthetic potential of rare metagenomic DNA using co-occurrence network analysis of targeted sequences
Soil microorganisms are a rich source of bioactive molecules. Here, the authors present a targeted sequencing workflow that reconstructs the clustered organization of biosynthetic domains in metagenomic libraries from amplicon data, thus guiding the discovery of novel metabolites from rare members of the soil microbiome.
- Vincent Libis
- , Niv Antonovsky
- & Sean F. Brady
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a microbial biosynthesis platform for de novo production of tropane alkaloids
Engineering a microbial biosynthesis platform for de novo production of tropane alkaloids
Tropane alkaloids (TAs) are a group of phytochemicals that are used to treat neurological disorders. Here, the authors engineer baker’s yeast to produce tropine, a key intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway of TAs, and cinnamoyltropine, a non-canonical TA, from simple carbon and nitrogen sources.
- Prashanth Srinivasan
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access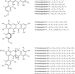 A role for antibiotic biosynthesis monooxygenase domain proteins in fidelity control during aromatic polyketide biosynthesis
A role for antibiotic biosynthesis monooxygenase domain proteins in fidelity control during aromatic polyketide biosynthesis
Formicapyridines are similar to pentacyclic fasamycin and formicamycin aromatic polyketides but with a pyridine moiety. Here the authors rationally mutate the biosynthetic gene cluster to increase production and identify a non-catalytic role for the ABM superfamily of proteins.
- Zhiwei Qin
- , Rebecca Devine
- & Barrie Wilkinson
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis of N-acyl-α-amino-β-lactone formation catalyzed by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase
The structural basis of N-acyl-α-amino-β-lactone formation catalyzed by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase
The antimicrobial β-lactone obafluorin is produced by a Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase (NRPS). Here the authors present the crystal structure of the obafluorin NRPS and develop a reconstitution assay that allows them to analyse product formation from obafluorin NRPS mutants and alternate substrates.
- Dale F. Kreitler
- , Erin M. Gemmell
- & Andrew M. Gulick
-
Article
| Open Access A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids
A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids
C19 hydroxylation is a unique feature of some bioactive steroids. Here, the authors developed a direct C19 hydroxylation approach to scalably access 19-OH-cortexolone in the host T. cucumeris and then converted the product into various pharmaceutically useful products via chemical synthesis.
- Junlin Wang
- , Yanan Zhang
- & Qianghui Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access The UbiX flavin prenyltransferase reaction mechanism resembles class I terpene cyclase chemistry
The UbiX flavin prenyltransferase reaction mechanism resembles class I terpene cyclase chemistry
The UbiD-UbiX decarboxylase system is required for the biosynthesis of quinone cofactors. Here, the authors combine structural and biochemical analyses to elucidate the UbiX reaction mechanism, showing that it resembles the mode of action of class I terpene cyclases.
- Stephen A. Marshall
- , Karl A. P. Payne
- & David Leys
-
Article
| Open Access Cyanobacterial antimetabolite 7-deoxy-sedoheptulose blocks the shikimate pathway to inhibit the growth of prototrophic organisms
Cyanobacterial antimetabolite 7-deoxy-sedoheptulose blocks the shikimate pathway to inhibit the growth of prototrophic organisms
Mother Nature is a valuable resource for the discovery of drug and agricultural chemicals. Here, the authors show that 7-deoxy-sedoheptulose produced by a cyanobacterium is an antimicrobial and herbicidal compound that acts through inhibition of 3-dehydroquniate synthase in the shikimate pathway.
- Klaus Brilisauer
- , Johanna Rapp
- & Karl Forchhammer
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based redesign of docking domain interactions modulates the product spectrum of a rhabdopeptide-synthesizing NRPS
Structure-based redesign of docking domain interactions modulates the product spectrum of a rhabdopeptide-synthesizing NRPS
Rhabdopeptides are synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) and the multiple NRPS subunits interact through docking domains (DD). Here the authors provide insights into DD interaction patterns and present the structures of three N-terminal docking domains (NDD) and a NDD-CDD complex and derive a set of recognition rules for DD interactions.
- Carolin Hacker
- , Xiaofeng Cai
- & Jens Wöhnert
-
Article
| Open Access Rifamycin congeners kanglemycins are active against rifampicin-resistant bacteria via a distinct mechanism
Rifamycin congeners kanglemycins are active against rifampicin-resistant bacteria via a distinct mechanism
Resistance to rifamycin antibiotics, which target bacterial RNA polymerases, is a growing problem. Here, the authors identify gene clusters from soil metagenomes encoding production of rifamycin analogues that are active against rifampicin-resistant bacteria through a distinct mechanism.
- James Peek
- , Mirjana Lilic
- & Sean F. Brady
-
Article
| Open Access Dereplication of microbial metabolites through database search of mass spectra
Dereplication of microbial metabolites through database search of mass spectra
New natural products can be identified via mass spectrometry by excluding all known ones from the analysis, a process called dereplication. Here, the authors extend a previously published dereplication algorithm to different classes of secondary metabolites.
- Hosein Mohimani
- , Alexey Gurevich
- & Pavel A. Pevzner
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a comprehensive understanding of the structural dynamics of a bacterial diterpene synthase during catalysis
Towards a comprehensive understanding of the structural dynamics of a bacterial diterpene synthase during catalysis
The bacterial diterpene synthase CotB2 catalyses the cyclisation of geranylgeranyl diphosphate to cyclooctat-9-en7-ol. Here the authors present various CotB2 structures including a trapped abrupt reaction product that were used for molecular dynamic simulations and allowed them to model all intermediates along the reaction cascade.
- Ronja Driller
- , Sophie Janke
- & Bernhard Loll
-
Article
| Open Access A rationally designed JAZ subtype-selective agonist of jasmonate perception
A rationally designed JAZ subtype-selective agonist of jasmonate perception
The phytohormone JA-Ile can promote plant resistance against herbivores and fungal pathogens but also inhibits growth, limiting its potential use in agriculture. Here, the authors design a stereoisomer of JA-Ile analog and demonstrate that it can promote defense while having minimal impact on growth.
- Yousuke Takaoka
- , Mana Iwahashi
- & Minoru Ueda
-
Article
| Open Access An antifungal polyketide associated with horizontally acquired genes supports symbiont-mediated defense in Lagria villosa beetles
An antifungal polyketide associated with horizontally acquired genes supports symbiont-mediated defense in Lagria villosa beetles
Burkholderia bacteria protect the offspring of Lagria beetles against pathogens. Here, Flórez et al. identify an antifungal polyketide that is likely encoded by a horizontally acquired gene cluster on the genome of a dominant, uncultured Burkholderia symbiont of Lagria villosa.
- Laura V. Flórez
- , Kirstin Scherlach
- & Martin Kaltenpoth
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of thiocarboxylic acid-containing natural products
Biosynthesis of thiocarboxylic acid-containing natural products
Thioplatensimycin (thioPTM) and thioplatencin (thioPTN) are recently discovered thiocarboxylic acid congeners of the antibacterial compounds PTM and PTN. Here, the authors identify a thioacid cassette encoding PtmA3 and PtmU4 that are responsible for carboxylate activation and sulfur transfer, respectively.
- Liao-Bin Dong
- , Jeffrey D. Rudolf
- & Ben Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Three previously unrecognised classes of biosynthetic enzymes revealed during the production of xenovulene A
Three previously unrecognised classes of biosynthetic enzymes revealed during the production of xenovulene A
Xenovulene A is a fungal compound that has the potential to be used as an antidepressant. Here, the authors unravel the pathway leading to its formation in fungi and discover a new class of enzymes, which accounts for some unusual chemistry in the synthesis of xenovulene.
- Raissa Schor
- , Carsten Schotte
- & Russell J. Cox
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of fragin is controlled by a novel quorum sensing signal
Biosynthesis of fragin is controlled by a novel quorum sensing signal
Fragin is a diazeniumdiolate metabolite with antifungal activity, produced by some bacteria. Here, Jenul et al. show that metal chelation is the molecular basis of fragin’s antifungal activity, and that a gene cluster directing fragin biosynthesis is also involved in the synthesis of a signal molecule.
- Christian Jenul
- , Simon Sieber
- & Leo Eberl
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable synthesis enabling multilevel bio-evaluations of natural products for discovery of lead compounds
Scalable synthesis enabling multilevel bio-evaluations of natural products for discovery of lead compounds
Isodon diterpenoids, promising anti-cancer agents found in certain tropical plants, are difficult to obtain. Here, the authors developed a synthetic strategy to synthesise several different members of this group, including neolaxiflorin L which emerged from this study as a promising drug candidate.
- Lizhi Zhu
- , Wenjing Ma
- & Chi-Sing Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Correlating chemical diversity with taxonomic distance for discovery of natural products in myxobacteria
Correlating chemical diversity with taxonomic distance for discovery of natural products in myxobacteria
It is thought that the chances for discovery of novel natural products increase by screening rare organisms. Here the authors analyse metabolites produced by over 2300 myxobacterial strains and, indeed, find a correlation between taxonomic distance and production of distinct secondary metabolite families.
- Thomas Hoffmann
- , Daniel Krug
- & Rolf Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of human cell selective effector molecules using single cell multiplexed activity metabolomics
Discovery of human cell selective effector molecules using single cell multiplexed activity metabolomics
Bioactive metabolites from plant and microbial extracts hold therapeutic potential. Here, the authors combine untargeted metabolomic arrays with flow cytometry-based single cell response profiling and identify metabolites with cell subset-specific activities in the bone marrow from an AML patient.
- David C. Earl
- , P. Brent Ferrell Jr
- & Brian O. Bachmann
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of a membrane-bound C-glucosyltransferase responsible for carminic acid biosynthesis in Dactylopius coccus Costa
Characterization of a membrane-bound C-glucosyltransferase responsible for carminic acid biosynthesis in Dactylopius coccus Costa
Carminic acid is a widely applied red colorant that is still harvested from insects because its biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors identify and characterize a membrane-bound C-glucosyltransferase catalyzing the final step during carminic acid biosynthesis.
- Rubini Kannangara
- , Lina Siukstaite
- & Birger Lindberg Møller

 Structural basis of the stereoselective formation of the spirooxindole ring in the biosynthesis of citrinadins
Structural basis of the stereoselective formation of the spirooxindole ring in the biosynthesis of citrinadins