Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Top-down fabricated silicon nanowires under tensile elastic strain up to 4.5%
Top-down fabricated silicon nanowires under tensile elastic strain up to 4.5%
Strain in Si nanostructures is used to achieve higher carrier mobility, making these devices candidates for the next generation of transistors. Minamisawaet al. fabricate silicon nanowires subject to elastic tensile strain up to 4.5%, exceeding the limit achievable with the use of SiGe virtual substrates.
- R.A. Minamisawa
- , M.J. Süess
- & H. Sigg
-
Article |
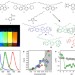 Monodisperse conjugated polymer particles by Suzuki–Miyaura dispersion polymerization
Monodisperse conjugated polymer particles by Suzuki–Miyaura dispersion polymerization
Well-defined, monodisperse colloids of semiconducting polymers are required as new photonic and optoelectronic materials. Here, a Suzuki–Miyaura dispersion polymerization is used to produce monodisperse sub-micrometer particles of a range of semiconducting polymers.
- Alexander J.C. Kuehne
- , Malte C. Gather
- & Joris Sprakel
-
Article |
 Insights into the biomedical effects of carboxylated single-wall carbon nanotubes on telomerase and telomeres
Insights into the biomedical effects of carboxylated single-wall carbon nanotubes on telomerase and telomeres
Single-walled carbon nanotubes can selectively stabilize telomeric i-motif DNA and have been suggested as a treatment for cancer. Here, carbon nanotubes are found to inhibit telomerase activity by stabilizing i-motif DNA, leading to telomere uncapping and altered telomere function in cancer cells.
- Yong Chen
- , Konggang Qu
- & Xiaogang Qu
-
Article
| Open Access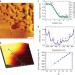 Observation of Landau levels in potassium-intercalated graphite under a zero magnetic field
Observation of Landau levels in potassium-intercalated graphite under a zero magnetic field
A signature of the Dirac-like physics of charge carriers in graphene is the occurrence of an anomalous Hall effect, resulting in a quantization of the Landau levels. Guoet al. observe Landau levels of Dirac fermions in potassium-intercalated graphite arising in the absence of an applied magnetic field.
- Donghui Guo
- , Takahiro Kondo
- & Junji Nakamura
-
Article |
 Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocrystalline boron carbide by nanoporosity and interface phases
Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocrystalline boron carbide by nanoporosity and interface phases
The mechanical properties of structural ceramics are characterized by a high degree of fragility and brittleness. This study demonstrates that, contrary to expectation, their brittleness can be reduced substantially by introducing nanopores together with weak grain boundary phases.
- K. Madhav Reddy
- , J.J. Guo
- & M.W. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Hard magnetic ferrite with a gigantic coercivity and high frequency millimetre wave rotation
Hard magnetic ferrite with a gigantic coercivity and high frequency millimetre wave rotation
Permanent magnets based on magnetic ferrites such as Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 are used in a wide range of applications. This study demonstrates that introducing rhodium into nanoparticles consisting of the ε phase of Fe2O3gives rise to a very high coercivity.
- Asuka Namai
- , Marie Yoshikiyo
- & Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
-
Article |
 Imaging enzyme-triggered self-assembly of small molecules inside live cells
Imaging enzyme-triggered self-assembly of small molecules inside live cells
Supramolecular interactions allow some small molecules to self-assemble into nanofibres and hydrogels in aqueous environments. Gaoet al.report a hydrogelator that forms fluorescent nanofibres within cells, leading to the visualization of their self-assembly at the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Yuan Gao
- , Junfeng Shi
- & Bing Xu
-
Article |
 Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
The spectral position of Raman peaks is a useful diagnostic for determining the degree of strain and excess electronic charges present in graphene. This study demonstrates that these two contributions can be separated from each other and therefore be obtained at the same time.
- Ji Eun Lee
- , Gwanghyun Ahn
- & Sunmin Ryu
-
Article |
 Flexible and transparent all-graphene circuits for quaternary digital modulations
Flexible and transparent all-graphene circuits for quaternary digital modulations
Signal modulation is a mechanism which embeds an information-carrying signal into a carrier wave to broadcast information and is essential for high-speed communication. Zhonget al. report a flexible, transparent all-graphene modulator circuit performing quaternary modulation schemes with only two transistors.
- Seunghyun Lee
- , Kyunghoon Lee
- & Zhaohui Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam
Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam
Generating arbitrary orientation of light polarization has been an elusive goal, yet it is important to light interactions with nano-objects. By combining azimuthally and radially polarized beams, Liet al. overcome this obstacle and demonstrate its use for polarization-based encryption with gold nanorods.
- Xiangping Li
- , Tzu-Hsiang Lan
- & Min Gu
-
Article |
 Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network
Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network
Understanding ultrafast demagnetisation is key to manipulating magnetic structures on fast timescales, yet laser sources limit the attainable spatial resolution. Here, a soft X-ray high harmonic source enables a high temporal and spatial resolution study of domain demagnetisation in [Co/Pt]30multilayer films.
- Boris Vodungbo
- , Julien Gautier
- & Jan Lüning
-
Article
| Open Access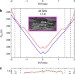 Observation of resistively detected hole spin resonance and zero-field pseudo-spin splitting in epitaxial graphene
Observation of resistively detected hole spin resonance and zero-field pseudo-spin splitting in epitaxial graphene
Along with its electronic characteristics, the spin properties of graphene have recently received increasing attention in the context of spintronic applications. Using microwave radiation, Maniet al. identify resistively detected spin resonance in monolayer and trilayer graphene sheets and extract the value for the Landé g-factor.
- Ramesh G. Mani
- , John Hankinson
- & Walter A. de Heer
-
Article |
 Symmetry breaking in the formation of magnetic vortex states in a permalloy nanodisk
Symmetry breaking in the formation of magnetic vortex states in a permalloy nanodisk
Vortex states in magnetic nanoislands are characterized by a curling of the magnetization in the plane of the disk. This study demonstrates experimentally that vortices tend to form with a preferred handedness that is dictated by the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction.
- Mi-Young Im
- , Peter Fischer
- & Teruo Ono
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Crystallization of noble metal atoms usually leads to the thermodynamically stable face-centred cubic phase. Sunet al. show that internal strain in silver nanoparticles leads to lattice distortion and a stable body-centred tetragonal phase.
- Yugang Sun
- , Yang Ren
- & Dean J. Miller
-
Article |
 Photoinduced handedness switching in terahertz chiral metamolecules
Photoinduced handedness switching in terahertz chiral metamolecules
Chiral metamaterials present interesting ways to manipulate and distinguish between different circular polarizations of light. Zhanget al. realize chiral metamaterials that exhibit photoinduced switching between left- and right-handed circular polarization interactions at terahertz frequencies.
- Shuang Zhang
- , Jiangfeng Zhou
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article |
 Towards a quantum representation of the ampere using single electron pumps
Towards a quantum representation of the ampere using single electron pumps
Single electron pumps have been proposed as potential candidates for redefining the ampere. This study reports measurements of the quantized current flowing through a semiconductor electron pump with a precision that makes a substantial step towards establishing a direct metric for electrical currents.
- S.P. Giblin
- , M. Kataoka
- & D.A. Ritchie
-
Article |
 Gate-defined quantum confinement in suspended bilayer graphene
Gate-defined quantum confinement in suspended bilayer graphene
The ability to manipulate single charges is a key requisite for novel nanoelectronic devices. Allenet al. show how to electrostatically confine electrons in suspended bilayer graphene quantum dots by local control of the graphene band structure.
- M. T. Allen
- , J. Martin
- & A. Yacoby
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional nanonetworks for giant stretchability in dielectrics and conductors
Three-dimensional nanonetworks for giant stretchability in dielectrics and conductors
Stretchable electronics based on conducting polymers offer new opportunities for designing flexible technologies. Parket al. build three-dimensional nanostructures from elastomers soaked with liquid metal to produce stretchable conductors with greatly improved strain properties over solid films.
- Junyong Park
- , Shuodao Wang
- & Seokwoo Jeon
-
Article
| Open Access Lifetime blinking in nonblinking nanocrystal quantum dots
Lifetime blinking in nonblinking nanocrystal quantum dots
Nanocrystal quantum dots can exhibit photoluminescence blinking, where the intensity of the emitted light fluctuates due to random charging and discharging. Gallandet al.study thick shell nanocrystals and find that the photoluminescence lifetime can also undergo blinking, without intensity changes.
- Christophe Galland
- , Yagnaseni Ghosh
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
 Anomalous high capacitance in a coaxial single nanowire capacitor
Anomalous high capacitance in a coaxial single nanowire capacitor
Devices made up of nanowires offer promise for a range of electronic, photonic and energy applications. Liuet al. fabricate a miniature capacitor by employing a thin layer of Cu2O as a separator between layers of carbon and copper.
- Zheng Liu
- , Yongjie Zhan
- & Pulickel M. Ajayan
-
Article |
 Electric-field control of magnetic domain-wall velocity in ultrathin cobalt with perpendicular magnetization
Electric-field control of magnetic domain-wall velocity in ultrathin cobalt with perpendicular magnetization
The manipulation of domain walls in magnetic materials is attracting interest because of its potential use in memory devices. Chibaet al. demonstrate that the velocity of domain walls in perpendicularly magnetized films can be changed by more than an order of magnitude by applying an electric field.
- D. Chiba
- , M. Kawaguchi
- & T. Ono
-
Article |
 Spin-motive force due to a gyrating magnetic vortex
Spin-motive force due to a gyrating magnetic vortex
The electromotive force is a well established phenomenon that is induced by a varying magnetic field. Here, Tanabeet al. report a compelling experimental confirmation of its spin-induced analogue, the spinmotive force.
- K. Tanabe
- , D. Chiba
- & T. Ono
-
Article |
 Closed network growth of fullerenes
Closed network growth of fullerenes
The formation mechanisms of fullerenes remain unclear. This study shows that fullerenes self-assemble through a closed network growth mechanism in which atomic carbon and C2are incorporated into the growing closed cages.
- Paul W. Dunk
- , Nathan K. Kaiser
- & Harold W. Kroto
-
Article
| Open Access Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size
Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size
Current top-down and bottom-up syntheses of graphene nanostructures suffer from low yields or do not produce structures with different and controlled shapes. Here, monodisperse graphene shapes are produced by diamond-edge cutting of pyrolytic graphite followed by exfoliation.
- Nihar Mohanty
- , David Moore
- & Vikas Berry
-
Article |
 Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Strain engineering has been proposed as a promising strategy for manipulating the electronic properties of graphene. This scanning tunnelling microscopy study demonstrates the feasibility of controlling strain patterns in graphene down to the nanoscale.
- Jiong Lu
- , A.H. Castro Neto
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene quilts for thermal management of high-power GaN transistors
Graphene quilts for thermal management of high-power GaN transistors
Electronic and optoelectronic devices based on gallium nitride suffer from self-heating arising as a result of their operation. This study presents and demonstrates a strategy for managing this problem that relies on graphene quilts which dissipate the heat away.
- Zhong Yan
- , Guanxiong Liu
- & Alexander A. Balandin
-
Article |
 Topological repulsion between domain walls in magnetic nanowires leading to the formation of bound states
Topological repulsion between domain walls in magnetic nanowires leading to the formation of bound states
The manipulation of domain walls in magnetic nanodevices is a topic of increasing technological relevance. This study examines the interactions that occur between vortex domain walls in permalloy nanowires, and finds that bound states occur between domain walls with opposite magnetic charge.
- Luc Thomas
- , Masamitsu Hayashi
- & Stuart Parkin
-
Article |
 Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel
Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel
Graphene is characterized by unique physical properties that offer substantial promise, most notably for electronic applications. Mannooret al. present a wireless graphene-based sensor for detecting bacteria on a range of biological tissues.
- Manu S. Mannoor
- , Hu Tao
- & Michael C. McAlpine
-
Article |
 Ultra-low carrier concentration and surface-dominant transport in antimony-doped Bi2Se3 topological insulator nanoribbons
Ultra-low carrier concentration and surface-dominant transport in antimony-doped Bi2Se3 topological insulator nanoribbons
The singular properties of topological insulators are defined by the topological nature of their metallic surface states. This study shows that by doping Bi2Se3nanoribbons with antimony, the transport properties of these surface states are measurable and can be distinguished from the contributions due to the bulk of the samples.
- Seung Sae Hong
- , Judy J. Cha
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel junctions
Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel junctions
The spin-dependent thermal and electrical transport properties of nanostructures are central for future applications of spintronic devices. Here, Linet al. report an enhanced spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in an Al2O3-based magnetic tunnel junction.
- Weiwei Lin
- , Michel Hehn
- & Stéphane Mangin
-
Article
| Open Access Bright single-photon sources in bottom-up tailored nanowires
Bright single-photon sources in bottom-up tailored nanowires
Single-photon sources are important for quantum optical technologies, although achieving efficient light extraction from them with waveguides is limited in top-down approaches. Reimeret al. show a high extraction efficiency using a bottom-up method to grow quantum dots on the axis of nanowire waveguides.
- Michael E. Reimer
- , Gabriele Bulgarini
- & Val Zwiller
-
Article |
 Probing charge scattering mechanisms in suspended graphene by varying its dielectric environment
Probing charge scattering mechanisms in suspended graphene by varying its dielectric environment
A factor limiting the mobility of charge carriers in graphene, and therefore its use in electronic applications, is the Coulomb scattering due to charged impurities. By exposing graphene devices to a range of non-polar liquids, Newazet al. observe an enhancement of the mobility due to screening.
- A.K.M. Newaz
- , Yevgeniy S. Puzyrev
- & Kirill I. Bolotin
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional imaging of single nanotube molecule endocytosis on plasmonic substrates
Three-dimensional imaging of single nanotube molecule endocytosis on plasmonic substrates
Imaging and tracking the motion of single molecules on cell plasma membranes requires high spatial resolution in three dimensions. Honget al. develop a plasmonic ruler based on the fluorescence enhancement of carbon nanotubes on a gold plasmonic substrate, allowing the observation of nanotube endocytosis in three dimensions.
- Guosong Hong
- , Justin Z. Wu
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Precise hierarchical self-assembly of multicompartment micelles
Precise hierarchical self-assembly of multicompartment micelles
Multicompartment micelles can be assembled from block copolymers but it is difficult to manipulate their hierarchical superstructures using straightforward concepts. Here, methods are developed that involve the pre-assembly of subunits for the structurally controlled production of micelles.
- André H. Gröschel
- , Felix H. Schacher
- & Axel H.E. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Repeated growth and bubbling transfer of graphene with millimetre-size single-crystal grains using platinum
Repeated growth and bubbling transfer of graphene with millimetre-size single-crystal grains using platinum
Grain boundaries in graphene degrade its properties, and large single-crystal graphene is desirable for electronic applications of graphene. Gaoet al. develop a method to produce millimetre-sized hexagonal single-crystal graphene grains, and films composed of the grains, on platinum by chemical vapour deposition.
- Libo Gao
- , Wencai Ren
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband omnidirectional antireflection coating based on subwavelength surface Mie resonators
Broadband omnidirectional antireflection coating based on subwavelength surface Mie resonators
Minimising reflection from the interface between materials is an important goal for optical devices such as solar cells or photodetectors. Spinelliet al. show almost total loss of reflection over a broad spectral range from a silicon surface using periodic arrays of sub-wavelength silicon nanocylinders.
- P. Spinelli
- , M.A. Verschuuren
- & A. Polman
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving the electromagnetic mechanism of surface-enhanced light scattering at single hot spots
Resolving the electromagnetic mechanism of surface-enhanced light scattering at single hot spots
Light scattering from nanoscale objects can be dramatically enhanced in the proximity of optical antennas. Here, by studying the amplitude and phase of the light scattered from a tip located at the hot spot of an antenna, the underlying electromagnetic mechanism of this enhancement is resolved.
- P. Alonso-González
- , P. Albella
- & R. Hillenbrand
-
Article |
 Fully inorganic oxide-in-oxide ultraviolet nanocrystal light emitting devices
Fully inorganic oxide-in-oxide ultraviolet nanocrystal light emitting devices
Light-emitting diodes in the form of nanocrystals offer promise for environmental and biomedical diagnostics. Brovelliet al. present a method for realizing mechanically robust and chemically stable nanocrystals emitting light in the ultraviolet range.
- Sergio Brovelli
- , Norberto Chiodini
- & Alberto Paleari
-
Article
| Open Access CMOS-based carbon nanotube pass-transistor logic integrated circuits
CMOS-based carbon nanotube pass-transistor logic integrated circuits
Field-effect transistors fabricated from carbon nanotubes have been investigated extensively over the past two decades. This study demonstrates a nanotube-based integrated circuit design that substantially improves the speed and power consumption with respect to silicon-based integrated circuits.
- Li Ding
- , Zhiyong Zhang
- & Lian-Mao Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Generation and control of polarization-entangled photons from GaAs island quantum dots by an electric field
Generation and control of polarization-entangled photons from GaAs island quantum dots by an electric field
As quantum information and communication experiments grow in sophistication, the need for efficient sources of entangled photons escalates. Using exciton and biexciton emission in GaAs island quantum dots, Ghaliet al. demonstrate the electric field-induced generation of entangled photons with high fidelity.
- Mohsen Ghali
- , Keita Ohtani
- & Hideo Ohno
-
Article |
 Broadband light management using low-Q whispering gallery modes in spherical nanoshells
Broadband light management using low-Q whispering gallery modes in spherical nanoshells
Control of light absorption in optical devices, such as solar cells, can be achieved through resonant features like whispering gallery modes. Here, these modes are exploited in spherical silicon nanoshells to enhance absorption over a broad spectral range in nanometre-scale flexible layers.
- Yan Yao
- , Jie Yao
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic toughening of composite fibres by self-alignment of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes
Synergistic toughening of composite fibres by self-alignment of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes
Composite fibres made of polymers reinforced by carbon nanotubes are known for their exceptional toughness. Shinet al. make these composites even tougher, by self-aligning carbon nanotubes and reduced graphene oxide flakes within the polymer matrix.
- Min Kyoon Shin
- , Bommy Lee
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article |
 Near room-temperature synthesis of transfer-free graphene films
Near room-temperature synthesis of transfer-free graphene films
Current methods for fabricating graphene rely on its transfer from metal surfaces to substrates suitable for device applications. This study demonstrates a transfer-free approach for growing graphene on substrates such as thermally oxidized silicon and plastic that forms the material underneath a nickel film, at the nickel–substrate interface.
- Jinsung Kwak
- , Jae Hwan Chu
- & Soon-Yong Kwon
-
Article |
 Chemical structures of hydrazine-treated graphene oxide and generation of aromatic nitrogen doping
Chemical structures of hydrazine-treated graphene oxide and generation of aromatic nitrogen doping
Parket al. use 13C and 15N solid-state NMR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to study the chemical structure of hydrazine-treated graphite oxide. Hydrazine treatment is shown to lead to the incorporation of aromatic N2moieties at the graphene edges and restore graphitic networks on the basal planes.
- Sungjin Park
- , Yichen Hu
- & Rodney S. Ruoff
-
Article
| Open Access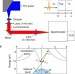 Extraordinary carrier multiplication gated by a picosecond electric field pulse
Extraordinary carrier multiplication gated by a picosecond electric field pulse
Studying carrier multiplication in materials is important to understand their transport properties and interaction with light. Hiroriet al. show that intense terahertz pulses can generate electron-hole pairs in GaAs quantum wells that then emit infrared light, contrary to the effect with a DC field.
- H. Hirori
- , K. Shinokita
- & K. Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene chiral liquid crystals and macroscopic assembled fibres
Graphene chiral liquid crystals and macroscopic assembled fibres
Chiral liquid crystals of two-dimensional colloids have not been extensively investigated. Xu and Gao show that graphene oxide can form chiral liquid crystals, and demonstrate that they can be spun into macroscopic fibres, and that subsequent chemical reduction provides graphene fibres with high conductivity.
- Zhen Xu
- & Chao Gao
-
Article |
 Plasmon resonance enhanced multicolour photodetection by graphene
Plasmon resonance enhanced multicolour photodetection by graphene
Among the wide range of potential applications of graphene, photodetection is believed to be among the most promising. By combining graphene with plasmonic nanostructures, Duan and colleagues observe dramatic improvements in the efficiency and spectral sensitivity of graphene-based photodetectors.
- Yuan Liu
- , Rui Cheng
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Suppression of the intrinsic stochastic pinning of domain walls in magnetic nanostripes
Suppression of the intrinsic stochastic pinning of domain walls in magnetic nanostripes
The propagation of magnetic domain walls in nanowires offers promise as the basis of future memory storage technologies. Muñoz and Prieto show that the random pinning of domain walls to structural defects in the nanowires can be suppressed at low fields, thus improving the reliability of the transmission of the domain walls substantially.
- Manuel Muñoz
- & José L. Prieto
-
Article |
 Towards hybrid superlattices in graphene
Towards hybrid superlattices in graphene
The controllable modification of graphene by chemical functionalization can modulate its optical and electronic properties. Sunet al. devise a functionalisation-based method to pattern graphane/graphene superlattices within a single sheet of graphene.
- Zhengzong Sun
- , Cary L. Pint
- & James M. Tour
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Carbon nanotubes and fullerenes
- Electronic properties and materials
- Graphene
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Metamaterials
- Molecular machines and motors
- Molecular self-assembly
- Nanoparticles
- Nanowires
- Organic–inorganic nanostructures
- Quantum dots
- Structural properties
- Synthesis and processing
- Two-dimensional materials

 Magnesium-free self-assembly of multi-layer DNA objects
Magnesium-free self-assembly of multi-layer DNA objects