Journal Club |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
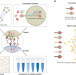 The diversification of methods for studying cell–cell interactions and communication
The diversification of methods for studying cell–cell interactions and communication
In this Review, the authors summarize recent progress in cell–cell interaction (CCI) research. They describe the recent evolution in computational tools that underpin CCI studies, discuss improvements in experimental methods enabling more high-throughput analyses of CCIs, and highlight future directions for the field.
- Erick Armingol
- , Hratch M. Baghdassarian
- & Nathan E. Lewis
-
Research Highlight |
 Optical filament recording of cellular events
Optical filament recording of cellular events
Two new studies in Nature Biotechnology describe cellular recording systems that incorporate time-resolved optical signals into self-assembling protein filaments.
- Darren J. Burgess
-
Research Highlight |
 New cuts for CRISPR effectors
New cuts for CRISPR effectors
Two new studies in Science characterize a CRISPR-associated nuclease–protease system that can be leveraged as a programmable protease-based RNA sensor.
- Darren J. Burgess
-
Review Article |
 Prime editing for precise and highly versatile genome manipulation
Prime editing for precise and highly versatile genome manipulation
In this Review, Chen and Liu discuss the latest developments in prime editing systems, including improvements to their editing efficiency and capabilities, as well as diverse emerging applications in research and preclinical therapeutic studies.
- Peter J. Chen
- & David R. Liu
-
Research Highlight |
 RADARs and READRs for programmable RNA sensing
RADARs and READRs for programmable RNA sensing
Two new papers report programmable systems that leverage ADAR adenosine deaminases for recording transcript abundance.
- Darren J. Burgess
-
Research Highlight |
 Neighbourly modulation of transcript isoforms
Neighbourly modulation of transcript isoforms
A paper in Science describes a system in synthetic yeast chromosomes in which the properties of genetic sequences change depending on the neighbouring transcriptional activity.
- Lucia Brunello
-
Research Highlight |
 Multitasking for base editors
Multitasking for base editors
Three new studies in Nature Biotechnology combine the adenine and cytosine deaminase activities of single base editors to generate dual base editor systems for combinatorial editing in human cells.
- Darren J. Burgess
-
Research Highlight |
 A platform for RNA virus cloning
A platform for RNA virus cloning
A study reports on the suitability of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a platform for the assembly and maintenance of diverse RNA virus genomes, including SARS-CoV-2.
- Linda Koch
-
Research Highlight |
 A sound strategy for gene expression
A sound strategy for gene expression
A new study in Science reports a synthetic biology approach to encode an ultrasound-based gene expression reporter that is applicable to mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Darren J. Burgess
-
Research Highlight |
 Early-life antibiotic use and gut microbiota
Early-life antibiotic use and gut microbiota
A recent study in Nature Microbiology reports metagenomic signatures of early-life antibiotic treatment and hospitalization associated with preterm birth that persist long-term.
- Linda Koch
-
Research Highlight |
 Expanding options for RNA based editors
Expanding options for RNA based editors
Two recent studies report innovative RNA base editing tools: adenine editing without the requirement for exogenous enzymes, and a new ability to edit cytosines.
- Darren J. Burgess
-
Review Article |
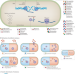 Sequencing-based methods and resources to study antimicrobial resistance
Sequencing-based methods and resources to study antimicrobial resistance
Next-generation sequencing has improved the identification and characterization of antimicrobial resistance. Focusing on sequence-based discovery of antibiotic resistance genes, this Review discusses computational strategies and resources for resistance gene identification in genomic and metagenomic samples, including recent deep-learning approaches.
- Manish Boolchandani
- , Alaric W. D’Souza
- & Gautam Dantas
-
Research Highlight |
 Synthetic readers and writers for mammalian chromatin
Synthetic readers and writers for mammalian chromatin
A study in Cell reports the development of a synthetic, modular and programmable read–write system that serves as a platform for programming epigenetic functions in mammalian cells and can aid the analysis of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms.
- Michelle Trenkmann
-
Review Article |
 Base editing: precision chemistry on the genome and transcriptome of living cells
Base editing: precision chemistry on the genome and transcriptome of living cells
Genome editing through direct editing of bases holds promise for achieving precise genomic changes at single-nucleotide resolution while minimizing the occurrence of potentially mutagenic double-strand DNA breaks. In this Review, Rees and Liu provide a comprehensive account of the state of the art of base editing of DNA and RNA, including the progressive improvements to methodologies, understanding and avoiding unintended edits, cellular and organismal delivery of editing reagents and diverse applications in research and therapeutic settings.
- Holly A. Rees
- & David R. Liu
-
Review Article |
 DNA-based memory devices for recording cellular events
DNA-based memory devices for recording cellular events
In this Review, Sheth and Wang describe emerging synthetic biology approaches for using DNA as a memory device for recording cellular events, including the various methodological steps from detecting diverse signals, converting them into DNA alterations and reading out and interpreting the recorded information. Furthermore, they discuss potential applications as biotechnological and environmental biosensors.
- Ravi U. Sheth
- & Harris H. Wang
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Emerging and evolving concepts in gene essentiality
Emerging and evolving concepts in gene essentiality
Identifying which genes in a genome are essential for survival has been a long-standing goal of geneticists. This Review discusses our evolving understanding of cellular gene essentiality across diverse organisms. It describes how essentiality is often non-absolute but is instead dependent on the environment or genetic background and how this knowledge can be exploited therapeutically.
- Giulia Rancati
- , Jason Moffat
- & Norman Pavelka
-
Opinion |
 Beyond editing to writing large genomes
Beyond editing to writing large genomes
Advances in genome sequencing, editing and synthetic biology have enhanced the feasibility of large-scale genome engineering, termed genome writing. In this Opinion article, Chari and Church discuss the strengths and limitations of diverse strategies for genome writing, including extensively modifying existing genomes versus synthesizing genomesde novo, and they provide future visions for writing large genomes.
- Raj Chari
- & George M. Church
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Cheating evolution: engineering gene drives to manipulate the fate of wild populations
Cheating evolution: engineering gene drives to manipulate the fate of wild populations
RNA-guided endonucleases have the potential to revolutionize the engineering of synthetic gene drives, which may be particularly useful for the control of vector-borne diseases. Here, the authors review different types of engineered gene drives and their potential applications, as well as considerations regarding the safety and regulation of gene drives for the manipulation of wild populations.
- Jackson Champer
- , Anna Buchman
- & Omar S. Akbari
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Genomes by design
Genomes by design
Genome engineering can be used to introduce targeted genetic changes to design and reprogramme organisms, to introduce new functionalities and to discover causal associations in evolving phenotypes. In this Review, the rationale, techniques and applications in genome engineering are described, outlining key advances, technological goals and challenges, as genome engineering approaches move towards massively parallel platforms.
- Adrian D. Haimovich
- , Paul Muir
- & Farren J. Isaacs
-
Review Article |
 Methods for the directed evolution of proteins
Methods for the directed evolution of proteins
Directed evolution uses laboratory-based evolution to enhance the properties of biomolecules, primarily to generate proteins with optimized or novel activities. This Review discusses the diverse range of technologies for the directed evolution of proteins, particularly methods for generating diversity in the gene library and approaches for screening and selecting for variants with desired properties. The relative strengths and limitations of these approaches are highlighted to guide readers to appropriate strategies.
- Michael S. Packer
- & David R. Liu
-
-
Review Article |
 Chromatin regulation at the frontier of synthetic biology
Chromatin regulation at the frontier of synthetic biology
Synthetic biology approaches to characterize gene regulation have largely used transcription factor circuits in bacteria. However, the multilayered regulation of genes by chromatin in eukaryotes provides opportunities for more sophisticated control of gene expression. This Review describes diverse approaches for engineering eukaryotic chromatin states, the insights gained into physiological gene regulation principles, and the broad potential applications throughout biomedical research and industry.
- Albert J. Keung
- , J. Keith Joung
- & James J. Collins
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Emerging biomedical applications of synthetic biology
Emerging biomedical applications of synthetic biology
Synthetic biological devices can be engineered to achieve high levels of precision and specificity, which makes them ideally suited for use in clinical settings. Devices are being developed to meet a range of biomedical needs, including specific cancer therapies and metabolic control.
- Wilfried Weber
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
-

 Expanding the reach of Cas9
Expanding the reach of Cas9 A drop in an ocean of gene variants
A drop in an ocean of gene variants Multiplex genome engineering in eukaryotes
Multiplex genome engineering in eukaryotes Shining a light on genetic screen strategies
Shining a light on genetic screen strategies Building a custom eukaryotic genome de novo
Building a custom eukaryotic genome de novo Systematic tuning of expression
Systematic tuning of expression Automating genetic circuit design
Automating genetic circuit design Genetic kill switches — a matter of life or death
Genetic kill switches — a matter of life or death UBER — a portable system for cross-species genetic engineering
UBER — a portable system for cross-species genetic engineering GMOs in lockdown
GMOs in lockdown Multi-tasking CRISPR RNA scaffolds
Multi-tasking CRISPR RNA scaffolds Just add water — programmable in vitro diagnostics
Just add water — programmable in vitro diagnostics A chromatin-based recruitment drive
A chromatin-based recruitment drive In vivo replication of semi-synthetic DNA
In vivo replication of semi-synthetic DNA Cut up to bring together
Cut up to bring together Fitness from drug resistance
Fitness from drug resistance Quality and quantity
Quality and quantity A circuit to remember
A circuit to remember Simplifying design
Simplifying design Licensing bacteria to kill
Licensing bacteria to kill Go ahead, make my DNA
Go ahead, make my DNA