Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of peptide-free and partially loaded MHC class I molecules reveal mechanisms of peptide selection
Structures of peptide-free and partially loaded MHC class I molecules reveal mechanisms of peptide selection
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) class I molecules present tightly binding peptides on the cell surface for recognition by cytotoxic T cells. Here, the authors present the crystal structures of a disulfide-stabilized human MHC class I molecule in the peptide-free state and bound with dipeptides, and find that peptide binding is accompanied by concerted conformational switches of the amino acid side chains in the binding pockets.
- Raghavendra Anjanappa
- , Maria Garcia-Alai
- & Rob Meijers
-
Article
| Open Access Decorating bacteria with self-assembled synthetic receptors
Decorating bacteria with self-assembled synthetic receptors
Cell surface proteins mediate the interactions between cells and their extracellular environment. Here the authors design synthetic biomemetic receptor-like sensors that facilitate programmable interactions between bacteria and their target.
- Naama Lahav-Mankovski
- , Pragati Kishore Prasad
- & David Margulies
-
Article
| Open Access A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening
A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening
Bacteria represent an unexploited reservoir of biosensing proteins. Here the authors use genomic screens and functional assays to isolate a progesterone sensing allosteric transcription factor and use a FRET-based method to develop an optical progesterone sensor.
- Chloé Grazon
- , R C. Baer
- & James E. Galagan
-
Article
| Open Access Blackjack mutations improve the on-target activities of increased fidelity variants of SpCas9 with 5′G-extended sgRNAs
Blackjack mutations improve the on-target activities of increased fidelity variants of SpCas9 with 5′G-extended sgRNAs
Mutations to SpCas9 can improve fidelity and mitigate off-target effects. Here the authors generate ‘Blackjack’ mutations that improve fidelity while retaining effectiveness with 21G-sgRNAs.
- Péter István Kulcsár
- , András Tálas
- & Ervin Welker
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro ribosome synthesis and evolution through ribosome display
In vitro ribosome synthesis and evolution through ribosome display
Directed evolution of the ribosome is challenging because the requirement of cell viability limits the mutations that can be made. Here the authors develop a platform for in vitro ribosome synthesis and evolution (RISE) to overcome these constraints.
- Michael J. Hammerling
- , Brian R. Fritz
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access A toxin-antidote CRISPR gene drive system for regional population modification
A toxin-antidote CRISPR gene drive system for regional population modification
CRISPR homing gene drives are highly invasive and can fail due to the rapid evolution of resistance. Here the authors present TARE drive, inspired by naturally occurring selfish genetic elements, which is less vulnerable to resistance and can potentially be confined to a target population.
- Jackson Champer
- , Esther Lee
- & Philipp W. Messer
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic engineering to probe the molecular choreography of STIM1-mediated cell signaling
Optogenetic engineering to probe the molecular choreography of STIM1-mediated cell signaling
Optogenetic tools have been used to control cellular behaviours but their use to probe structure-function relations of signalling proteins are underexplored. Here the authors engineer optogenetic modules into STIM1 to dissect molecular details of STIM1-mediated signalling and control various cellular events.
- Guolin Ma
- , Lian He
- & Yubin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access DNA-based artificial molecular signaling system that mimics basic elements of reception and response
DNA-based artificial molecular signaling system that mimics basic elements of reception and response
Cells communicate with the outside world to maintain homeostasis. Here the authors design a synthetic biology DNA-based signalling system AMSsys that responds to the presence of ATP.
- Ruizi Peng
- , Liujun Xu
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled division of cell-sized vesicles by low densities of membrane-bound proteins
Controlled division of cell-sized vesicles by low densities of membrane-bound proteins
Membrane fission of a cell into two daughters is a core ability of cell-based life. Here the authors show that in artificial cells division can be controlled by regulating membrane curvature using low protein density.
- Jan Steinkühler
- , Roland L. Knorr
- & Reinhard Lipowsky
-
Perspective
| Open Access Organizing genome engineering for the gigabase scale
Organizing genome engineering for the gigabase scale
Genome-scale engineering requires the integration of a wide range of in silico and in vivo technologies, as well data management procedures and legal infrastructure. Here the authors provide a list of recommendations to address these challenges.
- Bryan A. Bartley
- , Jacob Beal
- & Elizabeth A. Strychalski
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the physical limits of reliable DNA data retrieval
Probing the physical limits of reliable DNA data retrieval
The physical limits and reliability of PCR-based random access of DNA encoded data is unknown. Here the authors demonstrate reliable file recovery from as few as ten copies per sequence, providing a data density limit of 17 exabytes per gram.
- Lee Organick
- , Yuan-Jyue Chen
- & Luis Ceze
-
Article
| Open Access Rewiring of endogenous signaling pathways to genomic targets for therapeutic cell reprogramming
Rewiring of endogenous signaling pathways to genomic targets for therapeutic cell reprogramming
Current cellular rewiring designs are typically tailored to detect single inputs. Here the authors present GEARs that function independently of engineered receptor/reporter systems and directly reroute endogenous signaling pathways to alternative genomic loci using dCas9-directed gene expression.
- Krzysztof Krawczyk
- , Leo Scheller
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access An ultra-stable cytoplasmic antibody engineered for in vivo applications
An ultra-stable cytoplasmic antibody engineered for in vivo applications
Antibodies expressed in the cytosol often form insoluble aggregates, which makes it hard to target intracellular proteins. Here the authors engineer an ultra-stable cytoplasmic antibody (STAND) with a low isoelectric point that can be used in vivo.
- Hiroyuki Kabayama
- , Makoto Takeuchi
- & Katsuhiko Mikoshiba
-
Article
| Open Access A set of monomeric near-infrared fluorescent proteins for multicolor imaging across scales
A set of monomeric near-infrared fluorescent proteins for multicolor imaging across scales
Monomeric near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent proteins (FPs) from bacterial phytochromes bring potential advantages, but their brightness in cells is lower than dimeric NIR FPs. Here the authors develop enhanced monomeric NIR FPs enabling imaging across different scales without the trade-off between brightness and monomeric state.
- Mikhail E. Matlashov
- , Daria M. Shcherbakova
- & Vladislav V. Verkhusha
-
Article
| Open Access Non-invasive optical control of endogenous Ca2+ channels in awake mice
Non-invasive optical control of endogenous Ca2+ channels in awake mice
Optogenetic applications in the brain of live animals often require the use of optic fibers due to poor tissue-penetration of blue light. Here the authors present monSTIM1, an improved high sensitivity optogenetic tool able to modulate Ca2+ signaling in the brain of awake mice using non-invasive light stimulation.
- Sungsoo Kim
- , Taeyoon Kyung
- & Won Do Heo
-
Article
| Open Access Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits
Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits
DNA strand displacement reactions can be difficult to scale up for computational tasks. Here the authors develop DNA switching circuits that achieve high-speed computing with fewer molecules.
- Fei Wang
- , Hui Lv
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-functional genome-wide CRISPR system for high throughput genotype–phenotype mapping
Multi-functional genome-wide CRISPR system for high throughput genotype–phenotype mapping
Genome-scale engineering is generally limited to single methods of alteration such as overexpression, repression or deletion. Here the authors present a tri-functional CRISPR system that can engineer complex synergistic interactions in a genome-wide manner.
- Jiazhang Lian
- , Carl Schultz
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro implementation of robust gene regulation in a synthetic biomolecular integral controller
In vitro implementation of robust gene regulation in a synthetic biomolecular integral controller
Feedback mechanisms for synthetic gene circuits are necessary to provide robustness to external perturbations. Here the authors validate a biomolecular controller based on a sigma and anti-sigma factor to achieve stable gene expression in the face of external disturbances in an in vitro synthetic gene circuit.
- Deepak K. Agrawal
- , Ryan Marshall
- & Eduardo D Sontag
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering protein assemblies with allosteric control via monomer fold-switching
Engineering protein assemblies with allosteric control via monomer fold-switching
The design of protein assemblies is a major thrust for biomolecular engineering and nanobiotechnology. Here the authors demonstrate a general mechanism for designing allosteric macromolecular assemblies and showcase a proof of concept for engineered allosteric protein assembly.
- Luis A. Campos
- , Rajendra Sharma
- & Victor Muñoz
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Anti-inflammatory treatments for gastrointestinal diseases can often have detrimental side effects. Here the authors engineer E. coli Nissle 1917 to create a fibrous matrix that has a protective effect in DSS-induced colitis mice.
- Pichet Praveschotinunt
- , Anna M. Duraj-Thatte
- & Neel S. Joshi
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and tunable metabolite control for robust minimal-equipment assessment of serum zinc
Dynamic and tunable metabolite control for robust minimal-equipment assessment of serum zinc
Tightly controlling cell output is challenging, which has limited development and applications of bacterial sensors. Here the authors develop tunable, fast-responding sensors to control production of metabolic pigments and use them to assess zinc deficiency in a low-cost, minimal equipment fashion.
- Monica P. McNerney
- , Cirstyn L. Michel
- & Mark P. Styczynski
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic chimeric nucleases function for efficient genome editing
Synthetic chimeric nucleases function for efficient genome editing
CRISPR-Cas systems have well characterized, modular structures. Here the authors use that architecture to design a Cas12a library of 560 synthetic chimeras, with altered PAM preferences and specificities.
- R. M. Liu
- , L. L. Liang
- & R. T. Gill
-
Article
| Open Access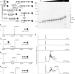 Cytoplasmic glycoengineering enables biosynthesis of nanoscale glycoprotein assemblies
Cytoplasmic glycoengineering enables biosynthesis of nanoscale glycoprotein assemblies
Established bacterial glycoengineering platforms limit access to protein and glycan substrates. Here the authors design a cytoplasmic protein glycosylation system, Glycoli, to generate a variety of multivalent glycostructures.
- Hanne L. P. Tytgat
- , Chia-wei Lin
- & Timothy G. Keys
-
Article
| Open Access A cell-free biosynthesis platform for modular construction of protein glycosylation pathways
A cell-free biosynthesis platform for modular construction of protein glycosylation pathways
Constructing biosynthetic pathways to study and engineer glycoprotein structures is difficult. Here, the authors use GlycoPRIME, a cell-free workflow for mixing-and-matching glycosylation enzymes, to evaluate 37 putative glycosylation pathways and discover routes to 18 new glycoprotein structures
- Weston Kightlinger
- , Katherine E. Duncker
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency and integrable DNA arithmetic and logic system based on strand displacement synthesis
High-efficiency and integrable DNA arithmetic and logic system based on strand displacement synthesis
Current DNA computational systems are constrained by integration efficiency, device structures and limited functions. Here the authors design a DNA arithmetic logic unit that uses polymerase-mediated strand displacement.
- Haomiao Su
- , Jinglei Xu
- & Xiang Zhou
-
Perspective
| Open Access Pathways to cellular supremacy in biocomputing
Pathways to cellular supremacy in biocomputing
Synthetic biology uses cells as its computing substrate, often based on the genetic circuit concept. In this Perspective, the authors argue that existing synthetic biology approaches based on classical models of computation limit the potential of biocomputing, and propose that living organisms have under-exploited capabilities.
- Lewis Grozinger
- , Martyn Amos
- & Angel Goñi-Moreno
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding the limits of the second genetic code with ribozymes
Expanding the limits of the second genetic code with ribozymes
Flexizymes have been used to expand the scope of chemical substrates for ribosome-directed polymerization in vitro. Here the authors deduce design rules of Flexizyme-mediated tRNA acylation that more effectively predict the incorporation of new monomers into peptides.
- Joongoo Lee
- , Kenneth E. Schwieter
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access An engineered human Fc domain that behaves like a pH-toggle switch for ultra-long circulation persistence
An engineered human Fc domain that behaves like a pH-toggle switch for ultra-long circulation persistence
Lee et al. report an engineered IgG1 Fc domain that behaves like an hFcRn binding pH toggle switch. The authors show that this new half-life extension Fc domain confers improved pharmacokinetics in new humanized knock-in mouse strains that recapitulate the key processes for antibody persistence in circulation.
- Chang-Han Lee
- , Tae Hyun Kang
- & George Georgiou
-
Article
| Open Access Oncolytic adenovirus programmed by synthetic gene circuit for cancer immunotherapy
Oncolytic adenovirus programmed by synthetic gene circuit for cancer immunotherapy
It is difficult to improve the efficacy of oncolytic virotherapy due to immune system responses and limited understanding of population dynamics. Here the authors use synthetic biology gene circuits to control adenoviral replication and release of immunomodulators in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
- Huiya Huang
- , Yiqi Liu
- & Zhen Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptional programming using engineered systems of transcription factors and genetic architectures
Transcriptional programming using engineered systems of transcription factors and genetic architectures
Successful approaches for controlling gene expression modulate mRNA synthesis by coupling it to inducible transcription effectors. Here the authors design 27 non-natural and non-synonymous transcription factors.
- Ronald E. Rondon
- , Thomas M. Groseclose
- & Corey J. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access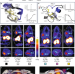 Evaluation of integrin αvβ6 cystine knot PET tracers to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Evaluation of integrin αvβ6 cystine knot PET tracers to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Knottin is a cystine knot peptide. Here, the authors develop a knottin-based tracer for positron emission tomography and demonstrate its ability to detect cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through selective binding to integrin αvβ6.
- Richard H. Kimura
- , Ling Wang
- & Sanjiv S. Gambhir
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial variability in the mammalian gut captured by a single-cell synthetic oscillator
Bacterial variability in the mammalian gut captured by a single-cell synthetic oscillator
Synthetic gene oscillators can be used to control timed function and periodic expression of genes. Here the authors demonstrate in vivo implementation in the mammalian gut that can keep time over several days.
- David T. Riglar
- , David L. Richmond
- & Pamela A. Silver
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated evolutionary analysis reveals antimicrobial peptides with limited resistance
Integrated evolutionary analysis reveals antimicrobial peptides with limited resistance
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are emerging as drug candidates, but the risk of pathogen resistance is not well understood. Here, the authors investigate AMP resistance evolution in E. coli, finding physicochemical features that make AMPs less prone to resistance and no cross- or horizontally-acquired resistance.
- Réka Spohn
- , Lejla Daruka
- & Csaba Pál
-
Article
| Open Access A tunable dual-input system for on-demand dynamic gene expression regulation
A tunable dual-input system for on-demand dynamic gene expression regulation
Cellular systems have numerous mechanisms to control gene expression. Here the authors build a Tet-On system with conditional destablising elements to regulate gene expression and protein stability, allowing fine modulation of mESC signalling pathways.
- Elisa Pedone
- , Lorena Postiglione
- & Lucia Marucci
-
Article
| Open Access Framework engineering to produce dominant T cell receptors with enhanced antigen-specific function
Framework engineering to produce dominant T cell receptors with enhanced antigen-specific function
Increasing TCR cell surface expression can potentiate T cell responses to low-concentrations of antigen. Here the authors identify aminoacids in human TCR variable domains that impact its surface expression, and demonstrate how editing these residues can improve T cell activation and effector function without altering antigen specificity.
- Sharyn Thomas
- , Fiyaz Mohammed
- & Hans J. Stauss
-
Article
| Open Access Human immunoglobulin G hinge regulates agonistic anti-CD40 immunostimulatory and antitumour activities through biophysical flexibility
Human immunoglobulin G hinge regulates agonistic anti-CD40 immunostimulatory and antitumour activities through biophysical flexibility
Conserved regions of the antibody molecule impact its downstream biological effects. Here the authors show that a rigid hinge conformation increases the agonistic activity of CD40 and DR5 antibodies, distinctly from FcγR-binding, suggesting that the hinge and FcR binding regions can be separately modified to optimize therapies.
- Xiaobo Liu
- , Yingjie Zhao
- & Fubin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Massively parallel RNA device engineering in mammalian cells with RNA-Seq
Massively parallel RNA device engineering in mammalian cells with RNA-Seq
Synthetic RNA-based devices can dynamically control a wide range of processes. Here the authors develop a quantitative and high-throughput mammalian cell-based RNA-seq assay to efficiently engineer ribozyme switches.
- Joy S. Xiang
- , Matias Kaplan
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced CRISPR-based DNA demethylation by Casilio-ME-mediated RNA-guided coupling of methylcytosine oxidation and DNA repair pathways
Enhanced CRISPR-based DNA demethylation by Casilio-ME-mediated RNA-guided coupling of methylcytosine oxidation and DNA repair pathways
DNA methylation plays an important role in regulating a wide variety of cellular processes and is implicated in a range of diseases. Here the authors present Casilio-ME to assemble protein complexes to demethylate target loci.
- Aziz Taghbalout
- , Menghan Du
- & Albert W. Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial co-culture with cell signaling translator and growth controller modules for autonomously regulated culture composition
Bacterial co-culture with cell signaling translator and growth controller modules for autonomously regulated culture composition
To avoid metabolic overload and divide tasks, synthetic biologists are turning to microbial consortia engineering. Here the authors design a co-culture controller that autonomously regulates population composition.
- Kristina Stephens
- , Maria Pozo
- & William E. Bentley
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered ribosomes with tethered subunits for expanding biological function
Engineered ribosomes with tethered subunits for expanding biological function
Ribo-T is a tethered ribosome complex capable of orthogonal ribosome-mRNA functionality, but has low activity. Here the authors evolve new tether designs that support faster growth and increased protein expression.
- Erik D. Carlson
- , Anne E. d’Aquino
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria
Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria
CRISPR activation strategies in bacteria are limited due to the reliance on σ70 promoters. Here the authors demonstrate eukaryote-like gene activation with high dynamic ranges using σ54- dependent promoters.
- Yang Liu
- , Xinyi Wan
- & Baojun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal monoterpenoid biosynthesis in yeast constructed on an isomeric substrate
Orthogonal monoterpenoid biosynthesis in yeast constructed on an isomeric substrate
Titers of monoterpenoids production in yeast are low due to the fact that the geranyl diphosphate (GPP)-based pathway can redirect metabolic fluxes to growth. Here, the authors build an orthogonal pathway by selecting the cis isomer of GPP as an alternative precursor and achieve high titer monoterpene production.
- Codruta Ignea
- , Morten H. Raadam
- & Sotirios C. Kampranis
-
Article
| Open Access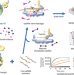 A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensing platform for the highly sensitive detection of diverse small molecules
A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensing platform for the highly sensitive detection of diverse small molecules
Bacterial allosteric transcription factors can sense and respond to a variety of small molecules. Here the authors present CaT-SMelor which uses Cas12a and allosteric transcription factors to detect small molecules in the nanomolar range.
- Mindong Liang
- , Zilong Li
- & Li-Xin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A standard for near-scarless plasmid construction using reusable DNA parts
A standard for near-scarless plasmid construction using reusable DNA parts
Construction of plasmids from multiple fragments often uses customised parts and leaves scars where fragments are joined. Here the authors develop a method for barcoding fragments and constructing plasmids in a scarless manner from a collection of standard parts.
- Xiaoqiang Ma
- , Hong Liang
- & Kang Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access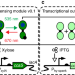 Optogenetic control of Bacillus subtilis gene expression
Optogenetic control of Bacillus subtilis gene expression
Bacillus subtilis has complex spatial and temporal gene expression patterns but currently lacks optogenetic tools to explore these processes. Here the authors import and debug a cyanobacterial green light sensor pathway and show that it enables precise optical control of gene expression.
- Sebastian M. Castillo-Hair
- , Elliot A. Baerman
- & Jeffrey J. Tabor
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial coiled coil biomineralisation protein for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Artificial coiled coil biomineralisation protein for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Proteins have been used in the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles but issues with aggregation limit this application. Here, the authors report on the synthesis of coiled proteins that display the active loop of the natural proteins to avoid aggregation and investigate the application in nanoparticle synthesis.
- Andrea E. Rawlings
- , Lori A. Somner
- & Sarah S. Staniland
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable mutually exclusive alternative splicing for generating RNA and protein diversity
Programmable mutually exclusive alternative splicing for generating RNA and protein diversity
Alternative splicing expands the genetic coding capacity and proteomic diversity of the cell. Here the authors create a synthetic biology platform for regulating four programmable exons in modular transcription factors.
- Melina Mathur
- , Cameron M. Kim
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access COMPASS for rapid combinatorial optimization of biochemical pathways based on artificial transcription factors
COMPASS for rapid combinatorial optimization of biochemical pathways based on artificial transcription factors
Metabolic engineering requires the balancing of gene expression to obtain optimal output. Here the authors present COMPASS – COMbinatorial Pathway ASSembly – which uses plant-derived artificial transcription factors and cloning of thousands of DNA constructs in parallel to rapidly optimise pathways.
- Gita Naseri
- , Jessica Behrend
- & Bernd Mueller-Roeber
-
Article
| Open Access Terminator-free template-independent enzymatic DNA synthesis for digital information storage
Terminator-free template-independent enzymatic DNA synthesis for digital information storage
Adoption of DNA as a data storage medium could be accelerated with specialized synthesis processes and codecs. The authors describe TdT-mediated DNA synthesis in which data is stored in transitions between non-identical nucleotides and the use of synchronization markers to provide error tolerance.
- Henry H. Lee
- , Reza Kalhor
- & George M. Church

 Cell-in-the-loop pattern formation with optogenetically emulated cell-to-cell signaling
Cell-in-the-loop pattern formation with optogenetically emulated cell-to-cell signaling