Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Efficiently accelerated free electrons by metallic laser accelerator
Efficiently accelerated free electrons by metallic laser accelerator
Accelerated electron beams are potentially useful for imaging and different type of light sources. Here the authors demonstrate electron acceleration using metallic laser acceleration with efficiency comparable to that of dielectric laser accelerators.
- Dingguo Zheng
- , Siyuan Huang
- & Jianqi Li
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space observation of ergodicity transitions in artificial spin ice
Real-space observation of ergodicity transitions in artificial spin ice
Artificial spin ice systems have been used to simulate a variety of phenomena including phase transitions. Here, the authors expand the scope of applications to encompass non-ergodic dynamics, by reporting real-space imaging of ergodicity transitions in a vortex-frustrated artificial spin ice.
- Michael Saccone
- , Francesco Caravelli
- & Alan Farhan
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant perovskite solar cells with extended band edge
Resonant perovskite solar cells with extended band edge
Further extending the band edge of perovskite approaching the ideal bandgap of single-junction solar cell is essential to improve device efficiency. Here, the authors integrate optical resonances with perovskite solar cells to extend the band edge, achieving EQE-integrated current of 26.0 mA/cm2.
- Jiangang Feng
- , Xi Wang
- & Yi Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Linear-to-circular polarization conversion with full-silica meta-optics to reduce nonlinear effects in high-energy lasers
Linear-to-circular polarization conversion with full-silica meta-optics to reduce nonlinear effects in high-energy lasers
Nonlinear effects and damage of optical components are unavoidable when laser intensity is very high. Here the authors demonstrate metamaterial-based wave plate for linear to circular polarization conversion of a high-energy (high-power) laser to significantly weaken these effects.
- Nicolas Bonod
- , Pierre Brianceau
- & Jérôme Neauport
-
Article
| Open Access Decorated bacteria-cellulose ultrasonic metasurface
Decorated bacteria-cellulose ultrasonic metasurface
The researchers report a class of silica-nanoparticle-decorated bacteria-cellulose ultrasonic metasurfaces that feature excellent stability in water and mechanical processability. They demonstrate it as holographic meta-lens and 3D imaging meta-lens.
- Zong-Lin Li
- , Kun Chen
- & Xue-Feng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves
A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves
The authors show a universal metasurface antenna capable of simultaneously and independently controlling all five fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves, including amplitude, phase, frequency, polarization, and momentum.
- Geng-Bo Wu
- , Jun Yan Dai
- & Chi Hou Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Correlating metasurface spectra with a generation-elimination framework
Correlating metasurface spectra with a generation-elimination framework
The authors present a generation-elimination framework that correlates the spectra from different frequency bands, where the inaccessible spectra are precisely forecasted without consulting structural information. The spectral correlation will accelerate the unification of all metasurface designs and facilitate versatile applications involving cross-wavelength information correlation.
- Jieting Chen
- , Chao Qian
- & Hongsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable trapping of single nanosized extracellular vesicles using plasmonics
Scalable trapping of single nanosized extracellular vesicles using plasmonics
Manipulation of nano-sized extracellular vesicles are of significant interest for disease detection, monitoring, and therapeutics, yet it is still challenging to expedite the process. Here, the authors presented geometry-induced electrohydrodynamic tweezers, which enable fast parallel transport and trapping of single vesicle within seconds.
- Chuchuan Hong
- & Justus C. Ndukaife
-
Article
| Open Access Over-coupled resonator for broadband surface enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA)
Over-coupled resonator for broadband surface enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA)
Nanoresonator is proven to be an excellent platform for molecular detection, yet a set of them is necessary to identify a molecule fingerprint. Here, the authors utilise low quality resonators with large radiative losses, despite its lower quality factor, to identify molecular absorption spectrum between 5 and 10 μm.
- Laura Paggi
- , Alice Fabas
- & Patrick Bouchon
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh-efficient material informatics inverse design of thermal metamaterials for visible-infrared-compatible camouflage
Ultrahigh-efficient material informatics inverse design of thermal metamaterials for visible-infrared-compatible camouflage
The progress development of multispectral camouflage technologies has been limited to the choice of materials and structural design. Here, authors propose a material-informatics-based inverse design framework to efficiently design multilayer metamaterials with satisfying visible-infrared camouflage performance.
- Wang Xi
- , Yun-Jo Lee
- & Run Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Superscattering emerging from the physics of bound states in the continuum
Superscattering emerging from the physics of bound states in the continuum
The scattering of light by small particles plays a central role in a myriad of fields. Here, the authors demonstrate a super dipole resonance that arises when two resonant modes of a small particle interfere, overcoming a widely accepted limitation to the cross section.
- Adrià Canós Valero
- , Hadi K. Shamkhi
- & Alexander S. Shalin
-
Article
| Open Access Adiabatic topological photonic interfaces
Adiabatic topological photonic interfaces
Smooth topological photonic interfaces lead to less localized boundary modes which improves their guiding characteristics in both spin- and valley Hall metasurfaces. The modes become insensitive to the lattice details, showcasing improved bandgap crossing and longer propagation distances.
- Anton Vakulenko
- , Svetlana Kiriushechkina
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Article
| Open Access Incandescent temporal metamaterials
Incandescent temporal metamaterials
Here the authors employ quantum electrodynamics to formulate thermal emission effects in time-modulated media, resulting in innovative thermal emitters. They show that time modulation induces strong field fluctuations in epsilon-near-zero bodies, enabling narrowband emission across the entire range of wavevectors, from near to far-field regimes.
- J. Enrique Vázquez-Lozano
- & Iñigo Liberal
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces
Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces
The authors present a high quality factor metasurface that enables sensitive and highly-parallelized detection of biomolecules. Amplification-free detection of gene fragments down to femtomolar levels is demonstrated within 5 minutes, for rapid nucleic acid analysis.
- Jack Hu
- , Fareeha Safir
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic control of hybrid grafted perfect vector vortex beams
Dynamic control of hybrid grafted perfect vector vortex beams
A metasurface is used to generate a hybrid grafted perfect vector vortex beam, which can be dynamically controlled with a half waveplate. The beam has spatially variant rates of polarization change due to the involvement of more topological charges.
- Hammad Ahmed
- , Muhammad Afnan Ansari
- & Xianzhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving near-perfect light absorption in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides through band nesting
Achieving near-perfect light absorption in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides through band nesting
The authors demonstrate near-perfect light absorption using only two atomic layers of transition metal dichalcogenides. This is achieved by reducing interlayer interaction which optimizes band nesting, and does not require the use of complex metasurfaces.
- Seungjun Lee
- , Dongjea Seo
- & Tony Low
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear multi-magnon scattering in artificial spin ice
Nonlinear multi-magnon scattering in artificial spin ice
Artificial spin ices are composed of tiny magnets arranged in a lattice. Despite their simplicity, they exhibit rich dynamic magnetic behaviour. Here, Lendinez et al demonstrate that, like continuous magnetic thin films, artificial spin ices can exhibit non-linear magnon-magnon scattering which, in conjunction with their reconfigurability, offers great potential for tuneable magnon transport.
- Sergi Lendinez
- , Mojtaba T. Kaffash
- & M. Benjamin Jungfleisch
-
Article
| Open Access Long-wave infrared photothermoelectric detectors with ultrahigh polarization sensitivity
Long-wave infrared photothermoelectric detectors with ultrahigh polarization sensitivity
Infrared polarization-sensitive photodetectors are attractive owing to their widespread applications. Here, the authors report a long-wave infrared photodetector with an ultrahigh polarization sensitivity by leveraging the 1D geometry of Tellurium nanoribbon and the finite-size effect of a perfect plasmonic absorber.
- Mingjin Dai
- , Chongwu Wang
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Eye accommodation-inspired neuro-metasurface focusing
Eye accommodation-inspired neuro-metasurface focusing
Here the authors propose for the first time the concept of supervised-evolving learning (SEL) and a corresponding SEL-driven adaptive focusing (SELAF) system. This metasurface can adaptively realize focusing at any specified position for waves incident from any direction. This work demonstrates unprecedented potential for tasks involving real-time, fast and complex electromagnetic wave manipulation.
- Huan Lu
- , Jiwei Zhao
- & Hongsheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Point singularity array with metasurfaces
Point singularity array with metasurfaces
Optical singularities are typically 1D structures like vortices. This study used metasurfaces to position ten identical point singularities with tight confinement. This could miniaturize optical systems for super-resolution microscopy and dark traps.
- Soon Wei Daniel Lim
- , Joon-Suh Park
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Topological quadratic-node semimetal in a photonic microring lattice
Topological quadratic-node semimetal in a photonic microring lattice
Topological semimetals can host coexisting higher-order topological nodes that may enable unique physical properties. Here, based on these topological principles, authors design and experimentally realise simultaneous massive and massless chiral quasiparticles in a photonic microring lattice.
- Zihe Gao
- , Haoqi Zhao
- & Liang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-patterned inverse-designed mid-infrared metaoptics
3D-patterned inverse-designed mid-infrared metaoptics
The authors show computationally optimized, multilayer scattering structures in the mid-infrared for high efficiency imaging. Multispectral and polarization sorting devices are fabricated via two-photon lithography and characterized optically.
- Gregory Roberts
- , Conner Ballew
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access Dispersion-engineered metasurfaces reaching broadband 90% relative diffraction efficiency
Dispersion-engineered metasurfaces reaching broadband 90% relative diffraction efficiency
Authors demonstrate a dispersion engineered set of eight nanostructures capable of providing 0 to 2π full-phase coverage. Their design offers a broadband and polarization-insensitive 90% relative diffraction efficiency from 450 nm to 700 nm in wavelength.
- Wei Ting Chen
- , Joon-Suh Park
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot isotropic differential interference contrast microscopy
Single-shot isotropic differential interference contrast microscopy
The authors present a metasurface-assisted isotropic DIC microscopy technique. It is based on an original pattern of radial shear interferometry, that converts rectilinear shear into rotationally symmetric radial shear, enabling single-shot isotropic imaging capabilities.
- Xinwei Wang
- , Hao Wang
- & Xumin Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Antichiral surface states in time-reversal-invariant photonic semimetals
Antichiral surface states in time-reversal-invariant photonic semimetals
Here the authors proposed an approach to realize the antichiral surface states in a time-reversal invariant photonic system. They harnessed a synthetic gauge flux and observed a kz-dependent antichiral surface transport in their 3D metacrystal.
- Jian-Wei Liu
- , Fu-Long Shi
- & Jian-Wen Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption
Meta-optics empowered vector visual cryptography for high security and rapid decryption
Usual methods for optical encryption suffer from a tradeoff between the level of security and the complexity of operation given by multiple optical measurements or digital postprocessing. Here, the authors show a multi-d.o.f. metasurface-based vector optical manipulation protocol enabling secure decryption in real time.
- Fei Zhang
- , Yinghui Guo
- & Xiangang Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging-based intelligent spectrometer on a plasmonic rainbow chip
Imaging-based intelligent spectrometer on a plasmonic rainbow chip
The authors develop an imaging-based intelligent spectrometer on a plasmonic “rainbow” chip. It can accurately and precisely determine the spectroscopic and polarimetric information of the illumination spectrum using a single image assisted by suitably trained deep learning algorithms.
- Dylan Tua
- , Ruiying Liu
- & Qiaoqiang Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Iridium oxide nanoribbons with metastable monoclinic phase for highly efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Iridium oxide nanoribbons with metastable monoclinic phase for highly efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Well-defined metastable phase nanostructures are a core issue for catalyst design. Here, the authors report metastable monoclinic phase IrO2 nanoribbons obtained via a molten-alkali mechanochemical method, which exhibit intrinsic high performance towards the acidic oxygen evolution reaction.
- Fan Liao
- , Kui Yin
- & Qi Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical metamaterials made of freestanding quasi-BCC nanolattices of gold and copper with ultra-high energy absorption capacity
Mechanical metamaterials made of freestanding quasi-BCC nanolattices of gold and copper with ultra-high energy absorption capacity
The fabrication of freestanding 3D lattice structures with beam diameters less than 100 nm is a considerable challenge. Here, the authors report quasi-BCC nanolattices of gold and copper, featuring beam diameters as low as 34 nm, that demonstrate an exceptionally high capacity for energy absorption.
- Hongwei Cheng
- , Xiaoxia Zhu
- & Jinglai Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Monocular metasurface camera for passive single-shot 4D imaging
Monocular metasurface camera for passive single-shot 4D imaging
The authors present a monocular camera equipped with a single-layer metalens for passive single-shot 4D imaging. It can simultaneously perform high-accuracy depth sensing and highfidelity polarization imaging over an extended depth of field.
- Zicheng Shen
- , Feng Zhao
- & Yuanmu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access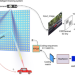 Intelligent metasurface system for automatic tracking of moving targets and wireless communications based on computer vision
Intelligent metasurface system for automatic tracking of moving targets and wireless communications based on computer vision
The authors present an intelligent metasurface system that uses a target detection algorithm combined with a depth camera, to automatically detect the position of moving targets and achieve real-time wireless communications. The system can operate for multiple targets in limited ambient light, outdoor and other realistic environments.
- Weihan Li
- , Qian Ma
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Gigahertz optoacoustic vibration in Sub-5 nm tip-supported nano-optomechanical metasurface
Gigahertz optoacoustic vibration in Sub-5 nm tip-supported nano-optomechanical metasurface
Nano-optomechanical systems plays an indispensable role in all-optical manipulation of light but high energy losses severely limit their development. Here the authors show ultrafast all-optical manipulation in a sub-5 nm tip-supported optomechanical metasurface.
- Renxian Gao
- , Yonglin He
- & Zhilin Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Giant polarization ripple in transverse pyroelectricity
Giant polarization ripple in transverse pyroelectricity
Pyroelectricity promises viable heat harvesting and sensing. Here, the authors identify transverse polarization ripple in pyroelectrics via heat localization and propagation decoupling and offer competitive power output to solar thermoelectrics.
- Yi Zhou
- , Tianpeng Ding
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative phase contrast imaging with a nonlocal angle-selective metasurface
Quantitative phase contrast imaging with a nonlocal angle-selective metasurface
The authors present an approach to phase imaging by using the non-local optical response of a guided-moderesonator metasurface. They demonstrate that this metasurface can be added to a conventional microscope to enable quantitative phase contrast imaging.
- Anqi Ji
- , Jung-Hwan Song
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot 3D imaging with point cloud projection based on metadevice
Single-shot 3D imaging with point cloud projection based on metadevice
The authors present a single-shot 3D imaging approach utilizing carefully designed point clouds projection based on a metasurface device. They show submillimeter depth accuracy and demonstrate the potential for hand gesture detection.
- Xiaoli Jing
- , Ruizhe Zhao
- & Lingling Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-decoupling of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers with complete phase modulation using on-chip integrated Jones matrix metasurfaces
Spin-decoupling of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers with complete phase modulation using on-chip integrated Jones matrix metasurfaces
Here the authors harness the on-chip integration of Jones matrix metasurfaces to demonstrate an ultra-compact approach to access and manipulate the optical spin states of vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) with previously unattainable phase controllability.
- Pei-Nan Ni
- , Pan Fu
- & Patrice Genevet
-
Article
| Open Access Radiative anti-parity-time plasmonics
Radiative anti-parity-time plasmonics
The parity-time symmetry has led to exotic phenomena and fruitful applications in optical systems. In this paper, the authors propose a leaky-wave-enabled anti-parity-time design and realize space-wave harnessing.
- Yumeng Yang
- , Xinrong Xie
- & Fei Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing symmetry-guaranteed pairs of bound states in the continuum in metasurfaces
Realizing symmetry-guaranteed pairs of bound states in the continuum in metasurfaces
Bound states in the continuum can enhance light-matter interactions across a wide range of optical systems. Here, the authors present a design paradigm for creating pairs of bound states whose optical responses can be predictably controlled.
- Chloe F. Doiron
- , Igal Brener
- & Alexander Cerjan
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of full-parameter Jones matrix in bilayer metasurface
Observation of full-parameter Jones matrix in bilayer metasurface
The realization of Jones matrix with full eight free parameters is particularly challenging. Here, the authors construct spatially varying Jones matrix with eight free parameters by cascading two-layer metasurfaces and use it for new optical functionalities.
- Yanjun Bao
- , Fan Nan
- & Baojun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-controlled tunable directional spin-driven photocurrents in a magnetic metamaterial with threefold rotational symmetry
Polarization-controlled tunable directional spin-driven photocurrents in a magnetic metamaterial with threefold rotational symmetry
By carefully structuring and patterning a material, it is possible to introduce emergent properties that would otherwise not exist. These metamaterials have allowed the development of a wide variety of new optical properties. Here, Matsubara et al present a magnetic metamaterial, where spin-currents can be directed by tuning the polarization of the incident light.
- Masakazu Matsubara
- , Takatsugu Kobayashi
- & Takeshi Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Stokes meta-hologram toward optical cryptography
Stokes meta-hologram toward optical cryptography
Achieving optical cryptography scheme with both high capacity and security is highly desirable. Here, authors report a Stokes meta-hologram with a hierarchical encryption strategy that allows vector encryptions to produce depth-masked ciphertexts.
- Xuyue Guo
- , Peng Li
- & Jianlin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access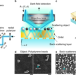 Hyperbolic material enhanced scattering nanoscopy for label-free super-resolution imaging
Hyperbolic material enhanced scattering nanoscopy for label-free super-resolution imaging
The authors demonstrate a label-free superresolution imaging method by using a hyperbolic material as a substrate for tailored light-matter interactions. The hyperbolic material enhanced scattering, combined with dark-field detection, result in 5.5-fold resolution improvement beyond the diffraction limit.
- Yeon Ui Lee
- , Shilong Li
- & Zhaowei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitivity and spectral control of network lasers
Sensitivity and spectral control of network lasers
Nanophotonic light sources with programmable emission spectrum are important building blocks for integrated photonics, sensing and optical computing. Here the authors tune the complex laser spectrum of a network laser achieving selective lasing of a single, two or more modes.
- Dhruv Saxena
- , Alexis Arnaudon
- & Riccardo Sapienza
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable metasurfaces via the humidity responsive swelling of single-step imprinted polyvinyl alcohol nanostructures
Tunable metasurfaces via the humidity responsive swelling of single-step imprinted polyvinyl alcohol nanostructures
PVA is a hydrogel that has attractive swelling properties for use in tunable photonic applications. Here, the authors exploit PVA with nanoimprint lithography to realize multiplexed optical encryption metasurfaces to display, hide, and destroy encrypted information.
- Byoungsu Ko
- , Trevon Badloe
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled filamentation instability as a scalable fabrication approach to flexible metamaterials
Controlled filamentation instability as a scalable fabrication approach to flexible metamaterials
The simple and scalable fabrication of high aspect ratio encapsulated flexible nanowire arrays with controlled size and periodicity is demonstrated and modelled, enabling nanophotonics applications requiring long-range order over several meters.
- William Esposito
- , Louis Martin-Monier
- & Fabien Sorin
-
Article
| Open Access Metasurface-driven full-space structured light for three-dimensional imaging
Metasurface-driven full-space structured light for three-dimensional imaging
3D depth sensing with structured light enables simultaneous imaging of multiple objects, but has limited field of view and low efficiency. Here, the authors demonstrate 3D imaging with scattered light from a metasurface composed of periodic supercells, covering a 180° field of view with a high-density dot array.
- Gyeongtae Kim
- , Yeseul Kim
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access Metamaterial-enabled asymmetric negative refraction of GHz mechanical waves
Metamaterial-enabled asymmetric negative refraction of GHz mechanical waves
Known examples of negative refraction in metamaterials do not distinguish between positive and negative angles of incidence. Here, the authors show that it is possible to break this symmetry using an asymmetric unit cell, and demonstrate it using a mechanical metamaterial working at GHz frequencies.
- Simone Zanotto
- , Giorgio Biasiol
- & Alessandro Pitanti
-
Article
| Open Access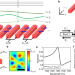 Nano-electromechanical spatial light modulator enabled by asymmetric resonant dielectric metasurfaces
Nano-electromechanical spatial light modulator enabled by asymmetric resonant dielectric metasurfaces
This work experimentally demonstrates nano-electromechanically tunable asymmetric dielectric metasurfaces. The metasurfaces enable large phase tuning, high reflection, a wavelength-scale pixel size, and electrical control of diffraction patterns.
- Hyounghan Kwon
- , Tianzhe Zheng
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling of nanocrystal hexagonal array and two-dimensional metastable substrate boosts H2-production
Coupling of nanocrystal hexagonal array and two-dimensional metastable substrate boosts H2-production
The construction of well-ordered nanoarrays, particularly invoking metastable material phases, remains a challenge. Here, authors prepared a well-ordered, rhodium nanoarray on two-dimensional, metastable rhodium oxide to enhance hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis.
- Zhenglong Fan
- , Fan Liao
- & Qi Shao

 High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface