Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A modular and synthetic biosynthesis platform for de novo production of diverse halogenated tryptophan-derived molecules
A modular and synthetic biosynthesis platform for de novo production of diverse halogenated tryptophan-derived molecules
De novo fermentation and synthetic pathway construction for halogen-containing molecules remain relatively underexplored. Here, the authors report a mix-and-match co-culture platform to de novo generate a large array of halogenated tryptophan derivatives in E. coli from glucose.
- Kevin B. Reed
- , Sierra M. Brooks
- & Hal S. Alper
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetically-primed adaptation of Pseudomonas putida to a non-native substrate D-xylose
Synthetically-primed adaptation of Pseudomonas putida to a non-native substrate D-xylose
Pseudomonas putida is becoming a host of choice for the valorization of lignocellulosic substrates. Here, the authors provide insight into the adaptation of this bacterium to the non-native substrate D-xylose, enabled by metabolic engineering and adaptive laboratory evolution.
- Pavel Dvořák
- , Barbora Burýšková
- & Martin Benešík
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of the highly oxygenated tetracyclic core skeleton of Taxol
Biosynthesis of the highly oxygenated tetracyclic core skeleton of Taxol
Despite intensive investigation, stepwise reactions from diol to Taxol tetracyclic core skeleton remain unclear. Here, authors fill this gap by identifying two P450s and confirming the reaction order.
- Chengshuai Yang
- , Yan Wang
- & Zhihua Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access A citric acid cycle-deficient Escherichia coli as an efficient chassis for aerobic fermentations
A citric acid cycle-deficient Escherichia coli as an efficient chassis for aerobic fermentations
While tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) is required for heterotrophic microbes, it reduces carbon yield of industrial products due to the release of excess CO2. Here, the authors construct an E. coli strain without a functional TCA cycle and demonstrate its feasibility as a chassis strain for production of four separate compounds.
- Hang Zhou
- , Yiwen Zhang
- & Baixue Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Edible mycelium bioengineered for enhanced nutritional value and sensory appeal using a modular synthetic biology toolkit
Edible mycelium bioengineered for enhanced nutritional value and sensory appeal using a modular synthetic biology toolkit
Fungi have the potential to produce sustainable foods for a growing population, but current products are based on a small number of strains with inherent limitations. Here, the authors develop genetic tools for an edible fungus and engineer its nutritional value and sensory appeal for alternative meat applications.
- Vayu Maini Rekdal
- , Casper R. B. van der Luijt
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article
| Open Access Increased CO2 fixation enables high carbon-yield production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid in yeast
Increased CO2 fixation enables high carbon-yield production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid in yeast
CO2 fixation plays an important role to make bioproduction cost competitive. Here, the authors take 3-hydroxypropionic acid as an example to showcase how to achieve high carbon yield production through increasing the accessible bicarbonate, minimizing native CO2 release and avoiding carbon waste.
- Ning Qin
- , Lingyun Li
- & Zihe Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Combinatorial optimization of gene expression through recombinase-mediated promoter and terminator shuffling in yeast
Combinatorial optimization of gene expression through recombinase-mediated promoter and terminator shuffling in yeast
Fine-tuning the expression of biosynthetic pathway genes is crucial to improve microbial production titres. Here, the authors present GEMbLeR, an optimization strategy to balance the expression of multiple genes simultaneously over a wide range.
- Charlotte Cautereels
- , Jolien Smets
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access Systems engineering of Escherichia coli for high-level glutarate production from glucose
Systems engineering of Escherichia coli for high-level glutarate production from glucose
Glutarate is a platform chemical widely used in the production of polyesters and polyamindes. Here, the authors design the shortest and thermodynamically favorable pathway, and increase glutarate production from glucose through systematic engineering of E. coli.
- Zhilan Zhang
- , Ruyin Chu
- & Cong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic carbon–carbon bond cleavage in lignin via manganese–zirconium-mediated autoxidation
Catalytic carbon–carbon bond cleavage in lignin via manganese–zirconium-mediated autoxidation
Efforts to produce aromatic monomers through catalytic lignin depolymerization were focused on aryl–ether bond cleavage, while the carbon–carbon bonds of a large fraction of aromatic monomers in lignin are difficult to cleave. Here, the authors report a catalytic autoxidation method using manganese and zirconium salts as catalysts to cleave the C–C bonds in lignin-derived dimers and oligomers from pine and poplar.
- Chad T. Palumbo
- , Nina X. Gu
- & Gregg T. Beckham
-
Article
| Open Access Compositional and temporal division of labor modulates mixed sugar fermentation by an engineered yeast consortium
Compositional and temporal division of labor modulates mixed sugar fermentation by an engineered yeast consortium
Synthetic microbial communities are suitable for mixed substrates fermentation and long metabolic pathway engineering. Here, the authors combine fermentation experiments with mathematical modeling to reveal the effect of compositional and temporal changes on division of labor in cellulosic ethanol production using two yeast strains.
- Jonghyeok Shin
- , Siqi Liao
- & Yong-Su Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Rational strain design with minimal phenotype perturbation
Rational strain design with minimal phenotype perturbation
No consensus exists on the computationally tractable use of dynamic models for strain design. To tackle this, the authors report a framework, nonlinear-dynamic-model-assisted rational metabolic engineering design, for efficiently designing robust, artificially engineered cellular organisms.
- Bharath Narayanan
- , Daniel Weilandt
- & Vassily Hatzimanikatis
-
Article
| Open Access De novo biosynthesis of antiarrhythmic alkaloid ajmaline
De novo biosynthesis of antiarrhythmic alkaloid ajmaline
Ajmaline is an antiarrhythmic monoterpenoid indole alkaloid produced by the root of Rauwolfia serpentina. Here, the authors complete the ajmaline biosynthetic pathway by identifying two reductases and two esterases, and achieve the de novo ajmaline biosynthesis by engineering Baker’s yeast.
- Jun Guo
- , Di Gao
- & Yang Qu
-
Article
| Open Access De novo biosynthesis of the hops bioactive flavonoid xanthohumol in yeast
De novo biosynthesis of the hops bioactive flavonoid xanthohumol in yeast
Xanthohumol is a prenylated flavonoid produced by hops and is an important flavor substance in beer. Here, the authors engineer brewing yeast for the de novo biosynthesis of xanthohumol from glucose by balancing the three parallel biosynthetic pathways.
- Shan Yang
- , Ruibing Chen
- & Yongjin J. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic spatial patterning of cooperation in yeast populations
Optogenetic spatial patterning of cooperation in yeast populations
Microbial communities are the siege of complex metabolic interactions including cooperation and competition. Here, the authors report the utilization of optogenetics and spatial light-patterning to activate the expression of the invertase SUC2 at selected locations and selectively switch cooperation and competition roles of the yeast cells.
- Matthias Le Bec
- , Sylvain Pouzet
- & Pascal Hersen
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfiguration of the reductive TCA cycle enables high-level succinic acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica
Reconfiguration of the reductive TCA cycle enables high-level succinic acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica
Redox imbalance limits succinic acid (SA) biosynthesis from glucose via the reductive tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in yeast. Here, the authors engineering the aerobic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for efficient SA production without pH control via coupling the oxidative and reductive TCA cycle for NADH regeneration in mitochondria.
- Zhiyong Cui
- , Yutao Zhong
- & Qingsheng Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a synthetic energy-efficient formaldehyde assimilation cycle in Escherichia coli
Engineering a synthetic energy-efficient formaldehyde assimilation cycle in Escherichia coli
One-carbon substrates are attractive feedstocks for circular bioeconomy. Here, the authors design an erythrulose monophosphate (EuMP) cycle for formaldehyde assimilation, demonstrate the activity of the core reactions in E. coli, and show its integration with pathway reactions existed in pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis.
- Tong Wu
- , Paul A. Gómez-Coronado
- & Hai He
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering artificial photosynthesis based on rhodopsin for CO2 fixation
Engineering artificial photosynthesis based on rhodopsin for CO2 fixation
Microbial rhodopsins are major contributors to global light harvesting on Earth, but their role in carbon fixation is unclear. Here, the authors construct an artificial photosynthesis system by combining rhodopsin with an extracellular electron uptake mechanism for photoelectrosynthetic CO2 fixation in Ralstonia eutropha.
- Weiming Tu
- , Jiabao Xu
- & Wei E. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Xylose and shikimate transporters facilitates microbial consortium as a chassis for benzylisoquinoline alkaloid production
Xylose and shikimate transporters facilitates microbial consortium as a chassis for benzylisoquinoline alkaloid production
It’s challenging to produce natural products using single strains of engineered microbes fed by renewable carbon sources. Here, the authors assemble a microbial consortium consisting of engineered S. stipitis and S. cerevisiae for streamlined production of (S)-norcoclaurine from glucose and xylose simultaneously.
- Meirong Gao
- , Yuxin Zhao
- & Zengyi Shao
-
Article
| Open Access The oxygen-tolerant reductive glycine pathway assimilates methanol, formate and CO2 in the yeast Komagataella phaffii
The oxygen-tolerant reductive glycine pathway assimilates methanol, formate and CO2 in the yeast Komagataella phaffii
One carbon compounds such as CO2, methanol and formate are cost-effective and environmentally friendly microbial feedstocks for biomanufacturing. Here, the authors report the oxygen tolerant reductive glycine pathway in Komagataella phaffii can co-assimilate CO2, methanol and formate.
- Bernd M. Mitic
- , Christina Troyer
- & Diethard Mattanovich
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and remodeling of Vibrio natriegens as a microbial platform for efficient formic acid biorefinery
Discovery and remodeling of Vibrio natriegens as a microbial platform for efficient formic acid biorefinery
Formic acid (FA) is a promising CO2-equivalent feedstock for onecarbon biorefinery, but microbial host that can efficiently utilize FA is unavailable. Here, the authors engineer a non-native closed loop in Vibrio natriegens and demonstrate its application in promoting FA utilization.
- Jinzhong Tian
- , Wangshuying Deng
- & Yang Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinated regulation of the entry and exit steps of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis supports the dual lignin pathway in grasses
Coordinated regulation of the entry and exit steps of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis supports the dual lignin pathway in grasses
The study by El-Azaz et al. uncovers how grasses fine-tune tyrosine and phenylalanine production to support their unique dual entry pathway to lignin and phenylpropanoids. The findings help improve sustainable production of aromatic chemicals in crops.
- Jorge El-Azaz
- , Bethany Moore
- & Hiroshi A. Maeda
-
Perspective
| Open Access The potential of CO2-based production cycles in biotechnology to fight the climate crisis
The potential of CO2-based production cycles in biotechnology to fight the climate crisis
The utilization of one-carbon assimilation pathways for bioproduction represents a promising direction towards a more sustainable bio-based economy. Here, the authors compare the thermodynamic efficiencies and energy demand of C1-assimilation pathways and discuss their implementation for energy, material, and food production.
- Simone Bachleitner
- , Özge Ata
- & Diethard Mattanovich
-
Article
| Open Access Redox signaling-driven modulation of microbial biosynthesis and biocatalysis
Redox signaling-driven modulation of microbial biosynthesis and biocatalysis
Microbial communication has significant implications for industrial applications, but constructing communication systems which support coordinated behaviors is challenging. Here, the authors report an electron transfer triggered redox communication network and demonstrate its ability to coordinate microbial metabolism.
- Na Chen
- , Na Du
- & Quan Yuan
-
Perspective
| Open Access Synergistic investigation of natural and synthetic C1-trophic microorganisms to foster a circular carbon economy
Synergistic investigation of natural and synthetic C1-trophic microorganisms to foster a circular carbon economy
Using one carbon (C1) molecules as primary feedstock for bioproduction holds great potential for a circular and carbon neutral economy. Here, the authors discuss the potential of merging knowledge gained from natural and synthetic C1-trophic organisms to expedite the development of efficient C1-based biomanufacturing.
- Enrico Orsi
- , Pablo Ivan Nikel
- & Stefano Donati
-
Article
| Open Access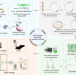 Repurposing conformational changes in ANL superfamily enzymes to rapidly generate biosensors for organic and amino acids
Repurposing conformational changes in ANL superfamily enzymes to rapidly generate biosensors for organic and amino acids
Biosensors have a wide number of potential applications, but rapidly constructing genetically encoded biosensors remains challenging. Here, authors report a method for rapidly converting ANL superfamily enzymes into biosensors for organic acids, based on their conformational changes upon binding.
- Jin Wang
- , Ning Xue
- & Meng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access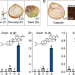 Characterization of the horse chestnut genome reveals the evolution of aescin and aesculin biosynthesis
Characterization of the horse chestnut genome reveals the evolution of aescin and aesculin biosynthesis
Horse chestnut (Aesculus chinensis) is a tree species that can produce medicinal compounds such as aescin and aesculin. Here, the authors assemble its genome, identify key genes involved in the biosynthesis of these two group of compounds, and achieve the de novo synthesis of aesculin in E. coli.
- Wei Sun
- , Qinggang Yin
- & Shilin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access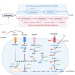 An end-to-end pipeline for succinic acid production at an industrially relevant scale using Issatchenkia orientalis
An end-to-end pipeline for succinic acid production at an industrially relevant scale using Issatchenkia orientalis
Microbial production of succinic acid at an industrially relevant scale has been hindered by high downstream processing costs arising from neutral pH fermentation. Here, the authors report an end-to-end pipeline for succinic acid production at low pH using engineered acid-tolerant Issatchenkia orientalis strain.
- Vinh G. Tran
- , Somesh Mishra
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Fitness cost associated with cell phenotypic switching drives population diversification dynamics and controllability
Fitness cost associated with cell phenotypic switching drives population diversification dynamics and controllability
Generating and controlling cell collective behavior is important for synthetic biology and bioproduction. Here, the authors show the diversification dynamic and the fitness cost associated with cell switching are coupled in yeast and bacteria, and demonstrate the feasibility of controlling diversification regimes.
- Lucas Henrion
- , Juan Andres Martinez
- & Frank Delvigne
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering microbial division of labor for plastic upcycling
Engineering microbial division of labor for plastic upcycling
Plastic pollution is rapidly increasing worldwide, causing adverse impacts on the environment, wildlife and human health. Here the authors present a synthetic microbial consortium that efficiently degrades polyethylene terephthalate hydrolysate and upcycles it to desired chemicals through cellular division of labor.
- Teng Bao
- , Yuanchao Qian
- & Ting Lu
-
Article
| Open Access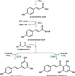 Membrane manipulation by free fatty acids improves microbial plant polyphenol synthesis
Membrane manipulation by free fatty acids improves microbial plant polyphenol synthesis
The inherent toxicity of the aromatic compounds to the chassis strain hampers further improvement of bioproduction. Here, the authors show that membrane rigidifying effect of resveratrol can be attenuated by exogenous supplementation of palmitelaidic acid or linoleic acid in fermentation of Corynebacterium glutamicum.
- Apilaasha Tharmasothirajan
- , Josef Melcr
- & Jan Marienhagen
-
Article
| Open Access Screening non-conventional yeasts for acid tolerance and engineering Pichia occidentalis for production of muconic acid
Screening non-conventional yeasts for acid tolerance and engineering Pichia occidentalis for production of muconic acid
Baker’s yeast is a workhorse of industrial biotechnology, but it is not suited to overproduce many bulk bioproducts, especially organic acids. Here, the authors identify Pichia occidentalis as an acid tolerant yeast and engineer it for the production of muconic acid using a newly developed genome editing toolkit.
- Michael E. Pyne
- , James A. Bagley
- & Vincent J. J. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Protein engineering and iterative multimodule optimization for vitamin B6 production in Escherichia coli
Protein engineering and iterative multimodule optimization for vitamin B6 production in Escherichia coli
Pyridoxine (PN), the most common commercial form of vitamin B6, has been chemically synthesized using expensive and toxic chemicals. Here, the authors employ parallel pathway engineering, protein engineering, and iterative multimodule optimization for high level PN production in E. coli.
- Linxia Liu
- , Jinlong Li
- & Dawei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Using a synthetic machinery to improve carbon yield with acetylphosphate as the core
Using a synthetic machinery to improve carbon yield with acetylphosphate as the core
In metabolic engineering, releasing of carbon in the form of CO2 leads to significant decrease of atomic economy. Here, the authors construct a carbon-conserving pathway, which converts glucose into acetyl phosphate without carbon loss, with oscillatory system to improve production of multiple target compounds.
- Likun Guo
- , Min Liu
- & Guang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Biosensor Guided Polyketide Synthases Engineering for Optimization of Domain Exchange Boundaries
Biosensor Guided Polyketide Synthases Engineering for Optimization of Domain Exchange Boundaries
Engineering polyketide synthases can be challenging due to the absence of efficient high-throughput methods. Here, the authors used a solubility biosensor to identify stable variants from libraries of modified polyketide synthases.
- Elias Englund
- , Matthias Schmidt
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article
| Open Access A neural-mechanistic hybrid approach improving the predictive power of genome-scale metabolic models
A neural-mechanistic hybrid approach improving the predictive power of genome-scale metabolic models
Mechanistic models estimate the phenotype of microorganisms in different environments but may have limited predictive capabilities. Here, authors develop trainable hybrid models with improved predictability using mechanistic insights and smaller training sets than conventional machine learning techniques.
- Léon Faure
- , Bastien Mollet
- & Jean-Loup Faulon
-
Article
| Open Access A tripartite microbial co-culture system for de novo biosynthesis of diverse plant phenylpropanoids
A tripartite microbial co-culture system for de novo biosynthesis of diverse plant phenylpropanoids
Plant-derived phenylpropanoids have diverse industrial applications ranging from flavours and fragrances to polymers and pharmaceuticals. Here the authors present a tripartite microbial coculture with mix-and-match flexibility and had improved stability within an engineered living material platform for de novo production of several plant-derived phenylpropanoids.
- Sierra M. Brooks
- , Celeste Marsan
- & Hal S. Alper
-
Article
| Open Access A polycistronic system for multiplexed and precalibrated expression of multigene pathways in fungi
A polycistronic system for multiplexed and precalibrated expression of multigene pathways in fungi
Unlike prokaryotic hosts, most genes in eukaryotes are transcribed to monocistronic mRNA for single protein translation. Here, the authors develop a polycistronic system for multiplexed and precalibrated expression of multiple genes, and show its application in constructing yeast cell factories for terpenoids production.
- Qun Yue
- , Jie Meng
- & Shuobo Shi
-
Article
| Open Access A Cas3-base editing tool for targetable in vivo mutagenesis
A Cas3-base editing tool for targetable in vivo mutagenesis
In vivo mutagenesis allows improving cell factories through directed evolution. Here, the authors present CoMuTER, a tool for targetable random mutagenesis of complete biosynthetic pathways using a Cas3 enzyme fused to a cytidine deaminase.
- Anna Zimmermann
- , Julian E. Prieto-Vivas
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking the potentials of cyanobacterial photosynthesis for directly converting carbon dioxide into glucose
Unlocking the potentials of cyanobacterial photosynthesis for directly converting carbon dioxide into glucose
Photosynthetic glucose production is well controlled due to its complex interactions with other cellular processes. Here, the authors identify that the native glucokinase activity is the bottleneck restricting the metabolism potential for glucose synthesis and engineer a cyanobacterium strain that can produce 5 g/L of glucose.
- Shanshan Zhang
- , Jiahui Sun
- & Xuefeng Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a new-to-nature cascade for phosphate-dependent formate to formaldehyde conversion in vitro and in vivo
Engineering a new-to-nature cascade for phosphate-dependent formate to formaldehyde conversion in vitro and in vivo
A key step in the assimilation of formate is its reduction into formaldehyde. Here, the authors develop a two-enzyme route in which formate is activated into formyl phosphate and reduced by NAD(P)H into formaldehyde and confirm its functionality in vitro and in vivo.
- Maren Nattermann
- , Sebastian Wenk
- & Tobias J. Erb
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal enzyme utilization suggests that concentrations and thermodynamics determine binding mechanisms and enzyme saturations
Optimal enzyme utilization suggests that concentrations and thermodynamics determine binding mechanisms and enzyme saturations
One of the main challenges hampering the development of kinetic models is the lack of kinetic parameters for many enzymatic reactions. Here, the authors introduce a framework to explore the catalytically optimal operating conditions of any complex enzyme mechanism from an evolutionary perspective.
- Asli Sahin
- , Daniel R. Weilandt
- & Vassily Hatzimanikatis
-
Article
| Open Access Teasing out missing reactions in genome-scale metabolic networks through hypergraph learning
Teasing out missing reactions in genome-scale metabolic networks through hypergraph learning
A computational method for rapid and accurate gap-filling of metabolic networks without using phenotypic data is unavailable. Here, the authors address this problem by developing a deep learning based method that can predict missing reactions using topological features of the metabolic networks.
- Can Chen
- , Chen Liao
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted and high-throughput gene knockdown in diverse bacteria using synthetic sRNAs
Targeted and high-throughput gene knockdown in diverse bacteria using synthetic sRNAs
Using synthetic sRNAs to knockdown target genes has been restricted to a limited number of bacteria. Here, the authors develop a broad-host-range synthetic sRNA platform and show its application in 16 bacterial species, including mitigating virulence-associated phenotypes in pathogens and production of chemicals via metabolic engineering.
- Jae Sung Cho
- , Dongsoo Yang
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Construction of a synthetic metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of 2,4-dihydroxybutyric acid from ethylene glycol
Construction of a synthetic metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of 2,4-dihydroxybutyric acid from ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol is an attractive two-carbon alcohol substrate for bioproduction as it can be derived from CO2 or syngas. Here, the authors design a five-step synthetic metabolic pathway in E. coli to enable the carbon-conserving biosynthesis of the platform chemical 2,4-dihydroxybutyric acid from ethylene glycol.
- Cláudio J. R. Frazão
- , Nils Wagner
- & Thomas Walther
-
Perspective
| Open Access A roadmap to establish a comprehensive platform for sustainable manufacturing of natural products in yeast
A roadmap to establish a comprehensive platform for sustainable manufacturing of natural products in yeast
Yeasts, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris, are promising chassis for the production of nature products (NPs). Here, the author discusses establishing a comprehensive platform for sustainable production of NPs via system-associated optimization at genetics, temporal controllers, productivity screening, and scalability levels.
- Gita Naseri
-
Article
| Open Access Data integration across conditions improves turnover number estimates and metabolic predictions
Data integration across conditions improves turnover number estimates and metabolic predictions
The construction of protein-constrained genome-scale metabolic models depends on the integration of organism-specific enzyme turnover numbers. Here, the authors show that correction of turnover numbers by simultaneous consideration of proteomics and physiological data leads to improved predictions of condition-specific growth rates.
- Philipp Wendering
- , Marius Arend
- & Zoran Nikoloski
-
Article
| Open Access Tandemly duplicated CYP82Ds catalyze 14-hydroxylation in triptolide biosynthesis and precursor production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Tandemly duplicated CYP82Ds catalyze 14-hydroxylation in triptolide biosynthesis and precursor production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Hydroxylation at the C-14 position of triptolide is critical for its potent antitumor activity. Here, the authors report two CYP82Ds catalyze the 14-hydroxylation reaction via metabolic grid and achieve heterologous bioproduction of triptolide precursor in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Yifeng Zhang
- , Jie Gao
- & Luqi Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulation of sterol homeostasis for the production of 24-epi-ergosterol in industrial yeast
Manipulation of sterol homeostasis for the production of 24-epi-ergosterol in industrial yeast
Brassinolide (BL) is one of the most active compounds among phytohormone brassinosteroids (BRs) and can be used for plant growth and development regulation. Here, the authors report the construction of an artificial pathway in baker’s yeast for scalable production of 24-epi-ergosterol, a precursor for BL semi-synthesis.
- Yiqi Jiang
- , Zhijiao Sun
- & Lirong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of mushroom-derived type II ganoderic acids by engineered yeast
Biosynthesis of mushroom-derived type II ganoderic acids by engineered yeast
The biosynthetic pathway of type II ganoderic acids (GAs) in Ganoderma lucidum, a traditional medicinal mushroom, is unknown. Here, the authors assemble the genome of type II GAs accumulating accession, identify CYPs involving in type II GAs biosynthesis, and achieve their production in engineered baker’s yeast.
- Wei Yuan
- , Chenjian Jiang
- & Han Xiao

 Unravelling and reconstructing the biosynthetic pathway of bergenin
Unravelling and reconstructing the biosynthetic pathway of bergenin