Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access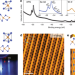 Observation of topologically protected states at crystalline phase boundaries in single-layer WSe2
Observation of topologically protected states at crystalline phase boundaries in single-layer WSe2
Transition metal dichalcogenides may host exotic topological phases in the two-dimensional limit, but detailed atomic properties have rarely been explored. Here, Ugeda et al. observe edge-states at the interface between a single layer quantum spin Hall insulator 1T′-WSe2 and a semiconductor 1H-WSe2.
- Miguel M. Ugeda
- , Artem Pulkin
- & Michael F. Crommie
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of complex optical susceptibility for individual carbon nanotubes by elliptically polarized light excitation
Measurement of complex optical susceptibility for individual carbon nanotubes by elliptically polarized light excitation
One-dimensional materials such as carbon nanotubes have many applications, but not all of their properties can be described in the same way as for conventional media. Here, the authors devise a method to measure the complex optical susceptibility in a 1D nanomaterial and demonstrate it for carbon nanotubes.
- Fengrui Yao
- , Can Liu
- & Kaihui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallographic character of grain boundaries resistant to hydrogen-assisted fracture in Ni-base alloy 725
Crystallographic character of grain boundaries resistant to hydrogen-assisted fracture in Ni-base alloy 725
Exactly how hydrogen renders metals brittle is still unclear, and it remains a challenge to predict component failure due to hydrogen embrittlement. Here, the authors identify a class of grain boundaries in a nickel superalloy that deflects propagating cracks and improves alloy resistance to hydrogen.
- John P. Hanson
- , Akbar Bagri
- & Michael J. Demkowicz
-
Article
| Open Access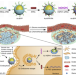 Reversal of pancreatic desmoplasia by re-educating stellate cells with a tumour microenvironment-activated nanosystem
Reversal of pancreatic desmoplasia by re-educating stellate cells with a tumour microenvironment-activated nanosystem
Stromal-tumour interactions play an important role in pancreatic cancer progression. Here, they describe the development of a tumour microenvironment-responsive gold nanoparticle system incorporating all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and siRNA against heat shock protein 47 (HSP47), for use in pancreatic cancer treatment.
- Xuexiang Han
- , Yiye Li
- & Guangjun Nie
-
Article
| Open Access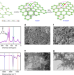 Selectively nitrogen-doped carbon materials as superior metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction
Selectively nitrogen-doped carbon materials as superior metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction
Doping carbon-based materials with nitrogen is effective for enhancing catalytic activity for oxygen reduction; however, directing nitrogen dopants to specific locations is difficult. Here the authors employ hydrogen-substituted graphdiyne as a matrix for nitrogen doping, leading to enhanced performance.
- Qing Lv
- , Wenyan Si
- & Yuliang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Comparison of atomic scale dynamics for the middle and late transition metal nanocatalysts
Comparison of atomic scale dynamics for the middle and late transition metal nanocatalysts
The atomistic behaviour of nanocatalysts still remains largely unknown. Here, the authors reveal and explore reactions of nm-sized clusters of 14 technologically important metals in carbon nano test tubes using time-series imaging by atomically-resolved transmission electron microscopy.
- Kecheng Cao
- , Thilo Zoberbier
- & Andrei N. Khlobystov
-
Article
| Open Access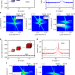 Ultra-low damping insulating magnetic thin films get perpendicular
Ultra-low damping insulating magnetic thin films get perpendicular
A magnetic material combining both low losses and strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) was so far missing in the field of magnon-spintronics. The authors here report on Bismuth doped YIG nanometer thick films showing both PMA and low magnetic losses for ultra-thin PMA materials.
- Lucile Soumah
- , Nathan Beaulieu
- & Abdelmadjid Anane
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacing with silica boosts the catalysis of copper
Interfacing with silica boosts the catalysis of copper
Metal-support interaction plays an important role in heterogeneous catalysis, but silica has been rarely reported as an effective support to create active metal-support interfaces for promoting catalytic reactions. Here, the authors discover that Cu/SiO2 interface creates an exceptional effect to promote catalytic hydrogenation of esters.
- Chaofa Xu
- , Guangxu Chen
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Half-metallic carbon nitride nanosheets with micro grid mode resonance structure for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Half-metallic carbon nitride nanosheets with micro grid mode resonance structure for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution
The “storage” of sunlight as a chemical fuel can provide renewable on-demand energy, although current earth-abundant materials usually show low activities. Here, authors construct a carbon nitride material whose half-metallicity and micro grid resonance structure boost light-driven H2 evolution.
- Gang Zhou
- , Yun Shan
- & Xinglong Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-generated dinuclear {Eu(II)}2 active sites for selective CO2 reduction in a photosensitizing metal-organic framework
Photo-generated dinuclear {Eu(II)}2 active sites for selective CO2 reduction in a photosensitizing metal-organic framework
Solar-to-chemical CO2 reduction provides a means to use light’s energy for CO2 removal and upgrading to useful products, although this photochemical conversion is challenging. Here, authors construct a Europium-containing metal-organic framework that selectively converts CO2 to formate with light.
- Zhi-Hao Yan
- , Ming-Hao Du
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral symmetry breaking yields the I-Au60 perfect golden shell of singular rigidity
Chiral symmetry breaking yields the I-Au60 perfect golden shell of singular rigidity
Chiral-icosahedral symmetry is exceptionally rare in molecular systems. Here, the authors predict the spontaneous formation of a stable chiral-icosahedral gold shell, in which all 60 atoms are symmetrically equivalent.
- S.-M. Mullins
- , H.-Ch. Weissker
- & X. López-Lozano
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-extensible ribbon-like magnetic microswarm
Ultra-extensible ribbon-like magnetic microswarm
Manipulation of paramagnetic microparticles can be exploited for drug delivery. Here the authors manipulate a swarm of such particles and control its shape with a magnetic field so that it can elongate reversibly, split into smaller swarms and thus be guided through a maze with multiple parallel channels.
- Jiangfan Yu
- , Ben Wang
- & Li Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional atomic-scale observation of structural evolution of cathode material in a working all-solid-state battery
Three-dimensional atomic-scale observation of structural evolution of cathode material in a working all-solid-state battery
Here, with the state-of-the-state electron microscope, the authors report three-dimensional atomic-scale observation of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 from various directions, revealing unprecedented insight into the evolution of both atomic and electronic structures during delithiation.
- Yue Gong
- , Yuyang Chen
- & Liquan Chen
-
Review Article
| Open Access Active nematics
Active nematics
Active matter systems are made up of self-driven components which extract energy from their surroundings to generate mechanical work. Here the authors review the subfield of active nematics and provide a comparison between theoretical findings and the corresponding experimental realisations.
- Amin Doostmohammadi
- , Jordi Ignés-Mullol
- & Francesc Sagués
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature mechanocaloric effects in lithium-based superionic materials
Room-temperature mechanocaloric effects in lithium-based superionic materials
Large mechanocaloric effects are disclosed in lithium-ion superionic conductors at room temperature. These occur in the absence of any structural phase transition, which is beneficial from a practical point of view, and are related to stress-induced variations in the ionic conductivity.
- Arun K. Sagotra
- , Dewei Chu
- & Claudio Cazorla
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic nanoflowers by self-assembly of nanozymes to induce intracellular oxidative damage against hypoxic tumors
Biomimetic nanoflowers by self-assembly of nanozymes to induce intracellular oxidative damage against hypoxic tumors
Hypoxic tumors are resistant to dynamic therapy, limiting potential treatment options. Here, the authors describe a nanoflower where oxidase mimicking PtCo nanoparticles are decorated with catalase mimicking MnO2 to reverse tumor hypoxia and generate reactive oxygen species for dynamic therapy.
- Zhenzhen Wang
- , Yan Zhang
- & Xiaogang Qu
-
Article
| Open Access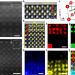 Direct observation of room-temperature out-of-plane ferroelectricity and tunneling electroresistance at the two-dimensional limit
Direct observation of room-temperature out-of-plane ferroelectricity and tunneling electroresistance at the two-dimensional limit
High temperature perpendicular ferroelectricity in nano thin films is crucial for miniaturization of electronic devices. Here the authors show the presence of stable and switchable out-of-plane ferroelectricity in tetragonal BiFeO3 thin films at the two-dimensional limit and 370% tunneling electroresistance in ferroelectric tunnel junctions.
- H. Wang
- , Z. R. Liu
- & J. S. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access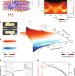 Ultrafast and highly sensitive infrared photodetectors based on two-dimensional oxyselenide crystals
Ultrafast and highly sensitive infrared photodetectors based on two-dimensional oxyselenide crystals
Two-dimensional (2D) bismuth oxyselenide crystals with suitable electronic band-gap and ultrahigh carrier mobility enable near-infrared photodetection. Here, the authors report an infrared photodetector based on 2D-bismuth oxyselenide with high responsivity, ultrafast photoresponse of ~ 1 ps at room temperature and a detectable frequency limit of up to 500 GHz.
- Jianbo Yin
- , Zhenjun Tan
- & Hailin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-photon near-infrared emission saturation nanoscopy using upconversion nanoparticles
Multi-photon near-infrared emission saturation nanoscopy using upconversion nanoparticles
Upconversion nanoparticles offer the potential for deep tissue biological imaging. Here, Chen et al. develop super resolution optical imaging in the near-infrared for imaging with sub-50 nm resolution through almost 100 microns of tissue.
- Chaohao Chen
- , Fan Wang
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding how excess lead iodide precursor improves halide perovskite solar cell performance
Understanding how excess lead iodide precursor improves halide perovskite solar cell performance
Excess lead iodide in the mixed halide perovskites solar cells leads to high device performance but its origin remains elusive. Here Park et al. unveil the underlying microscopic mechanism to be promoting the oriented growth of the perovskites crystals and reducing the defect concentration.
- Byung-wook Park
- , Nir Kedem
- & Sang Il Seok
-
Article
| Open Access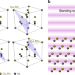 Element- and momentum-resolved electronic structure of the dilute magnetic semiconductor manganese doped gallium arsenide
Element- and momentum-resolved electronic structure of the dilute magnetic semiconductor manganese doped gallium arsenide
The knowledge of the electronic structure of composite material is essential for tailoring their properties. The authors introduce a method based on standing wave angle-resolved hard X-ray photoemission to determine the element- and momentum-resolved electronic band structure simultaneously.
- Slavomír Nemšák
- , Mathias Gehlmann
- & Charles S. Fadley
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical glass transition revealed by the fracture toughness of metallic glasses
Mechanical glass transition revealed by the fracture toughness of metallic glasses
Understanding the fracture toughness of metallic glasses remains challenging. Here, the authors show that a fictive temperature controls an abrupt mechanical toughening transition in metallic glasses, and can explain the scatter in previously reported fracture toughness data.
- Jittisa Ketkaew
- , Wen Chen
- & Jan Schroers
-
Article
| Open Access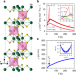 Large anomalous Hall effect in the chiral-lattice antiferromagnet CoNb3S6
Large anomalous Hall effect in the chiral-lattice antiferromagnet CoNb3S6
Anomalous Hall effect (AHE) in antiferromagnets is intriguing and requires further understanding. Here the authors report large AHE in a chiral-lattice antiferromagnet CoNb3S6 of which the origin can be due to complex magnetic texture or broken time-reversal symmetry on the electronic band structure.
- Nirmal J. Ghimire
- , A. S. Botana
- & J. F. Mitchell
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of bosonic condensation in a hybrid monolayer MoSe2-GaAs microcavity
Observation of bosonic condensation in a hybrid monolayer MoSe2-GaAs microcavity
Atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides are an ideal platform to investigate the underlying physics of strongly bound excitons in low dimensions. Here, the authors demonstrate the formation of a bosonic condensate driven by excitons in two-dimensional MoSe2 strongly coupled to light in a solid-state resonator.
- Max Waldherr
- , Nils Lundt
- & Christian Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding voltage decay in lithium-excess layered cathode materials through oxygen-centred structural arrangement
Understanding voltage decay in lithium-excess layered cathode materials through oxygen-centred structural arrangement
There is growing interest in the fundamental understanding of the voltage decay mechanism in Li-excess layered cathode materials. Here, the authors report a multilateral and macroscopic analysis that considers interaction between oxygen and atomic arrangement of Li1+xNiyCozMn1−x−y−zO2.
- Seungjun Myeong
- , Woongrae Cho
- & Jaephil Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Local structure in deeply supercooled liquids exhibits growing lengthscales and dynamical correlations
Local structure in deeply supercooled liquids exhibits growing lengthscales and dynamical correlations
The glass transition remains an unsolved problem due to the scarcity of particle-resolved data over a large dynamic range. Hallett et al. probe an unprecedented time window and show a strong correlation between local structure and slow dynamics in a deeply supercooled liquid of colloids.
- James E. Hallett
- , Francesco Turci
- & C. Patrick Royall
-
Article
| Open Access Ohmic transition at contacts key to maximizing fill factor and performance of organic solar cells
Ohmic transition at contacts key to maximizing fill factor and performance of organic solar cells
The importance of ohmic contacts for organic solar cells has been recognized, but how the transition to ohmic behavior occurs is unknown. Tan et al. show that this transition happens separately beyond Fermi-level pinning, when the interfacial contact resistivity becomes sufficiently low.
- Jun-Kai Tan
- , Rui-Qi Png
- & Peter K. H. Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Confined small-sized cobalt catalysts stimulate carbon-chain growth reversely by modifying ASF law of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis
Confined small-sized cobalt catalysts stimulate carbon-chain growth reversely by modifying ASF law of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis
Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) is theoretically limited by Anderson–Schulz–Flory (ASF) law. Here, the authors successfully tune the selectivity of products from diesel-range hydrocarbons to gasoline-range hydrocarbons in FTS by controlling the crystallite sizes of confined cobalt, and modify the ASF law.
- Qingpeng Cheng
- , Ye Tian
- & Xingang Li
-
Article
| Open Access A possible candidate for triply degenerate point fermions in trigonal layered PtBi2
A possible candidate for triply degenerate point fermions in trigonal layered PtBi2
Triply degenerate point (TP) fermions have been reported in MoP but the TPs are far below the Fermi level. Here, Guo et al. predict and verify the possible existence of TP fermions in trigonal layered PtBi2, where the TP points are close to the Fermi level.
- Wenshuai Gao
- , Xiangde Zhu
- & Mingliang Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Charge carrier-selective contacts for nanowire solar cells
Charge carrier-selective contacts for nanowire solar cells
Balancing the carrier selectivity and extraction by the selective contacts is of vital importance to the performance of the nanowire solar cells. Here Oener et al. employ a permanent local gate to overcome this tradeoff and substantially increase the open-circuit voltage by 335 mV.
- Sebastian Z. Oener
- , Alessandro Cavalli
- & Erik C. Garnett
-
Article
| Open Access Spin and orbital structure of the first six holes in a silicon metal-oxide-semiconductor quantum dot
Spin and orbital structure of the first six holes in a silicon metal-oxide-semiconductor quantum dot
For solid state qubits, silicon MOS structures offer great scalability, while hole spins promise high performance qubit operation. Liles et al. have combined these two features in a planar silicon quantum dot device that operates as an artificial atom down to the single-hole limit.
- S. D. Liles
- , R. Li
- & A. R. Hamilton
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional type-II Dirac fermions in layered oxides
Two-dimensional type-II Dirac fermions in layered oxides
Many predicted topological quasi-particles still await experimental discovery. Here, Horio et al. reveal the existence of two-dimensional type-II Dirac fermions in the high-temperature superconductor La1.77Sr0.23CuO4, promoting layered oxides as promising topological materials.
- M. Horio
- , C. E. Matt
- & J. Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced mechanical response in crosslinked liquid-crystalline polymers with photoswitchable glass transition temperatures
Light-induced mechanical response in crosslinked liquid-crystalline polymers with photoswitchable glass transition temperatures
Energy conversion of light into mechanical work is of fundamental interest for a wide range of applications, but the development of efficient light responsive polymers is challenging. Here the authors demonstrate photoswitchable glass transition temperatures contribute to the photomechanical bending in a crosslinked azobenzene polymer.
- Youfeng Yue
- , Yasuo Norikane
- & Emiko Koyama
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of winner-takes-all connectivity paths in random nanowire networks
Emergence of winner-takes-all connectivity paths in random nanowire networks
Nanowire networks with memristive properties are promising for neuromorphic applications. Here, the authors observe the formation of a preferred conduction pathway which uses the lowest possible energy to get through the network and could be exploited for the design of optimal brain-inspired devices.
- Hugh G. Manning
- , Fabio Niosi
- & John J. Boland
-
Article
| Open Access Self-organization of active particles by quorum sensing rules
Self-organization of active particles by quorum sensing rules
Bacteria communicate and organize via quorum sensing which is determined by biochemical processes. Here the authors aim to reproduce this behaviour in a system of synthetic active particles whose motion is induced by an external beam which is in turn controlled by a feedback-loop which mimics quorum sensing.
- Tobias Bäuerle
- , Andreas Fischer
- & Clemens Bechinger
-
Article
| Open Access Creating solvation environments in heterogeneous catalysts for efficient biomass conversion
Creating solvation environments in heterogeneous catalysts for efficient biomass conversion
Solvents play important roles in chemical transformations, but isolating products from solvents is cumbersome and energy-consuming. Here, the authors develop promising alternatives by anchoring the solvent moieties onto porous materials for creating solvation environments in heterogeneous catalysts for efficient biomass conversion.
- Qi Sun
- , Sai Wang
- & Feng-Shou Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Post-polymerisation functionalisation of conjugated polymer backbones and its application in multi-functional emissive nanoparticles
Post-polymerisation functionalisation of conjugated polymer backbones and its application in multi-functional emissive nanoparticles
Functionalisation of conjugated polymers is essential for performance in many applications, yet there are limited approaches to achieve this. Here the authors developed a method for the direct postpolymerisation modification of the aromatic backbone of conjugated polymers and used them to create multifunctional semiconducting nanoparticles.
- Adam Creamer
- , Christopher S. Wood
- & Martin Heeney
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule detection with a millimetre-sized transistor
Single-molecule detection with a millimetre-sized transistor
The sensing capability of nanometric transducers designed for label-free single molecule detection has been limited by the small number of recognition elements. Here, the authors demonstrate a millimetre-sized field effect transistor capable of selective single-molecule Immunoglobulin-G detection.
- Eleonora Macchia
- , Kyriaki Manoli
- & Luisa Torsi
-
Article
| Open Access Iron-based trinuclear metal-organic nanostructures on a surface with local charge accumulation
Iron-based trinuclear metal-organic nanostructures on a surface with local charge accumulation
Polynuclear metal-organic coordination complexes are often inaccessible by traditional synthetic chemistry methods. Here, the authors use on-surface supramolecular chemistry to form a planar trinuclear Fe complex, in which an accumulation of electrons around the positive mixed-valence polynuclear centre suggests a catalytically active core.
- Cornelius Krull
- , Marina Castelli
- & Agustin Schiffrin
-
Article
| Open Access Capacitive neural network with neuro-transistors
Capacitive neural network with neuro-transistors
Though memristors can potentially emulate neuron and synapse functionality, useful signal energy is lost to Joule heating. Here, the authors demonstrate neuro-transistors with a pseudo-memcapacitive gate that actively process signals via energy-efficient capacitively-coupled neural networks.
- Zhongrui Wang
- , Mingyi Rao
- & J. Joshua Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid nanodiamond quantum sensors enabled by volume phase transitions of hydrogels
Hybrid nanodiamond quantum sensors enabled by volume phase transitions of hydrogels
Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamonds are used for quantum sensing but NV centers are not sensitive to parameters such as temperature, pressure and biomolecules. Here the authors propose a scheme based on a magnetic nanoparticle docked responsive hydrogel which acts as a transducer between the particles and the diamond.
- Ting Zhang
- , Gang-Qin Liu
- & Quan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Crystalline polymeric carbon dioxide stable at megabar pressures
Crystalline polymeric carbon dioxide stable at megabar pressures
The nature and stability of carbon dioxide under extreme conditions relevant to the Earth’s mantle is still under debate, in view of its possible role within the deep carbon cycle. Here, the authors perform high-pressure experiments providing evidence that polymeric crystalline CO2 is stable under megabaric conditions.
- Kamil F. Dziubek
- , Martin Ende
- & Ronald Miletich
-
Article
| Open Access Exceptional electrocatalytic oxygen evolution via tunable charge transfer interactions in La0.5Sr1.5Ni1−xFexO4±δ Ruddlesden-Popper oxides
Exceptional electrocatalytic oxygen evolution via tunable charge transfer interactions in La0.5Sr1.5Ni1−xFexO4±δ Ruddlesden-Popper oxides
Water electrolysis provides a potential means to large-scale renewable fuel generation, although sluggish oxygen evolution kinetics challenges progress. Here, authors report on Ruddlesden–Popper oxides as active oxygen evolution electrocatalysts that provide impetus for overcoming kinetic barriers.
- Robin P. Forslund
- , William G. Hardin
- & Keith J. Stevenson
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly by thermal hysteresis
Mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly by thermal hysteresis
Complex assembly pathways often involve transient, partly-formed intermediates that are challenging to characterize. Here, the authors present a simple and rapid spectroscopic thermal hysteresis method for mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly.
- Robert W. Harkness V
- , Nicole Avakyan
- & Anthony K. Mittermaier
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-narrow-band near-infrared thermal exciton radiation in intrinsic one-dimensional semiconductors
Ultra-narrow-band near-infrared thermal exciton radiation in intrinsic one-dimensional semiconductors
Narrow-band thermal emitters are still scarce despite their potential for infrared energy conversion applications. Here the thermal emission of one-dimensional carbon nanotubes up to 2000 K is reported to exhibit very narrow excitonic emission with a full-width at half-maximum of approximately 170 meV.
- Taishi Nishihara
- , Akira Takakura
- & Kenichiro Itami
-
Article
| Open Access A gate-free monolayer WSe2 pn diode
A gate-free monolayer WSe2 pn diode
Bringing together p- and n-type monolayers of semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides results in the formation of atomically thin pn junctions. Here, the authors laterally manipulate carrier density to create a WSe2 pn homojunction on a supporting ferroelectric BiFeO3 substrate.
- Jhih-Wei Chen
- , Shun-Tsung Lo
- & Chung-Lin Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A highly reactive precursor in the iron sulfide system
A highly reactive precursor in the iron sulfide system
Mackinawite is commonly assumed to be the first solid phase in the iron sulfide system. Here, the authors report the existence of a highly reactive nanocrystalline solid phase that is a necessary precursor to the formation of mackinawite.
- Adriana Matamoros-Veloza
- , Oscar Cespedes
- & Liane G. Benning
-
Article
| Open Access Local orthorhombic lattice distortions in the paramagnetic tetragonal phase of superconducting NaFe1−xNixAs
Local orthorhombic lattice distortions in the paramagnetic tetragonal phase of superconducting NaFe1−xNixAs
The interplay between nematic, antiferromagnetic order and superconductivity in the iron pnictide superconductors remains obscured. Here, Wang et al. demonstrate well-separated nematic and Neel transition temperatures near optimal superconductivity in NaFe1−xNixAs and uncover local distortions which could account for rotational symmetry breaking common in iron pnictides.
- Weiyi Wang
- , Yu Song
- & Pengcheng Dai
-
Article
| Open Access A dynamic and multi-responsive porous flexible metal–organic material
A dynamic and multi-responsive porous flexible metal–organic material
Stimuli-responsive porous materials are attractive for a range of applications, but each material typically exhibits only one type of transformation. Here, the authors report on a metal–organic material that exhibits six distinct phases as a result of four types of structural transformation in response to different stimuli.
- Mohana Shivanna
- , Qing-Yuan Yang
- & Michael J. Zaworotko

 Intertidal exposure favors the soft-studded armor of adaptive mussel coatings
Intertidal exposure favors the soft-studded armor of adaptive mussel coatings