Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Turning a native or corroded Mg alloy surface into an anti-corrosion coating in excited CO2
Turning a native or corroded Mg alloy surface into an anti-corrosion coating in excited CO2
Magnesium alloys usually have poor corrosion resistance, which inhibits their use in the automotive and biomedical industries. Here, the authors use an environmental TEM to carbonate the natural corrosion products at the surface of magnesium alloys and form a compact and protective surface layer.
- Yuecun Wang
- , Boyu Liu
- & Zhiwei Shan
-
Article
| Open Access High-content ductile coherent nanoprecipitates achieve ultrastrong high-entropy alloys
High-content ductile coherent nanoprecipitates achieve ultrastrong high-entropy alloys
High entropy alloys usually emphasize equiatomic compositions, which restrict the compositions available to induce strengthening via precipitation. Here the authors use spinodal decomposition in a five-element alloy to obtain high content nanophases and the highest tensile strength reported to date.
- Yao-Jian Liang
- , Linjing Wang
- & Hongnian Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate
Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate
3D hydrogels have provided information on the physical requirements of stem cell fate, but the contribution of interactions with the pericellular environment are under-explored. Here the authors show that pericellular matrix secreted by human bone marrow stromal cells (hMSC) embedded in a HA-based hydrogel contribute to hMSC fate.
- Silvia A. Ferreira
- , Meghna S. Motwani
- & Eileen Gentleman
-
Article
| Open Access Polymerization driven monomer passage through monolayer chemical vapour deposition graphene
Polymerization driven monomer passage through monolayer chemical vapour deposition graphene
Translocation of larger molecules through graphene holds potential for molecular sieving, however it is rarely observed. Here, the authors show the radical polymerization of vinyl monomers via their translocation through a single layer graphene to a monolayer initiator and additionally study the monomer-graphene interactions.
- Tao Zhang
- , Zhongquan Liao
- & Rainer Jordan
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring manganese oxide with atomic precision to increase surface site availability for oxygen reduction catalysis
Tailoring manganese oxide with atomic precision to increase surface site availability for oxygen reduction catalysis
Controlling structures at the atomic level provides an opportunity to design and understand catalysts. Here the authors use thin-film deposition to fabricate perovskite heterostructures in a non-equilibrium manner to assess the effects on electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction.
- C. John Eom
- , Ding-Yuan Kuo
- & Jin Suntivich
-
Article
| Open Access Tensorial neutron tomography of three-dimensional magnetic vector fields in bulk materials
Tensorial neutron tomography of three-dimensional magnetic vector fields in bulk materials
Mapping the distribution of magnetic fields inside bulk materials is challenging but crucial to understand and develop functional magnetic materials. Here the authors demonstrate the capability to visualize 3D vector magnetic fields inside materials using spin-polarized neutron tomography and tensorial reconstruction techniques.
- A. Hilger
- , I. Manke
- & J. Banhart
-
Article
| Open Access Observing of the super-Planckian near-field thermal radiation between graphene sheets
Observing of the super-Planckian near-field thermal radiation between graphene sheets
Though monolayer graphene has the potential to be used in near-field thermal management applications, no experimental verification has been provided to date. Here, the authors directly measure plasmon-enhanced near-field heat transfer between graphene sheets on intrinsic silicon substrates.
- Jiang Yang
- , Wei Du
- & Yungui Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional amorphous NiO as a plasmonic photocatalyst for solar H2 evolution
Two-dimensional amorphous NiO as a plasmonic photocatalyst for solar H2 evolution
While photocatalysis offers a means to store solar energy as chemical fuels, photocatalysts typically require crystalline structures and expensive noble-metal cocatalysts. Here, authors prepare 2D amorphous nano-nickel oxide capable of plasmonic, photodriven H2 evolution without cocatalysts.
- Zhaoyong Lin
- , Chun Du
- & Guowei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Advanced sulfide solid electrolyte by core-shell structural design
Advanced sulfide solid electrolyte by core-shell structural design
Sulfide electrolyte materials offer the opportunity for the development of solid-state batteries. Here the authors further improve the voltage stability of core-shell structured sulfides by modifying the microstructures, and pair the optimized electrolytes with lithium metal anode into battery devices.
- Fan Wu
- , William Fitzhugh
- & Xin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Interface dominated cooperative nanoprecipitation in interstitial alloys
Interface dominated cooperative nanoprecipitation in interstitial alloys
The specifics of nanoscale precipitation in steels remain complex. Here the authors combine high-resolution microscopy and atomistic simulations to identify a cooperative growth mechanism leading to the preferential growth of cementite nanoprecipitates along a specific crystallographic direction.
- Hongcai Wang
- , Xie Zhang
- & Gunther Eggeler
-
Article
| Open Access Digital coding of mechanical stress in a dynamic covalent shape memory polymer network
Digital coding of mechanical stress in a dynamic covalent shape memory polymer network
Stresses are often detrimental to the mechanical properties of materials but when well controlled can lead to unusual opportunities in various technological areas. Here the authors report a digital photothermal mechanism enabled laser printing that allows freedom in stress manipulation in dynamic covalent shape memory polymers.
- Guogao Zhang
- , Wenjun Peng
- & Tao Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with ligand engineered all-inorganic InP and InP/ZnS colloidal quantum dots
Efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with ligand engineered all-inorganic InP and InP/ZnS colloidal quantum dots
While quantum dots show high efficiency solar-to-fuel conversion for renewable energy, the frequently toxic elements employed present severe safety concerns. Here, authors demonstrate indium phosphide quantum dots as low-toxicity alternatives alongside efficient hydrogen evolution photocatalysis.
- Shan Yu
- , Xiang-Bing Fan
- & Greta R. Patzke
-
Article
| Open Access Superplasticity in an organic crystal
Superplasticity in an organic crystal
Superplasticity enables processing on hard-to-work solids but superelastic deformation, especially in a single-crystal-to-single-crystal manner, was not demonstrated for organic crystals so far. Here the authors demonstrate a single-crystal-to-single-crystal superplasticity in a crystal of N,N-dimethyl-4-nitroaniline.
- Satoshi Takamizawa
- , Yuichi Takasaki
- & Noriaki Ozaki
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-momentum locking and spin-orbit torques in magnetic nano-heterojunctions composed of Weyl semimetal WTe2
Spin-momentum locking and spin-orbit torques in magnetic nano-heterojunctions composed of Weyl semimetal WTe2
The Fermi arcs, topological surface states of Weyl semimetals can enable the intriguing spin control and facilitate topological spintronics. Here the authors report the spin-orbit torque at the interface of WTe2/Py and attribute it to the enhanced spin accumulation by the spin-momentum locking effect of the Fermi arcs of WTe2.
- Peng Li
- , Weikang Wu
- & Xi-xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically precise graphene etch stops for three dimensional integrated systems from two dimensional material heterostructures
Atomically precise graphene etch stops for three dimensional integrated systems from two dimensional material heterostructures
Fabrication methods to pattern thin materials are a critical tool to build molecular scale devices. Here the authors report a selective etching method using XeF2 gas to pattern graphene based heterostructures with multiple active layers and achieve 1D contacts with low contact resistivity of 80 Ω·µm
- Jangyup Son
- , Junyoung Kwon
- & Arend M. van der Zande
-
Article
| Open Access Curvotaxis directs cell migration through cell-scale curvature landscapes
Curvotaxis directs cell migration through cell-scale curvature landscapes
The effect that microscale surface curvature has on cell migration has not been evaluated. Here the authors fabricate sinusoidal 3D surfaces and show that the cell nucleus and cytoskeleton cooperate to guide cells to concave valleys in a process they coin curvotaxis.
- Laurent Pieuchot
- , Julie Marteau
- & Karine Anselme
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant torsion magnetometry in anisotropic quantum materials
Resonant torsion magnetometry in anisotropic quantum materials
Insights into the behavior of quantum materials are only possible because of the development of suitable experimental probes. Modic et. al. develop the theoretical and experimental basis for resonant torsion magnetometry—a technique to measure anisotropic magnetic responses with high sensitivity.
- K. A. Modic
- , Maja D. Bachmann
- & Philip J. W. Moll
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial heterogeneity as the structure feature for structure–property relationship of metallic glasses
Spatial heterogeneity as the structure feature for structure–property relationship of metallic glasses
Directly relating the mechanical properties of metallic glasses to their atomic structure remains a challenge. Here, the authors use high resolution microscopy to show many mechanical properties of metallic glasses depend on a single structural parameter, the characteristic length of spatial heterogeneity.
- Fan Zhu
- , Shuangxi Song
- & Mingwei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Uniform doping of graphene close to the Dirac point by polymer-assisted assembly of molecular dopants
Uniform doping of graphene close to the Dirac point by polymer-assisted assembly of molecular dopants
Incorporating dopants in the graphene lattice to tune its electronic properties is a challenging task. Here, the authors report a strategy to dope epitaxial large-area graphene on SiC by means of spin-coating deposition of F4TCNQ polymers in ambient conditions.
- Hans He
- , Kyung Ho Kim
- & Samuel Lara-Avila
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-organic framework patterns and membranes with heterogeneous pores for flow-assisted switchable separations
Metal-organic framework patterns and membranes with heterogeneous pores for flow-assisted switchable separations
Tailoring MOFs to allow access of complex and large molecules is a challenging task due to their inherent microporous nature. Here the authors engineer meso- and macroporous MOF patterns and membranes via a mild decarboxylation applicable to different substrates, demonstrating their potential in macromolecule separations.
- Guan-Young Jeong
- , Ajay K. Singh
- & Dong-Pyo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A bioinspired multilegged soft millirobot that functions in both dry and wet conditions
A bioinspired multilegged soft millirobot that functions in both dry and wet conditions
Despite the enormous potential of magnetically-guided soft robots for various applications, challenges related to inefficient locomotion in harsh environments hinder its development. Here, the authors demonstrate a multi-legged millirobot with excellent locomotion capability in harsh environments.
- Haojian Lu
- , Mei Zhang
- & Yajing Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Probing ultrafast spin-relaxation and precession dynamics in a cuprate Mott insulator with seven-femtosecond optical pulses
Probing ultrafast spin-relaxation and precession dynamics in a cuprate Mott insulator with seven-femtosecond optical pulses
Understanding the dynamics of cuprates following photoexcitation can provide insights into the complex coupling mechanisms that underlie their exotic equilibrium behaviour. Here the authors use pump-probe reflection spectroscopy to investigate the nonequilibrium spin dynamics of Mott-insulating Nd2CuO4.
- T. Miyamoto
- , Y. Matsui
- & H. Okamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral self-sorted multifunctional supramolecular biocoordination polymers and their applications in sensors
Chiral self-sorted multifunctional supramolecular biocoordination polymers and their applications in sensors
Chiral supramolecules may be used in chiral recognition, sensing and catalysis. Here the authors selectively synthesized homochiral and heterochiral supramolecular biocoordination polymers of naphthalene diimide ligands with alanine termini and Zn ions.
- Xiaobo Shang
- , Inho Song
- & Joon Hak Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality amplification by desymmetrization of chiral ligand-capped nanoparticles to nanorods quantified in soft condensed matter
Chirality amplification by desymmetrization of chiral ligand-capped nanoparticles to nanorods quantified in soft condensed matter
The mechanisms by which molecular chirality is amplified through space and across length scales is of great interest. Here the authors show how gold nanorods covered in chiral dopants are more efficient in transducing chiral information compared to other gold nanoparticles decorated with chiral ligands.
- Ahlam Nemati
- , Sasan Shadpour
- & Torsten Hegmann
-
Article
| Open Access Modulating the hierarchical fibrous assembly of Au nanoparticles with atomic precision
Modulating the hierarchical fibrous assembly of Au nanoparticles with atomic precision
Constructing nanoparticle assemblies with atomic precision remains a major challenge in nanoscience. Here, the authors realize atomic‐level control over the 1D, 2D and hierarchical 3D assembly of Au nanoparticles by modulating the site‐specific surface ligands and associated counterions.
- Qi Li
- , Jake C. Russell
- & Rongchao Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Atom-hybridization for synthesis of polymetallic clusters
Atom-hybridization for synthesis of polymetallic clusters
Multimetallic clusters are difficult to synthesize with control over elemental composition and organization. Here, the authors use dendrimers to precisely template the formation of five-element sub-nanoclusters, providing an elegant route to otherwise-inaccessible multinary compounds.
- Takamasa Tsukamoto
- , Tetsuya Kambe
- & Kimihisa Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Solution-processed perovskite light emitting diodes with efficiency exceeding 15% through additive-controlled nanostructure tailoring
Solution-processed perovskite light emitting diodes with efficiency exceeding 15% through additive-controlled nanostructure tailoring
Crystal sizes play a vital role in pushing up the efficiency of organometal halide perovskites based LEDs. Here Ban et al. incorporate a molecular additive to control the crystallite distribution and phase separation in the perovskite devices, resulting in high external quantum efficiency of 15.5%.
- Muyang Ban
- , Yatao Zou
- & Baoquan Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Gas-solid reaction based over one-micrometer thick stable perovskite films for efficient solar cells and modules
Gas-solid reaction based over one-micrometer thick stable perovskite films for efficient solar cells and modules
Perovskite solar cells often suffer from poor uniformity and reproducibility especially in case of large area devices. Here Liu et al. developed a gas−solid reaction method that enables facile fabrication of over 1 µm thick perovskite films for solar modules with high efficiency, stability and reproducibility.
- Zonghao Liu
- , Longbin Qiu
- & Yabing Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Complex strain evolution of polar and magnetic order in multiferroic BiFeO3 thin films
Complex strain evolution of polar and magnetic order in multiferroic BiFeO3 thin films
To fully exploit the potential of multiferroic materials the control of their intrinsic degrees of freedom is a prerequisite. Here, the control of spin orientation in strained BiFeO3 films is demonstrated elucidating the microscopic mechanism of the complex interplay of polar and magnetic order.
- Zuhuang Chen
- , Zhanghui Chen
- & Lane W. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable colloid trajectories in nematic liquid crystals near wavy walls
Tunable colloid trajectories in nematic liquid crystals near wavy walls
Nematic liquid crystals have a rich energy landscape which can define elastic fields to guide colloidal assembly. Here the authors show controllable trapping of colloidal particles by placing them in a system with wavy walls which are exploited to obtain stable, metastable and unstable equilibria.
- Yimin Luo
- , Daniel A. Beller
- & Kathleen J. Stebe
-
Article
| Open Access Gallium nitride nanowire as a linker of molybdenum sulfides and silicon for photoelectrocatalytic water splitting
Gallium nitride nanowire as a linker of molybdenum sulfides and silicon for photoelectrocatalytic water splitting
Sunlight-harvesting materials require the clean integration of light-absorbing and catalytic components to be efficient. Here, authors link silicon photoelectrodes and molybdenum sulfide catalysts with defect-free gallium nitride nanowire to improve photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution.
- Baowen Zhou
- , Xianghua Kong
- & Zetian Mi
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfiguring surface functions using visible-light-controlled metal-ligand coordination
Reconfiguring surface functions using visible-light-controlled metal-ligand coordination
Configuring surfaces on-demand for desired functionalities is an ongoing challenge. Here, diverse and tailorable modifications of quartz and porous silica surfaces that are rapidly and reversibly switchable by the use of visible light are achieved via ruthenium-thioether coordination.
- Chaoming Xie
- , Wen Sun
- & Si Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of PEDOT:PSS crystallinity and composition on electrochemical transistor performance and long-term stability
Influence of PEDOT:PSS crystallinity and composition on electrochemical transistor performance and long-term stability
The lack of understanding of mixed transport in ion-permeable conjugated polymer films hinders the advance of organic electrochemical transistors for bioelectronics. Here, the authors elucidate the structure-property-performance relationships for conventional and crystallized PEDOT:PSS films.
- Seong-Min Kim
- , Chang-Hyun Kim
- & Myung-Han Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Active particles bound by information flows
Active particles bound by information flows
Synthetic active particles with inter-particle propulsion have been served as a model system to study the collective animal behaviors. Here, Khadka et al. add complexity to the model by spatially controlling particle motions through a laser feedback loop in response to the collective dynamics of particles.
- Utsab Khadka
- , Viktor Holubec
- & Frank Cichos
-
Article
| Open Access Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors
Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors
The development of potassium-ion batteries requires cathode materials that can maintain the structural stability during cycling. Here the authors have developed honeycomb-layered tellurates K2M2TeO6 that afford high ionic conductivity and reversible intercalation of large K ions at high voltages.
- Titus Masese
- , Kazuki Yoshii
- & Masahiro Shikano
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of active sites on supported metal catalysts with carbon nanotube hydrogen highways
Identification of active sites on supported metal catalysts with carbon nanotube hydrogen highways
Understanding the location and nature of the catalytic active site is critical for controlling a catalyst’s activity and selectivity. Here, the authors separate the metal from the support by a controlled distance while maintaining the ability to promote defects via the use of carbon nanotube hydrogen highways.
- Nicholas M. Briggs
- , Lawrence Barrett
- & Steven P. Crossley
-
Article
| Open Access Copper-on-nitride enhances the stable electrosynthesis of multi-carbon products from CO2
Copper-on-nitride enhances the stable electrosynthesis of multi-carbon products from CO2
While multi-carbon (C2+) products present high-value species attainable from emitted carbon dioxide, it is challenging to prepare stable, C2+ selective catalysts. Here, authors support copper on copper nitride to improve copper’s electrocatalytic stability and selectivity toward C2+ synthesis.
- Zhi-Qin Liang
- , Tao-Tao Zhuang
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Sounding-rocket microgravity experiments on alumina dust
Sounding-rocket microgravity experiments on alumina dust
Alumina is thought to be the main condensate to form in the gas outflow from oxygen-rich evolved stars. Here, the authors perform a condensation experiment with alumina in a low-gravity environment, and find spectroscopic evidence for a sharp feature at a wavelength of 13.55 μm.
- Shinnosuke Ishizuka
- , Yuki Kimura
- & Yuko Inatomi
-
Article
| Open Access Zigzag carbon as efficient and stable oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Zigzag carbon as efficient and stable oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Cost and stability of catalysts hinder widespread use of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Here the authors synthesize zigzag-edged graphene nanoribbons for electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction. Employment of such a metal-free catalyst in a fuel cell yields remarkable power density and durability.
- Longfei Xue
- , Yongcheng Li
- & Jianglan Shui
-
Article
| Open Access Mechano-regulated metal–organic framework nanofilm for ultrasensitive and anti-jamming strain sensing
Mechano-regulated metal–organic framework nanofilm for ultrasensitive and anti-jamming strain sensing
High performance flexible strain sensors with accurate signal detection and noise screening are key to the development of smart sensing systems. Here, the authors demonstrate metal–organic framework based strain sensors that are ultrasensitive, robust, and non-responsive to environmental noise.
- Liang Pan
- , Gang Liu
- & Run-Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Exceptional thermoelectric properties of flexible organic−inorganic hybrids with monodispersed and periodic nanophase
Exceptional thermoelectric properties of flexible organic−inorganic hybrids with monodispersed and periodic nanophase
The potential of flexible organic/inorganic hybrids for thermoelectrics is limited by the inability to control their microstructure. Here, the authors demonstrate polymer-nanoparticle hybrids with a monodispersed, periodic nanophase that shows high thermoelectric performance at room temperature.
- Liming Wang
- , Zimeng Zhang
- & Shiren Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Deep neural networks for accurate predictions of crystal stability
Deep neural networks for accurate predictions of crystal stability
Crystal stability prediction is of paramount importance for novel material discovery, with theoretical approaches alternative to expensive standard schemes highly desired. Here the authors develop a deep learning approach which, just using two descriptors, provides crystalline formation energies with very high accuracy.
- Weike Ye
- , Chi Chen
- & Shyue Ping Ong
-
Article
| Open Access Solvatochromic covalent organic frameworks
Solvatochromic covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) find increasing application as sensor material, but fast switching solvatochromism was not realized. Here the authors demonstrate that combination of electron-rich and -deficient building blocks leads to COFs which fast and reversibly change of their electronic structure depending on the surrounding atmosphere.
- Laura Ascherl
- , Emrys W. Evans
- & Florian Auras
-
Article
| Open Access Macroscopic helical chirality and self-motion of hierarchical self-assemblies induced by enantiomeric small molecules
Macroscopic helical chirality and self-motion of hierarchical self-assemblies induced by enantiomeric small molecules
Chirality transfer by chemical self-assembly has been studied intensively for years but chirality transfers along the same path remains elusive. Here the authors use a multiscale chemo-mechanical model to elucidate the mechanism underlying the chirality transfer via self-assembly in hierarchical camphorsulfonic acid doped polyaniline.
- Yang Yang
- , Jie Liang
- & Zhixiang Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Water printing of ferroelectric polarization
Water printing of ferroelectric polarization
Controlling ferroelectric polarization is conventionally achieved by applying electric fields, mechanical force or similar. Here reversible switching of the bulk polarization of a BiFeO3 thin film is demonstrated by pattering aqueous solution on to the surface enabling large-scale switching.
- Yu Tian
- , Lanying Wei
- & Jinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ cross-linking strategy for efficient and operationally stable methylammoniun lead iodide solar cells
In-situ cross-linking strategy for efficient and operationally stable methylammoniun lead iodide solar cells
The stability of perovskite solar cell remains the biggest challenge that hinders its commercialization. Here Li et al. incorporate crosslinkable molecules to form a crosslinked perovskite film and increase the device operational stability by 590 times to 400 h under standard Xenon lamp without filters.
- Xiaodong Li
- , Wenxiao Zhang
- & Junfeng Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Control of coordinatively unsaturated Zr sites in ZrO2 for efficient C–H bond activation
Control of coordinatively unsaturated Zr sites in ZrO2 for efficient C–H bond activation
Identifying active sites and designing rationally heterogeneous catalysts are not inherently straightforward due to their complexity. Here, the authors reveal the nature of active sites for efficient C–H bond activation in C1-C4 alkanes over bare ZrO2 and provide fundamentals for controlling their concentration.
- Yaoyuan Zhang
- , Yun Zhao
- & Evgenii V. Kondratenko
-
Article
| Open Access Highly-sensitive optical organic vapor sensor through polymeric swelling induced variation of fluorescent intensity
Highly-sensitive optical organic vapor sensor through polymeric swelling induced variation of fluorescent intensity
Traditional optical organic vapor sensors with solvatochromic shift mechanisms have lower sensitivity due to weak intermolecular interactions. Here, the authors report a general strategy to prepare a higher sensitivity optical organic vapor sensor through polymeric swelling-induced variation of fluorescent intensity.
- Xiangyu Jiang
- , Hanfei Gao
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional X-ray diffraction imaging of dislocations in polycrystalline metals under tensile loading
Three-dimensional X-ray diffraction imaging of dislocations in polycrystalline metals under tensile loading
Identifying atomic defects during deformation is crucial to understand material response but remains challenging in three dimensions. Here, the authors couple X-ray Bragg coherent diffraction imaging and atomistic simulations to correlate a strain field to a screw dislocation in a single copper grain.
- Mathew J. Cherukara
- , Reeju Pokharel
- & Richard L. Sandberg

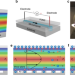 Enhanced voltage generation through electrolyte flow on liquid-filled surfaces
Enhanced voltage generation through electrolyte flow on liquid-filled surfaces