News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Near-frictionless ion transport within triazine framework membranes
Near-frictionless ion transport within triazine framework membranes
The authors develop a strategy that allows the diffusion limit of ions in water to be approached for large-area, free-standing, synthetic membranes using covalently bonded polymer frameworks with rigidity-confined ion channels.
- Peipei Zuo
- , Chunchun Ye
- & Tongwen Xu
-
Article |
 Tunable electron–flexural phonon interaction in graphene heterostructures
Tunable electron–flexural phonon interaction in graphene heterostructures
Experimental observation and calculations show that broken reflection symmetry in graphene heterostructures allows tunable electron–flexural phonon coupling, providing a way to control quantum matter at the atomic scale.
- Mir Mohammad Sadeghi
- , Yajie Huang
- & Li Shi
-
Article |
 Dynamic crosslinking compatibilizes immiscible mixed plastics
Dynamic crosslinking compatibilizes immiscible mixed plastics
A new compatibilization strategy installs dynamic crosslinkers into several classes of binary, ternary and postconsumer immiscible polymer mixtures in situ, with the resulting compatibilized dynamic thermosets exhibiting intrinsic reprocessability and enhanced tensile strength and creep resistance.
- Ryan W. Clarke
- , Tobias Sandmeier
- & Eugene Y.-X. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A 3D printable alloy designed for extreme environments
A 3D printable alloy designed for extreme environments
The authors develop a new oxide-dispersion-strengthened NiCoCr-based alloy using a model-driven alloy design approach and laser-based additive manufacturing, showing how such designs can provide superior compositions using far fewer resources than previous methods.
- Timothy M. Smith
- , Christopher A. Kantzos
- & John W. Lawson
-
Research Briefing |
 Plastic polymers split into reusable monomers using an electrical heating method
Plastic polymers split into reusable monomers using an electrical heating method
An innovative approach has been developed to break down plastic polymers into their monomer building blocks. It uses a continuous melting, wicking, vaporization and reaction process in a porous carbon-bilayer structure, and can convert two model plastic polymers to their monomers at high yields without a catalyst.
-
Article |
 Depolymerization of plastics by means of electrified spatiotemporal heating
Depolymerization of plastics by means of electrified spatiotemporal heating
A depolymerization method is described that uses electrified spatiotemporal heating to selectively generate monomers from the commodity plastics polypropylene and poly(ethylene terephthalate), allowing control over the pyrolysis of plastic waste and reducing the formation of side products.
- Qi Dong
- , Aditya Dilip Lele
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 pH-dependent water permeability switching and its memory in MoS2 membranes
pH-dependent water permeability switching and its memory in MoS2 membranes
We demonstrate the memory effects and stimuli-regulated transport of molecules through an intelligent, phase-changing MoS2 membrane in response to external pH, a phenomenon unique to the 1T′ phase of MoS2.
- C. Y. Hu
- , A. Achari
- & R. R. Nair
-
Research Briefing |
 Quantization observed for ‘heavy’ electrons
Quantization observed for ‘heavy’ electrons
Quantum materials can host exotic phases of matter in which electrons form unusual collective states. Scientists have struggled to observe the quantization that these electronic states are expected to show, but this phenomenon has now been detected in heavy states at the surface of a superconducting quantum material.
-
News & Views |
 Elusive excited states identified from cutting-edge molecular movies
Elusive excited states identified from cutting-edge molecular movies
A molecular process called singlet fission might boost solar-cell efficiency, but the mechanism must first be determined. A technique that probes molecules undergoing this process finally reveals the excited states involved.
- Andrew J. Musser
- & Hannah Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital-resolved observation of singlet fission
Orbital-resolved observation of singlet fission
Time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy is used to observe the primary step of singlet fission with orbital resolution indicating a charge-transfer mediated mechanism with a hybridization of states in the lowest bright singlet exciton.
- Alexander Neef
- , Samuel Beaulieu
- & Ralph Ernstorfer
-
Article
| Open Access Dehydration of a crystal hydrate at subglacial temperatures
Dehydration of a crystal hydrate at subglacial temperatures
A porous organic crystal readily and reversibly adsorbs water, with dehydration occurring well below the freezing point of water, which could be seen by a change in colour.
- Alan C. Eaby
- , Dirkie C. Myburgh
- & Leonard J. Barbour
-
Article
| Open Access Giant magnetoresistance of Dirac plasma in high-mobility graphene
Giant magnetoresistance of Dirac plasma in high-mobility graphene
A Dirac plasma in high-mobility graphene shows anomalous magnetotransport and giant magnetoresistance that reaches more than 100 per cent in a low magnetic field at room temperature.
- Na Xin
- , James Lourembam
- & Alexey I. Berdyugin
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
A single-element ferroelectric state is observed in a black phosphorus-like bismuth layer, in which the ordered charge transfer and the regular atom distortion between sublattices happen simultaneously and ferroelectric switching is further visualized experimentally.
- Jian Gou
- , Hua Bai
- & Andrew Thye Shen Wee
-
Article |
 Deforming lanthanum trihydride for superionic conduction
Deforming lanthanum trihydride for superionic conduction
By creating nanosized grains and defects in lanthanum trihydride, its electronic conductivity can be suppressed, transforming it into a superionic conductor at −40 °C with a record high H− conductivity.
- Weijin Zhang
- , Jirong Cui
- & Ping Chen
-
Article |
 Self-powered perovskite photon-counting detectors
Self-powered perovskite photon-counting detectors
Suppression of shallow traps responsible for dark count rates in polycrystalline methylammonium lead triiodide using diphenyl sulfide enables the production of metal-halide perovskite photon-counting detectors that allow sensitive detection of γ-ray spectra.
- Ying Zhou
- , Chengbin Fei
- & Jinsong Huang
-
Article |
 A LaCl3-based lithium superionic conductor compatible with lithium metal
A LaCl3-based lithium superionic conductor compatible with lithium metal
A LaCl3-based lithium superionic conductor is developed that has excellent interfacial compatibility with lithium metal electrodes, with its optimized Li0.388Ta0.238La0.475Cl3 electrolyte exhibiting good Li+ conductivity and low activation energy.
- Yi-Chen Yin
- , Jing-Tian Yang
- & Hong-Bin Yao
-
Research Briefing |
 Memristor devices denoised to achieve thousands of conductance levels
Memristor devices denoised to achieve thousands of conductance levels
The number of distinguishable conductance levels in memristor devices — electronic components that store information without power — has been limited by noise. An understanding of the source of the noise, and development of an effective denoising process, have now enabled 2,048 conductance levels to be achieved in memristors in large arrays fabricated in a chip factory.
-
News |
 Could grinding up lithium batteries help to recycle them?
Could grinding up lithium batteries help to recycle them?
Researchers use ‘mechanochemistry’ to recover the metal from batteries at a small scale.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
Article |
 Tracking cubic ice at molecular resolution
Tracking cubic ice at molecular resolution
Tracking the formation of cubic ice (ice Ic) using transmission electron microscopy and low-dose imaging shows preferential nucleation of ice Ic at low-temperature interfaces and two types of stacking disorder.
- Xudan Huang
- , Lifen Wang
- & Xuedong Bai
-
Article |
 Thousands of conductance levels in memristors integrated on CMOS
Thousands of conductance levels in memristors integrated on CMOS
Chips with 256 × 256 memristor arrays that were monolithically integrated on complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) circuits in a commercial foundry achieved 2,048 conductance levels in individual memristors.
- Mingyi Rao
- , Hao Tang
- & J. Joshua Yang
-
Article |
 Improving interface quality for 1-cm2 all-perovskite tandem solar cells
Improving interface quality for 1-cm2 all-perovskite tandem solar cells
A self-assembled monolayer of (4-(7H-dibenzo[c,g]carbazol-7-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid is integrated in wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells, which enables a high power conversion efficiency and low open-circuit voltage deficiency, as well as efficient centimetre-scale all-perovskite tandem solar cells.
- Rui He
- , Wanhai Wang
- & Dewei Zhao
-
Article |
 Mechanistic formulation of inorganic membranes at the air–liquid interface
Mechanistic formulation of inorganic membranes at the air–liquid interface
By switching the nucleation preferences in aqueous systems of inorganic precursors to bias formation and growth at the air–liquid interface, the mechanistic formation of inorganic membranes from the floating-particle system is demonstrated.
- Chen Zhang
- , Wanheng Lu
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Research Highlight |
 Life’s wondrous forms recreated in graphene and more
Life’s wondrous forms recreated in graphene and more
A design strategy that relies on virtual lattices allows scientists to recreate biological shapes in a wide variety of materials.
-
Article |
 Suppressed phase segregation for triple-junction perovskite solar cells
Suppressed phase segregation for triple-junction perovskite solar cells
All-perovskite triple-junction solar cell devices have been fabricated, with a certified efficiency of 23.3%; these devices retain 80% of their initial efficiency following 420 hours of operation.
- Zaiwei Wang
- , Lewei Zeng
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid 2D–CMOS microchips for memristive applications
Hybrid 2D–CMOS microchips for memristive applications
High-integration-density 2D–CMOS hybrid microchips for memristive applications are made demonstrating in-memory computation and electrical response suitable for the implementation of spiking neural networks representing an advance towards integration of 2D materials in microelectronic products and memristive applications.
- Kaichen Zhu
- , Sebastian Pazos
- & Mario Lanza
-
Research Highlight |
 A gem of a material could provide a shield for spacecraft
A gem of a material could provide a shield for spacecraft
Material that includes carbon with the same structure as diamond could be used to protect satellites from space radiation.
-
Article |
 2D fin field-effect transistors integrated with epitaxial high-k gate oxide
2D fin field-effect transistors integrated with epitaxial high-k gate oxide
The epitaxial synthesis of high-density, vertically aligned arrays of two-dimensional (2D) fin-oxide heterostructures is described, enabling the fabrication of 2D fin field-effect transistors with high electron mobility and desirable low-power specifications.
- Congwei Tan
- , Mengshi Yu
- & Hailin Peng
-
News & Views |
 Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Particles that self-assemble from nanoribbons into bow-tie-shaped structures can be tailored to change the degree of their twist. A search for how best to quantify this twist homes in on a measure of how the bow ties respond to light.
- Bart Kahr
-
Article |
 Photonically active bowtie nanoassemblies with chirality continuum
Photonically active bowtie nanoassemblies with chirality continuum
Self-limited assembly of 'imperfect' chiral nanoparticles enables formation of bowtie-shaped microparticles with size monodispersity and continuously variable chirality to be used for printing photonically active metasurfaces.
- Prashant Kumar
- , Thi Vo
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Article |
 Bright and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes in the near-infrared range
Bright and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes in the near-infrared range
Perovskite LEDs with exceptional performance at high brightness are demonstrated achieving an operational half-lifetime of 32 hours, an important step towards commercialization opening up new opportunities beyond conventional LED technologies, such as perovskite electrically pumped lasers.
- Yuqi Sun
- , Lishuang Ge
- & Neil C. Greenham
-
Research Highlight |
 A slimy self-healing gel helps a robotic snail to slither
A slimy self-healing gel helps a robotic snail to slither
The chemical bonds in a stretchy gel quickly reform if the material is severed.
-
Nature Index |
 Japan’s rising research stars: Ken-ichi Otake
Japan’s rising research stars: Ken-ichi Otake
Otake uses novel materials to isolate ‘heavy water’ cheaply and efficiently.
- Sandy Ong
-
Research Briefing |
 Ensembles of synthetic polymers engineered to mimic protein mixtures
Ensembles of synthetic polymers engineered to mimic protein mixtures
The compatibility of a material with its environment is important for real-world applications. A framework has been developed to translate the amino-acid sequence of segments of proteins into engineered synthetic polymers, enabling the creation of ensembles of polymers with properties matching those of mixtures of proteins.
-
News & Views |
 Hopes raised for room-temperature superconductivity, but doubts remain
Hopes raised for room-temperature superconductivity, but doubts remain
A hydrogen-rich compound has taken the lead in the race for a material that can conduct electricity with zero resistance at room temperature and ambient pressure — the conditions required for many technological applications.
- ChangQing Jin
- & David Ceperley
-
Article
| Open Access Population-based heteropolymer design to mimic protein mixtures
Population-based heteropolymer design to mimic protein mixtures
Information from natural protein libraries was extracted and used to design heteropolymer ensembles as mixtures of disordered, partially folded and folded proteins, providing valuable guiding principles to synthetically realize protein properties.
- Zhiyuan Ruan
- , Shuni Li
- & Ting Xu
-
Article |
 RETRACTED ARTICLE: Evidence of near-ambient superconductivity in a N-doped lutetium hydride
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Evidence of near-ambient superconductivity in a N-doped lutetium hydride
A nitrogen-doped lutetium hydride was synthesized under high-pressure high-temperature conditions and, following full recoverability, examination along compression pathways showed evidence of superconductivity at room temperature and near-ambient pressures.
- Nathan Dasenbrock-Gammon
- , Elliot Snider
- & Ranga P. Dias
-
Article |
 Anomalous intense coherent secondary photoemission from a perovskite oxide
Anomalous intense coherent secondary photoemission from a perovskite oxide
The reconstructed surface of single crystals of SrTiO3(100), prepared by simple vacuum annealing, produces discrete secondary photoemission spectra at room temperature and has increased peak intensities at low temperatures.
- Caiyun Hong
- , Wenjun Zou
- & Rui-Hua He
-
Article
| Open Access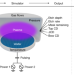 Human–machine collaboration for improving semiconductor process development
Human–machine collaboration for improving semiconductor process development
A virtual process game to benchmark the performance of humans and computers for the fabrication of semiconductors leads to a strategy combining human expert design with optimization algorithms to improve semiconductor process development.
- Keren J. Kanarik
- , Wojciech T. Osowiecki
- & Richard A. Gottscho
-
Article |
 Ladderphane copolymers for high-temperature capacitive energy storage
Ladderphane copolymers for high-temperature capacitive energy storage
A class of dielectric copolymers called ladderphanes is shown to outperform existing dielectric polymers and composites, with high discharged energy density and charge–discharge efficiency even at temperatures up to 200 °C.
- Jie Chen
- , Yao Zhou
- & Qing Wang
-
Article |
 Critical role of hydrogen for superconductivity in nickelates
Critical role of hydrogen for superconductivity in nickelates
In optimally doped Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2H epitaxial film, combined state-of-the-art experimental and theoretical approaches show abundant hydrogen with zero resistivity, and its critical role in superconductivity in epitaxial infinite-layer nickelates.
- Xiang Ding
- , Charles C. Tam
- & Liang Qiao
-
Article |
 Disorder-tuned conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon
Disorder-tuned conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon
Varying growth temperatures enables the tuning of the degree of disorder, which is fully described by the absence/presence of medium-range order and temperature-dependent densities of nanocrystallites, and electrical conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon films.
- Huifeng Tian
- , Yinhang Ma
- & Lei Liu
-
Research Highlight |
 Kevlar helps to make one tough synthetic tendon
Kevlar helps to make one tough synthetic tendon
A water-filled gel has the strength and elasticity of natural tendon.
-
News & Views |
 A twist in the bid to probe electrons in solids
A twist in the bid to probe electrons in solids
Two microscopy techniques have been merged into a tool for twisting ultrathin sheets of atoms relative to each other. The approach offers a new angle for studying the electronic properties of exotic layered materials.
- Rebeca Ribeiro-Palau
-
Article |
 Geometric frustration of Jahn–Teller order in the infinite-layer lattice
Geometric frustration of Jahn–Teller order in the infinite-layer lattice
A distorted infinite-layer lattice of single-crystal CaCoO2 originates from competition between an ordered Jahn–Teller effect and geometric frustration.
- Woo Jin Kim
- , Michelle A. Smeaton
- & Harold Y. Hwang
-
Article |
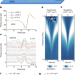 Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene
Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene
By using new on-chip terahertz spectroscopy techniques to measure the absorption spectra of a graphene microribbon as well as the energy waves close to charge neutrality, hydrodynamic collective excitations are observed.
- Wenyu Zhao
- , Shaoxin Wang
- & Feng Wang
-
Research Briefing |
 Stretchy electronic devices assembled in a Lego-like way
Stretchy electronic devices assembled in a Lego-like way
In current stretchable electronic devices, connection points between modules are made using commercially available pastes and break easily under mechanical deformation. An innovative connection interface has been developed to enable robust stretchable devices to be reliably assembled in a Lego‑like manner by simply pressing the interfaces of two modules together without pastes.
-
Article |
 A universal interface for plug-and-play assembly of stretchable devices
A universal interface for plug-and-play assembly of stretchable devices
A universal interface connects soft, rigid and encapsulation modules together to form robust, stretchable devices in a plug-and-play manner by pressing without using pastes, which will simplify and accelerate development of on-skin and implantable devices.
- Ying Jiang
- , Shaobo Ji
- & Xiaodong Chen
-
Article |
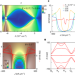 Evidence for Dirac flat band superconductivity enabled by quantum geometry
Evidence for Dirac flat band superconductivity enabled by quantum geometry
The authors investigate the effect of small velocity in a superconducting Dirac flat band system, finding evidence for small pairs and that superfluid stiffness is not dominated by kinetic energy.
- Haidong Tian
- , Xueshi Gao
- & Marc W. Bockrath
-
Article |
 Autonomous self-burying seed carriers for aerial seeding
Autonomous self-burying seed carriers for aerial seeding
A study describes a wood-based, three-tailed, biodegradable seed carrier that self-drills into the ground in response to moisture fluctuations with a success rate higher than that of natural self-drilling seeds.
- Danli Luo
- , Aditi Maheshwari
- & Lining Yao

 Mixed plastics upcycled dynamically
Mixed plastics upcycled dynamically