Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Glowing nanocrystals enable 3D X-ray imaging
Glowing nanocrystals enable 3D X-ray imaging
Persistently luminescent nanocrystals have been used to make flexible X-ray detectors that produce better images of 3D objects than do the flat-panel detectors currently widely used in radiography.
- Albano N. Carneiro Neto
- & Oscar L. Malta
-
News & Views |
 High-performance plastic made from renewable oils is chemically recyclable by design
High-performance plastic made from renewable oils is chemically recyclable by design
Plastics are invaluable materials, but they use up petroleum resources and persist in the environment. A high-performance plastic derived from renewable oils has been designed at the molecular level to be truly recyclable.
- Charlotte K. Williams
- & Georgina L. Gregory
-
Article |
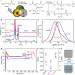 Closed-loop recycling of polyethylene-like materials
Closed-loop recycling of polyethylene-like materials
Polycarbonates and polyesters with materials properties like those of high-density polyethylene can be recycled chemically by depolymerization to their constituent monomers, re-polymerization yielding material with uncompromised processing and materials properties.
- Manuel Häußler
- , Marcel Eck
- & Stefan Mecking
-
Article |
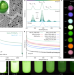 High-resolution X-ray luminescence extension imaging
High-resolution X-ray luminescence extension imaging
Using lanthanide-doped nanomaterials and flexible substrates, an approach that enables flat-panel-free, high-resolution, three-dimensional imaging is demonstrated and termed X-ray luminescence extension imaging.
- Xiangyu Ou
- , Xian Qin
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article |
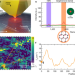 Localization of lattice dynamics in low-angle twisted bilayer graphene
Localization of lattice dynamics in low-angle twisted bilayer graphene
Nano-Raman spectroscopy reveals localization of some vibrational modes in reconstructed twisted bilayer graphene and provides qualitative insights into how electron–phonon coupling affects the vibrational and electronic properties of the material.
- Andreij C. Gadelha
- , Douglas A. A. Ohlberg
- & Ado Jorio
-
Article |
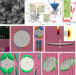 Thermally reconfigurable monoclinic nematic colloidal fluids
Thermally reconfigurable monoclinic nematic colloidal fluids
Dispersion of colloidal disks in a nematic liquid crystal reveals several low-symmetry phases, including monoclinic colloidal nematic order, with interchange between them achieved through variations in temperature, concentration and surface charge.
- Haridas Mundoor
- , Jin-Sheng Wu
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article |
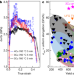 Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility
Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility
Bulk ultrafine-grained steel is prepared by an approach that involves the rapid production of coherent, disordered nanoprecipitates, which restrict grain growth but do not interfere with twinning or dislocation motion, resulting in high strength and ductility.
- Junheng Gao
- , Suihe Jiang
- & W. Mark Rainforth
-
Research Highlight |
 These gels jump into the air with a snap and a pop
These gels jump into the air with a snap and a pop
Gel discs launch themselves upwards again and again, with no external power source needed.
-
Perspective |
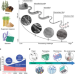 Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material
Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material
Opportunities for the application of fibrillated cellulose materials—which can be extracted from renewable resources—and broader manufacturing issues of scale-up, sustainability and synergy with the paper-making industry are discussed.
- Tian Li
- , Chaoji Chen
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Matters Arising |
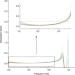 Reply to: On the measured dielectric constant of amorphous boron nitride
Reply to: On the measured dielectric constant of amorphous boron nitride
- Seokmo Hong
- , Min-Hyun Lee
- & Hyeon Suk Shin
-
Matters Arising |
On the measured dielectric constant of amorphous boron nitride
- Lei Li
- & Xiang Ming Chen
-
Article |
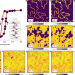 Antiferromagnetic half-skyrmions and bimerons at room temperature
Antiferromagnetic half-skyrmions and bimerons at room temperature
A family of topological antiferromagnetic spin textures is realized at room temperature in α-Fe2O3, and their reversible and field-free stabilization using a Kibble–Zurek-like temperature cycling is demonstrated.
- Hariom Jani
- , Jheng-Cyuan Lin
- & Paolo G. Radaelli
-
Article |
 Viscoelastic control of spatiotemporal order in bacterial active matter
Viscoelastic control of spatiotemporal order in bacterial active matter
Introducing viscoelasticity by addition of DNA into the fluid surrounding a suspension of Escherichia coli produces a giant oscillating vortex with a period controllable through the DNA concentration.
- Song Liu
- , Suraj Shankar
- & Yilin Wu
-
Article |
 Metastability of diamond ramp-compressed to 2 terapascals
Metastability of diamond ramp-compressed to 2 terapascals
X-ray diffraction measurements of solid carbon compressed to pressures of about two terapascals (approximately twenty million atmospheres) find that carbon retains a diamond structure even under these extreme conditions.
- A. Lazicki
- , D. McGonegle
- & J. S. Wark
-
Research Highlight |
 A material cracks barriers to asymmetrical toughness
A material cracks barriers to asymmetrical toughness
Precise engineering generates a structure that fractures more easily in one direction than the other.
-
Article |
 A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with stable memory
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with stable memory
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial constructed of bistable unit cells that can be switched independently and reversibly between two stable states with distinct mechanical properties using magnetic actuation is demonstrated.
- Tian Chen
- , Mark Pauly
- & Pedro M. Reis
-
News & Views |
 Mechanical memory written and read remotely
Mechanical memory written and read remotely
A device has been developed that consists of mechanical bits, analogous to the magnetic bits used in computer hard drives. Information encoded in the bits programs the mechanical properties of the device.
- Corentin Coulais
-
News & Views |
 Electrons broken into pieces at crystal defects
Electrons broken into pieces at crystal defects
Fractional electric charges have been observed at crystal defects in artificial structures resembling materials called topological crystalline insulators. Such fractional charges could have various engineering applications.
- Carmine Ortix
-
Article |
 A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
A stable, low-temperature water–gas shift catalyst is achieved by crowding platinum atoms and clusters on α-molybdenum carbide; the crowding protects the support from oxidation that would cause catalyst deactivation.
- Xiao Zhang
- , Mengtao Zhang
- & Ding Ma
-
Article |
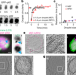 Wetting regulates autophagy of phase-separated compartments and the cytosol
Wetting regulates autophagy of phase-separated compartments and the cytosol
A theoretical model, in vitro reconstitution and in vivo experimentation show that competition between droplet surface tension and membrane sheet instability dictates the form and function of autophagosomal membranes.
- Jaime Agudo-Canalejo
- , Sebastian W. Schultz
- & Roland L. Knorr
-
Article |
 Bulk–disclination correspondence in topological crystalline insulators
Bulk–disclination correspondence in topological crystalline insulators
It is experimentally shown that topological states exist at crystallographic defects in the bulk and that disclination defects trap fractional charges characteristic of topological crystalline insulators.
- Yang Liu
- , Shuwai Leung
- & Jian-Hua Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Accurate machine learning in materials science facilitated by using diverse data sources
Accurate machine learning in materials science facilitated by using diverse data sources
A strategy for machine learning has been developed that exploits the fact that data are often collected in different ways with varying levels of accuracy. The approach was used to build a model that predicts a key property of materials.
- Rohit Batra
-
News & Views |
 Giant photon avalanches observed in nanoparticles
Giant photon avalanches observed in nanoparticles
In some materials, the absorption of a single photon can trigger a chain reaction that produces a large burst of light. The discovery of these photon avalanches in nanostructures opens the way to imaging and sensing applications.
- Andries Meijerink
- & Freddy T. Rabouw
-
Article |
 Giant nonlinear optical responses from photon-avalanching nanoparticles
Giant nonlinear optical responses from photon-avalanching nanoparticles
Room-temperature photon avalanching realized in single thulium-doped upconverting nanocrystals enables super-resolution imaging at near-infrared wavelengths of maximal biological transparency and provides a material platform potentially suitable for other optical technologies.
- Changhwan Lee
- , Emma Z. Xu
- & P. James Schuck
-
Where I Work |
 ‘I was no longer pretending or hiding’: a trans scientist finds a lab to call home
‘I was no longer pretending or hiding’: a trans scientist finds a lab to call home
Materials scientist Clara Barker praises the University of Oxford for creating a welcoming space.
- Josie Glausiusz
-
Article |
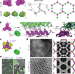 Design of biologically active binary protein 2D materials
Design of biologically active binary protein 2D materials
Design of a two-component protein array enables robust formation of complex large-scale ordered biologically active materials.
- Ariel J. Ben-Sasson
- , Joseph L. Watson
- & David Baker
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning reveals the complexity of dense amorphous silicon
Machine learning reveals the complexity of dense amorphous silicon
Transitions between amorphous forms of solids and liquids are difficult to study. Machine learning has now provided fresh insight into pressure-induced transformations of amorphous silicon, opening the way to studies of other systems.
- Paul F. McMillan
-
Article |
 Origins of structural and electronic transitions in disordered silicon
Origins of structural and electronic transitions in disordered silicon
Machine learning models enable atomistic simulations of phase transitions in amorphous silicon, predict electronic fingerprints, and show that the pressure-induced crystallization occurs over three distinct stages.
- Volker L. Deringer
- , Noam Bernstein
- & Stephen R. Elliott
-
Article |
 Single-defect phonons imaged by electron microscopy
Single-defect phonons imaged by electron microscopy
State-of-the-art electron energy-loss spectroscopy in a transmission electron microscope maps the detailed phonon spectra of single defects in silicon carbide
- Xingxu Yan
- , Chengyan Liu
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article |
 Landau quantization and highly mobile fermions in an insulator
Landau quantization and highly mobile fermions in an insulator
Pronounced quantum oscillations in magnetoresistance, a phenomenon that was only expected in metals with highly mobile carriers, are observed in the strongly insulating state of two-dimensional WTe2.
- Pengjie Wang
- , Guo Yu
- & Sanfeng Wu
-
News & Views |
 High-resolution 3D printing in seconds
High-resolution 3D printing in seconds
A 3D-printing technique has been developed that can produce millimetre- to centimetre-scale objects with micrometre-scale features. It relies on chemical reactions triggered by the intersection of two light beams.
- Cameron Darkes-Burkey
- & Robert F. Shepherd
-
Article |
 Xolography for linear volumetric 3D printing
Xolography for linear volumetric 3D printing
By combining the use of photoswitchable photoinitators and intersecting light beams, objects and complex systems can be produced rapidly with higher definition than is possible using state-of-the art macroscopic volumetric methods.
- Martin Regehly
- , Yves Garmshausen
- & Stefan Hecht
-
Article |
 Tuning the Chern number in quantum anomalous Hall insulators
Tuning the Chern number in quantum anomalous Hall insulators
The number of edge channels in quantum anomalous Hall insulators is controlled by varying either the magnetic dopant concentration or the interior spacer layer thickness, yielding Chern numbers up to 5.
- Yi-Fan Zhao
- , Ruoxi Zhang
- & Cui-Zu Chang
-
Article |
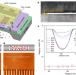 Capillary condensation under atomic-scale confinement
Capillary condensation under atomic-scale confinement
In the tiniest of capillaries, barely larger than a water molecule, condensation is surprisingly predictable from the macroscopic Kelvin condensation equation, a coincidence partially owing to elastic deformation of the capillary walls.
- Qian Yang
- , P. Z. Sun
- & A. K. Geim
-
Article |
 Global human-made mass exceeds all living biomass
Global human-made mass exceeds all living biomass
Estimates of global total biomass (the mass of all living things) and anthopogenic mass (the mass embedded in inanimate objects made by humans) over time show that we are roughly at the timepoint when anthropogenic mass exceeds total biomass.
- Emily Elhacham
- , Liad Ben-Uri
- & Ron Milo
-
Research Highlight |
 Presto chango: tiny particles get a chemical makeover but keep their shape
Presto chango: tiny particles get a chemical makeover but keep their shape
Self-assembling particles exhibit a mind-boggling array of structure and composition.
-
Article |
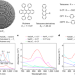 Lanthanide-doped inorganic nanoparticles turn molecular triplet excitons bright
Lanthanide-doped inorganic nanoparticles turn molecular triplet excitons bright
Optically dark (non-emitting) triplet excitons on organic molecules may be rendered bright by coupling the molecules to lanthanide-doped nanoparticles, providing a way to control such excitons in optoelectronic systems.
- Sanyang Han
- , Renren Deng
- & Akshay Rao
-
Where I Work |
 Flame thrower
Flame thrower
Fire-safety researcher Luke Bisby investigates which materials can take the heat.
- Kendall Powell
-
Article |
 Electrical switching of magnetic order in an orbital Chern insulator
Electrical switching of magnetic order in an orbital Chern insulator
Non-volatile electrical switching of magnetic order in an orbital Chern insulator is experimentally demonstrated using a moiré heterostructure and analysis shows that the effect is driven by topological edge states.
- H. Polshyn
- , J. Zhu
- & A. F. Young
-
Article |
 Unconventional ferroelectricity in moiré heterostructures
Unconventional ferroelectricity in moiré heterostructures
Electronic ferroelectricity is observed in a graphene-based moiré heterostructure, which is explained using a spontaneous interlayer charge-transfer model driven by layer-specific on-site Coulomb repulsion.
- Zhiren Zheng
- , Qiong Ma
- & Pablo Jarillo-Herrero
-
Article |
 Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Spectroscopic studies and theoretical calculations of the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction establish that reaction rates depend on the amount of charge stored in the electrocatalyst, and not on the applied potential.
- Hong Nhan Nong
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Travis E. Jones
-
Article |
 Ultra-sensitive and resilient compliant strain gauges for soft machines
Ultra-sensitive and resilient compliant strain gauges for soft machines
Strain gauges with both high sensitivity and high mechanical resilience, based on strain-mediated contact in anisotropically resistive structures, are demonstrated within a sensor-integrated, textile-based sleeve that can recognize human hand motions via muscle deformations.
- Oluwaseun A. Araromi
- , Moritz A. Graule
- & Robert J. Wood
-
News |
 Astronauts have conducted nearly 3,000 science experiments aboard the ISS
Astronauts have conducted nearly 3,000 science experiments aboard the ISS
A graphical guide to the research carried out on the International Space Station — and who did it.
- Alexandra Witze
-
Research Highlight |
 How to make violently reactive metals and watch them grow
How to make violently reactive metals and watch them grow
A standard laboratory tool allows researchers to produce two potentially dangerous metals and to observe them as they form.
-
News & Views |
 Eye of a skull reveals details of cometary materials
Eye of a skull reveals details of cometary materials
The Philae spacecraft was meant to anchor itself to the surface of the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, but instead bounced into a hidden grotto. The telltale markings of its passage reveal details of the comet’s fragile boulders.
- Erik Asphaug
-
Article |
 High-throughput calculations of magnetic topological materials
High-throughput calculations of magnetic topological materials
High-throughput calculations are performed to predict approximately 130 magnetic topological materials, with complete electronic structure calculations and topological phase diagrams.
- Yuanfeng Xu
- , Luis Elcoro
- & B. Andrei Bernevig
-
Article |
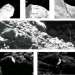 The Philae lander reveals low-strength primitive ice inside cometary boulders
The Philae lander reveals low-strength primitive ice inside cometary boulders
When the Philae lander bounced on the surface of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, it exposed primitive icy-dust material within cometary boulders; the intrinsic strength and porosity of this material is reported.
- Laurence O’Rourke
- , Philip Heinisch
- & Holger Sierks
-
Article |
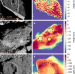 Bennu’s near-Earth lifetime of 1.75 million years inferred from craters on its boulders
Bennu’s near-Earth lifetime of 1.75 million years inferred from craters on its boulders
Analysis of the size and depth of craters on boulders on the asteroid (101955) Bennu indicates that Bennu has been in near-Earth space for 1.75 ± 0.75 million years.
- R.-L. Ballouz
- , K. J. Walsh
- & D. S. Lauretta
-
News & Views |
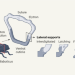 Diabolical ironclad beetles inspire tougher joints for engineering applications
Diabolical ironclad beetles inspire tougher joints for engineering applications
Intriguing structures have been observed that link sections of the diabolical ironclad beetle’s amazingly crush-resistant armour. These findings suggest fresh approaches for making tough, reliable joints for use in engineering.
- Po-Yu Chen

 Self-similar mesocrystals form via interface-driven nucleation and assembly
Self-similar mesocrystals form via interface-driven nucleation and assembly