Article |
Featured
-
-
Nature Podcast |
 Sea squirts teach new lessons in evolution
Sea squirts teach new lessons in evolution
Spineless sea squirts shed light on vertebrate evolution, and an iodine-fuelled engine powering a satellite in space.
- Shamini Bundell
- & Benjamin Thompson
-
Book Review |
 Friction: from fingerprints to climate change
Friction: from fingerprints to climate change
An enthusiastic exploration of how surfaces interact both intrigues and frustrates.
- Anna Novitzky
-
News |
 Diamond delivers long-sought mineral from the deep Earth
Diamond delivers long-sought mineral from the deep Earth
Davemaoite is a vehicle for radioactive isotopes that help to heat the planet’s mantle.
- Alexandra Witze
-
Article |
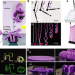 Bubble casting soft robotics
Bubble casting soft robotics
An all-in-one methodology for fabricating soft robotics reported here uses interfacial flows in elastomers that cure to produce actuators that can be tailored to suit applications from artificial muscles to grippers.
- Trevor J. Jones
- , Etienne Jambon-Puillet
- & P.-T. Brun
-
Article
| Open Access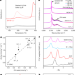 In situ formation of ZnOx species for efficient propane dehydrogenation
In situ formation of ZnOx species for efficient propane dehydrogenation
Propene is obtained through propane dehydrogenation using catalysts that are toxic, expensive or demanding to regenerate with ecologically harmful compounds, but the ZnO-based alternative reported here is cheap, clean and scalable.
- Dan Zhao
- , Xinxin Tian
- & Evgenii V. Kondratenko
-
Editorial |
 Glass is the hidden gem in a carbon-neutral future
Glass is the hidden gem in a carbon-neutral future
Recycling glass does not degrade it, and manufacturing it can be carbon-free. So why are many countries still burying glass in the ground?
-
Article |
 Transition metal-catalysed molecular n-doping of organic semiconductors
Transition metal-catalysed molecular n-doping of organic semiconductors
Electron doping of organic semiconductors is typically inefficient, but here a precursor molecular dopant is used to deliver higher n-doping efficiency in a much shorter doping time.
- Han Guo
- , Chi-Yuan Yang
- & Xugang Guo
-
Article |
 Percolation transitions in compressed SiO2 glasses
Percolation transitions in compressed SiO2 glasses
Amorphous–amorphous phase transitions in silicon dioxide are shown to proceed through a sequence of percolation transitions, a process that has relevance to a range of important liquid and glassy systems.
- A. Hasmy
- , S. Ispas
- & B. Hehlen
-
Obituary |
 Abdul Qadeer Khan (1936–2021)
Abdul Qadeer Khan (1936–2021)
Materials scientist behind Pakistan’s nuclear-weapons business.
- Ehsan Masood
-
Article |
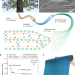 Copper-coordinated cellulose ion conductors for solid-state batteries
Copper-coordinated cellulose ion conductors for solid-state batteries
By coordinating copper ions with the oxygen-containing groups of cellulose nanofibrils, the molecular spacing in the nanofibrils is increased, allowing fast transport of lithium ions and offering hopes for solid-state batteries.
- Chunpeng Yang
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 Perovskite solar cells with atomically coherent interlayers on SnO2 electrodes
Perovskite solar cells with atomically coherent interlayers on SnO2 electrodes
An atomically coherent interlayer between the electron-transporting and perovskite layers in perovskite solar cells enhances charge extraction and transport from the perovskite, enabling high power conversion efficiency.
- Hanul Min
- , Do Yoon Lee
- & Sang Il Seok
-
News & Views |
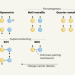 Untwisted trilayer graphene hosts superconductivity and magnetism
Untwisted trilayer graphene hosts superconductivity and magnetism
Superconductivity and magnetism have been observed in layered graphene in which the sheets are twisted with respect to each other. But a simpler, more stable graphene system also exhibits these phases.
- Thiti Taychatanapat
-
Article |
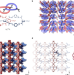 An elastic metal–organic crystal with a densely catenated backbone
An elastic metal–organic crystal with a densely catenated backbone
A rubber-like, metal–organic crystal is reported with a mechanically interlocked catenane backbone, which could allow for easy guest molecule uptake and release.
- Wenjing Meng
- , Shun Kondo
- & Hiroshi Sato
-
Perspective |
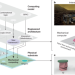 Mechanical computing
Mechanical computing
Computing approaches based on mechanical mechanisms are discussed, with a view towards a framework in which adaptable materials and structures act as a distributed information processing network.
- Hiromi Yasuda
- , Philip R. Buskohl
- & Jordan R. Raney
-
News & Views |
 Platinum catalysts strained controllably by size-changing nanocubes
Platinum catalysts strained controllably by size-changing nanocubes
The distance between the surface atoms of noble metals, such as platinum, affects the catalytic activity of these elements. An experimental approach using nanoparticles enables this effect to be systematically controlled and measured.
- Sylvain Brimaud
-
Article |
 Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
By depositing platinum shells on palladium-based nanocubes, the strain can be controlled by through phosphorization and dephosphorization, making it possible to tune the electrocatalytic activity of the platinum shells.
- Tianou He
- , Weicong Wang
- & Mingshang Jin
-
Research Highlight |
 A magnetic patch on a twitchy arm makes a useful current
A magnetic patch on a twitchy arm makes a useful current
Scientists have developed a material whose magnetic properties change when it’s deformed — and that is also soft enough to respond to small movements.
-
News & Views |
 Heat management with a twist in layered materials
Heat management with a twist in layered materials
The misalignment of crystal lattices in stacked monolayers of materials has been shown to prevent heat flow between the layers, while retaining flow within them. This finding opens up an inventive way to control heat at the nanoscale.
- Mariusz Zdrojek
-
News & Views |
 Electron crystals come under the microscope
Electron crystals come under the microscope
In 2D materials, electrons at low densities can freeze into well-defined positions and form exotic structures called Wigner crystals. A non-invasive technique has been developed to image these crystals directly.
- Carmen Rubio-Verdú
-
Article |
 The role of charge recombination to triplet excitons in organic solar cells
The role of charge recombination to triplet excitons in organic solar cells
A substantial pathway for energy loss in organic solar cells may be suppressed by engineering hybridization between non-fullerene acceptor triplet excitons and spin-triplet charge transfer excitons.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Alberto Privitera
- & Richard H. Friend
-
Article
| Open Access Extremely anisotropic van der Waals thermal conductors
Extremely anisotropic van der Waals thermal conductors
Extremely anisotropic thermal conductors based on large-area van der Waals thin films with random interlayer rotations are reported here.
- Shi En Kim
- , Fauzia Mujid
- & Jiwoong Park
-
Editorial |
 Concrete needs to lose its colossal carbon footprint
Concrete needs to lose its colossal carbon footprint
Concrete will be crucial for much-needed climate-resilient construction. But the cement industry must set out its plan for decarbonization.
-
Article |
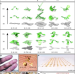 Three-dimensional electronic microfliers inspired by wind-dispersed seeds
Three-dimensional electronic microfliers inspired by wind-dispersed seeds
With a design inspired by wind-dispersed seeds, a series of three-dimensional passive fliers at the macro-, meso- and microscale are realized that can bear active electronic payloads.
- Bong Hoon Kim
- , Kan Li
- & John A. Rogers
-
News & Views |
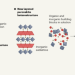 Triple-decker layered perovskite materials
Triple-decker layered perovskite materials
Layered perovskites are useful materials that contain sheets of a perovskite semiconductor enclosed by organic molecules. Crystals of layered perovskites that include sheets of a second inorganic lattice can now be grown from solution.
- Roman Krahne
- & Milena P. Arciniegas
-
Research Highlight |
 Flowing crystals for quick camouflage
Flowing crystals for quick camouflage
A soft material can be guided to rapidly assume the same colour pattern as its background.
-
Article |
 Transmembrane transport in inorganic colloidal cell-mimics
Transmembrane transport in inorganic colloidal cell-mimics
Hollow colloidal capsules, each with a single micropore, act as artificial cell-like structures that can capture and release payloads such as solid particles or bacteria from the external environment.
- Zhe Xu
- , Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Review Article |
 Interface nano-optics with van der Waals polaritons
Interface nano-optics with van der Waals polaritons
This Review discusses the state of the art of interface optics—including refractive optics, meta-optics and moiré engineering—for the control of van der Waals polaritons.
- Qing Zhang
- , Guangwei Hu
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article |
 Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Gold nanoflake pairs form by self-assembly in an aqueous ligand solution and offer stable and tunable microcavities by virtue of equilibrium between attractive Casimir forces and repulsive electrostatic forces.
- Battulga Munkhbat
- , Adriana Canales
- & Timur O. Shegai
-
Research Highlight |
 How to grow a long-sought wonder material: on a silver platter
How to grow a long-sought wonder material: on a silver platter
Two sheets of boron, each only one atom thick, are coaxed to take shape on crystals of silver.
-
News & Views |
 Molecular memristors offer a path to ultra-efficient computing
Molecular memristors offer a path to ultra-efficient computing
Future progress in computing calls for innovative ways to map the physical characteristics of materials to the logic functions needed by computing architectures. An electronic device called a molecular memristor provides a way forward.
- Matthew J. Marinella
- & A. Alec Talin
-
Article |
 Decision trees within a molecular memristor
Decision trees within a molecular memristor
Multiple redox transitions in a molecular memristor can be harnessed as ‘decision trees’ to undertake complex and reconfigurable logic operations in a single time step.
- Sreetosh Goswami
- , Rajib Pramanick
- & R. Stanley Williams
-
Matters Arising |
 Unusual width of the superconducting transition in a hydride
Unusual width of the superconducting transition in a hydride
- J. E. Hirsch
- & F. Marsiglio
-
Article |
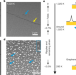 Single-crystal, large-area, fold-free monolayer graphene
Single-crystal, large-area, fold-free monolayer graphene
Restricting the initial growth temperatures used for chemical vapour deposition of graphene on metal foils produces optimum conditions for growing large areas of fold-free, single-crystal graphene.
- Meihui Wang
- , Ming Huang
- & Rodney S. Ruoff
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic solar hydrogen production from water on a 100-m2 scale
Photocatalytic solar hydrogen production from water on a 100-m2 scale
Carbon-neutral hydrogen can be produced through photocatalytic water splitting, as demonstrated here with a 100-m2 array of panel reactors that reaches a maximum conversion efficiency of 0.76%.
- Hiroshi Nishiyama
- , Taro Yamada
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article |
 Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries
Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries
Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries are produced with a microporous carbon positive electrode, aluminium chloride in thionyl chloride as the electrolyte, and either sodium or lithium as the negative electrode.
- Guanzhou Zhu
- , Xin Tian
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Research Highlight |
 Electric-blue phosphorescence made easy
Electric-blue phosphorescence made easy
Crystal engineering produces sustained molecular glows at room temperature.
-
Article |
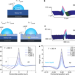 Mobility gradients yield rubbery surfaces on top of polymer glasses
Mobility gradients yield rubbery surfaces on top of polymer glasses
Surface enhancements in glass mobility are complicated in polymers by the interplay of the surface mobile layer thickness with a second length scale (the size of the polymer chains), giving rise to a transient rubbery surface even in polymers with short chains.
- Zhiwei Hao
- , Asieh Ghanekarade
- & Biao Zuo
-
Nature Podcast |
 What’s the isiZulu for dinosaur? How science neglected African languages
What’s the isiZulu for dinosaur? How science neglected African languages
A team is creating bespoke words for scientific terms in African languages, and the sustainability of the electric car boom.
- Shamini Bundell
- & Benjamin Thompson
-
Article |
 How to design an icosahedral quasicrystal through directional bonding
How to design an icosahedral quasicrystal through directional bonding
Model patchy colloids with directional bonding are designed that assemble into icosahedral quasicrystals through the propagation of an icosahedral network of bonds and may be realized using DNA origami particles.
- Eva G. Noya
- , Chak Kui Wong
- & Jonathan P. K. Doye
-
Article |
 Ghost hyperbolic surface polaritons in bulk anisotropic crystals
Ghost hyperbolic surface polaritons in bulk anisotropic crystals
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons that exhibit long-distance, ray-like propagation and oblique wavefronts are described at the surface of an anisotropic bulk crystal.
- Weiliang Ma
- , Guangwei Hu
- & Peining Li
-
News Feature |
 Electric cars and batteries: how will the world produce enough?
Electric cars and batteries: how will the world produce enough?
Reducing the use of scarce metals — and recycling them — will be key to the world’s transition to electric vehicles.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Research Highlight |
 From drab to dazzling: seaweed yields sparkling coloured inks
From drab to dazzling: seaweed yields sparkling coloured inks
Cheap, eco-friendly materials can be formed into vibrant 2D or 3D shapes.
-
Nature Video |
 The smart chain mail fabric that can stiffen on demand
The smart chain mail fabric that can stiffen on demand
The new 3D-printed material can switch from flexible to stiff and back again
- Shamini Bundell
-
News & Views |
 Chain-mail fabric stiffens under confining pressure
Chain-mail fabric stiffens under confining pressure
The mechanical properties of chain mail have been revisited. The findings reveal that, under confining pressure, chain-mail-inspired materials can switch from pliable to stiff structures that have outstanding load-bearing capacities.
- Laurent Orgéas
-
Article |
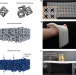 Structured fabrics with tunable mechanical properties
Structured fabrics with tunable mechanical properties
A structured fabric constructed of linked hollow polyhedral particles (resembling chain mail) can be simply and reversibly tuned between flexible and rigid states; when it is compressed, its linked particles become jammed.
- Yifan Wang
- , Liuchi Li
- & Chiara Daraio
-
Article |
 Actively variable-spectrum optoelectronics with black phosphorus
Actively variable-spectrum optoelectronics with black phosphorus
High-performance optoelectronic devices that operate in the infrared regime at room temperature exhibit wide-range, active and reversible tunability of the operating wavelengths with black phosphorus.
- Hyungjin Kim
- , Shiekh Zia Uddin
- & Ali Javey
-
Article |
 Pseudogap in a crystalline insulator doped by disordered metals
Pseudogap in a crystalline insulator doped by disordered metals
A back-bending band structure and an emerging pseudogap are observed at the interface between a crystalline solid (black phosphorus) and disordered alkali-metal dopants.
- Sae Hee Ryu
- , Minjae Huh
- & Keun Su Kim
-
Research Highlight |
 Mini ‘metavehicles’ zip and swerve on light power
Mini ‘metavehicles’ zip and swerve on light power
Light can be used to both propel and steer tiny vehicles made with materials that have distinctive optical properties.
-
Article |
 Linear-in temperature resistivity from an isotropic Planckian scattering rate
Linear-in temperature resistivity from an isotropic Planckian scattering rate
Angle-dependent magnetoresistance measurements of a strange-metal phase of a hole-doped cuprate show a well defined Fermi surface and an isotropic linear-in-temperature scattering rate that saturates at the Planckian limit.
- Gaël Grissonnanche
- , Yawen Fang
- & B. J. Ramshaw

 Exploding and weeping ceramics
Exploding and weeping ceramics