Featured
-
-
Article |
 New class of nonaqueous electrolytes for long-life and safe lithium-ion batteries
New class of nonaqueous electrolytes for long-life and safe lithium-ion batteries
Safe lithium-ion batteries require stable electrolytes with high chemical resistance and high thermal tolerance. Chen et al. find a solid lithium-salt electrolyte that is able to give rise to a prolonged battery life and a delayed decomposition of battery cathodes.
- Zonghai Chen
- , Yang Ren
- & Khalil Amine
-
Article |
 Stretchable batteries with self-similar serpentine interconnects and integrated wireless recharging systems
Stretchable batteries with self-similar serpentine interconnects and integrated wireless recharging systems
Components for flexible electronics capable of both bending and stretching have been reported but the fabrication of similarly pliable power sources remains challenging. Here, the authors present stretchable lithium ion batteries exploiting segmented layouts and deformable electrical interconnects.
- Sheng Xu
- , Yihui Zhang
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Porous materials with pre-designed single-molecule traps for CO2 selective adsorption
Porous materials with pre-designed single-molecule traps for CO2 selective adsorption
The synthesis of porous materials designed with specific applications in mind is fundamentally challenging. Here, the authors fabricate single-molecule trap cavities designed for complimentary interactions with CO2 and show that these traps can be assembled into materials with high CO2selectivity.
- Jian-Rong Li
- , Jiamei Yu
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article |
 Surface-passivated GaAsP single-nanowire solar cells exceeding 10% efficiency grown on silicon
Surface-passivated GaAsP single-nanowire solar cells exceeding 10% efficiency grown on silicon
The use of III-V semiconductor nanowires can overcome the need for lattice matching in multi-junction solar cells, which restricts the choice of materials and their bandgaps. This work demonstrates efficient solar cells with GaAsP single nanowires with tunable bandgap and grown on low-cost Si substrates.
- Jeppe V. Holm
- , Henrik I. Jørgensen
- & Martin Aagesen
-
Article
| Open Access GaAs nanopillar-array solar cells employing in situ surface passivation
GaAs nanopillar-array solar cells employing in situ surface passivation
Arrays of III–V semiconductor nanopillars are promising photovoltaic materials due to their favourable optical properties, however, they show low power conversion efficiencies. Mariani et al. fabricate a GaAs nanopillar solar cell achieving an efficiency of 6.63% owing to surface passivation.
- Giacomo Mariani
- , Adam C. Scofield
- & Diana L. Huffaker
-
Article |
 A new class of Solvent-in-Salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries
A new class of Solvent-in-Salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries
Commercial lithium-ion batteries normally use a liquid electrolyte. Suo et al. show that a glassy-like electrolyte containing a high concentration of lithium salt leads to a substantially enhanced battery performance because of suppressed formation of lithium dendrites on the lithium metal anodes.
- Liumin Suo
- , Yong-Sheng Hu
- & Liquan Chen
-
Article |
 Aromatic porous-honeycomb electrodes for a sodium-organic energy storage device
Aromatic porous-honeycomb electrodes for a sodium-organic energy storage device
A huge demand for lithium batteries necessitates more affordable alternatives. Sakaushi et al. describe rechargeable sodium batteries containing organic electrodes with a porous-honeycomb structure that are comparable to lithium batteries and capable of over 7,000 cycles.
- Ken Sakaushi
- , Eiji Hosono
- & Jürgen Eckert
-
Article
| Open Access A polymer tandem solar cell with 10.6% power conversion efficiency
A polymer tandem solar cell with 10.6% power conversion efficiency
Tandem solar cell structures combine high- and low-bandgap materials, allowing a broader spectral absorption of solar radiation. The authors report the synthesis of a high performance low-bandgap polymer which enables fabrication of a tandem solar cell with a certified power conversion efficiency of 10.6%.
- Jingbi You
- , Letian Dou
- & Yang Yang
-
Article |
 Sulphur–TiO2 yolk–shell nanoarchitecture with internal void space for long-cycle lithium–sulphur batteries
Sulphur–TiO2 yolk–shell nanoarchitecture with internal void space for long-cycle lithium–sulphur batteries
The practical performance of lithium–sulphur batteries is lower than expected because of polysulphide dissolution into the electrolyte over time. Sehet al. show that a yolk–shell nanoarchitecture is able to encapsulate sulphur cathode materials efficiently and thus allows over 1,000 charge/discharge cycles.
- Zhi Wei Seh
- , Weiyang Li
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access High internal quantum efficiency in fullerene solar cells based on crosslinked polymer donor networks
High internal quantum efficiency in fullerene solar cells based on crosslinked polymer donor networks
The conversion efficiency of organic solar cells depends on the shape of the interface between their donor and acceptor components. Liuet al. demonstrate a scalable method using crosslinked polymer networks to fabricate the finely interpenetrating structures needed to achieve near-perfect internal quantum efficiency.
- Bo Liu
- , Rui-Qi Png
- & Peter K.H. Ho
-
Article |
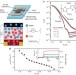 Hopping transport and the Hall effect near the insulator–metal transition in electrochemically gated poly(3-hexylthiophene) transistors
Hopping transport and the Hall effect near the insulator–metal transition in electrochemically gated poly(3-hexylthiophene) transistors
Understanding charge transport and the fundamental limits on conductivity in polymer semiconductors is important for improving device performance. Wanget al. report a transport regime close to band-like conduction and the observation of the Hall effect in an electrochemically-doped polymer semiconductor.
- Shun Wang
- , Mingjing Ha
- & C Leighton
-
Article |
 Lithium–sulphur batteries with a microporous carbon paper as a bifunctional interlayer
Lithium–sulphur batteries with a microporous carbon paper as a bifunctional interlayer
The practical performance of lithium sulphide batteries is much less than their predicted performance because redox products dissolve over time. Su and Manthiram show that microporous carbon membranes inserted between cathode and separator localize soluble polysulphide species and improve battery cycling characteristics.
- Yu-Sheng Su
- & Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article |
 A high-rate and long cycle life aqueous electrolyte battery for grid-scale energy storage
A high-rate and long cycle life aqueous electrolyte battery for grid-scale energy storage
The integration of volatile renewable energy sources into the electrical power grid will require a significant increase in electrical storage capacity. Here a new type of safe, fast, inexpensive and long-life aqueous electrolyte battery is reported, which may aid the development of increased grid capacity.
- Mauro Pasta
- , Colin D. Wessells
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Highly stable Pt monolayer on PdAu nanoparticle electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
Highly stable Pt monolayer on PdAu nanoparticle electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
Platinum is used as a cathode in fuel cells but undergoes dissolution during potential changes, hindering commercial application in electric vehicles. Sasakiet al.report a new class of stable electrocatalysts that consist of platinum monolayers on palladium–gold alloy nanoparticles.
- Kotaro Sasaki
- , Hideo Naohara
- & Radoslav R. Adzic
-
Article |
 Spin-enhanced organic bulk heterojunction photovoltaic solar cells
Spin-enhanced organic bulk heterojunction photovoltaic solar cells
One of the obstacles to improving the efficiency of organic photovoltaic solar cells is the recombination of polaron pairs at the interface between donor and acceptor molecules. By doping cells with galvinoxyl radicals, Zhanget al. demonstrate a mechanism that overcomes this problem via a spin-flip process.
- Ye Zhang
- , Tek P. Basel
- & Z. Valy Vardeny
-
Article |
 In situ measurement of exciton energy in hybrid singlet-fission solar cells
In situ measurement of exciton energy in hybrid singlet-fission solar cells
Singlet fission converts single singlet excitons into pairs of triplet excitons, and it has been proposed to give additional photocurrent to solar cells. Ehrleret al. use lead selenide nanocrystals of varying sizes to measure the triplet energy in pentacene photovoltaic cells, and achieve efficiencies approaching 5%.
- Bruno Ehrler
- , Brian J. Walker
- & Neil C. Greenham
-
Article |
 An ultrafast nickel–iron battery from strongly coupled inorganic nanoparticle/nanocarbon hybrid materials
An ultrafast nickel–iron battery from strongly coupled inorganic nanoparticle/nanocarbon hybrid materials
Fast rechargeable batteries made from low-cost and abundant electrode materials are attractive for energy storage. Wanget al. develop an ultrafast Ni–Fe battery with carbon/inorganic hybrid electrodes in which the charge and discharge rates are nearly 1,000-fold higher than traditional Ni–Fe batteries.
- Hailiang Wang
- , Yongye Liang
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Superionic glass-ceramic electrolytes for room-temperature rechargeable sodium batteries
Superionic glass-ceramic electrolytes for room-temperature rechargeable sodium batteries
Rechargeable solid-state batteries are promising sources of energy for a range of applications. Hayashiet al. examine the electrochemistry of solid-state sodium batteries, and present an electrolyte that operates at room temperature.
- Akitoshi Hayashi
- , Kousuke Noi
- & Masahiro Tatsumisago
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin and lightweight organic solar cells with high flexibility
Ultrathin and lightweight organic solar cells with high flexibility
Organic solar cells are promising for technological applications, as they are lightweight and mechanically robust. This study presents flexible organic solar cells that are less than 2 μm thick, have very low specific weight and maintain their photovoltaic performance under repeated mechanical deformation.
- Martin Kaltenbrunner
- , Matthew S. White
- & Siegfried Bauer
-
Article |
 Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel junctions
Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel junctions
The spin-dependent thermal and electrical transport properties of nanostructures are central for future applications of spintronic devices. Here, Linet al. report an enhanced spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in an Al2O3-based magnetic tunnel junction.
- Weiwei Lin
- , Michel Hehn
- & Stéphane Mangin
-
Article |
 Integrated photosystem II-based photo-bioelectrochemical cells
Integrated photosystem II-based photo-bioelectrochemical cells
The photosynthetic reaction centres, photosystems I and II, have been investigated for the light-induced generation of fuels and electrical power. Now, Yehezkeliet al. report a photobiofuel cell that generates electricity upon irradiation of photosystem II-functionalized electrodes in aqueous solutions.
- Omer Yehezkeli
- , Ran Tel-Vered
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article
| Open Access Geometry analysis and systematic synthesis of highly porous isoreticular frameworks with a unique topology
Geometry analysis and systematic synthesis of highly porous isoreticular frameworks with a unique topology
Zhanget al. show that simple geometry analysis can be used to predict how linker length and length ratios affect pore shape and size of porous coordination polymers. The accuracy of the predictions is confirmed by the synthesis of a series of 13 highly porous isoreticular frameworks.
- Yue-Biao Zhang
- , Hao-Long Zhou
- & Xiao-Ming Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A cobalt complex redox shuttle for dye-sensitized solar cells with high open-circuit potentials
A cobalt complex redox shuttle for dye-sensitized solar cells with high open-circuit potentials
Dye-sensitized solar cells are a promising alternative to traditional inorganic semiconductor-based solar cells. Yumet al. use a molecularly engineered cobalt complex as a redox mediator to achieve an open-circuit voltage of over 1,000 mV in a mesoscopic dye-sensitized solar cell.
- Jun-Ho Yum
- , Etienne Baranoff
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article |
 Metal-adeninate vertices for the construction of an exceptionally porous metal-organic framework
Metal-adeninate vertices for the construction of an exceptionally porous metal-organic framework
Metal‐organic framework (MOFs) with metal‐carboxylate cluster vertices and long, branched organic linkers are highly porous. Anet al. develop an alternative route to MOFs in which metal‐biomolecule clusters are used as vertices to construct a mesoporous MOF.
- Jihyun An
- , Omar K. Farha
- & Nathaniel L. Rosi
-
Article |
 Copper hexacyanoferrate battery electrodes with long cycle life and high power
Copper hexacyanoferrate battery electrodes with long cycle life and high power
Batteries that operate at high power and cycling efficiencies could facilitate the development of large-scale energy storage systems. Wessellset al.report a metal–organic framework electrode that operates in an inexpensive aqueous electrolyte with excellent capacity retention over a very large number of cycles.
- Colin D. Wessells
- , Robert A. Huggins
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 A high-rate long-life Li4Ti5O12/Li[Ni0.45Co0.1Mn1.45]O4 lithium-ion battery
A high-rate long-life Li4Ti5O12/Li[Ni0.45Co0.1Mn1.45]O4 lithium-ion battery
Advanced rechargeable lithium-ion batteries have potential applications in the renewable energy and sustainable road transport fields. Junget al. have developed a lithium battery that uses pre-existing concepts but has highly competitive energy densities, life span and cycling properties.
- Hun-Gi Jung
- , Min Woo Jang
- & Bruno Scrosati
-
Article |
 Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule–metal contacts
Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule–metal contacts
The ability to control the charge and spin of single molecules at metal interfaces underpins the concept of molecular electronics. Mugarzaet al. examine these properties using scanning tunnelling microscopy, and uncover their influence on the magnetism and transport properties of the molecule/metal systems.
- Aitor Mugarza
- , Cornelius Krull
- & Pietro Gambardella
-
Article
| Open Access Reverse electrowetting as a new approach to high-power energy harvesting
Reverse electrowetting as a new approach to high-power energy harvesting
High-power mechanical energy harvesting could be an alternative to batteries, but efficient energy conversion technology has been missing. Here, a novel mechanical-to-electrical energy conversion method is described that is based on reverse electrowetting and is uniquely suited for high-power energy harvesting.
- Tom Krupenkin
- & J. Ashley Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and compatibility of a magnesium electrolyte with a sulphur cathode
Structure and compatibility of a magnesium electrolyte with a sulphur cathode
Magnesium is an ideal rechargeable battery anode material, but coupling it with a low-cost sulphur cathode, requires a non-nucleophilic electrolyte. Kimet al. prepare a non-nucleophilic electrolyte from hexamethyldisilazide magnesium chloride and aluminium trichloride, and show its compatibility with a sulphur cathode.
- Hee Soo Kim
- , Timothy S. Arthur
- & John Muldoon
-
Article |
 Iron-based cathode catalyst with enhanced power density in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
Iron-based cathode catalyst with enhanced power density in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
Replacing platinum in polymer-electrolyte-membrane fuel cells with iron-based catalysts could provide low-cost power generators, but often leads to low power densities. Here, a new iron-based cathode catalyst is developed with enhanced power density, volumetric activity and mass-transport properties.
- Eric Proietti
- , Frédéric Jaouen
- & Jean-Pol Dodelet
-
Article |
 Porous covalent electron-rich organonitridic frameworks as highly selective sorbents for methane and carbon dioxide
Porous covalent electron-rich organonitridic frameworks as highly selective sorbents for methane and carbon dioxide
Materials that can separate and capture carbon dioxide from power plant flue gases could help to stabilize atmospheric levels of the gas. Mohantyet al. develop inexpensive porous organonitridic frameworks with high selectivity and sorption capacities for carbon dioxide and methane.
- Paritosh Mohanty
- , Lilian D. Kull
- & Kai Landskron
-
Article
| Open Access Gross violation of the Wiedemann–Franz law in a quasi-one-dimensional conductor
Gross violation of the Wiedemann–Franz law in a quasi-one-dimensional conductor
Interacting electrons in one dimension are predicted to have independent spin and charge excitations. Wakehamet al. show evidence of this behaviour in a bulk conductor by measuring a ratio of thermal to electrical conductivity orders of magnitude larger than in conventional three-dimensional metals.
- Nicholas Wakeham
- , Alimamy F. Bangura
- & Nigel E. Hussey
-
Article
| Open Access Promotion of water-mediated carbon removal by nanostructured barium oxide/nickel interfaces in solid oxide fuel cells
Promotion of water-mediated carbon removal by nanostructured barium oxide/nickel interfaces in solid oxide fuel cells
Anodes composed of nickel/yttria-stabilized zirconia in solid oxide fuel cells are known to suffer from coking, which reduces their performance. Here, Yang and colleagues report a new barium oxide/nickel anode, which efficiently oxidizes fuel with minimum carbon buildup.
- Lei Yang
- , YongMan Choi
- & Meilin Liu
-
Article |
 Flexible concentrator photovoltaics based on microscale silicon solar cells embedded in luminescent waveguides
Flexible concentrator photovoltaics based on microscale silicon solar cells embedded in luminescent waveguides
Photovoltaic systems comprising monocrystalline silicon have many applications in solar power generation. Yoonet al. describe a composite luminescent concentrator photovoltaic system containing arrays of microscale silicon solar cells, which can be implemented in ultrathin, mechanically bendable formats.
- Jongseung Yoon
- , Lanfang Li
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Stabilizing lithium–sulphur cathodes using polysulphide reservoirs
Stabilizing lithium–sulphur cathodes using polysulphide reservoirs
Lithium–sulphur batteries may achieve higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion cells, but the dissolution of sulphur intermediates is a continuing challenge. Here this problem is overcome using a cathode with a mesoporous structure that is able to accommodate intermediate polysulphide anions.
- Xiulei Ji
- , Scott Evers
- & Linda F. Nazar
-
Article |
 Imaging oxygen defects and their motion at a manganite surface
Imaging oxygen defects and their motion at a manganite surface
Oxygen diffusion processes are critical for the catalytic action of manganites but a full understanding of these processes is elusive. The authors perform atomic resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy imaging of layered manganites and show oxygen and defect dynamics on these surfaces.
- B. Bryant
- , Ch. Renner
- & G. Aeppli
-
Article |
 Porous organic molecular solids by dynamic covalent scrambling
Porous organic molecular solids by dynamic covalent scrambling
The construction of porous solids from discrete organic molecules usually involves the formation of regular porous crystals. In this study, a covalent scrambling reaction gives molecules with a range of shapes that do not pack effectively — manipulation of the reagent ratio allows fine control of porosity.
- Shan Jiang
- , James T. A. Jones
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 Rationally tuned micropores within enantiopure metal-organic frameworks for highly selective separation of acetylene and ethylene
Rationally tuned micropores within enantiopure metal-organic frameworks for highly selective separation of acetylene and ethylene
Separation of acetylene and ethylene is an important industrial challenge, which may be aided by selectively adsorbant materials. In this study, a metal-organic framework material is reported, which allows highly selective separation of acetylene and ethylene.
- Sheng-Chang Xiang
- , Zhangjing Zhang
- & Banglin Chen
-
Article |
 Enhanced proton transport in nanostructured polymer electrolyte/ionic liquid membranes under water-free conditions
Enhanced proton transport in nanostructured polymer electrolyte/ionic liquid membranes under water-free conditions
One challenge in the development of proton exchange fuel cells is the requirement for durable, high-conductivity electrolytes. The authors show that incorporating ionic liquids into synthetic block co-polymer electrolytes results in nanostructured membranes with much higher conductivities than currently available.
- Sung Yeon Kim
- , Suhan Kim
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article |
 Engineering hybrid nanotube wires for high-power biofuel cells
Engineering hybrid nanotube wires for high-power biofuel cells
Miniaturizing fuel cells for biological applications is challenging due to poor performance at these small scales. Now Gao and coworkers show that electrodes made with porous microfibers composed of oriented carbon nanotubes are capable of delivering fast mass transport of the reagents and greatly enhanced currents.
- Feng Gao
- , Lucie Viry
- & Nicolas Mano

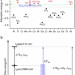 Rational screening low-cost counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells
Rational screening low-cost counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells