Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Chlorine bridge bond-enabled binuclear copper complex for electrocatalyzing lithium–sulfur reactions
Chlorine bridge bond-enabled binuclear copper complex for electrocatalyzing lithium–sulfur reactions
Here, the authors report a homonuclear cooper dual-atom electrocatalyst with high activity designed for synchronously boosting the sulfur and lithium evolutions.
- Qin Yang
- , Jinyan Cai
- & Yingze Song
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulating the diffusion energy barrier at the lithium metal electrolyte interface for dendrite-free long-life batteries
Manipulating the diffusion energy barrier at the lithium metal electrolyte interface for dendrite-free long-life batteries
Constructing an artificial solid electrolyte interphase to protect the lithium metal electrode is promising but challenging. Here, authors report a facile approach to form a layer to simultaneously overcome diffusion and advection-limited ion transport to achieve dendrite-free Li plating/stripping.
- Jyotshna Pokharel
- , Arthur Cresce
- & Yue Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming low initial coulombic efficiencies of Si anodes through prelithiation in all-solid-state batteries
Overcoming low initial coulombic efficiencies of Si anodes through prelithiation in all-solid-state batteries
All-solid-state batteries with silicon anodes have high capacities but low initial coulombic efficiencies (ICEs) because of first cycle irreversible capacity loss. Here, the authors report a prelithiation strategy to improve ICEs and reversibility.
- So-Yeon Ham
- , Elias Sebti
- & Ying Shirley Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Activating reversible carbonate reactions in Nasicon solid electrolyte-based Na-air battery via in-situ formed catholyte
Activating reversible carbonate reactions in Nasicon solid electrolyte-based Na-air battery via in-situ formed catholyte
Metal-air batteries, operated in ambient air, suffer from irreversible redox reactions, limiting their energy density. Herein, the authors present a solid electrolyte-based sodium-air battery with a reversible carbonate reaction, facilitated by the in-situ formed catholyte enabled by moisture.
- Heetaek Park
- , Minseok Kang
- & Byoungwoo Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aqueous batteries have a short lifespan due to Al current collector corrosion and Li loss from side reactions on the anode. Here, the authors propose a prototype of self-prolonging aqueous Li-ion batteries by introducing hydrolyzation-type anodic additives to regulate Al corrosion-passivation.
- Binghang Liu
- , Tianshi Lv
- & Liumin Suo
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on garnet electrolyte elucidated by ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies
Dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on garnet electrolyte elucidated by ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies
Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 (LLZO) is a promising solid electrolyte but suffers from severe surface degradation in air. Here, authors use mapping of resonant Auger spectroscopy and various ambient pressure X-ray spectroscopies to elucidate the dynamical evolution of CO2 and H2O on clean LLZO surfaces.
- Nian Zhang
- , Guoxi Ren
- & Xiaosong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated high-throughput robotic platform and active learning approach for accelerated discovery of optimal electrolyte formulations
An integrated high-throughput robotic platform and active learning approach for accelerated discovery of optimal electrolyte formulations
Solubility determines energy density in redox flow batteries. Here, authors combine automated experiments with machine learning to efficiently identify solvents that significantly enhance solubility, testing less than 10% of over 2000 candidates.
- Juran Noh
- , Hieu A. Doan
- & Yangang Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Single [0001]-oriented zinc metal anode enables sustainable zinc batteries
Single [0001]-oriented zinc metal anode enables sustainable zinc batteries
The authors present a single [0001]-oriented Zn metal anode with high reversibility and demonstrate the significance of the Zn(0002) metal anode, characterized by a single crystalline orientation, for promoting ultra-sustainable homoepitaxial growth.
- Xiaotan Zhang
- , Jiangxu Li
- & Jiang Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Grave-to-cradle photothermal upcycling of waste polyesters over spent LiCoO2
Grave-to-cradle photothermal upcycling of waste polyesters over spent LiCoO2
The increasing production of lithium-ion batteries and plastics presents significant challenges to resource sustainability and ecosystem integrity. This study highlights the utilization of spent lithium cobalt oxide cathodes as photothermal catalysts to transform various waste polyesters into valuable monomers.
- Xiangxi Lou
- , Penglei Yan
- & Jinxing Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphonate-based iron complex for a cost-effective and long cycling aqueous iron redox flow battery
Phosphonate-based iron complex for a cost-effective and long cycling aqueous iron redox flow battery
Here, authors report an iron flow battery, using earth-abundant materials like iron, ammonia, and phosphorous acid. This work offers a solution to reduce materials cost and extend cycle life in energy storage applications for grid decarbonization.
- Gabriel S. Nambafu
- , Aaron M. Hollas
- & Guosheng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering the critical role of interstitial volume in glassy sulfide superionic conductors
Deciphering the critical role of interstitial volume in glassy sulfide superionic conductors
Glass sulfide electrolytes are promising materials for solid-state Li metal batteries, yet limited understanding hinders their progress. Here, the authors decipher the dissolution process of halogen dopants in glass and introduce a synthetic strategy to increase halogen dopant’s dissolution capacity.
- Han Su
- , Yu Zhong
- & Jiangping Tu
-
Article
| Open Access An entanglement association polymer electrolyte for Li-metal batteries
An entanglement association polymer electrolyte for Li-metal batteries
Here, the authors report an entanglement association polymer electrolyte with a polymer matrix and copolymer stabilizer. The developed entangled structure forms a stable interface for the polymer electrolyte during charging and discharging.
- Hangchao Wang
- , Yali Yang
- & Dingguo Xia
-
Article
| Open Access A solid-state lithium-ion battery with micron-sized silicon anode operating free from external pressure
A solid-state lithium-ion battery with micron-sized silicon anode operating free from external pressure
Applying high stack pressure is primarily done to address the mechanical failure issue of solid-state batteries. Here, the authors propose a mechanical optimization strategy involving elastic electrolyte to realize solid-state batteries operating without external pressurizing.
- Hui Pan
- , Lei Wang
- & Haoshen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering the contributing motifs of reconstructed cobalt (II) sulfides catalysts in Li-CO2 batteries
Deciphering the contributing motifs of reconstructed cobalt (II) sulfides catalysts in Li-CO2 batteries
Improving catalyst efficiency is vital for Li-CO2 batteries, but understanding catalyst structures during battery operation is hard. Here, the authors uncover catalyst reconstruction and its link to activity, highlighting a self-constructed oxysulfide structure with high activity and stability in Li-CO2 batteries.
- Yingqi Liu
- , Zhiyuan Zhang
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Proton-selective coating enables fast-kinetics high-mass-loading cathodes for sustainable zinc batteries
Proton-selective coating enables fast-kinetics high-mass-loading cathodes for sustainable zinc batteries
Sluggish Zn2+-dominated Faradic reactions lead to suboptimal charge-storage capacity and durability of aqueous zinc battery cathodes. Here, the authors present a proton-selective interfacial coating strategy that enables high-performance cathodes with fast-kinetics proton-dominated Faradic reactions.
- Quanquan Guo
- , Wei Li
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Electric vehicle battery chemistry affects supply chain disruption vulnerabilities
Electric vehicle battery chemistry affects supply chain disruption vulnerabilities
Electric vehicle battery supply chains are currently vulnerable to supply disruptions in China, but research shows that the cumulative effect of multiple supply chain steps creates additional vulnerabilities across multiple critical battery minerals.
- Anthony L. Cheng
- , Erica R. H. Fuchs
- & Jeremy J. Michalek
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular anchoring of free solvents for high-voltage and high-safety lithium metal batteries
Molecular anchoring of free solvents for high-voltage and high-safety lithium metal batteries
Advanced electrolyte is essential for high-energy-density lithium metal batteries. Here, the authors design a molecular anchoring dilute electrolyte via intermolecular hydrogen bonding with free solvents to improve the battery electrochemical and thermal stabilities.
- Zhuangzhuang Cui
- , Zhuangzhuang Jia
- & Xiaodi Ren
-
Article
| Open Access An acetate electrolyte for enhanced pseudocapacitve capacity in aqueous ammonium ion batteries
An acetate electrolyte for enhanced pseudocapacitve capacity in aqueous ammonium ion batteries
Ammonium ion batteries are of growing interest for energy storage research. Here, the authors observe two-step pseudocapacitive storage behavior in an ammonium acetate electrolyte, resulting in a superior ammonium ion storage capacity.
- Zhuoheng Bao
- , Chengjie Lu
- & ZhengMing Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling atomic and nanoscale structure in the silicon–oxygen system through active machine learning
Modelling atomic and nanoscale structure in the silicon–oxygen system through active machine learning
Understanding the silicon-oxygen system is crucial for various applications. Here, the authors present an interatomic potential covering a wide range of the Si-O configurational space and showcase applications to silica and Si-SiO2 interfaces.
- Linus C. Erhard
- , Jochen Rohrer
- & Volker L. Deringer
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient direct repairing of lithium- and manganese-rich cathodes by concentrated solar radiation
Efficient direct repairing of lithium- and manganese-rich cathodes by concentrated solar radiation
Rapid capacity decay and voltage drop hinder lithium- and manganese-rich cathode material (LMRO) development. Here, the authors apply concentrated solar radiation arrays on cycled LMRO electrodes, inducing inverse spinel phase to boost redox activity and reversibility, yielding enhanced electrochemical performance.
- Hailong Wang
- , Xin Geng
- & Xin He
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Electrode potential in any electrochemical systems has long been discussed by classical Debye-Hückel theory which holds only under extremely dilute concentrations. Here, the authors establish the concept ‘liquid Madelung potential’ to comprehensively describe the potential shift at practical concentrations.
- Norio Takenaka
- , Seongjae Ko
- & Atsuo Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access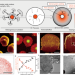 Kirkendall effect-induced uniform stress distribution stabilizes nickel-rich layered oxide cathodes
Kirkendall effect-induced uniform stress distribution stabilizes nickel-rich layered oxide cathodes
Nickel-rich layered oxide cathodes offer high energy density yet suffer from mechanical degradation during (de)lithiation. Here, the authors present a strategy that leverages the Kirkendall effect to equalize stress within the cathode particles, thereby stabilizing their structure and enhancing the cycling stability.
- Ziyao Gao
- , Chenglong Zhao
- & Baohua Li
-
Article
| Open Access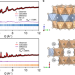 Promoting high-voltage stability through local lattice distortion of halide solid electrolytes
Promoting high-voltage stability through local lattice distortion of halide solid electrolytes
Solid electrolytes play a crucial role as ion conductors and separator between electrodes in all-solid-state batteries. Here, the authors report a high-entropy halide solid electrolyte, which reveals the structure evolution with the increasing configurational entropy and improves the high-voltage stability.
- Zhenyou Song
- , Tengrui Wang
- & Wei Luo
-
Article
| Open Access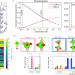 Ca-dimers, solvent layering, and dominant electrochemically active species in Ca(BH4)2 in THF
Ca-dimers, solvent layering, and dominant electrochemically active species in Ca(BH4)2 in THF
Alternatives to lithium-ion electrochemistry present challenges due to undesirable phenomena at the electrode-electrolyte interface. Through simulations, the authors find that the performance of a calcium-based electrolyte is driven entirely by molecular-scale processes within approximately 1 nm of the electrode.
- Ana Sanz Matias
- , Fabrice Roncoroni
- & David Prendergast
-
Article
| Open Access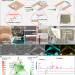 Hierarchical Li electrochemistry using alloy-type anode for high-energy-density Li metal batteries
Hierarchical Li electrochemistry using alloy-type anode for high-energy-density Li metal batteries
Utilizing an ultra-thin Li anode with a thickness below 50 μm is crucial for enhancing the energy density of batteries. Here, the authors develop a finely tunable, thin alloy-based Li anode that features a hierarchical Li electrochemistry, enabling stable cycling and superior energy density in Li metal batteries.
- Jiaqi Cao
- , Yuansheng Shi
- & Xia Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Structurally robust lithium-rich layered oxides for high-energy and long-lasting cathodes
Structurally robust lithium-rich layered oxides for high-energy and long-lasting cathodes
O2-type Li-rich layered cathodes suppress voltage decay and aid in oxygen redox research. Here, the authors report trilateral relationship among anionic redox utilization, bulk chemo-mechanical degradation, and electrochemical fading, which can be mitigated by balancing the redox center capabilities.
- Ho-Young Jang
- , Donggun Eum
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Solvation-property relationship of lithium-sulphur battery electrolytes
Solvation-property relationship of lithium-sulphur battery electrolytes
In the Li-S battery, a promising next-generation battery chemistry, electrolytes are vital because of solvated polysulfide species. Here, the authors investigate solvation-property relationships via the measurement of solvation free energy of the electrolytes, guiding advanced electrolyte design for Li-S batteries.
- Sang Cheol Kim
- , Xin Gao
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Re-evaluation of battery-grade lithium purity toward sustainable batteries
Re-evaluation of battery-grade lithium purity toward sustainable batteries
Due to recent fluctuations in lithium prices, the instability of lithium-ion batteries prices is on the rise. Here, through a re-evaluation of purity criteria, the authors report that the presence of magnesium impurity in lithium precursor actually improves cathode performance, economics, and environmental aspects.
- Gogwon Choe
- , Hyungsub Kim
- & Yong-Tae Kim
-
Article
| Open Access High voltage electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries with micro-sized silicon anodes
High voltage electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries with micro-sized silicon anodes
Micro-sized silicon are promising anode materials due to low-cost and high-energy, yet their application is hindered by inaccessible electrolytes. Here, the authors report sulfolane-based electrolytes that form silicon-phobic interphases and enable high-voltage pouch cells to achieve superior cycle life.
- Ai-Min Li
- , Zeyi Wang
- & Chunsheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Capacitive tendency concept alongside supervised machine-learning toward classifying electrochemical behavior of battery and pseudocapacitor materials
Capacitive tendency concept alongside supervised machine-learning toward classifying electrochemical behavior of battery and pseudocapacitor materials
Analysis of capacitive behavior of electrode materials used in batteries and pseudocapacitors is challenging. Here, authors report an electrochemical signal analysis method available as an online tool to classify the charge storage behavior of a material as battery-like or a pseudocapacitor-like.
- Siraprapha Deebansok
- , Jie Deng
- & Olivier Fontaine
-
Article
| Open Access Designing lithium halide solid electrolytes
Designing lithium halide solid electrolytes
The pursuit of all-solid-state batteries has motivated advancements in materials design. Here, the authors present a methodology demonstrating that ionic potential effectively captures crucial interactions within halide materials, guiding the design of the new materials with enhanced performance.
- Qidi Wang
- , Yunan Zhou
- & Marnix Wagemaker
-
Article
| Open Access Subtractive transformation of cathode materials in spent Li-ion batteries to a low-cobalt 5 V-class cathode material
Subtractive transformation of cathode materials in spent Li-ion batteries to a low-cobalt 5 V-class cathode material
Direct recycling or upcycling is promising for sustainable battery resource management. Here, the authors report a subtractive transformation strategy for upcycling spent cathode materials to high-performance 5 V-class cathodes, reducing reliance on rare elements for the sustainable Li-ion battery industry.
- Jun Ma
- , Junxiong Wang
- & Guangmin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled hydrated copper coordination compounds as ionic conductors for room temperature solid-state batteries
Self-assembled hydrated copper coordination compounds as ionic conductors for room temperature solid-state batteries
The design of inorganic-organic hybrid solid-state electrolytes is expected to merge the merits of both inorganic and organic material. Here, the authors craft Li-ion-implanted copper maleate hydrate nanoflakes via a bottom-up self-assembly approach to reveal superior room-temperature Li-ion conductivity.
- Xiao Zhan
- , Miao Li
- & Li Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing potassium polysulfides for high performance potassium-sulfur batteries
Optimizing potassium polysulfides for high performance potassium-sulfur batteries
Potassium-sulfur battery are promising materials for next-generation high energy, low cost batteries. Here the authors explore a tungsten based catalytic composite for optimizing potassium polysulfides and improve K-S electrochemistry in batteries
- Wanqing Song
- , Xinyi Yang
- & Wenbin Hu
-
Comment
| Open Access The rise of high-entropy battery materials
The rise of high-entropy battery materials
The emergence of high-entropy materials has inspired the exploration of novel materials in diverse technologies. In electrochemical energy storage, high-entropy design has shown advantageous impacts on battery materials such as suppressing undesired short-range order, frustrating energy landscape, decreasing volumetric change and reducing the reliance on critical metals. This comment addresses the definition and potential improper use of the term “high entropy” in the context of battery materials design, highlights the unique properties of high-entropy materials in battery applications, and outlines the remaining challenges in the synthesis, characterization, and computational modeling of high-entropy battery materials.
- Bin Ouyang
- & Yan Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated energy storage and CO2 conversion using an aqueous battery with tamed asymmetric reactions
Integrated energy storage and CO2 conversion using an aqueous battery with tamed asymmetric reactions
A system integrating CO2 conversion and energy storage holds great promise, but faces a major challenge due to degraded catalysts on charge. Here, the authors present a highly efficient energy storage and CO2 reduction method in an aqueous battery, achieved through oxidation of reducing molecules.
- Yumei Liu
- , Yun An
- & Quanquan Pang
-
Article
| Open Access A rechargeable Ca/Cl2 battery
A rechargeable Ca/Cl2 battery
The development of practical Ca metal batteries has been hindered by the cathode chemistry. Here, the authors report a rechargeable Ca/Cl2 battery, which involves the reversible cathode redox reaction between CaCl2 and Cl2.
- Shitao Geng
- , Xiaoju Zhao
- & Hao Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of solid-electrolyte pellet density on failure of solid-state batteries
Effect of solid-electrolyte pellet density on failure of solid-state batteries
A critical challenge of solid-state batteries is Li-filament penetration. Here, by quantifying microstructural properties and employing modeling techniques, the authors provide insight into solid-state battery failure modes and offer design guidelines to enhance safety and performance.
- Mouhamad S. Diallo
- , Tan Shi
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting a practical Li-CO2 battery through dimerization reaction based on solid redox mediator
Boosting a practical Li-CO2 battery through dimerization reaction based on solid redox mediator
Li–CO2 batteries following Li2CO3-product route suffers from low output voltage and severe parasitic reactions. Here, the authors introduce a copper-based solid redox mediator in Li–CO2 batteries with an efficient Li2C2O4 product route to circumvent the shuttle effect and sluggish kinetics caused by soluble mediators.
- Wei Li
- , Menghang Zhang
- & Haoshen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access An extended substrate screening strategy enabling a low lattice mismatch for highly reversible zinc anodes
An extended substrate screening strategy enabling a low lattice mismatch for highly reversible zinc anodes
The growth of dendrites and the occurrence of side reactions at zinc anodes currently impede the practical use of aqueous zinc batteries. Here, the authors present an advanced substrate screening approach aimed at stabilizing zinc anodes, thereby enabling the development of high-rate zinc-metal batteries.
- Zhiyang Zheng
- , Xiongwei Zhong
- & Guangmin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid-charging aluminium-sulfur batteries operated at 85 °C with a quaternary molten salt electrolyte
Rapid-charging aluminium-sulfur batteries operated at 85 °C with a quaternary molten salt electrolyte
Molten salt aluminium-sulfur batteries exhibit high-rate capability and moderate energy density, but suffer from high operating temperature. Here the authors demonstrate a rapidly charging aluminum-sulfur battery operating at 85 °C enabled by a quaternary alkali chloroaluminate electrolyte.
- Jiashen Meng
- , Xufeng Hong
- & Quanquan Pang
-
Article
| Open Access Alkaline-based aqueous sodium-ion batteries for large-scale energy storage
Alkaline-based aqueous sodium-ion batteries for large-scale energy storage
Aqueous sodium-ion batteries show promise for large-scale energy storage, yet face challenges due to water decomposition, limiting their energy density and lifespan. Here, the authors report a cathode surface coating strategy in an alkaline electrolyte to enhance the stability of both electrolyte and battery.
- Han Wu
- , Junnan Hao
- & Shi-Zhang Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access A dicarbonate solvent electrolyte for high performance 5 V-Class Lithium-based batteries
A dicarbonate solvent electrolyte for high performance 5 V-Class Lithium-based batteries
Rechargeable lithium batteries featuring 5 V cathodes offer high energy density yet struggle with stability. Here, the authors formulate an electrolyte incorporating dimethyl 2,5-dioxahexanedioate solvent, which facilitates stable lithium plating and stripping while offering an extended cycle life.
- Xiaozhe Zhang
- , Pan Xu
- & Alexandru Vlad
-
Article
| Open Access Improving rechargeable magnesium batteries through dual cation co-intercalation strategy
Improving rechargeable magnesium batteries through dual cation co-intercalation strategy
Rechargeable magnesium batteries suffer from poor mobility of Mg-ions, severely affecting the electrochemical performance. Here, authors demonstrate a strategy of co-intercalation of monovalent ions into the host lattice, which substantially improves Mg-ion mobility and battery performance.
- Ananyo Roy
- , Mohsen Sotoudeh
- & Zhenyou Li
-
Article
| Open Access Cobalt-free composite-structured cathodes with lithium-stoichiometry control for sustainable lithium-ion batteries
Cobalt-free composite-structured cathodes with lithium-stoichiometry control for sustainable lithium-ion batteries
As electric vehicle batteries adopt cobalt-free layered cathodes to tackle supply chain issues, it greatly impacts battery lifespan. Here, the authors develop a lithium stoichiometry control method to synthesize cobalt-free composite-structured cathodes with high cycling stability, enabling long-life sustainable batteries.
- Ke Chen
- , Pallab Barai
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial self-healing polymer electrolytes for long-cycle solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries
Interfacial self-healing polymer electrolytes for long-cycle solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries
Low ion conductivity, large interfacial resistance, and dendrite growth hinder the practical use of solid-state batteries. Here, the authors introduce a self-healing poly(ether-urethane)-based solid-state polymer electrolyte to address these issues, resulting in high performance solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Fei Pei
- , Lin Wu
- & Yunhui Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A weakly solvating electrolyte towards practical rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries
A weakly solvating electrolyte towards practical rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries
The practical deployment of aqueous zinc-ion batteries is hindered by the structure deterioration and side reactions at electrodes. Here, the authors introduce a weakly solvating electrolyte with butanone as an electrolyte additive to stabilize both the cathode and anode of aqueous zinc-ion batteries simultaneously.
- Xin Shi
- , Jinhao Xie
- & Xihong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access A cross-scale framework for evaluating flexibility values of battery and fuel cell electric vehicles
A cross-scale framework for evaluating flexibility values of battery and fuel cell electric vehicles
Electrified transportation exhibits great potential to provide flexibility. This article analyzed and compared the flexibility values of battery electric vehicles and fuel cell electric vehicles for planning and operating interdependent electricity and hydrogen supply chains.
- Ruixue Liu
- , Guannan He
- & Benben Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic paddle-wheels in a solid-state electrolyte
Electronic paddle-wheels in a solid-state electrolyte
Conduction in solid-state electrolytes composed of monatomic ions is found to be analogous to the paddle-wheel mechanism in molecular solid electrolytes, facilitated by rotational motion of lone pair electrons, helping unify understanding of mechanisms.
- Harender S. Dhattarwal
- , Rahul Somni
- & Richard C. Remsing

 Hybridizing carbonate and ether at molecular scales for high-energy and high-safety lithium metal batteries
Hybridizing carbonate and ether at molecular scales for high-energy and high-safety lithium metal batteries