Featured
-
-
Article |
 A trident dithienylethene-perylenemonoimide dyad with super fluorescence switching speed and ratio
A trident dithienylethene-perylenemonoimide dyad with super fluorescence switching speed and ratio
Photoswitchable fluorophores hold promise for organic photonic devices. Here Li et al. report that a trident perylenemonoimide modified by diethienylethenes shows a large on/off ratio and high switching speed, which enables erasable fluorescence patterning, all-optical transistors and optical nanoimaging.
- Chong Li
- , Hui Yan
- & Ming-Qiang Zhu
-
Article |
 High-Tc superconductivity in ultrathin Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x down to half-unit-cell thickness by protection with graphene
High-Tc superconductivity in ultrathin Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x down to half-unit-cell thickness by protection with graphene
So-called two-dimensional superconductivity has been reported in several material systems but just how thin a system can be and maintain a superconducting state has been difficult to determine. Da Jiang and colleagues demonstrate that Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+xcontinues to be superconducting even when it is just half a unit cell thick.
- Da Jiang
- , Tao Hu
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access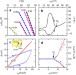 Anomalous critical fields in quantum critical superconductors
Anomalous critical fields in quantum critical superconductors
Superconductivity in the iron pnictides is believed to be related to quantum critical fluctuations. Putzke et al. observe unexpected anomalies in the critical fields of BaFe2(As1−xPx)2that emerge close to its magnetic critical point, which they argue is a generic feature of quantum critical superconductivity.
- C. Putzke
- , P. Walmsley
- & A. Carrington
-
Article |
 Kinetically tuned dimensional augmentation as a versatile synthetic route towards robust metal–organic frameworks
Kinetically tuned dimensional augmentation as a versatile synthetic route towards robust metal–organic frameworks
The synthesis of ultra-stable, single crystalline metal–organic frameworks is challenging. Here, the authors describe a kinetically tuned augmentation synthetic route for the preparation of a range of robust crystalline materials from preformed trimetallic components.
- Dawei Feng
- , Kecheng Wang
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer collapse in miscible good solvents is a generic phenomenon driven by preferential adsorption
Polymer collapse in miscible good solvents is a generic phenomenon driven by preferential adsorption
Smart polymers exhibit a swelling–collapse–swelling transition in mixed (co)solvents and the underlined mechanism remains a matter of debate. Mukherji et al. explain this transition using a generic model based purely on a thermodynamic treatment of preferential polymer–cosolvent interaction.
- Debashish Mukherji
- , Carlos M. Marques
- & Kurt Kremer
-
Article |
 A general and scalable synthesis approach to porous graphene
A general and scalable synthesis approach to porous graphene
Scalable routes towards porous graphene are useful for developing materials for mass transfer applications. Here, the authors report the fabrication of porous graphene with controllable pore size and nitrogen content via the carbothermal reaction of graphene and (poly)oxometallates.
- Ding Zhou
- , Yi Cui
- & Bao-Hang Han
-
Article |
 Control superstructure of rigid polyelectrolytes in oppositely charged hydrogels via programmed internal stress
Control superstructure of rigid polyelectrolytes in oppositely charged hydrogels via programmed internal stress
Biomaterials composed of macromolecules display complex structures with long range order, but it is difficult to create similarly complex superstructures in hydrogels. Here, the authors control the orientation of polyelectrolytes in hydrogels by introducing programmed swelling patterns and internal stresses.
- Riku Takahashi
- , Zi Liang Wu
- & Jian Ping Gong
-
Article |
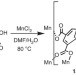 Engineering chiral porous metal-organic frameworks for enantioselective adsorption and separation
Engineering chiral porous metal-organic frameworks for enantioselective adsorption and separation
The separation of chiral molecules is a fundamental and industrially relevant challenge. Here, the authors report a chiral metal-organic framework that functions as a solid-state host capable of absorbing and separating mixtures of a range of chiral amines, with high enatioselectivity.
- Yongwu Peng
- , Tengfei Gong
- & Yong Cui
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of colloid-cholesteric composites provides a possible route to switchable optical materials
Self-assembly of colloid-cholesteric composites provides a possible route to switchable optical materials
Colloidal particles dispersed in liquid crystal hold promise for new functional materials with tunable elastic and electro-optic properties. Through simulations, Stratford et al.predict a new class of colloidal networks in a chiral liquid crystal host, which could guide the design of these materials.
- K. Stratford
- , O. Henrich
- & D. Marenduzzo
-
Article
| Open Access A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
Chiral determination of vapours is possible in biological systems as an important part of the olfactory system. Here, the authors describe a system that is capable of visually detecting and distinguishing the chirality of vapour-phase molecules by structural changes in a liquid crystal confined in open microchannels.
- Takuya Ohzono
- , Takahiro Yamamoto
- & Jun-ichi Fukuda
-
Article |
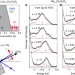 High-energy spin and charge excitations in electron-doped copper oxide superconductors
High-energy spin and charge excitations in electron-doped copper oxide superconductors
Understanding spin dynamics in the cuprates is vital to understanding the origin high-temperature superconductivity. X-ray and neutron spectra obtained by Ishii et al.suggest that the spins in electron-doped cuprates are itinerant, in contrast to recent evidence that in hole-doped cuprates they are localized.
- K. Ishii
- , M. Fujita
- & J. Mizuki
-
Article |
 Spatially and temporally reconfigurable assembly of colloidal crystals
Spatially and temporally reconfigurable assembly of colloidal crystals
Controlling colloidal assemblies without the need of a template or electrode is still a challenging goal. Here Kim et al.use photo-induced ion flow in an indium tin oxide-coated substrate to control this process, allowing reversible assembly of colloidal crystals in a three-dimensional manner.
- Youngri Kim
- , Aayush A. Shah
- & Michael J. Solomon
-
Article |
 Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
The structure of hydrogels is normally isotropic, but anisotropic hydrogels with a periodic lamellar structure can also be synthesized. Here the confined water layers in a lamellar hydrogel are used to guide the growth of large area, single-crystalline gold membranes with two-dimensional properties.
- Jian Niu
- , Dong Wang
- & Jian Jin
-
Article |
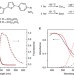 Electrofluorochromism in π-conjugated ionic liquid crystals
Electrofluorochromism in π-conjugated ionic liquid crystals
The ability to easily modulate a material’s photoluminescent properties in response to stimuli is difficult to achieve in liquid crystals. Here the authors report ionic liquid crystals exhibiting high fluorescent quantum yields with redox-dependent photoluminescence.
- Amerigo Beneduci
- , Sante Cospito
- & Giuseppe Chidichimo
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal–organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation
Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal–organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation
Although many metal–organic frameworks are luminescent, few are capable of white-light emission. Here, the authors incorporate a yellow-emitting guest molecule into the cavities of a blue-emitting metal–organic framework, and tune the composition to emit white light with relatively high quantum yield.
- Chun-Yi Sun
- , Xin-Long Wang
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Confinement of pyridinium hemicyanine dye within an anionic metal-organic framework for two-photon-pumped lasing
Confinement of pyridinium hemicyanine dye within an anionic metal-organic framework for two-photon-pumped lasing
Two-photon-pumped dye lasers are useful for applications such as biological imaging; however, loss processes reduce their efficiency. Here, metal-organic frameworks, into which the laser dye is incorporated, demonstrate enhanced laser operation because losses such as dye aggregation-caused quenching are reduced.
- Jiancan Yu
- , Yuanjing Cui
- & Guodong Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Localized cell stimulation by nitric oxide using a photoactive porous coordination polymer platform
Localized cell stimulation by nitric oxide using a photoactive porous coordination polymer platform
Localized cell stimulation is useful in the analysis of biological signalling networks. Here the authors develop a photosensitive porous framework to achieve spatiotemporally controlled cellular delivery of the gaseous biomolecule nitric oxide, using it to regulate intracellular calcium levels.
- Stéphane Diring
- , Dan Ohtan Wang
- & Shuhei Furukawa
-
Article |
 Revealing the ultrafast process behind the photoreduction of graphene oxide
Revealing the ultrafast process behind the photoreduction of graphene oxide
Photoreduction is a promising method for the synthesis of reduced graphene oxide, but the dynamics of the process are unclear. Here, the authors explore the process via a pump–probe technique, revealing its ultrafast nature and the involvement of solvated electrons produced by irradiation of the solvent.
- Régis Y. N. Gengler
- , Daniel S. Badali
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article |
 Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Crystalline porous materials are commonly based around negatively charged frameworks, so ion-exchange is limited to cations. Here, the authors report a series of positive metal-organic frameworks, capable of ion exchange of large organic anions, with potential in separation and purification applications.
- Xiang Zhao
- , Xianhui Bu
- & Pingyun Feng
-
Article |
 Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Compositionally and geometrically complex nano-objects are an important goal in medicinal, photonic and electronic materials research. Here, the authors fabricate disk-sphere and disk-cylinder nanoparticles with defined multicompartments from binary mixtures of block copolymers.
- Jiahua Zhu
- , Shiyi Zhang
- & Darrin J. Pochan
-
Article |
 Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Techniques for shape-controlling of hydrogels, that is, crosslinked networks of polymers, could make possible various biomimetic applications. Palleau et al.propose a strategy to pattern three-dimensional hydrogels using electric potential, which allows directed bending and fast controllable actuation.
- Etienne Palleau
- , Daniel Morales
- & Orlin D. Velev
-
Article |
 Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Proteins are ideal building blocks for self-assembly of artificial cell-like architectures, but their realization is rare. Huang et al.report an interfacial assembly of protein–polymer conjugates, which exhibit cellular properties such as encapsulating guest molecules and switching enzyme activity.
- Xin Huang
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
 An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
Small interfering RNA is degraded by plasma and can’t cross the cell membrane due to its negative charge. Here, the authors present an influenza inspired polymer carrier, capable of local RNA delivery, which degrades to a non-toxic by-product, and is thus suitable for multiple doses.
- Nghia P Truong
- , Wenyi Gu
- & Michael J Monteiro
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels
A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels
Hierarchically porous metal-organic monoliths are potential materials for mass transfer applications. Here, the authors synthesize metal-organic aerogels via the gelation of metal-organic frameworks, and are able to tune their porosity exploiting the properties of both crystalline and aerogel materials.
- Lei Li
- , Shenglin Xiang
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article |
 New materials for methane capture from dilute and medium-concentration sources
New materials for methane capture from dilute and medium-concentration sources
Methane is an important greenhouse gas but its capture presents a challenge due to its weak interactions with most materials. Here the authors perform a systematic screening of liquid solvents and nanoporous zeolites, and identify zeolite structures with good potential for methane uptake and separation.
- Jihan Kim
- , Amitesh Maiti
- & Roger D. Aines
-
Article |
 Moderate doping leads to high performance of semiconductor/insulator polymer blend transistors
Moderate doping leads to high performance of semiconductor/insulator polymer blend transistors
Blends of different polymer compounds are widely used for organic field-effect transistors. Here, Neher and colleagues show that moderate carrier doping is important to achieve maximum performance in blends of insulating and semiconducting polymers.
- Guanghao Lu
- , James Blakesley
- & Dieter Neher
-
Article |
 Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour
Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour
Graphene oxide has been proposed as an alternative to precious metals for the catalysis of aerobic oxidative reactions; however, high catalyst loadings are needed. Here a simple base and acid treatment is shown to enhance its catalytic activity for the oxidative coupling of amines under ambient conditions.
- Chenliang Su
- , Muge Acik
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article |
 Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths
Biomimetic superelastic graphene-based cellular monoliths
The exploitation of the properties of graphene, such as mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, in deformable macroscopic materials is desirable. Here, a combination of graphene chemistry and ice physics is used to fabricate biomimetic, ultralight and superelastic graphene cellular monoliths.
- Ling Qiu
- , Jeffery Z. Liu
- & Dan Li
-
Article |
 Monodisperse conjugated polymer particles by Suzuki–Miyaura dispersion polymerization
Monodisperse conjugated polymer particles by Suzuki–Miyaura dispersion polymerization
Well-defined, monodisperse colloids of semiconducting polymers are required as new photonic and optoelectronic materials. Here, a Suzuki–Miyaura dispersion polymerization is used to produce monodisperse sub-micrometer particles of a range of semiconducting polymers.
- Alexander J.C. Kuehne
- , Malte C. Gather
- & Joris Sprakel
-
Article |
 Stirring competes with chemical induction in chiral selection of soft matter aggregates
Stirring competes with chemical induction in chiral selection of soft matter aggregates
Chirality can be induced both by physical forces and by chemical induction processes. Here, a self-assembled system is reported in which chiral selection is controlled by the combined action of a chiral dopant and vortical stirring, which can act either constructively or destructively.
- Núria Petit-Garrido
- , Josep Claret
- & Francesc Sagués
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Crystallization of noble metal atoms usually leads to the thermodynamically stable face-centred cubic phase. Sunet al. show that internal strain in silver nanoparticles leads to lattice distortion and a stable body-centred tetragonal phase.
- Yugang Sun
- , Yang Ren
- & Dean J. Miller
-
Article |
 Microporous metal-organic framework with potential for carbon dioxide capture at ambient conditions
Microporous metal-organic framework with potential for carbon dioxide capture at ambient conditions
Metal-organic frameworks are promising candidates for capturing and sequestering carbon dioxide. Chen and co-workers report a metal-organic framework that exhibits high uptake of carbon dioxide at ambient conditions, and is a potentially useful adsorbent for post-combustion carbon dioxide capture.
- Shengchang Xiang
- , Yabing He
- & Banglin Chen
-
Article |
 Tuning the magneto-structural properties of non-porous coordination polymers by HCl chemisorption
Tuning the magneto-structural properties of non-porous coordination polymers by HCl chemisorption
Tuning the properties of responsive materials by applying an external stimulus could lead to their application as chemical switches or molecular sensors. Coronadoet al. develop a non-porous one-dimensional coordination polymer, the magnetic properties of which undergo drastic changes on chemisorption of gaseous HCl.
- Eugenio Coronado
- , Mónica Giménez-Marqués
- & Lee Brammer
-
Article |
 Local chiral symmetry breaking in triatic liquid crystals
Local chiral symmetry breaking in triatic liquid crystals
Studying the structures of dense colloidal systems of anisotropic Brownian particles provides insight into fundamental processes like protein crystallization. Zhaoet al. study the phases of two-dimensional triatic liquid crystals and find that one of them exhibits local chiral-symmetry breaking.
- Kun Zhao
- , Robijn Bruinsma
- & Thomas G. Mason
-
Article |
 Prominent electrochromism through vacancy-order melting in a complex oxide
Prominent electrochromism through vacancy-order melting in a complex oxide
Electrochromic materials reversibly change their colour upon application of an electric field. Seidelet al. measure the optical properties of doped bismuth ferrite and report the largest electrochromic response for an inorganic material, which they attribute to the melting of oxygen-vacancy ordering.
- J. Seidel
- , W. Luo
- & R. Ramesh
-
Article |
 Spin waves and magnetic exchange interactions in insulating Rb0.89Fe1.58Se2
Spin waves and magnetic exchange interactions in insulating Rb0.89Fe1.58Se2
Unlike the other iron-based superconductors, the parent compounds of the alkaline iron selenide superconductors are insulators. Dai and colleagues examine the spin-wave excitations in these materials and uncover evidence for a common magnetic origin for all iron-based superconductors.
- Miaoyin Wang
- , Chen Fang
- & Pengcheng Dai
-
Article |
 Superconductivity at 5 K in alkali-metal-doped phenanthrene
Superconductivity at 5 K in alkali-metal-doped phenanthrene
Intercalating alkali metals into picene—a hydrocarbon with five linearly fused benzene rings—results in superconducting materials. Now, alkali-metal-doped phenanthrene, which consists of three fused benzene rings, is also found to be superconducting, opening up a broader class of organic superconductors.
- X.F. Wang
- , R.H. Liu
- & X.H. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access High pressure route to generate magnetic monopole dimers in spin ice
High pressure route to generate magnetic monopole dimers in spin ice
Spin ices are magnetic materials in which excitations equivalent to monopoles can occur. Using high-pressure techniques, Zhouet al. synthesize a new member of the spin ice family, Dy2Ge2O7, in which monopoles exist at higher densities, and can stabilize as dimers.
- H.D. Zhou
- , S.T. Bramwell
- & J.S. Gardner
-
Article
| Open Access Advantageous grain boundaries in iron pnictide superconductors
Advantageous grain boundaries in iron pnictide superconductors
High critical temperature superconductors could be used to produce ideal electric power lines, but the misalignment of crystalline grain boundaries reduces current density. Here, pnictide superconductors are found to be more tolerant to misaligned grain boundaries than cuprates.
- Takayoshi Katase
- , Yoshihiro Ishimaru
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Article
| Open Access Proximity of iron pnictide superconductors to a quantum tricritical point
Proximity of iron pnictide superconductors to a quantum tricritical point
In some iron-based materials, unconventional superconductivity can emerge near a quantum phase transition where long-range magnetic order vanishes. Giovannettiet al.show that the magnetic quantum phase transition in an iron pnictide superconductor is very close to the quantum tricritical point.
- Gianluca Giovannetti
- , Carmine Ortix
- & José Lorenzana
-
Article
| Open Access A new method to position and functionalize metal-organic framework crystals
A new method to position and functionalize metal-organic framework crystals
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have potential catalysis, filtration and sensing applications, but device fabrication will require controlled MOF growth. Here, α-hopeite microparticles are used to achieve spatial control of MOF nucleation, and accelerate MOF growth.
- Paolo Falcaro
- , Anita J. Hill
- & Dario Buso
-
Article |
 Spherical hyperlens for two-dimensional sub-diffractional imaging at visible frequencies
Spherical hyperlens for two-dimensional sub-diffractional imaging at visible frequencies
Although hyperlenses made of metamaterials can image sub-diffraction-limited objects, they are limited to one-dimensional magnification and ultraviolet frequencies. Here, the authors demonstrate a spherical hyperlens for visible light far-field imaging, with a resolution of 160 nm in both lateral dimensions.
- Junsuk Rho
- , Ziliang Ye
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article |
 Pseudogap in a thin film of a conventional superconductor
Pseudogap in a thin film of a conventional superconductor
In high-temperature superconductors, a very low density of states, the pseudogap, exists even above the critical temperature. Here, the authors show that this is also the case for a conventional superconductor, titanium nitride thin films, and that this pseudogap is induced by superconducting fluctuations.
- Benjamin Sacépé
- , Claude Chapelier
- & Marc Sanquer
-
Article
| Open Access All-linear time reversal by a dynamic artificial crystal
All-linear time reversal by a dynamic artificial crystal
Signal processing by time reversal has thus far only been realized through nonlinear mechanisms. The authors describe an all-linear, and thus low-power, time-reversal process based on frequency inversion in a dynamically controlled artificial periodic structure, a dynamic magnonic crystal.
- Andrii V. Chumak
- , Vasil S. Tiberkevich
- & Burkard Hillebrands
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional broadband and broad-angle transformation-optics lens
Three-dimensional broadband and broad-angle transformation-optics lens
Lenses with superior performance with respect to conventional uniform materials are desirable. The authors show a three-dimensional lens, made of multilayered metamaterials and based on approximate transformation optics, which works in different polarizations at broad viewing angles and with wide bandwidth.
- Hui Feng Ma
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article |
 Dilatancy in the flow and fracture of stretched colloidal suspensions
Dilatancy in the flow and fracture of stretched colloidal suspensions
Colloidal suspensions are important in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Here, the breaking of filaments of a colloidal liquid under tensile loading is shown to be closely related to the jamming transition seen in its shear rheology; surprising viscoelasticity is also observed in the fluid under tension.
- M.I. Smith
- , R. Besseling
- & V. Bertola
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic structure of the order parameter in FeSe0.45Te0.55 revealed by angle-resolved specific heat
Anisotropic structure of the order parameter in FeSe0.45Te0.55 revealed by angle-resolved specific heat
The structure of the superconducting gap of iron pnictide superconductors is controversial. In this paper, angle-resolved specific heat measurements are used to show that the gap is anisotropic, which is consistent with an extended s-wave model of superconducting pairing.
- B. Zeng
- , G. Mu
- & H.-H. Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling spins in adsorbed molecules by a chemical switch
Controlling spins in adsorbed molecules by a chemical switch
Chemical systems with switchable molecular spins could allow the development of materials with controllable spintronic properties. Here, the authors show that nitric oxide coordination to cobalt(II)tetraphenylporphyrin on a nickel surface, followed by thermal dissociation, leads to off-on spin switching.
- Christian Wäckerlin
- , Dorota Chylarecka
- & Nirmalya Ballav
-
Article
| Open Access Surface-wetting effects on the liquid–liquid transition of a single-component molecular liquid
Surface-wetting effects on the liquid–liquid transition of a single-component molecular liquid
A phase transition between two liquid states is a counterintuitive phenomenon, but one that is known to happen in certain materials. Murata and Tanaka now show in tryphenyl phosphite that this can also produce a change in the wetting of a surface, from partial to complete, at the transition temperature.
- Ken-ichiro Murata
- & Hajime Tanaka

 Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality
Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality