Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Poly(4-styrenesulfonate)-induced sulfur vacancy self-healing strategy for monolayer MoS2 homojunction photodiode
Poly(4-styrenesulfonate)-induced sulfur vacancy self-healing strategy for monolayer MoS2 homojunction photodiode
Two-dimensional MoS2 homojunctions, considered potential building blocks for next generation flexible electronics, currently suffer from quick degradation. Here, Zhang and co-workers use a self-healing sulfur vacancy mechanism to produce a MoS2photodiode that possesses long term stability.
- Xiankun Zhang
- , Qingliang Liao
- & Yue Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access In situ dynamic observations of perovskite crystallisation and microstructure evolution intermediated from [PbI6]4− cage nanoparticles
In situ dynamic observations of perovskite crystallisation and microstructure evolution intermediated from [PbI6]4− cage nanoparticles
The photovoltaic performances of perovskite materials are strongly influenced by their crystallinity and film morphology. Here, the authors investigate the formation and morphology evolution mechanisms of lead halide perovskites and reveal that bulk polycrystals grow from intermediate [PbI6]4−cage nanoparticles.
- Qin Hu
- , Lichen Zhao
- & Qihuang Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Growth of organic crystals via attachment and transformation of nanoscopic precursors
Growth of organic crystals via attachment and transformation of nanoscopic precursors
Multistage crystallization pathways involving nanoscopic precursors or intermediates have been proposed for various systems. Here, the authors find compelling evidence that nanoscopic species participate in the crystallization of glutamic acid monohydrate, extending this non-classical growth mechanism to organic crystals.
- Yuan Jiang
- , Matthias Kellermeier
- & Helmut Cölfen
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
2D nanomaterials are promising capacitive energy storage materials, but their tendency to restack hinders electrolyte transport. Here, Yamauchi and colleagues introduce 2D ordered mesoporous carbons in between MXene layers, and metal removal affords all-carbon porous 2D–2D heterostructures in which restacking is prevented.
- Jie Wang
- , Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Regulating guest access and release in porous materials remains an important goal. Here, May and colleagues elucidate the mechanism by which guest admission can be temperature-regulated in typical microporous materials, and experimentally exploit this process to achieve appreciable and reversible hydrogen storage.
- Gang (Kevin) Li
- , Jin Shang
- & Eric F. May
-
Article
| Open Access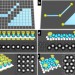 Vector assembly of colloids on monolayer substrates
Vector assembly of colloids on monolayer substrates
Precise assembly of undecorated colloids demands a clever approach. Here, the authors draw unlikely inspiration from vector graphics to direct colloids into 2D structures, pinning the ends and corners of assembled patterns with optical tweezers and manipulating the segments like vectors.
- Lingxiang Jiang
- , Shenyu Yang
- & Steve Granick
-
Article
| Open Access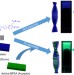 Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix
Chirality and energy transfer amplified circularly polarized luminescence in composite nanohelix
Energy and chirality transfer play a crucial role in living systems. Here, the authors show that achiral acceptors and chiral donor gelators can assemble in a chirally-controlled manner into a supramolecular nanohelix that can additionally harvest circularly polarized energy.
- Dong Yang
- , Pengfei Duan
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Free-standing supramolecular hydrogel objects by reaction-diffusion
Free-standing supramolecular hydrogel objects by reaction-diffusion
Reaction-diffusion controls the spatial formation of many natural structures but is rarely applied to organic materials. Here, the authors couple reaction-diffusion to the self-assembly of a supramolecular gelator, introducing a strategy to forming soft, free-standing objects with controlled shape and functionality.
- Matija Lovrak
- , Wouter E. J. Hendriksen
- & Jan H. van Esch
-
Article
| Open Access Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots
Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots
Growth of colloidal semiconductor quantum dots involves several stages, including an enigmatic induction period preceding nucleation. Here, the authors identify two distinct intermediates in the induction period, mapping their evolution from precursors all the way to either magic-size clusters or quantum dots.
- Mingyang Liu
- , Kun Wang
- & Kui Yu
-
Article
| Open Access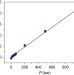 Giant barocaloric effect in the ferroic organic-inorganic hybrid [TPrA][Mn(dca)3] perovskite under easily accessible pressures
Giant barocaloric effect in the ferroic organic-inorganic hybrid [TPrA][Mn(dca)3] perovskite under easily accessible pressures
Solid-state materials that exhibit large caloric effects have the potential to replace compressed greenhouse gases in refrigeration technologies. Here the authors report near room temperature giant barocaloric effects in hybrid perovskite [TPrA][Mn(dca)3] under easily accessible pressures.
- Juan M. Bermúdez-García
- , Manuel Sánchez-Andújar
- & María A. Señarís-Rodríguez
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic cavitation in Stokes flow of anisotropic fluids
Hydrodynamic cavitation in Stokes flow of anisotropic fluids
Cavitation is the formation of vapour bubbles within a liquid and is undesirable in many industrial applications. Here Stiegeret al. show how the anisotropic fluids influence this process in a nematic liquid crystal and find that orientational ordering of molecules can tune the onset of cavitation.
- Tillmann Stieger
- , Hakam Agha
- & Anupam Sengupta
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the crystallization and designability issues in the ultrastable zirconium phosphonate framework system
Overcoming the crystallization and designability issues in the ultrastable zirconium phosphonate framework system
Zirconium phosphonate based metal-organic frameworks often exhibit superior chemical stabilities, but typically exist as poorly crystalline or amorphous materials. Here the authors exploit an ionothermal method to obtain highly porous and remarkably stable single crystalline zirconium phosphonate frameworks that can efficiently remove uranyl ions from aqueous solutions.
- Tao Zheng
- , Zaixing Yang
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchically structured lithium titanate for ultrafast charging in long-life high capacity batteries
Hierarchically structured lithium titanate for ultrafast charging in long-life high capacity batteries
Both electronic and ionic transport must be optimized in Li4Ti5O12for its use in Li-ion batteries, most promisingly against high voltage cathodes. Here authors synthesize hierarchical porous micrometre-scale structures composed of primary nanoparticles to demonstrate an attractive combination of rate performance, capacity and cycling stability.
- Mateusz Odziomek
- , Frédéric Chaput
- & Stephane Parola
-
Article
| Open Access Construction of hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks through linker labilization
Construction of hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks through linker labilization
Expanding pore sizes and volumes in metal-organic frameworks is challenging, but crucial for the encapsulation of larger guest molecules. Here, Zhou and colleagues report a linker labilization strategy to construct MOFs containing hierarchical pore architectures with dimensions ranging from 1.5 to 18 nm.
- Shuai Yuan
- , Lanfang Zou
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying similarity of pore-geometry in nanoporous materials
Quantifying similarity of pore-geometry in nanoporous materials
Pore structure plays an important role in dictating gas storage performance for nanoporous materials. Here, Smit and colleagues develop a topological approach to quantify pore structure similarity, and exploit the resulting descriptor to screen for materials that possess structural similarities with top-performers.
- Yongjin Lee
- , Senja D. Barthel
- & Berend Smit
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-stimuli responsive and reversibly activatable theranostic nanoprobe for precision tumor-targeting and fluorescence-guided photothermal therapy
Dual-stimuli responsive and reversibly activatable theranostic nanoprobe for precision tumor-targeting and fluorescence-guided photothermal therapy
A number of nanomaterials for dual diagnostic and therapeutic application have a number of limitations including poor signal-to-noise ratio. Here, the authors developed dual stimuli-responsive and reversibly activatable nanoprobes for tumour targeting and fluorescence-guided photothermal therapy.
- Xu Zhao
- , Cheng-Xiong Yang
- & Xiu-Ping Yan
-
Article
| Open Access High conductance values in π-folded molecular junctions
High conductance values in π-folded molecular junctions
Foldamers are synthetic oligomers that adopt folded conformations through non-covalent intramolecular interactions. Here, Cariniet al. describe a family of foldamers with a large number of anthracene units that are able to transport charge efficiently at the single-molecule level.
- Marco Carini
- , Marta P. Ruiz
- & Aurelio Mateo-Alonso
-
Article
| Open Access Optical determination of crystal phase in semiconductor nanocrystals
Optical determination of crystal phase in semiconductor nanocrystals
Identifying crystallographic phases in solution is not possible with standard diffraction methods. Here, Limet al. demonstrate the in situidentification of cubic and hexagonal phases of cadmium selenide nanocrystals using optical methods based on first-principles electronic theory.
- Sung Jun Lim
- , André Schleife
- & Andrew M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access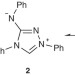 New Blatter-type radicals from a bench-stable carbene
New Blatter-type radicals from a bench-stable carbene
Blatter’s radicals are highly valuable stable organic free radicals, comprising a heterocyclic ring system functionalized with a heteroaryl or alkyl group at the C-3 position. Here, the authors report a synthetic strategy to obtain Blatter’s radical substituted with an amine and amide group.
- Jacob A. Grant
- , Zhou Lu
- & AnnMarie C. O’Donoghue
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and interstitial iodide migration in hybrid perovskite methylammonium lead iodide
Structure and interstitial iodide migration in hybrid perovskite methylammonium lead iodide
The mechanism underpinning the photovoltaic effect in hybrid perovskite solar cells has remained unclear. Here, Green and co-workers suggest that iodide ions in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite migrate via interstitial sites and undergo a redox reaction to form molecular iodine and free electrons.
- J. L. Minns
- , P. Zajdel
- & M. A. Green
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE: Precise determination of graphene functionalization by in situ Raman spectroscopy
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Precise determination of graphene functionalization by in situ Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a versatile tool to gain insight into the functionalization of graphene-based materials, yet unequivocal assignment of the vibrational modes associated with covalent binding has so far remained elusive. Here, the authors succeed in an experimental and theoretical identification of this molecular fingerprint.
- Philipp Vecera
- , Julio C. Chacón-Torres
- & Andreas Hirsch
-
Article
| Open Access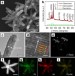 Platinum-nickel alloy excavated nano-multipods with hexagonal close-packed structure and superior activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction
Platinum-nickel alloy excavated nano-multipods with hexagonal close-packed structure and superior activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction
While crystal phase modification may endow materials with altered functionality, the fabrication of allomorphic noble metal nanomaterials is challenging. Here, the authors synthesize an unusual hexagonal close-packed platinum-nickel alloy and demonstrate its enhanced hydrogen evolution catalytic activity.
- Zhenming Cao
- , Qiaoli Chen
- & Lansun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access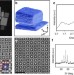 Structure and vacancy distribution in copper telluride nanoparticles influence plasmonic activity in the near-infrared
Structure and vacancy distribution in copper telluride nanoparticles influence plasmonic activity in the near-infrared
CuTe nanocrystals may be used as an alternative to noble metals for plasmonics but requires understanding of the atomic structure and the influence of defects. Here Willhammaret al. use electron tomography to reveal the distribution of vacancies in the nanocrystals and their effect on the optical properties.
- Tom Willhammar
- , Kadir Sentosun
- & Gustaaf Van Tendeloo
-
Article
| Open Access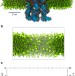 Stability and dynamics of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores
Stability and dynamics of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores
Although DNA nanopores are widely explored as synthetic membrane proteins, it is still unclear how the anionic DNA assemblies stably reside within the hydrophobic core of a lipid bilayer. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal the key dynamic interactions and energetics stabilizing the nanopore-membrane interaction.
- Vishal Maingi
- , Jonathan R. Burns
- & Mark S. P. Sansom
-
Article
| Open Access Optical imaging of localized chemical events using programmable diamond quantum nanosensors
Optical imaging of localized chemical events using programmable diamond quantum nanosensors
The use of nanoscale sensors capable of detection of biological parameters is of great interest in diagnosis. Here, the authors use experimental and theoretical methods to develop a nanodiamond sensor with nitrogen vacancy defects for detection of pH and redox in a microfluidic device.
- Torsten Rendler
- , Jitka Neburkova
- & Jörg Wrachtrup
-
Article
| Open Access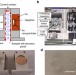 Superfast assembly and synthesis of gold nanostructures using nanosecond low-temperature compression via magnetic pulsed power
Superfast assembly and synthesis of gold nanostructures using nanosecond low-temperature compression via magnetic pulsed power
Gold nanostructures have shape-dependent properties, making synthetic control over their morphology critical. Here, the authors use dynamic compression to obtain a variety of gold nanoarchitectures, which are formed at very fast timescales by the controlled coalescence of spherical particle arrays.
- Binsong Li
- , Kaifu Bian
- & Hongyou Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Highly selective and active CO2 reduction electrocatalysts based on cobalt phthalocyanine/carbon nanotube hybrid structures
Highly selective and active CO2 reduction electrocatalysts based on cobalt phthalocyanine/carbon nanotube hybrid structures
Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide is a sustainable way of producing carbon-neutral fuels. Here, the authors take a combined nanoscale and molecular approach to develop a highly active and selective cobalt phthalocyanine/carbon nanotube hybrid electrocatalyst for carbon dioxide reduction to carbon monoxide.
- Xing Zhang
- , Zishan Wu
- & Hailiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast fluxional exchange dynamics in electrolyte solvation sheath of lithium ion battery
Ultrafast fluxional exchange dynamics in electrolyte solvation sheath of lithium ion battery
The lithium solvation structure in the electrolyte solution for lithium-ion batteries has not been fully understood. Here, the authors show ultrafast fluxional exchange of carbonate solvent molecules in and out of lithium-ion solvation sheath utilizing coherent two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy.
- Kyung-Koo Lee
- , Kwanghee Park
- & Minhaeng Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Room temperature organic magnets derived from sp3 functionalized graphene
Room temperature organic magnets derived from sp3 functionalized graphene
Developing room-temperature magnets from materials containing onlysporbitals has remained an elusive but important goal. Here, Zbořil and co-workers report hydroxofluorographenes that exhibit room-temperature antiferromagnetic ordering and low-temperature ferromagnetic behaviour with high magnetic moments.
- Jiří Tuček
- , Kateřina Holá
- & Radek Zbořil
-
Article
| Open Access Local pH oscillations witness autocatalytic self-organization of biomorphic nanostructures
Local pH oscillations witness autocatalytic self-organization of biomorphic nanostructures
Silica biomorphs have similar structural features found in natural biominerals, but consist of inorganic components that self-assemble spontaneously. Here the authors show that pH oscillates in the local environment during the growth of self-organized silica-carbonates nanostructures.
- M. Montalti
- , G. Zhang
- & J. M. García-Ruiz
-
Article
| Open Access Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation
Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation
Reducing membrane thickness to nanometre scale should increase the throughput of gas separation sieves. Here, the authors report a sieving membrane composed of two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets, exhibiting both high permeation flux and thermally switchable behaviour.
- Xuerui Wang
- , Chenglong Chi
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Proton tautomerism for strong polarization switching
Proton tautomerism for strong polarization switching
Ferroelectrics based on proton tautomerism are promising in low-field and above-roomtemperature operations. Here the authors establish a procedure to optimize spontaneous polarizations, finding that the polarization in croconic acid breaks its own record for organic systems.
- Sachio Horiuchi
- , Kensuke Kobayashi
- & Shoji Ishibashi
-
Article
| Open Access Selective sulfur dioxide adsorption on crystal defect sites on an isoreticular metal organic framework series
Selective sulfur dioxide adsorption on crystal defect sites on an isoreticular metal organic framework series
The widespread emission of sulfur oxide gases from fossil fuel combustion presents major health risks. Here, the authors show that the selective sulfur dioxide capture performance of a metal organic framework is improved by the introduction of missing linker defects and extra-framework barium cations.
- L. Marleny Rodríguez-Albelo
- , Elena López-Maya
- & Jorge A.R. Navarro
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular weaving via surface-templated epitaxy of crystalline coordination networks.
Molecular weaving via surface-templated epitaxy of crystalline coordination networks.
The self-assembly of polymer threads into interwoven textiles is an important goal in polymer chemistry. Here the authors assemble interwoven polymer chains by cross-linking acetylene functionalized ligands in surface-mounted MOFs and subsequent removal of the metal ions affords 2D textile sheets.
- Zhengbang Wang
- , Alfred Błaszczyk
- & Marcel Mayor
-
Article
| Open Access Modulating supramolecular binding of carbon dioxide in a redox-active porous metal-organic framework
Modulating supramolecular binding of carbon dioxide in a redox-active porous metal-organic framework
Gaining molecular-level insight into host–guest binding interactions is fundamentally important, but experimentally challenging. Here, Schröder and co-workers study CO2–host hydrogen bonding interactions in a pair of isostructural redox-active VIII/VIVMOFs using neutron scattering and diffraction techniques.
- Zhenzhong Lu
- , Harry G. W. Godfrey
- & Martin Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable thermal expansion in framework materials through redox intercalation
Tunable thermal expansion in framework materials through redox intercalation
The positive thermal expansion exhibited by most materials at increased temperatures is a severe issue for many high precision applications. Here, Xing and co-workers show that redox intercalation of Li ions into a ScF3framework offers effective control of the thermal expansion for this simple material.
- Jun Chen
- , Qilong Gao
- & Xianran Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling exceptional acetylene and carbon dioxide adsorption within a tetra-amide functionalized metal-organic framework
Unravelling exceptional acetylene and carbon dioxide adsorption within a tetra-amide functionalized metal-organic framework
Understanding the mechanism of gas-sorbent interactions at a molecular level is important for the design of improved gas storage materials. Here, the authors study the binding domains of carbon dioxide and acetylene in a tetra-amide functionalized metal-organic framework at crystallographic resolution.
- Florian Moreau
- , Ivan da Silva
- & Martin Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Ellipsoidal analysis of coordination polyhedra
Ellipsoidal analysis of coordination polyhedra
Simple polyhedra in crystalline compounds are often deformed, so methods for analysing their distortions are useful. Here, the authors demonstrate that analysis of the minimum bounding ellipsoid of a coordination polyhedron provides a general method for studying distortion.
- James Cumby
- & J. Paul Attfield
-
Article
| Open Access Self-surface charge exfoliation and electrostatically coordinated 2D hetero-layered hybrids
Self-surface charge exfoliation and electrostatically coordinated 2D hetero-layered hybrids
Synthesis of atomically thin 2D hetero-layered structures remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a scalable approach to fabricating 2D hetero-layered metal chalcogenides of various compositions: self-surface charge exfoliation, followed by electrostatic coupling.
- Min-Quan Yang
- , Yi-Jun Xu
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Solid-state NMR can in principle be used to study calcium environments in biomaterials such as bones/teeth, but43Ca lacks receptivity. Here the authors present an approach to acquire 43Ca data for hydroxyapatite at its natural isotopic abundance, distinguishing between core and surface Ca sites.
- Daniel Lee
- , César Leroy
- & Gaël De Paëpe
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-dependent ordering of gold nanocrystals into large-scale superlattices
Shape-dependent ordering of gold nanocrystals into large-scale superlattices
Ordered self-assembly is a promising way to realize collective properties in nanocrystals, but reliable routes to such macroscopic structures are missing. Here the authors make cm-scale ordered superlattice films from gold nanoclusters, correlating film properties with the shape of the building blocks
- Jianxiao Gong
- , Richmond S. Newman
- & Zhiyong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Cubosomes from hierarchical self-assembly of poly(ionic liquid) block copolymers
Cubosomes from hierarchical self-assembly of poly(ionic liquid) block copolymers
Generally cubosomes are formed by the self-assembly of surfactants such as lipids and are used as adsorbents or in host-guest applications. Here the authors have shown that an amphiphilic block copolymer can form nanoscale cuboidal particles with a bicontinuous cubic phase.
- Hongkun He
- , Khosrow Rahimi
- & Krzysztof Matyjaszewski
-
Article
| Open Access Direct visualization of hydrogen absorption dynamics in individual palladium nanoparticles
Direct visualization of hydrogen absorption dynamics in individual palladium nanoparticles
It remains unclear why energy storage systems with nanoscale constituents are less susceptible to stress-induced damage than their bulk counterparts. Here, the authors probe in real time the intercalation-driven phase transitions of nanoscale palladium hydride, finding that these nanoparticles are able to fix crystallographic flaws as they form.
- Tarun C. Narayan
- , Fariah Hayee
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
Article
| Open Access A minimal length rigid helical peptide motif allows rational design of modular surfactants
A minimal length rigid helical peptide motif allows rational design of modular surfactants
Emulsifiers are used in the pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, and biomedical industry. Here the authors fabricate rigid helical peptides that can perform as emulsifiers and thickeners, which typically requires synergistic effects of surfactants and polysaccharides.
- Sudipta Mondal
- , Maxim Varenik
- & Ehud Gazit
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of high-performance low-cost n-type Mg3Sb2-based thermoelectric materials with multi-valley conduction bands
Discovery of high-performance low-cost n-type Mg3Sb2-based thermoelectric materials with multi-valley conduction bands
Zintl-phase thermoelectrics are predominantly p-type. Here, Zhanget al. use tellurium to n-dope Mg3Sb1.5Bi0.5and obtain thermoelectric figures of merit up to 1.6 at 700 K. Calculations show that these performances result from a conduction band with sixfold valley degeneracy.
- Jiawei Zhang
- , Lirong Song
- & Bo Brummerstedt Iversen
-
Article
| Open Access One-dimensional organic lead halide perovskites with efficient bluish white-light emission
One-dimensional organic lead halide perovskites with efficient bluish white-light emission
Low-dimensional systems exhibit unique optical properties. Yuanet al. demonstrate one-dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid metal halide perovskites with highly efficient bluish white-light emission due to efficient exciton self-trapping in the quantum-confined structure.
- Zhao Yuan
- , Chenkun Zhou
- & Biwu Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Electronically decoupled stacking fault tetrahedra embedded in Au(111) films
Electronically decoupled stacking fault tetrahedra embedded in Au(111) films
Stacking faults in nanocrystals are generally considered unwelcome structural defects. Here, the authors find that stacking fault tetrahedra in Au exhibit quantized, particle-in-a-box electronic behaviour, revealing a potential synthetic route to decoupled nanoparticles in metal films.
- Koen Schouteden
- , Behnam Amin-Ahmadi
- & Chris Van Haesendonck
-
Article
| Open Access A plant tendril mimic soft actuator with phototunable bending and chiral twisting motion modes
A plant tendril mimic soft actuator with phototunable bending and chiral twisting motion modes
Plant tendrils are able to undergo both bending and chiral twisting motions but unfortunately synthetic mimics are unable to do this. Here the authors show a dual-layer polysiloxane-based liquid crystal soft actuator capable of two different 3D reversible transformations via light stimuli.
- Meng Wang
- , Bao-Ping Lin
- & Hong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for ion migration in hybrid perovskite solar cells with minimal hysteresis
Evidence for ion migration in hybrid perovskite solar cells with minimal hysteresis
Ion migration has been related to hysteresis in perovskite solar cells, but not all perovskite cells exhibit a hysteresis. Here, Caladoet al. show that ion migration occurs regardless of hysteresis, but photogenerated carriers screen the effects of ionic charge for some solar cell architectures.
- Philip Calado
- , Andrew M. Telford
- & Piers R.F. Barnes

 Adaptive and freeze-tolerant heteronetwork organohydrogels with enhanced mechanical stability over a wide temperature range
Adaptive and freeze-tolerant heteronetwork organohydrogels with enhanced mechanical stability over a wide temperature range